Microfluidic Sensors
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Physical Sensors".
Viewed by 6613
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Sabina Merlo
Prof. Dr. Sabina Merlo
 Prof. Dr. Sabina Merlo
Prof. Dr. Sabina Merlo
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e dell'Informazione, Università degli Studi di Pavia, 27100 Pavia, Italy
Interests: MEMS; MOEMS; optical sensors; interferometry; microphotonics; biophotonics; biosensors; lab on a chip
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The field of microfluidics is attracting an increasing amount of interest, both in the worlds of academia as well as industry. Indeed, a wide plethora of sensing methods in the fields of biology, nanomedicine, physics, chemistry, material science and nanotechnology have already been presented. Microfluidics is little by little reaching maturity and progressively showing its potential regarding enabling measurements that would otherwise not be feasible or viable. However, it still remains a challenging field due to its strong interdisciplinary nature; thus, in order to develop suitable solutions, a combination of knowledge from different fields, ranging from materials science to photonics and microelectronics, from fluidics to molecular biology, is required.
This Topical Collection aims to collect the latest research in the field of microfluidic sensors as essential elements for a variety of applications. Contributions may refresh the state-of-the-art technology, specify the benefits of emerging technologies, or investigate novel schemes and applications, topics of interest including, but not limited to:
- Microfluidic sensor design, fabrication and characterization;
- Medical, industrial, consumer and environmental applications of microfluidic sensors;
- Lab applications for analytical chemistry, biochemistry and biology;
- Microfluidic sensors for toxicological testing.
We look forward to receiving your submissions.
Prof. Dr. Sabina Merlo
Prof. Dr. Klaus Stefan Drese
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (3 papers)
Open AccessReview
On-Chip Photonic Detection Techniques for Non-Invasive In Situ Characterizations at the Microfluidic Scale
by
Tamar Kurdadze, Fabrice Lamadie, Karen A. Nehme, Sébastien Teychené, Béatrice Biscans and Isaac Rodriguez-Ruiz
Viewed by 1228
Abstract
Microfluidics has emerged as a robust technology for diverse applications, ranging from bio-medical diagnostics to chemical analysis. Among the different characterization techniques that can be used to analyze samples at the microfluidic scale, the coupling of photonic detection techniques and on-chip configurations is
[...] Read more.
Microfluidics has emerged as a robust technology for diverse applications, ranging from bio-medical diagnostics to chemical analysis. Among the different characterization techniques that can be used to analyze samples at the microfluidic scale, the coupling of photonic detection techniques and on-chip configurations is particularly advantageous due to its non-invasive nature, which permits sensitive, real-time, high throughput, and rapid analyses, taking advantage of the microfluidic special environments and reduced sample volumes. Putting a special emphasis on integrated detection schemes, this review article explores the most relevant advances in the on-chip implementation of UV–vis, near-infrared, terahertz, and X-ray-based techniques for different characterizations, ranging from punctual spectroscopic or scattering-based measurements to different types of mapping/imaging. The principles of the techniques and their interest are discussed through their application to different systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
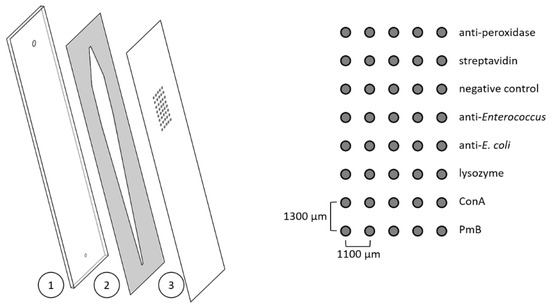
Flow-Based Chemiluminescence Microarrays as Screening Platform for Affinity Binders to Capture and Elute Bacteria
by
Julia Neumair, Martin Elsner and Michael Seidel
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1458
Abstract
Affinity describes the non-covalent but selective interaction between an affinity binder (e.g., proteins, antibiotics, or antibodies) and its counterpart (e.g., bacteria). These affinity binders can serve to detect bacteria and respond to the need for selective concentration via affinity chromatography for trace analysis.
[...] Read more.
