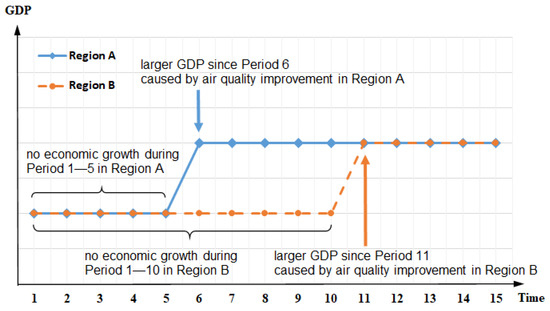
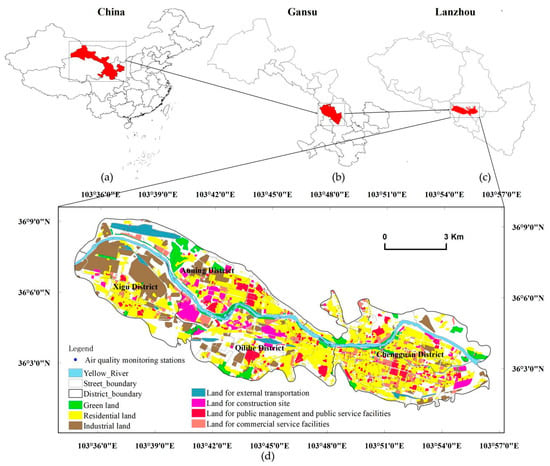
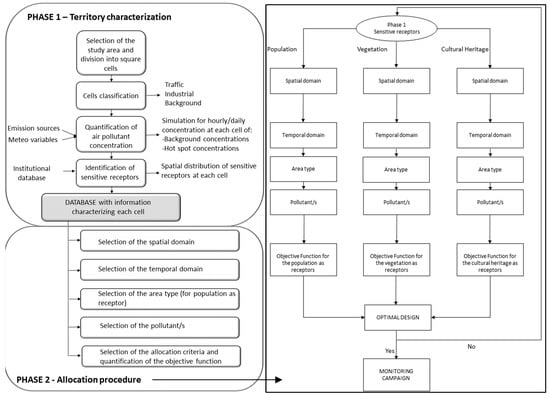
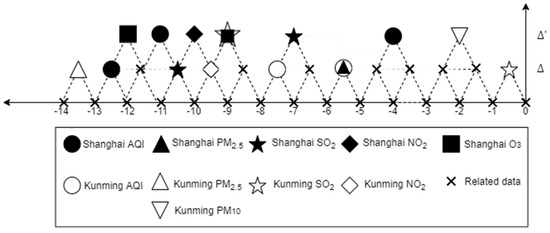
Air Pollution Control and Sustainable Development
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Air, Climate Change and Sustainability".
Viewed by 86031Editors
Interests: digital economy and finance; sustainable development
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: system modeling; information economy; data mining; algorithm design
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: digital industrialization; internet platform research; game theory
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The atmosphere is one of the key bases for human survival and development. During the rapid economic growth and remarkable pace of global industrialization, massive amounts of fossil fuels including coal, petroleum, and natural gas have been consumed. The whole world—especially the developing countries—is facing a growing issue of air pollution.
Air pollution has caused a great threat to the world, especially the developing countries. On the one hand, particles with diameter under 10 (so-called inhalable particles PM10) can enter the bronchus in the human lower respiratory tract—especially particles with diameter under 2.5 (PM2.5) which can enter the alveoli in human lungs. When such particles (PM2.5) reach human lungs, they attach themselves to the alveoli and stay within the human body for years. They can even travel to other organs of the human body through blood circulation and therefore could cause great damage to people’s health. In China, due to the huge population and planning layout in large and medium-sized cities, the cities have low tolerance in terms of air pollution. According to a study lasting two decades, in the northern part of Huaihe River which relies heavily on coal-fired power, the average life expectancy of people is 5.52 years shorter than that of those in southern areas.
On the other hand, air pollution has also posed a great threat to the sustainable development of the world. The dust and fume contained in waste gases seriously impact agricultural and industrial production as well as transportation. Hazardous substances such as SO2 and NO2 become acid deposition and cause damage and erosion to soil, vegetables, industrial plants, and other buildings. Moreover, the particles in waste gas directly and indirectly cause climatic effects, and result in an imbalance in solar irradiance between the Earth and the Sun so that drought regions will suffer more drought while flood-prone regions will suffer more floods. As a result, it will cause abnormal atmospheric circulation both horizontally and vertically, and even cause irreversible climate change.
In the face of the serious consequences of air pollution, governments have adopted various policies and measures to control and mitigate the adverse effects of air pollution, including China’s “Blue Sky Defense War” action plan, India’s “National Clean Air Program”, and Brazil’s new “Air Quality standards (PI-1, PI-2, PI-3, PF)”. These policies have played a positive role in improving air quality and promoting sustainable development. However, some problems have also been exposed in the implementation process.
Therefore, we organized this Topical Collection to discuss air pollution control and sustainable development in the world, including but not limited to the serious situation of air pollution faced by the world, the effectiveness of current air pollution control policies and measures, and how to improve these policies to better achieve sustainable development.
Submissions for this Topical Collection could relate, but are not limited, to the following topics:
- Main sources and characteristics of air pollution;
- The impact of air pollution on sustainable development;
- The formulation mechanism of air pollution control policies;
- The effects of air pollution control policies and measures;
- How to improve current air pollution control policies for the promotion of sustainable development;
- The cooperation among governments to control air pollution and promote sustainable development.
Dr. Weixin Yang
Prof. Dr. Guanghui Yuan
Dr. Yunpeng Yang
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- air pollution
- air pollution control
- sustainable development
- control policy