Biometric Sensing
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Biosensors".
Viewed by 48781
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Marcin Kowalski
Dr. Marcin Kowalski
 Dr. Marcin Kowalski
Dr. Marcin Kowalski
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Military University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland
Interests: biometric recognition (cross-spectral face recognition, multispectral counter spoofing); object detection (concealed object detection); computer vision (image classification)
 Prof. James Ferryman
Prof. James Ferryman
 Prof. James Ferryman
Prof. James Ferryman
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
University of Reading, Reading, UK
Interests: computer vision; biometrics; surveillance
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Biometric recognition systems are becoming increasingly popular. Measuring the physical or behavioral properties of a subject and detecting spoofing attacks require specific sensors operating across a wide spectrum of radiation. While some biometric modalities require simple sensors to capture samples, others use complicated equipment. These sensors may either output the raw signal or additionally convert the raw signal to the feature domain to distinguish individuals.
This Topical Collection aims to highlight advances in biometric sensing as this relates to biometric recognition. MDPI’s Sensors solicits paper submissions and aims to bring together researchers and application developers on any of the critical issues involved. This Topical Collection will cover a wide range of topics including works on new approaches to biometric sensing, multimodal sensors, biometric sensors’ performance assessment, as well as new concepts for vulnerability detection.
Dr. Marcin Kowalski
Prof. James Ferryman
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- biometric sensors
- biometrics modality
- biometric recognition
- face sensing
- vascular sensors
- multispectral biometrics
- anthropometrics
- fingerprint sensing
- liveness sensing
- counter spoofing detection
Published Papers (15 papers)
Open AccessReview
Biomimetic Polarized Light Navigation Sensor: A Review
by
Shunzi Li, Fang Kong, Han Xu, Xiaohan Guo, Haozhe Li, Yaohuang Ruan, Shouhu Cao and Yinjing Guo
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2117
Abstract
A polarized light sensor is applied to the front-end detection of a biomimetic polarized light navigation system, which is an important part of analyzing the atmospheric polarization mode and realizing biomimetic polarized light navigation, having received extensive attention in recent years. In this
[...] Read more.
A polarized light sensor is applied to the front-end detection of a biomimetic polarized light navigation system, which is an important part of analyzing the atmospheric polarization mode and realizing biomimetic polarized light navigation, having received extensive attention in recent years. In this paper, biomimetic polarized light navigation in nature, the mechanism of polarized light navigation, point source sensor, imaging sensor, and a sensor based on micro nano machining technology are compared and analyzed, which provides a basis for the optimal selection of different polarized light sensors. The comparison results show that the point source sensor can be divided into basic point source sensor with simple structure and a point source sensor applied to integrated navigation. The imaging sensor can be divided into a simple time-sharing imaging sensor, a real-time amplitude splitting sensor that can detect images of multi-directional polarization angles, a real-time aperture splitting sensor that uses a light field camera, and a real-time focal plane light splitting sensor with high integration. In recent years, with the development of micro and nano machining technology, polarized light sensors are developing towards miniaturization and integration. In view of this, this paper also summarizes the latest progress of polarized light sensors based on micro and nano machining technology. Finally, this paper summarizes the possible future prospects and current challenges of polarized light sensor design, providing a reference for the feasibility selection of different polarized light sensors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermal–Visible Face Recognition Based on CNN Features and Triple Triplet Configuration for On-the-Move Identity Verification
by
Marcin Kowalski, Artur Grudzień and Krzysztof Mierzejewski
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2079
Abstract
Face recognition operating in visible domains exists in many aspects of our lives, while the remaining parts of the spectrum including near and thermal infrared are not sufficiently explored. Thermal–visible face recognition is a promising biometric modality that combines affordable technology and high
[...] Read more.