Affinity describes the non-covalent but selective interaction between an affinity binder (e.g., proteins, antibiotics, or antibodies) and its counterpart (e.g., bacteria). These affinity binders can serve to detect bacteria and respond to the need for selective concentration via affinity chromatography for trace analysis. By changing the pH value or salt and protein contents, affinity bindings can be reversed, and bacteria can be recovered for characterisation. Analytical microarrays use multiple affinity binders immobilised on the surface in a distinct pattern, which immensely reduces screening time for the discovery of superior binding motifs. Here, flow-based microarray systems can inform not only about binding, but also about desorption. In this work, we pioneer a screening assay for affinity binders against both gram-positive and negative bacteria based on an automated flow-based chemiluminescence (CL) microarray. Biotinylation of model organisms
E. coli and
E. faecalis enabled labelling with horseradish-peroxidase-coupled streptavidin, and detection with CL. Polymyxin B, an antibiotic against gram-negative bacteria, was found to bind both
E. coli and
E. faecalis. Simultaneous screening for desorption methods unexpectedly revealed methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside as a promising buffer for desorption from Polymyxin B. This proof-of-principle study shows that our new platform greatly facilitates the screening of new affinity binders against bacteria, with promise for future automation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
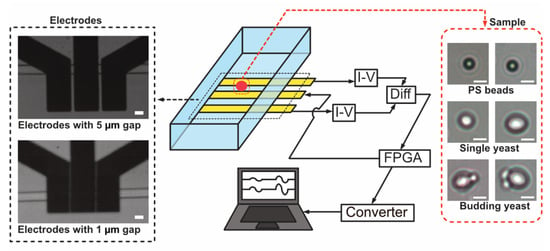
Identification of Single Yeast Budding Using Impedance Cytometry with a Narrow Electrode Span
by
Xun Liu, Tao Tang, Po-Wei Yi, Yapeng Yuan, Cheng Lei, Ming Li, Yo Tanaka, Yoichiroh Hosokawa and Yaxiaer Yalikun
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1539
Abstract
Impedance cytometry is wildly used in single-cell detection, and its sensitivity is essential for determining the status of single cells. In this work, we focus on the effect of electrode gap on detection sensitivity. Through comparing the electrode span of 1 µm and
[...] Read more.
Impedance cytometry is wildly used in single-cell detection, and its sensitivity is essential for determining the status of single cells. In this work, we focus on the effect of electrode gap on detection sensitivity. Through comparing the electrode span of 1 µm and 5 µm, our work shows that narrowing the electrode span could greatly improve detection sensitivity. The mechanism underlying the sensitivity improvement was analyzed via numerical simulation. The small electrode gap (1 µm) allows the electric field to concentrate near the detection area, resulting in a high sensitivity for tiny particles. This finding is also verified with the mixture suspension of 1 µm and 3 µm polystyrene beads. As a result, the electrodes with 1 µm gap can detect more 1 µm beads in the suspension than electrodes with 5 µm gap. Additionally, for single yeast cells analysis, it is found that impedance cytometry with 1 µm electrodes gap can easily distinguish budding yeast cells, which cannot be realized by the impedance cytometry with 5 µm electrodes gap. All experimental results support that narrowing the electrode gap is necessary for tiny particle detection, which is an important step in the development of submicron and nanoscale impedance cytometry.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Advancements in EMAT Sensor Design for Enhanced Ultrasonic Signal Detection in Steel Cables
Authors: Immanuel Roßteutscher, Oliver Blaschke, Klaus Stefan Drese
Affiliation: Institute for Sensor and Actuator Technology, Coburg University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Am Hofbräuhaus 1B, 96450 Coburg, Germany.
Abstract: This study focused on optimizing Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer (EMAT) sensors for enhanced sound signal generation in steel cables, using CAD and modern manufacturing to enable contactless ultrasonic signal transmission and reception. A lab test rig with advanced measurement and data processing was set up to test the sensors' ability to detect cable damage, like wire breaks and abrasion, while also examining the effect of potential disruptors such as rope soiling. Machine learning algorithms were applied to improve damage detection accuracy, leading to significant advancements in magnetostrictive measurement methods and laying a solid groundwork for future development in this area.