Journal Description
Standards
Standards
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on standardization, inspection, verification, certification, testing and quality control published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access—free for readers to download, share, and reuse content. Authors receive recognition for their contribution when the paper is reused.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 45.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Standards is a companion journal of Sustainability.
Latest Articles
Are Stakeholders’ Opinions Redundant?
Standards 2024, 4(2), 39-51; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards4020003 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Decision-making, bringing in the opinions of several stakeholders, may be a rather time- and resource-demanding process. Partial order-based methods like generalized linear aggregation (GLA) and average ranking appear as advantageous tools for considering several stakeholders’ opinions simultaneously. The present study presents an approach
[...] Read more.
Decision-making, bringing in the opinions of several stakeholders, may be a rather time- and resource-demanding process. Partial order-based methods like generalized linear aggregation (GLA) and average ranking appear as advantageous tools for considering several stakeholders’ opinions simultaneously. The present study presents an approach where stakeholders’ opinions/weights are substituted by a series of randomly generated weight regimes, leading to virtually identical rankings as demonstrated through comparisons to examples where true stakeholder opinions are applied, as demonstrated through a study on food sustainability. This study showed a high degree of agreement between the ranking based on random data and that based on real stakeholder data. The method, which is a top-down approach to the decision process, appears to be a highly resource-reducing decision-supporting process. However, the method, by default, excludes the possibility of incorporating specific knowledge from, e.g., employees or other stakeholders in the decision process.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Quick Roadmap for Exposure Assessment of Contaminants in Food
by
Bozidar Udovicki and Ilija Djekic
Standards 2024, 4(1), 25-38; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards4010002 - 08 Mar 2024
Abstract
The presence of chemical contaminants in food is often unavoidable and associated with many adverse health effects. Exposure assessment is the essential element of an overall risk assessment process. While the specific purpose of the exposure assessment process can vary, the main goal
[...] Read more.
The presence of chemical contaminants in food is often unavoidable and associated with many adverse health effects. Exposure assessment is the essential element of an overall risk assessment process. While the specific purpose of the exposure assessment process can vary, the main goal is to provide a foundation for health-protective decisions. In recent years, there have been significant advances in exposure assessment methodologies and procedures, subsequently contributing to an increased complexity of the process. This paper aims to provide a generalized, simplified, and practical road map for exposure assessment, pointing to the pros and cons of different methods and challenges that occur while performing this type of study.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Challenges in Standardizing Exposure Assessment Studies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Educational Technology Procurement at Canadian Colleges and Universities: An Environmental Scan
by
Hannah Ali, Sapolnach Prompiengchai and Steve Joordens
Standards 2024, 4(1), 1-24; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards4010001 - 23 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There has been an increase in the use of education technology (EdTech) within post-secondary institutions, which has resulted in an unprecedented overflow of EdTech in the market. Institutions then make decisions on which EdTech to procure. This procurement process occurs on a continuum,
[...] Read more.
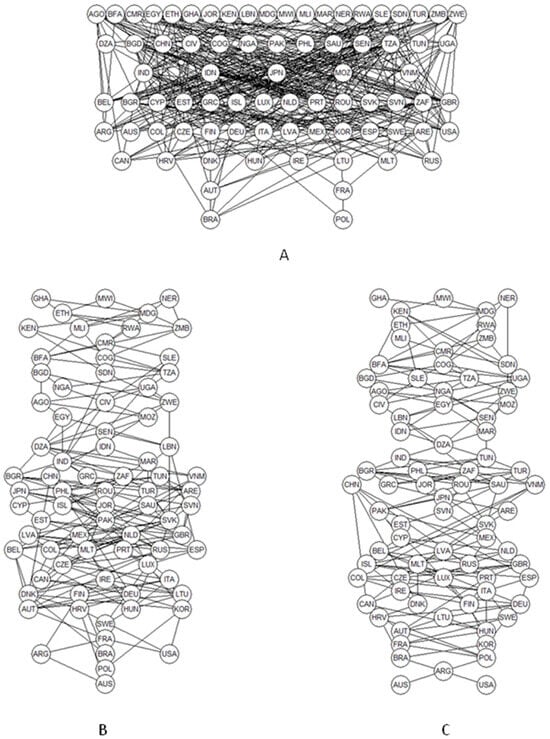
There has been an increase in the use of education technology (EdTech) within post-secondary institutions, which has resulted in an unprecedented overflow of EdTech in the market. Institutions then make decisions on which EdTech to procure. This procurement process occurs on a continuum, where on one extreme, an institution takes a decentralized (bottom–up) approach where individuals within an institution independently decide on EdTech procurement, or a centralized (top–down) approach where the institution decides on criteria and standards that the EdTech must meet. This study administered a questionnaire and conducted structured interviews to explore how important standards are, and to identify the associated challenges with implementing centralized procurement. It was distributed to individuals involved in EdTech procurement at universities and colleges across Canada. The results showed that standards related to Privacy and Security, Accessibility, and Care of Data Practices play a larger role in EdTech procurement within most institutions. The use of standards is increasing as institutions become more centralized; however, they are not yet relied on in a structured way. This study suggests ways to move towards a procurement process that incorporates standards and addresses many of the identified challenges with procuring EdTech, thus, improving the efficiency and efficacy of EdTech procurement.