Face recognition operating in visible domains exists in many aspects of our lives, while the remaining parts of the spectrum including near and thermal infrared are not sufficiently explored. Thermal–visible face recognition is a promising biometric modality that combines affordable technology and high imaging qualities in the visible domain with low-light capabilities of thermal infrared. In this work, we present the results of our study in the field of thermal–visible face verification using four different algorithm architectures tested using several publicly available databases. The study covers Siamese, Triplet, and Verification Through Identification methods in various configurations. As a result, we propose a triple triplet face verification method that combines three CNNs being used in each of the triplet branches. The triple triplet method outperforms other reference methods and achieves TAR @FAR 1% values up to 90.61%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Decision Fusion Methods for Multimodal Biometrics in the Banking Application
by
Piotr Szczuko, Arkadiusz Harasimiuk and Andrzej Czyżewski
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2178
Abstract
An evaluation of decision fusion methods based on Dempster-Shafer Theory (DST) and its modifications is presented in the article, studied over real biometric data from the engineered multimodal banking client verification system. First, the approaches for multimodal biometric data fusion for verification are
[...] Read more.
An evaluation of decision fusion methods based on Dempster-Shafer Theory (DST) and its modifications is presented in the article, studied over real biometric data from the engineered multimodal banking client verification system. First, the approaches for multimodal biometric data fusion for verification are explained. Then the proposed implementation of comparison scores fusion is presented, including details on the application of DST, required modifications, base probability, and mass conversions. Next, the biometric verification process is described, and the engineered biometric banking system principles are provided. Finally, the validation results of three fusion approaches on synthetic and real data are presented and discussed, considering the desired outcome manifested by minimized false non-match rates for various assumed thresholds and biometric verification techniques.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
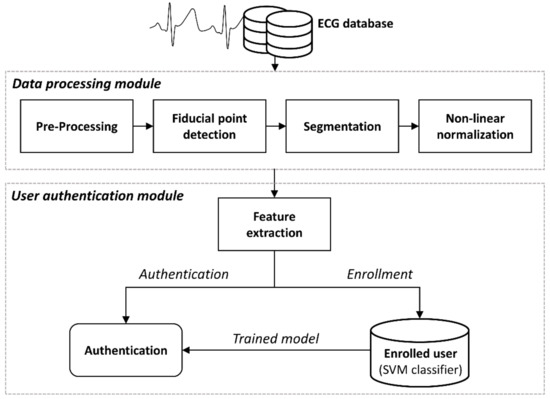
ECG Authentication Based on Non-Linear Normalization under Various Physiological Conditions
by
Ho Bin Hwang, Hyeokchan Kwon, Byungho Chung, Jongshill Lee and In Young Kim
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3316
Abstract
The development and use of wearable devices require high levels of security and have sparked interest in biometric authentication research. Among the available approaches, electrocardiogram (ECG) technology is attracting attention because of its strengths in spoofing. However, morphological changes of ECG, which are
[...] Read more.
The development and use of wearable devices require high levels of security and have sparked interest in biometric authentication research. Among the available approaches, electrocardiogram (ECG) technology is attracting attention because of its strengths in spoofing. However, morphological changes of ECG, which are affected by physical and psychological factors, can make authentication difficult. In this paper, we propose authentication using non-linear normalization of ECG beats that is robust to changes in ECG waveforms according to heart rate fluctuations in various daily activities. We performed a non-linear normalization method through the analysis of ECG alongside heart rate, evaluating similarities and authenticating the performance of our new method compared to existing methods. Compared with beats before normalization, the average similarity of the proposed method increased 23.7% in the resting state and 43% in the non-resting state. After learning in the resting state, authentication performance reached 99.05% accuracy for the resting state and 88.14% for the non-resting state. The proposed method can be applicable to an ECG-based authentication system under various physiological conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Vascular Auscultation of Carotid Artery: Towards Biometric Identification and Verification of Individuals
by
Rutuja Salvi, Patricio Fuentealba, Jasmin Henze, Pinar Bisgin, Thomas Sühn, Moritz Spiller, Anja Burmann, Axel Boese, Alfredo Illanes and Michael Friebe
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2637
Abstract
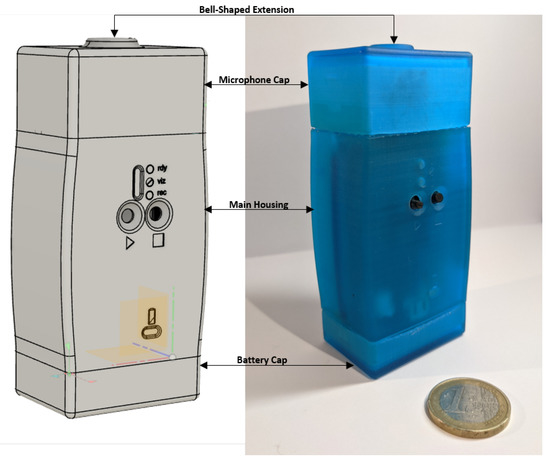
Background: Biometric sensing is a security method for protecting information and property. State-of-the-art biometric traits are behavioral and physiological in nature. However, they are vulnerable to tampering and forgery. Methods: The proposed approach uses blood flow sounds in the carotid artery as a
[...] Read more.
