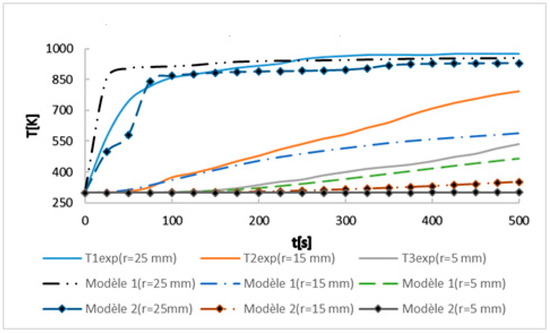
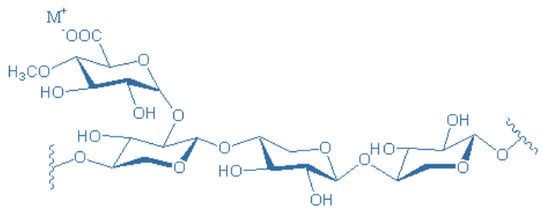
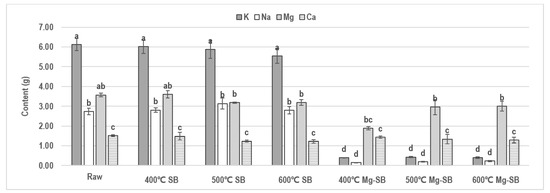
Advances in Biomass Waste Valorization
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Sustainability and Applications".
Viewed by 41404Editors
Interests: cellulose fibres; papermaking; paper packaging; polysaccharides; biopolymers; lignocellulosic materials; wastewater treatment; waste recycling
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: organic compounds; plant extracts; bioactive compounds; polyphenols; essential oils; antioxidants; antimicrobials; cytotoxicity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: heterocycles chemistry; organic synthesis; natural compounds; antimicrobials; chromatography; spectroscopy; toxicology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In the context of world population increase and the industrialization of emerging economies, the availability of raw materials is becoming a serious problem with economic and social impact. The identification of alternative raw materials obtained from renewable sources such as biomass waste is of high interest for specialists in research, academia, and industry.
Nowadays, it is recognized that a high number of biomass waste side streams are created by the processing sectors (e.g., agricultural, food, forestry, and industrial). The optimal valorization of these waste streams by their conversion to high added value products or the extraction of valuable components will lead to more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. This contributes to converting the linear economy to a more bio-based circular economy. Therefore, residual biomass is an ideal and sustainable candidate to substitute petroleum-derived products.
This Special Issue aims to cover recent and emerging strategies for the development of sustainable biomass waste conversion processes, focusing on the aspects that drive research to upgrade the existing technologies to obtain bio-based products (e.g., more green processes).
Attention will be paid to multidisciplinary approaches in various fields of engineering (chemical, food, civil, environmental, materials, and agricultural) dealing with the valorization of biomass waste for the sustainable production of valuable and useful products with large industrial applications (e.g., packaging, building, foods, cosmetics, pharmaceutical, chemistry, de-pollution, and automotive). Furthermore, the processes and practices that contribute to reducing environmental emissions and the life cycle assessment of the systems considered (technologies and materials) are also of interest.
Papers that present theoretical and quantitative analysis of the topic as well as qualitative research based on case studies (pilot-plant and full-scale) are welcome for review and publication.
Prof. Dr. Petronela Nechita
Prof. Dr. Rodica-Mihaela Dinicǎ
Dr. Bianca Furdui
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- biomass waste
- lignocellulosic residues
- agroresidues
- renewable resources
- bioprocesses
- green chemistry
- biocatalysis
- added value products
- plant extracts
- biorefinery
- recycling
- de-pollution
- environmental
- biocomposites
- biopolymers
- life cycle assessment