Full article
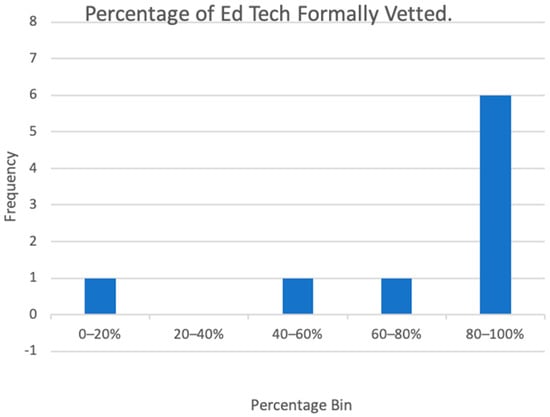
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Expansion of Data Science: Dataset Standardization
by
Nuno Pessanha Santos
Standards 2023, 3(4), 400-410; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3040028 - 30 Nov 2023
Abstract
With recent advances in science and technology, more processing capability and data have become available, allowing a more straightforward implementation of data analysis techniques. Fortunately, available online data storage capacity follows this trend, and vast amounts of data can be stored online freely
[...] Read more.
With recent advances in science and technology, more processing capability and data have become available, allowing a more straightforward implementation of data analysis techniques. Fortunately, available online data storage capacity follows this trend, and vast amounts of data can be stored online freely or at accessible costs. As happens with every evolution (or revolution) in any science field, organizing and sharing these data is essential to contribute to new studies or validate obtained results quickly. To facilitate this, we must guarantee interoperability between existing datasets and developed software, whether commercial or open-source. This article explores this issue and analyzes the current initiatives to establish data standards and compares some of the existing online dataset storage platforms. Through a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis, it is possible to better understand the strategy that should be taken to improve the efficiency in this field, which directly depends on the data’s characteristics. The development of dataset standards will directly increase the collaboration and data sharing between academia and industry, allowing faster research and development through direct interoperability.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Standardization: A Necessary Support for the Utilization of Sludge/Biosolids in Agriculture
by
Ludovico Spinosa and Livia Molinari
Standards 2023, 3(4), 385-399; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3040027 - 14 Nov 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
One of the issues facing modern society, regardless of the socio-economic level of the communities involved, is the development of sustainable strategies for the management of sludge/biosolids. Nowadays, it is imperative to replace solutions aimed at simply “disposing of” with those oriented toward
[...] Read more.
One of the issues facing modern society, regardless of the socio-economic level of the communities involved, is the development of sustainable strategies for the management of sludge/biosolids. Nowadays, it is imperative to replace solutions aimed at simply “disposing of” with those oriented toward “maximizing recovery benefits”. It is desirable that agricultural use remains the main option in sludge/biosolids management; however, to ensure effective and safe agronomic benefits, correctly fulfill the legal requirements, and build stakeholder and public confidence, rigorous and sustainable procedures need to be established. The development of realistic and enforceable regulations is crucial, as they represent the right balance between the different aspects of coordinated and effective management. Furthermore, it is important to recognize that regulations must be supported by standardized characterization procedures and good practice guidelines because well-defined procedures allow the legal requirements to be correctly and uniformly met, as well as to reliably compare the results obtained under different conditions and their wide application in different regulatory contexts. In this article, the main aspects for (i) the sustainable application of sludge/biosolids in agriculture and (ii) the development of standardized characterization methods and procedures, thus ensuring effective agronomic benefits and guaranteeing quality/safety of agricultural products, are discussed. Some pieces on the evolution of European legislation in this field are also provided. Details and results of the research activities behind the development of these methods/procedures can be found in the referenced documents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Standards Promoting Food Safety and Quality)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Noise and Legal Dispute: Applications and Limits of the Italian Standard UNI/TS 11844
by
Fabio Serpilli, Samantha Di Loreto, Valter Lori and Sergio Montelpare
Standards 2023, 3(4), 373-384; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3040026 - 30 Oct 2023
Abstract
In forensic acoustics, a possible area of analysis is represented by unwanted sound that is perceived as a source of intrusion or disturbance within a certain auditory context. This context is defined as the “auditory scene” and refers to the set of sounds
[...] Read more.