Background: Biometric sensing is a security method for protecting information and property. State-of-the-art biometric traits are behavioral and physiological in nature. However, they are vulnerable to tampering and forgery. Methods: The proposed approach uses blood flow sounds in the carotid artery as a source of biometric information. A handheld sensing device and an associated desktop application were built. Between 80 and 160 carotid recordings of 11 s in length were acquired from seven individuals each. Wavelet-based signal analysis was performed to assess the potential for biometric applications. Results: The acquired signals per individual proved to be consistent within one carotid sound recording and between multiple recordings spaced by several weeks. The averaged continuous wavelet transform spectra for all cardiac cycles of one recording showed specific spectral characteristics in the time-frequency domain, allowing for the discrimination of individuals, which could potentially serve as an individual fingerprint of the carotid sound. This is also supported by the quantitative analysis consisting of a small convolutional neural network, which was able to differentiate between different users with over 95% accuracy. Conclusion: The proposed approach and processing pipeline appeared promising for the discrimination of individuals. The biometrical recognition could clinically be used to obtain and highlight differences from a previously established personalized audio profile and subsequently could provide information on the source of the deviation as well as on its effects on the individual’s health. The limited number of individuals and recordings require a study in a larger population along with an investigation of the long-term spectral stability of carotid sounds to assess its potential as a biometric marker. Nevertheless, the approach opens the perspective for automatic feature extraction and classification.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
On the Impact of the Data Acquisition Protocol on ECG Biometric Identification
by
Mariana S. Ramos, João M. Carvalho, Armando J. Pinho and Susana Brás
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2533
Abstract
Electrocardiographic (ECG) signals have been used for clinical purposes for a long time. Notwithstanding, they may also be used as the input for a biometric identification system. Several studies, as well as some prototypes, are already based on this principle. One of the
[...] Read more.
Electrocardiographic (ECG) signals have been used for clinical purposes for a long time. Notwithstanding, they may also be used as the input for a biometric identification system. Several studies, as well as some prototypes, are already based on this principle. One of the methods already used for biometric identification relies on a measure of similarity based on the Kolmogorov Complexity, called the Normalized Relative Compression (NRC)—this approach evaluates the similarity between two ECG segments without the need to delineate the signal wave. This methodology is the basis of the present work. We have collected a dataset of ECG signals from twenty participants on two different sessions, making use of three different kits simultaneously—one of them using dry electrodes, placed on their fingers; the other two using wet sensors placed on their wrists and chests. The aim of this work was to study the influence of the ECG protocol collection, regarding the biometric identification system’s performance. Several variables in the data acquisition are not controllable, so some of them will be inspected to understand their influence in the system. Movement, data collection point, time interval between train and test datasets and ECG segment duration are examples of variables that may affect the system, and they are studied in this paper. Through this study, it was concluded that this biometric identification system needs at least 10 s of data to guarantee that the system learns the essential information. It was also observed that “off-the-person” data acquisition led to a better performance over time, when compared to “on-the-person” places.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
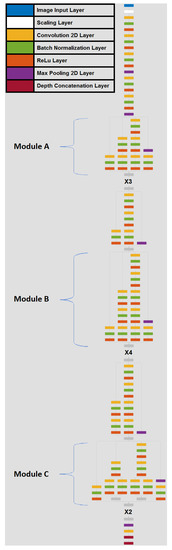
Face Recognition on a Smart Image Sensor Using Local Gradients
by
Wladimir Valenzuela, Javier E. Soto, Payman Zarkesh-Ha and Miguel Figueroa
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4065
Abstract
