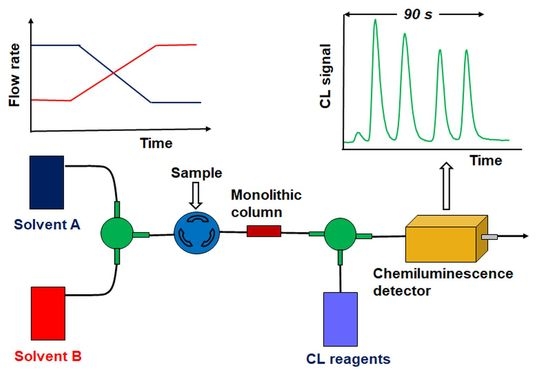
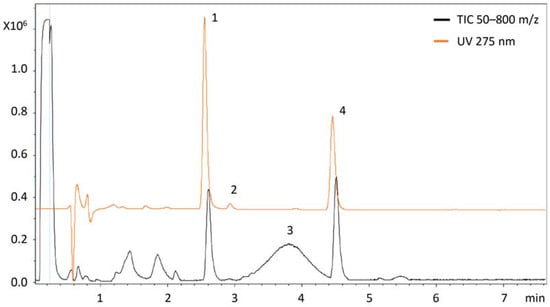
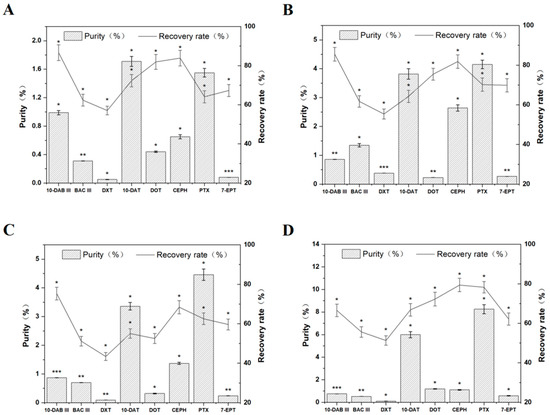
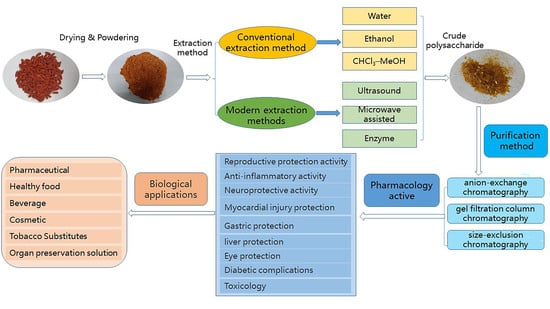
Recent Trends in the Separation of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals
A topical collection in Separations (ISSN 2297-8739). This collection belongs to the section "Analysis of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals".
Viewed by 17385
Editors
Interests: automation; sequential injection analysis; separation techniques (HPLC, CE); post-column derivatization; microextraction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: capillary electrophoresis; capillary liquid chromatography; physico-chemical characterization; cytotoxicity; liposomes; ionic liquids
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In general terms, “natural products” can be defined as compounds that are synthesized/produced by living organisms (plants, animals, etc.). The importance of natural products has been recognized for thousands of years, and a considerable proportion of new drugs are still based on the discovery of natural biogenic molecules.
In the Topical Collection on “Recent Trends in the Separation of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals”, we welcome original research and review articles on the development and application of analytical separation technologies to both natural product and pharmaceutical sciences.
Research on the analysis and separation of natural products should ideally increase the current knowledge on the extraction, separation, isolation, identification, structure elucidation, and quantification of bioactive compounds. All aspects of instrumental analytical separation and analysis methodologies that can be used as a tool to achieve these tasks are welcome. Reports on the quality control and standardization of natural products will also be considered on the basis of their significance in the field.
Analysis of pharmaceuticals, on the other hand, is an extremely broad topic ranging from quality control or raw materials to the impurity profiling of active ingredients and to bioanalytical applications. Original work on all aspects of related research is welcome. Impurity profiling and especially the identification/quantification of genotoxic impurities are of particular interest, while simple assays using HPLC should provide clear advantages from an analytical point of view to be processed further. Research work from industries reporting results from real-world analytical problems is also warmly welcome. All pharmaceutical-related analytical methods should be fully validated.
Bioanalytical methods including pharmacokinetic, bioequivalence, protein, and DNA-binding studies are welcome on the basis of analytical novelty, including sample preparation. Real-world applications (endogenous analytes or sampling from patients) are highly recommended versus demonstration through the spiking of blank biological matrices.
In all cases, novelty will be the major suitability criterion of submitted articles. Authors must therefore always address the question of how their proposed methodology compares with previously reported methods. We look forward many interesting submissions!
Dr. Paraskevas D. Tzanavaras
Prof. Dr. Susanne K. Wiedmer
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Separations is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- natural products
- pharmaceuticals
- automation
- sequential injection analysis
- separation techniques (HPLC, CE)
- post-column derivatization
- microextraction