In forensic acoustics, a possible area of analysis is represented by unwanted sound that is perceived as a source of intrusion or disturbance within a certain auditory context. This context is defined as the “auditory scene” and refers to the set of sounds present in a specific environment. The presence of unwanted sounds in the auditory scene can cause a wide range of negative effects, including disturbance, discomfort, moral or immoral harm, and other types of negative impacts on the health and well-being of individuals exposed to noise. In 2022, the technical specification UNI/TS 11844:2022 dedicated to the measurement and analysis of intrusive noise was published. The standard introduces the concept of intrusive noise and defines its calculation methods based on environmental measurements. The purposes of this technical specification is to provide an objective support to methods already in used in acoustic disputes, where the assessment of the annoyance of a noise is often a subjective evaluation of the technician. This work delves into application to some real cases, identifying the potentiality and limits of the standardized method.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Standards in Environmental Sciences)
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Rating Scale Paradox: An Application to the Solvency 2 Framework
by
Jacopo Giacomelli
Standards 2023, 3(4), 356-372; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3040025 - 12 Oct 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work aims to identify the optimal rating scale for the rating system used by a credit insurance company subjected to the Solvency 2 regulatory framework. To do so, we apply and further develop a previously published result concerning the rating scale properties.
[...] Read more.
This work aims to identify the optimal rating scale for the rating system used by a credit insurance company subjected to the Solvency 2 regulatory framework. To do so, we apply and further develop a previously published result concerning the rating scale properties. The partition underlying a given rating scale must satisfy two needs of the rating model user: efficient information synthesis and stable semantics. Those needs cannot be addressed together in general. Nonetheless, it is possible to specify the partition as a linear combination of the two choices that meet one requirement each. We numerically show that, in general, the optimal combination is nontrivial under realistic assumptions and is mainly driven by the target return fixed by the company’s stakeholders and the debtors’ probability of default distribution.
Full article
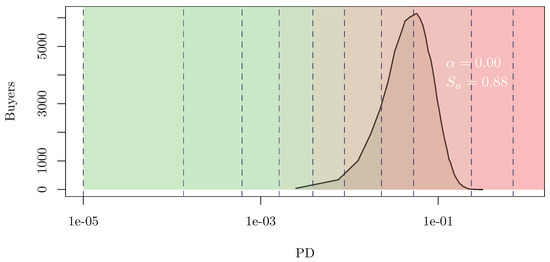
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Digital Certificate System That Complies with International Standards: Taiwan Digital COVID-19 Certificate
by
Tzu-Chia Yu, I-Ming Parng, Jing-Sun Yeh, Gang-Wei Cao and Fu-Chung Wang
Standards 2023, 3(4), 341-355; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3040024 - 27 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The first reported infections from COVID-19 were in 2019 and, since then, an outbreak has spread rapidly to other parts of the world, resulting in many deaths. As a result, governments began to implement border restrictions and quarantine measures, bringing the travel industry
[...] Read more.
The first reported infections from COVID-19 were in 2019 and, since then, an outbreak has spread rapidly to other parts of the world, resulting in many deaths. As a result, governments began to implement border restrictions and quarantine measures, bringing the travel industry to a halt and plunging the global economy into a severe contraction. Many regions chose to coexist with COVID-19 and gradually eased their border restrictions with certain conditions, such as using personal health status certificates, vaccination certificates, etc. Digital certificates are becoming a global trend, and Taiwan has invested in developing related tools. This paper presents a technical evaluation from the government’s point of view. Taiwan uses the European Union (EU) Digital COVID Certificate as a basis to build a digital certificate that can fully meet the residents’ current international business and tourism needs. The government hopes that this digital proof will promote the public’s return to normal life and overcome the inconveniences brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. In the post-pandemic era, finding a way to coexist with the virus while gradually relaxing border and community epidemic-prevention policies without impacting our Taiwan’s medical capacity is a significant challenge. Providing key technological solutions to assist in risk stratification is essential in addressing this issue.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Improving the Quality and Utility of Electronic Health Record Data through Ontologies
by
Asiyah Yu Lin, Sivaram Arabandi, Thomas Beale, William D. Duncan, Amanda Hicks, William R. Hogan, Mark Jensen, Ross Koppel, Catalina Martínez-Costa, Øystein Nytrø, Jihad S. Obeid, Jose Parente de Oliveira, Alan Ruttenberg, Selja Seppälä, Barry Smith, Dagobert Soergel, Jie Zheng and Stefan Schulz
Standards 2023, 3(3), 316-340; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3030023 - 15 Sep 2023
Abstract
The translational research community, in general, and the Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSA) community, in particular, share the vision of repurposing EHRs for research that will improve the quality of clinical practice. Many members of these communities are also aware that electronic
[...] Read more.