In this paper, we present the architecture of a smart imaging sensor (SIS) for face recognition, based on a custom-design smart pixel capable of computing local spatial gradients in the analog domain, and a digital coprocessor that performs image classification. The SIS uses
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we present the architecture of a smart imaging sensor (SIS) for face recognition, based on a custom-design smart pixel capable of computing local spatial gradients in the analog domain, and a digital coprocessor that performs image classification. The SIS uses spatial gradients to compute a lightweight version of local binary patterns (LBP), which we term ringed LBP (RLBP). Our face recognition method, which is based on Ahonen’s algorithm, operates in three stages: (1) it extracts local image features using RLBP, (2) it computes a feature vector using RLBP histograms, (3) it projects the vector onto a subspace that maximizes class separation and classifies the image using a nearest neighbor criterion. We designed the smart pixel using the TSMC 0.35 μm mixed-signal CMOS process, and evaluated its performance using postlayout parasitic extraction. We also designed and implemented the digital coprocessor on a Xilinx XC7Z020 field-programmable gate array. The smart pixel achieves a fill factor of 34% on the 0.35 μm process and 76% on a 0.18 μm process with 32 μm × 32 μm pixels. The pixel array operates at up to 556 frames per second. The digital coprocessor achieves 96.5% classification accuracy on a database of infrared face images, can classify a
-pixel image in 94 μs, and consumes 71 mW of power.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Bi-FPNFAS: Bi-Directional Feature Pyramid Network for Pixel-Wise Face Anti-Spoofing by Leveraging Fourier Spectra
by
Koushik Roy, Md. Hasan, Labiba Rupty, Md. Sourave Hossain, Shirshajit Sengupta, Shehzad Noor Taus and Nabeel Mohammed
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4954
Abstract
The emergence of biometric-based authentication using modern sensors on electronic devices has led to an escalated use of face recognition technologies. While these technologies may seem intriguing, they are accompanied by numerous implicit drawbacks. In this paper, we look into the problem of
[...] Read more.
The emergence of biometric-based authentication using modern sensors on electronic devices has led to an escalated use of face recognition technologies. While these technologies may seem intriguing, they are accompanied by numerous implicit drawbacks. In this paper, we look into the problem of face anti-spoofing (FAS) on a frame level in an attempt to ameliorate the risks of face-spoofed attacks in biometric authentication processes. We employed a bi-directional feature pyramid network (BiFPN) that is used for convolutional multi-scaled feature extraction on the EfficientDet detection architecture, which is novel to the task of FAS. We further use these convolutional multi-scaled features in order to perform deep pixel-wise supervision. For all of our experiments, we performed evaluations across all major datasets and attained competitive results for the majority of the cases. Additionally, we showed that introducing an auxiliary self-supervision branch tasked with reconstructing the inputs in the frequency domain demonstrates an average classification error rate (ACER) of 2.92% on Protocol IV of the OULU-NPU dataset, which is significantly better than the currently available published works on pixel-wise face anti-spoofing. Moreover, following the procedures of prior works, we performed inter-dataset testing, which further consolidated the generalizability of the proposed models, as they showed optimum results across various sensors without any fine-tuning procedures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Towards Using Police Officers’ Business Smartphones for Contactless Fingerprint Acquisition and Enabling Fingerprint Comparison against Contact-Based Datasets
by
Christof Kauba, Dominik Söllinger, Simon Kirchgasser, Axel Weissenfeld, Gustavo Fernández Domínguez, Bernhard Strobl and Andreas Uhl
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3334
Abstract
Recent developments enable biometric recognition systems to be available as mobile solutions or to be even integrated into modern smartphone devices. Thus, smartphone devices can be used as mobile fingerprint image acquisition devices, and it has become feasible to process fingerprints on these
[...] Read more.
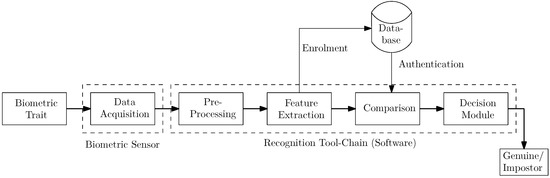
Recent developments enable biometric recognition systems to be available as mobile solutions or to be even integrated into modern smartphone devices. Thus, smartphone devices can be used as mobile fingerprint image acquisition devices, and it has become feasible to process fingerprints on these devices, which helps police authorities carry out identity verification. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive and in-depth engineering study on the different stages of the fingerprint recognition toolchain. The insights gained throughout this study serve as guidance for future work towards developing a contactless mobile fingerprint solution based on the iPhone 11, working without any additional hardware. The targeted solution will be capable of acquiring 4 fingers at once (except the thumb) in a contactless manner, automatically segmenting the fingertips, pre-processing them (including a specific enhancement), and thus enabling fingerprint comparison against contact-based datasets. For fingertip detection and segmentation, various traditional handcrafted feature-based approaches as well as deep-learning-based ones are investigated. Furthermore, a run-time analysis and first results on the biometric recognition performance are included.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Fingerprint Presentation Attack Detection Utilizing Spatio-Temporal Features
by
Anas Husseis, Judith Liu-Jimenez and Raul Sanchez-Reillo
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2354
Abstract
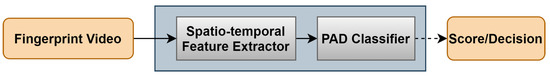
This paper presents a novel mechanism for fingerprint dynamic presentation attack detection. We utilize five spatio-temporal feature extractors to efficiently eliminate and mitigate different presentation attack species. The feature extractors are selected such that the fingerprint ridge/valley pattern is consolidated with the temporal
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a novel mechanism for fingerprint dynamic presentation attack detection. We utilize five spatio-temporal feature extractors to efficiently eliminate and mitigate different presentation attack species. The feature extractors are selected such that the fingerprint ridge/valley pattern is consolidated with the temporal variations within the pattern in fingerprint videos. An SVM classification scheme, with a second degree polynomial kernel, is used in our presentation attack detection subsystem to classify bona fide and attack presentations. The experiment protocol and evaluation are conducted following the ISO/IEC 30107-3:2017 standard. Our proposed approach demonstrates efficient capability of detecting presentation attacks with significantly low BPCER where BPCER is 1.11% for an optical sensor and 3.89% for a thermal sensor at 5% APCER for both.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
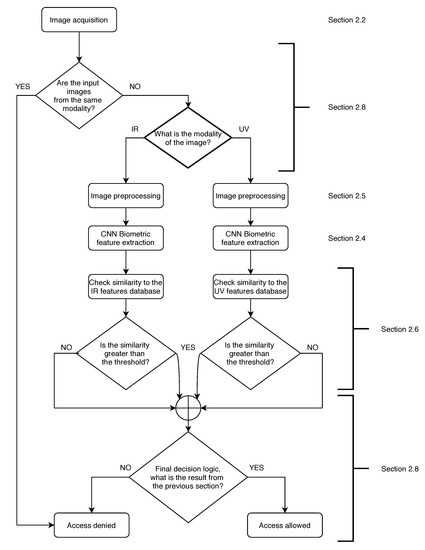
Contact-Free Multispectral Identity Verification System Using Palm Veins and Deep Neural Network
by
Maciej Stanuch, Marek Wodzinski and Andrzej Skalski
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2573
Abstract
Devices and systems secured by biometric factors became a part of our lives because they are convenient, easy to use, reliable, and secure. They use information about unique features of our bodies in order to authenticate a user. It is possible to enhance
[...] Read more.