The translational research community, in general, and the Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSA) community, in particular, share the vision of repurposing EHRs for research that will improve the quality of clinical practice. Many members of these communities are also aware that electronic health records (EHRs) suffer limitations of data becoming poorly structured, biased, and unusable out of original context. This creates obstacles to the continuity of care, utility, quality improvement, and translational research. Analogous limitations to sharing objective data in other areas of the natural sciences have been successfully overcome by developing and using common ontologies. This White Paper presents the authors’ rationale for the use of ontologies with computable semantics for the improvement of clinical data quality and EHR usability formulated for researchers with a stake in clinical and translational science and who are advocates for the use of information technology in medicine but at the same time are concerned by current major shortfalls. This White Paper outlines pitfalls, opportunities, and solutions and recommends increased investment in research and development of ontologies with computable semantics for a new generation of EHRs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Certification and Standardization and Market Access of Medical Devices)
Open AccessArticle
Investigation on the Quality of Commercially Available GABA Tea in Taiwan
by
Mu-Chen Wu, Shih-Lun Liu, Bo-Kang Liou, Chun-Yeh Chen and Yuh-Shuen Chen
Standards 2023, 3(3), 297-315; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3030022 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study collected 220 commercially available samples of γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) tea produced in Taiwan from 2016 to 2021. The 220 tea samples were categorized into five types of GABA tea, including 108 GABA Oolong tea, 71 GABA Black tea, 21 GABA Paochong
[...] Read more.
This study collected 220 commercially available samples of γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) tea produced in Taiwan from 2016 to 2021. The 220 tea samples were categorized into five types of GABA tea, including 108 GABA Oolong tea, 71 GABA Black tea, 21 GABA Paochong tea, 12 GABA Green tea, and 8 GABA Puerh tea samples. The most common type of GABA tea in Taiwan is GABA Oolong tea, followed by GABA Black tea. The physico-chemical constituents and consumer acceptance of the GABA tea samples were analyzed. The GABA content varied among the different types of GABA tea: GABA Oolong tea ranged from 128–286 mg/100 g, GABA Black tea ranged from 182–360 mg/100 g, GABA Paochong tea ranged from 98–203 mg/100 g, GABA Green tea ranged from 56–174 mg/100 g, and GABA Puerh tea ranged from 142–191 mg/100 g. In terms of the commercial standard of GABA tea, 22 out of the 220 GABA tea samples failed to meet the commercial standard, with a failure rate of 10%. During the fermentation process of GABA tea, the contents of GABA increased significantly, but the total polyphenol and total catechin contents remained stable. In terms of consumer acceptance, GABA Black tea is the most accepted by consumers, followed by GABA Puerh tea, GABA Paochong, and GABA Oolong tea. The sour flavor in GABA tea is similar to the original sour sensory properties found in black tea. It is assumed that this is the main reason GABA Black tea has the highest acceptance.
Full article
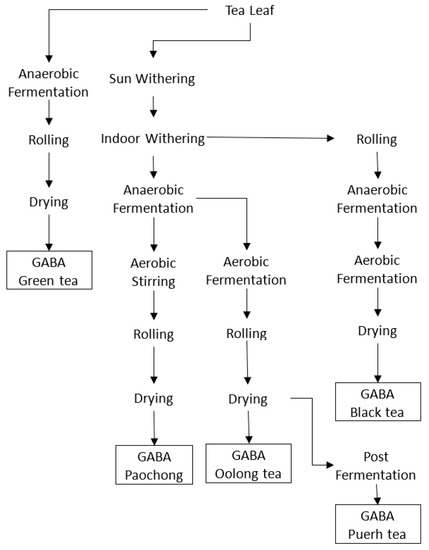
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unlocking Drone Potential in the Pharma Supply Chain: A Hybrid Machine Learning and GIS Approach
by
Raj Bridgelall
Standards 2023, 3(3), 283-296; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3030021 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In major metropolitan areas, the growing levels of congestion pose a significant risk of supply chain disruptions by hindering surface transportation of commodities. To address this challenge, cargo drones are emerging as a potential mode of transport that could improve the reliability of
[...] Read more.
In major metropolitan areas, the growing levels of congestion pose a significant risk of supply chain disruptions by hindering surface transportation of commodities. To address this challenge, cargo drones are emerging as a potential mode of transport that could improve the reliability of the pharmaceutical supply chain and enhance healthcare. This study proposes a novel hybrid workflow that combines machine learning and a geographic information system to identify the fewest locations where providers can initiate cargo drone services to yield the greatest initial benefits. The results show that by starting a service in only nine metropolitan areas across four regions of the contiguous United States, drones with a robust 400-mile range can initially move more than 28% of the weight of all pharmaceuticals. The medical community, supply chain managers, and policymakers worldwide can use this workflow to make data-driven decisions about where to access the largest opportunities for pharmaceutical transport by drones. The proposed approach can inform policies and standards such as Advanced Air Mobility to help address supply chain disruptions, reduce transportation costs, and improve healthcare outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Composition of Probabilistic Preferences in Multicriteria Problems with Variables Measured in Likert Scales and Fitted by Empirical Distributions
by
Luiz Octávio Gavião, Annibal Parracho Sant’Anna, Gilson Brito Alves Lima and Pauli Adriano de Almada Garcia
Standards 2023, 3(3), 268-282; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3030020 - 17 Jul 2023
Abstract
The aim of this article is to demonstrate the advantages of the Composition of Probabilistic Preferences method in multicriteria problems with data from Likert scales. Multicriteria decision aids require a database as a decision matrix, in which two or more alternatives are evaluated
[...] Read more.
The aim of this article is to demonstrate the advantages of the Composition of Probabilistic Preferences method in multicriteria problems with data from Likert scales. Multicriteria decision aids require a database as a decision matrix, in which two or more alternatives are evaluated according to two or more variables selected as decision criteria. Several problems of this nature use measures by Likert scales. Depending on the method, parameters from these data (e.g., means, modes or medians) are required for calculations. This parameterization of data in ordinal scales has fueled controversy for decades between authors who favor mathematical/statistical rigor and argue against the procedure, stating that ordinal scales should not be parameterized, and scientists from other areas who have shown gains from the process that compensates for this relaxation. The Composition of Probabilistic Preferences can allay the protests raised and obtain more accurate results than descriptive statistics or parametric models can bring. The proposed algorithm in R-code involves the use of probabilities with empirical distributions and fitting histograms of data measured by Likert scales. Two case studies with simulated datasets having peculiar characteristics and a real case illustrate the advantages of the Composition of Probabilistic Preferences.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Quality and Process Management in the New Industrial Era: Standards, Theories, Methodologies, Maturity Assessment Frameworks and Excellence Awards)
►▼
Show Figures
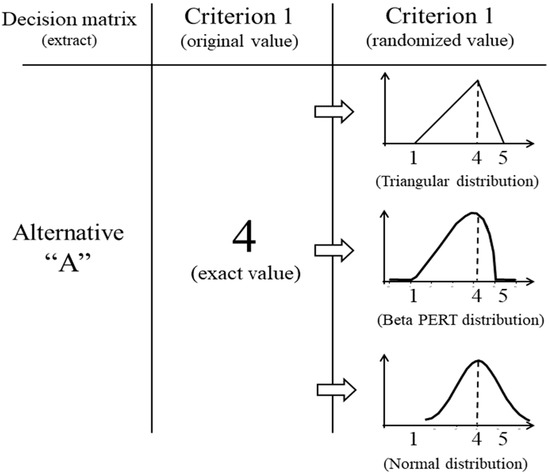
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Improving Indoor Air Quality through Standardization
by
John Saffell and Sascha Nehr
Standards 2023, 3(3), 240-267; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3030019 - 03 Jul 2023
Cited by 5
Abstract
Human beings experience a large fraction of their exposure to air pollutants in indoor environments. Air pollution is a large environmental health risk, and exposure to ambient air pollution and indoor air pollution contribute equally to the total number of fatalities worldwide. Although
[...] Read more.
Human beings experience a large fraction of their exposure to air pollutants in indoor environments. Air pollution is a large environmental health risk, and exposure to ambient air pollution and indoor air pollution contribute equally to the total number of fatalities worldwide. Although legislative authorities have established limit values for ambient outdoor air and stack emissions, there are inconsistent and variable national and regional limit values for gaseous substances and airborne particulate matter in the built environment (schools, homes, healthcare facilities, offices, and other public spaces). This lack of regulation is unsurprising, because indoor spaces are characterized by complex air chemistry, and their construction materials and types of activities vary significantly. The current understanding of indoor pollutants, including short-lived oxidants, degradation of VOCs, particle formation, and particle composition, is incomplete. It is necessary to identify and assess emerging pollutants and their toxicity, and to consider new consumer products and green construction materials and their impact on indoor air quality (IAQ). Learning from IAQ surveys and audit protocols, research methodologies should be regularized for cross-research comparisons. Some indoor air quality guidance and standards have been written, and several more are in development, with the international ISO 16000 series of indoor standards leading the way for improving indoor air data quality. The WHO has established some ambient air limit values which can mostly be translated into indoor limit values. The built environment needs to harmonize energy efficiency, thermal comfort and air quality standards and guidance. In this review, we discuss the next steps for improving international, regional and national standards and guidance, leading to better and more complete indoor air quality regulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Standards in Environmental Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Assessment of EMF Troubles of Biological and Instrumental Medical Questions and Analysis of Their Compliance with Standards
by
Adel Razek
Standards 2023, 3(2), 227-239; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020018 - 19 Jun 2023
Cited by 3
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This contribution aims to analyze compliance with the rules relating to disturbances in the domain of health due to exposure to electromagnetic fields (EMF). This concerns safety standards for exposed living tissue and the integrity of exposed medical devices acting on the body.
[...] Read more.
This contribution aims to analyze compliance with the rules relating to disturbances in the domain of health due to exposure to electromagnetic fields (EMF). This concerns safety standards for exposed living tissue and the integrity of exposed medical devices acting on the body. This investigation is carried out by reviewing and analyzing these exposure effects. In the paper, the EMF exposure, the nature of sources and the characters of their interactions with objects are first illustrated. Then, EMF exposure restrictions accounting for living tissues safety standards as well as medical devices constancy are discussed. Exposure biological effects comprising both thermal and non-thermal effects are then detailed. The verification and control of EMF effects are next illustrated including mathematical modeling of EMF effects, governing equations and body tissues representation in the solution of these equations. At the end of the paper, two examples representing the cases of tissues and devices are given to check the rules under exposure to EMF: biological effects on exposed human tissues and integrity of a magnetic resonance imager under external disturbance.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Statistical Analysis of Wood Durability Data and Its Effect on a Standardised Classification Scheme
by
Christian Brischke, Felix Haase, Lea Bächle and Susanne Bollmus
Standards 2023, 3(2), 210-226; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020017 - 16 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The biological durability of wood is an important property for outdoor applications of wood-based products. In temperate climate zones, the most critical biological hazard is wood-destroying fungi, and the European standard EN 350 in combination with EN 113-2 provide guidance on sampling, testing,
[...] Read more.
The biological durability of wood is an important property for outdoor applications of wood-based products. In temperate climate zones, the most critical biological hazard is wood-destroying fungi, and the European standard EN 350 in combination with EN 113-2 provide guidance on sampling, testing, and classifying wood durability against brown and white rot fungi. However, in their latest revised versions, both standards recommend the use of probability density functions for fitting mass loss data (ML). Subsequently, the durability of wood and its variability should be further characterised. The aim of this study was to statistically analyse the ML data from laboratory agar plate tests with different European-grown wood species and to examine the effect of different statistical treatments on the standardised classification scheme of wood durability. It was concluded that more precise guidance is needed on the sampling procedure since significant differences in durability exist between stem zones. The assignment of dispersion indicators requires a revision to ensure clear, unmistakable, and reproducible durability classification of wood. Deficits in the description of the proposed statistical treatments in both standards became evident. It can be questioned whether the application of probability density functions provides additional information about the variability of wood durability.
Full article
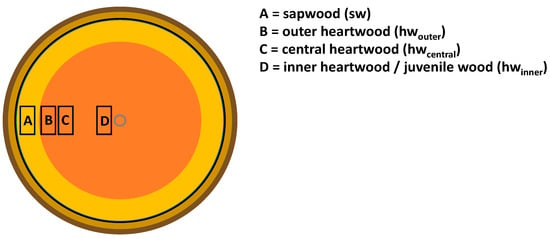
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Multicriteria Standard to Rank Plea Bargain Proposals
by
Annibal Parracho Sant’Anna, Luiz Octávio Gavião and Tiago Lezan Sant’Anna
Standards 2023, 3(2), 198-209; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020016 - 06 Jun 2023
Abstract
This article presents a model for the comparison of plea bargain proposals. The use of the model increases the possibility of the satisfactory development of the negotiation of rewarded collaboration agreements recently permitted under Brazilian law. A novelty in the model is the
[...] Read more.
This article presents a model for the comparison of plea bargain proposals. The use of the model increases the possibility of the satisfactory development of the negotiation of rewarded collaboration agreements recently permitted under Brazilian law. A novelty in the model is the objective consideration of society’s interest in adequately punishing defendants whose guilt can be proven. To allow for the inclusion of this element, a multicriteria approach that adds the criteria representing the prosecution’s aims to the criteria regarding the accused’s positions is adopted. The importance of the criteria is derived without direct criteria weighting. A novel joint treatment to criteria collinearity and interaction is developed, which enables the model to accommodate any number of defendants, proposals, and criteria. The framework so developed enhances transparency and encourages collaboration. By assigning a new meaning to the plea bargain, it is able to bring about the necessary shift in cultural standards that can lead to the effective weakening of criminal organizations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exclusive Papers Collection of Editorial Board Members and Invited Scholars in Standards)
Open AccessCommunication
Service Quality Methods and Practices to Improve Library Administration: A Pilot Study
by
Chao-Chung Ho, Yi-Horng Lai and Ming-Shu Chen
Standards 2023, 3(2), 187-197; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020015 - 29 May 2023
Abstract
The aim of this study is to identify the differentiated services university libraries are able to offer students by prioritizing service quality factors using the various dimensions and factors of service quality. The paper proposes a study that adopts the Parasuraman, Zeithaml, and
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study is to identify the differentiated services university libraries are able to offer students by prioritizing service quality factors using the various dimensions and factors of service quality. The paper proposes a study that adopts the Parasuraman, Zeithaml, and Berry (PZB) service quality model to construct a model for measuring the service quality of a university library. The study conducts analysis using an expert questionnaire and the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to identify students’ needs with respect to the library’s service quality. This study covered 44 different graduate institutes, but it is aimed at postgraduate student-oriented university libraries, which may not reveal the real status of different types of libraries. The five dimensions of service quality identified in this study by order of importance are responsiveness, tangibility, reliability, assurance, and empathy. The first three criteria of the twenty-two assessment criteria are “The staff is unwilling to help students”, “The library’s facilities match up with the type of services” and “Students are unable to receive fast services from staff”. This article seeks to provide innovative methods for previous library management in the university library and the research results could also provide useful references with social implications and novel value to the university library’s management team to improve the library’s service quality.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
“Zero Residue” Concept—Implementation and Certification Challenges
by
Ilija Djekic, Nada Smigic, Bozidar Udovicki and Nikola Tomic
Standards 2023, 3(2), 177-186; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020014 - 17 May 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
This paper gives an overview of scientific challenges in implementing and certifying “Zero residue” approach. The rationale behind the concept is that final control of commodities during/immediately after harvesting should confirm that traces of all used plant protection products are less than or
[...] Read more.
This paper gives an overview of scientific challenges in implementing and certifying “Zero residue” approach. The rationale behind the concept is that final control of commodities during/immediately after harvesting should confirm that traces of all used plant protection products are less than or equal to 0.01 mg/kg. To evaluate the risks in applying this concept, FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis) as a tool has been used. Among the most common factors affecting the pesticide residue levels in fresh produce, the following three appeared to be the biggest challenges in the “Zero residue” concept implementation and certification process: the use of unregistered plant protection products, inadequate sampling plan, and inappropriate laboratory methods. The analysis showed that all three factors have strong influence on achieving “Zero residue” limits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Standards Promoting Food Safety and Quality)
Open AccessArticle
Influence of the Concrete Block on the Tile Adhesive Strength Measured According to EN 12004
by
Michael Faatz and Agnes Ehmann
Standards 2023, 3(2), 169-176; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020013 - 16 May 2023
Abstract
Ceramic tile adhesives (CTA) are playing a dominant role for the business of dry-mix producers. Their quality is classified according to EN 12004. In addition, this standard describes the procedure of a CTA’s performance evaluation. Therefore, a defined ceramic tile, a concrete substrate,
[...] Read more.
Ceramic tile adhesives (CTA) are playing a dominant role for the business of dry-mix producers. Their quality is classified according to EN 12004. In addition, this standard describes the procedure of a CTA’s performance evaluation. Therefore, a defined ceramic tile, a concrete substrate, and the actual tile adhesive is required. In our study, we investigated the influence of different concrete slabs on the results of two tile adhesives. In two cases, the influence of an additional thermal storage of the concrete slabs was evaluated. The tests were strictly performed according to EN 12004-2:2017. The highest variation for the same tile adhesive was found for the adhesion after heat storage measured on different concrete substrates. With a higher polymer content the influence tended to level out. Additionally, a significant deviation was observed for the adhesion strength after water storage, even causing a lower CTA classification on one substrate. The results of our investigation show that the quality of concrete slabs and their storage conditions should be seriously considered in comparing the performance of tile adhesive according to EN 12004.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Standards and Assessment of Construction Products)
►▼
Show Figures
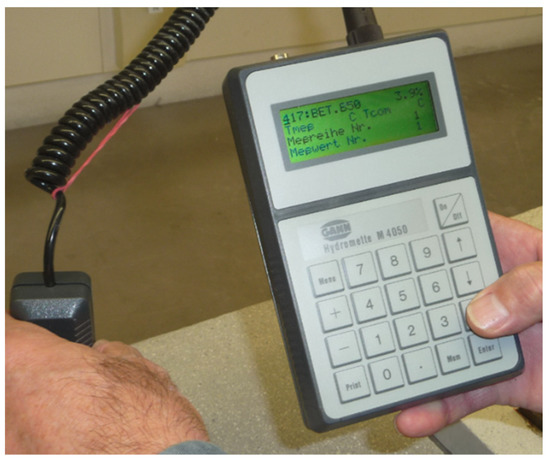

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Finest Magic Cloth or a Naked Emperor? The SKQuest Data Set on Software Metrics for Improving Transparency and Quality
by
Christian R. Prause and Ralf Gerlich
Standards 2023, 3(2), 136-168; https://doi.org/10.3390/standards3020012 - 04 May 2023
Abstract
Software development has a problem with transparency/visibility. As an intangible product, software and its intermediate development results are hard to see or touch. Customers of custom software have difficulties checking progress, and risk coming out with costly but low-quality software. In the space
[...] Read more.
Software development has a problem with transparency/visibility. As an intangible product, software and its intermediate development results are hard to see or touch. Customers of custom software have difficulties checking progress, and risk coming out with costly but low-quality software. In the space domain with its often expensive and one-of-a-kind devices, which are developed in complex multitier supply chains, the risk is even greater. This paper presents the SKQuest data set. It contains the completed responses with 190 variables from an empirical study with over 100 software experts. The data set covers distinct aspects of measuring metrics and transparency in software projects. To show what information lies in the data set, the paper investigates, and affirms, from different perspectives, the following questions: Is transparency a problem in software development projects? Is there a desire for more transparency in projects? Can metrics contribute to improving the situation? Moreover, it attempts to replicate the results of an earlier study. The main contribution of this paper is, however, the SKQuest data set that is published with this paper in CSV formatas. It is a tool that enables systematic investigations of software metrics and allows research on how they can improve the efficiency of the software lifecycle, not limited to, but particularly with respect to transparency. Consequently, the paper may serve as a starting point for future research avenues in academia and industry and help to improve existing and future standards in software development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Software Quality Metrics and Measurement)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, JMMP, Materials, Metrology, Sensors, Standards
Measurement Strategies and Standardization in Manufacturing
Topic Editors: Manuel Rodríguez-Martín, João Ribeiro, Roberto García MartínDeadline: 20 December 2024
Topic in
GeoHazards, Geosciences, Geotechnics, Remote Sensing, Sensors, Standards
Advanced Risk Assessment in Geotechnical Engineering
Topic Editors: Meho-Saša Kovačević, Vassilis MarinosDeadline: 31 December 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Standards
Standards and Developments in the Field of Sustainability and Life Cycle Assessment of the Construction Sector
Guest Editors: Raphaele Malheiro, Ricardo Mateus, Rute EiresDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Standards
Sustainable Process Quality with Links to Standards
Guest Editor: Marcela MalindzakovaDeadline: 15 August 2024
Special Issue in
Standards
Challenges in Standardizing Exposure Assessment Studies
Guest Editors: Ilija Djekic, Božidar UdovičkiDeadline: 31 December 2024