Devices and systems secured by biometric factors became a part of our lives because they are convenient, easy to use, reliable, and secure. They use information about unique features of our bodies in order to authenticate a user. It is possible to enhance the security of these devices by adding supplementary modality while keeping the user experience at the same level. Palm vein systems are based on infrared wavelengths used for capturing images of users’ veins. It is both convenient for the user, and it is one of the most secure biometric solutions. The proposed system uses IR and UV wavelengths; the images are then processed by a deep convolutional neural network for extraction of biometric features and authentication of users. We tested the system in a verification scenario that consisted of checking if the images collected from the user contained the same biometric features as those in the database. The True Positive Rate (TPR) achieved by the system when the information from the two modalities were combined was 99.5% by the threshold of acceptance set to the Equal Error Rate (EER).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
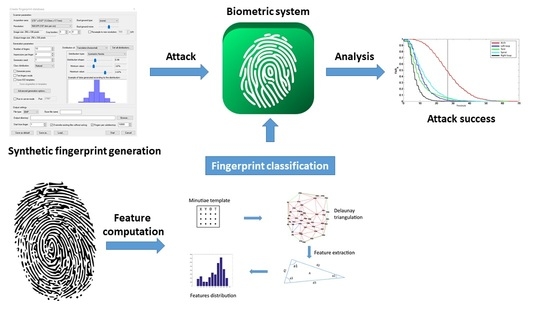
Logical Attacks and Countermeasures for Fingerprint On-Card-Comparison Systems
by
Benoit Vibert, Jean-Marie Le Bars, Christophe Charrier and Christophe Rosenberger
Viewed by 2628
Abstract
Digital fingerprints are being used more and more to secure applications for logical and physical access control. In order to guarantee security and privacy trends, a biometric system is often implemented on a secure element to store the biometric reference template and for
[...] Read more.
Digital fingerprints are being used more and more to secure applications for logical and physical access control. In order to guarantee security and privacy trends, a biometric system is often implemented on a secure element to store the biometric reference template and for the matching with a probe template (on-card-comparison). In order to assess the performance and robustness against attacks of these systems, it is necessary to better understand which information could help an attacker successfully impersonate a legitimate user. The first part of the paper details a new attack based on the use of a priori information (such as the fingerprint classification, sensor type, image resolution or number of minutiae in the biometric reference) that could be exploited by an attacker. In the second part, a new countermeasure against brute force and zero effort attacks based on fingerprint classification given a minutiae template is proposed. These two contributions show how fingerprint classification could have an impact for attacks and countermeasures in embedded biometric systems. Experiments show interesting results on significant fingerprint datasets.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
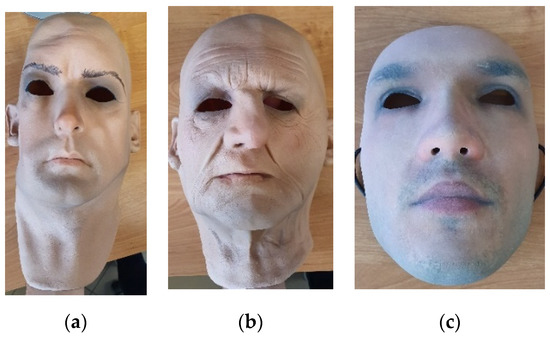
A Study on Presentation Attack Detection in Thermal Infrared
by
Marcin Kowalski
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4082
Abstract
Face recognition systems face real challenges from various presentation attacks. New, more sophisticated methods of presentation attacks are becoming more difficult to detect using traditional face recognition systems. Thermal infrared imaging offers specific physical properties that may boost presentation attack detection capabilities. The
[...] Read more.
Face recognition systems face real challenges from various presentation attacks. New, more sophisticated methods of presentation attacks are becoming more difficult to detect using traditional face recognition systems. Thermal infrared imaging offers specific physical properties that may boost presentation attack detection capabilities. The aim of this paper is to present outcomes of investigations on the detection of various face presentation attacks in thermal infrared in various conditions including thermal heating of masks and various states of subjects. A thorough analysis of presentation attacks using printed and displayed facial photographs, 3D-printed, custom flexible 3D-latex and silicone masks is provided. The paper presents the intensity analysis of thermal energy distribution for specific facial landmarks during long-lasting experiments. Thermalization impact, as well as varying the subject’s state due to physical effort on presentation attack detection are investigated. A new thermal face spoofing dataset is introduced. Finally, a two-step deep learning-based method for the detection of presentation attacks is presented. Validation results of a set of deep learning methods across various presentation attack instruments are presented.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Image-Based Somatotype as a Biometric Trait for Non-Collaborative Person Recognition at a Distance and On-The-Move
by
Antonios Danelakis and Theoharis Theoharis
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2505
Abstract
It has recently been shown in Re-Identification (Re-ID) work that full-body images of people reveal their somatotype, even after change in apparel. A significant advantage of this biometric trait is that it can easily be captured, even at a distance, as a full-body
[...] Read more.
It has recently been shown in Re-Identification (Re-ID) work that full-body images of people reveal their somatotype, even after change in apparel. A significant advantage of this biometric trait is that it can easily be captured, even at a distance, as a full-body image of a person, taken by a standard 2D camera. In this work, full-body image-based somatotype is investigated as a novel soft biometric feature for person recognition at a distance and on-the-move. The two common scenarios of (i) identification and (ii) verification are both studied and evaluated. To this end, two different deep networks have been recruited, one for the identification and one for the verification scenario. Experiments have been conducted on popular, publicly available datasets and the results indicate that somatotype can indeed be a valuable biometric trait for identity recognition at a distance and on-the-move (and hence also suitable for non-collaborative individuals) due to the ease of obtaining the required images. This soft biometric trait can be especially useful under a wider biometric fusion scheme.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Towards Fingerprint Spoofing Detection in the Terahertz Range
by
Norbert Pałka and Marcin Kowalski
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4054
Abstract
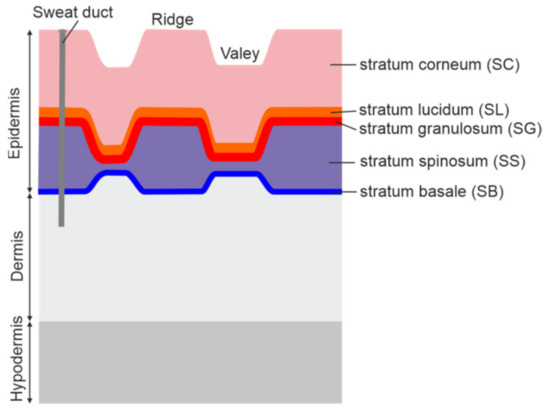
Spoofing attacks using imitations of fingerprints of legal users constitute a serious threat. In this study, a terahertz time domain spectroscopy (TDS) setup in a reflection configuration was used for the non-intrusive detection of fingerprint spoofing. Herein, the skin structure of the finger
[...] Read more.
Spoofing attacks using imitations of fingerprints of legal users constitute a serious threat. In this study, a terahertz time domain spectroscopy (TDS) setup in a reflection configuration was used for the non-intrusive detection of fingerprint spoofing. Herein, the skin structure of the finger pad is described with a focus on the outermost stratum corneum. We identified and characterized five representative spoofing materials and prepared thin and thick finger imitations. The complex refractive index of the materials was determined in TDS in the transmission configuration. For dataset collection, we selected a group of 16 adults of various ages and genders. The reflection results were analyzed both in the time (reflected signal) and frequency (reflectivity) domains. The measured signals were positively verified with the theoretical calculations. The signals corresponding to samples differ from the finger-related signals, which facilitates spoofing detection. Thanks to deconvolution, we provide a basic explanation of the observed phenomena. We propose two spoofing detection methods, predefined time–frequency features and deep learning based. The methods achieved high true detection rates of 87.9% and 98.8%. Our results show that the terahertz technology can be successfully applied for spoofing detection with high detection probability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures