Biomedical Optical Nanosensors
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Biomedical Sensors".
Viewed by 40680
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Alexey Popov
Prof. Dr. Alexey Popov
 Prof. Dr. Alexey Popov
Prof. Dr. Alexey Popov
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Kaitovayla 1, 90590 Oulu, Finland
Interests: spectroscopy; optical trapping; optical properties; nanotechnology; sensing; light-nanoparticles-biotissue interaction
 Dr. Vladimir Sivakov
Dr. Vladimir Sivakov
 Dr. Vladimir Sivakov
Dr. Vladimir Sivakov
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology (Leibniz IPHT), Albert-Einstein-Straße 9, 07745 Jena, Germany
Interests: material sciences; biophotonics; nanomedicine
 Dr. Yury Ryabchikov
Dr. Yury Ryabchikov
 Dr. Yury Ryabchikov
Dr. Yury Ryabchikov
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
HiLASE Centre of the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Za Radnici 828, 252 41 Dolni Brezany, Czech Republic
Interests: nanomaterials, optical and electronic spectroscopy, laser-matter interaction, nanomedicine
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Rapid development of nanotechnology enables the design of miniaturized sensors for in vivo and in vitro monitoring vital signs at different levels, ranging from single cells to the whole organism. Synergy with another key-enabling technology, optics/photonics, provides unlimited opportunities for remote non-invasive sensing based on a variety of light properties (wavelength, intensity, polarization, coherence, pulse width, angular momentum, etc.).
This Topical Collection is devoted to technological advancements in the area of optical nanosensors for in vivo and in vitro biomedical applications (including bioimaging). The sensing materials and the sensing physiological properties are not limited; the only requirement is that the measured quantity is encoded into properties of the detected light.
Prof. Dr. Alexey Popov
Dr. Vladimir Sivakov
Dr. Yury Ryabchikov
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- nanosensor
- nanotechnology
- imaging
- theranostics
- optics
- photonics
- biophotonics
- biomedical optics
- biomedicine
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Photoemission of Plasmonic Gold Nanostars in Laser-Controlled Electron Current Devices for Technical and Biomedical Applications
by
Alexander N. Yakunin, Yury A. Avetisyan, Garif G. Akchurin, Sergey V. Zarkov, Nikolay P. Aban’shin, Vitaly A. Khanadeev and Valery V. Tuchin
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2156
Abstract
The main goal of this work was to modify the previously developed blade-type planar structure using plasmonic gold nanostars in order to stimulate photofield emission and provide efficient laser control of the electron current. Localization and enhancement of the field at the tips
[...] Read more.
The main goal of this work was to modify the previously developed blade-type planar structure using plasmonic gold nanostars in order to stimulate photofield emission and provide efficient laser control of the electron current. Localization and enhancement of the field at the tips of gold nanostars provided a significant increase in the tunneling electron current in the experimental sample (both electrical field and photofield emission). Irradiation at a wavelength in the vicinity of the plasmon resonance (red laser) provided a gain in the photoresponse value of up to 5 times compared to irradiation far from the resonance (green laser). The prospects for transition to regimes of structure irradiation by femtosecond laser pulses at the wavelength of surface plasmon resonance, which lead to an increase in the local optical field, are discussed. The kinetics of the energy density of photoinduced hot and thermalized electrons is estimated. The proposed laser-controlled matrix current source is promising for use in X-ray computed tomography systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
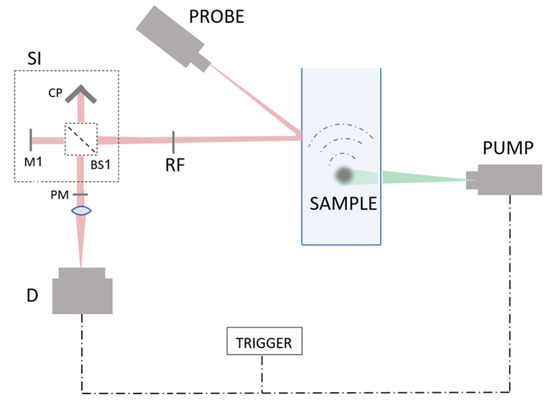
All Optical Speckle Contrast-Based Vibration Sensor for Photoacoustic Signal Detection
by
Matan Benyamin and Zeev Zalevsky
Viewed by 1480
Abstract
Remote detection of photoacoustic signals is a well desired ability, enabling to perform advanced imaging in scenarios where contact is not possible. Various unique solutions have been suggested, including a camera-based speckle contrast photoacoustic detection. In this manuscript, a significant upgrade to the
[...] Read more.
Remote detection of photoacoustic signals is a well desired ability, enabling to perform advanced imaging in scenarios where contact is not possible. Various unique solutions have been suggested, including a camera-based speckle contrast photoacoustic detection. In this manuscript, a significant upgrade to the camera-based speckle contrast approach is presented and experimentally demonstrated. This solution is based on all-optical vibration sensing setup. The technique is based on spectral estimation of speckle pattern contrast and relies on several pre-developed works. First, it relies on the suggested application of speckle contrast to vibration sensing, and then on the realization of intensity pattern spectral manipulation, using a shearing interferometer. The method is evaluated and compared to traditional contrast estimation, and demonstrated in several applications in various vibration frequency band such as photoacoustic signal analysis and phonocardiographic heart sounds. The method is also applicable to measuring contrast changes due to a general speckle changing behavior, rather than surface vibration alone.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
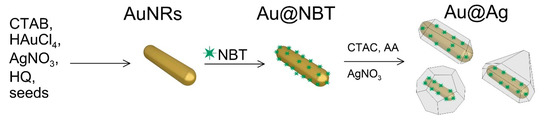
SERS and Indicator Paper Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide Using Au@Ag Nanorods
by
Boris N. Khlebtsov, Andrey M. Burov, Andrey M. Zakharevich and Nikolai G. Khlebtsov
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1804
Abstract
The detection of hydrogen peroxide and the control of its concentration are important tasks in the biological and chemical sciences. In this paper, we developed a simple and quantitative method for the non-enzymatic detection of H
2O
2 based on the selective
[...] Read more.
The detection of hydrogen peroxide and the control of its concentration are important tasks in the biological and chemical sciences. In this paper, we developed a simple and quantitative method for the non-enzymatic detection of H
2O
2 based on the selective etching of Au@Ag nanorods with embedded Raman active molecules. The transfer of electrons between silver atoms and hydrogen peroxide enhances the oxidation reaction, and the Ag shell around the Au nanorod gradually dissolves. This leads to a change in the color of the nanoparticle colloid, a shift in LSPR, and a decrease in the SERS response from molecules embedded between the Au core and Ag shell. In our study, we compared the sensitivity of these readouts for nanoparticles with different Ag shell morphology. We found that triangle core–shell nanoparticles exhibited the highest sensitivity, with a detection limit of 10
−4 M, and the SERS detection range of 1 × 10
−4 to 2 × 10
−2 M. In addition, a colorimetric strategy was applied to fabricate a simple indicator paper sensor for fast detection of hydrogen peroxide in liquids. In this case, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide was qualitatively determined by the change in the color of the nanoparticles deposited on the nitrocellulose membrane.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
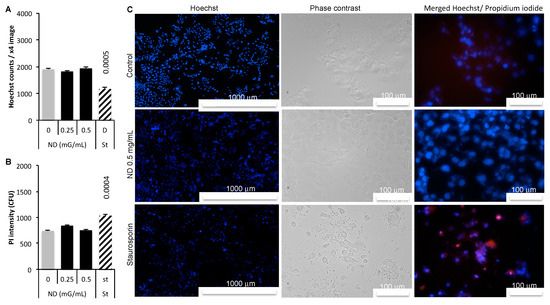
Intracellular Detection and Localization of Nanoparticles by Refractive Index Measurement
by
Alain Géloën, Karyna Isaieva, Mykola Isaiev, Olga Levinson, Emmanuelle Berger and Vladimir Lysenko
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2522
Abstract
The measuring of nanoparticle toxicity faces an important limitation since it is based on metrics exposure, the concentration at which cells are exposed instead the true concentration inside the cells. In vitro studies of nanomaterials would benefit from the direct measuring of the
[...] Read more.
The measuring of nanoparticle toxicity faces an important limitation since it is based on metrics exposure, the concentration at which cells are exposed instead the true concentration inside the cells. In vitro studies of nanomaterials would benefit from the direct measuring of the true intracellular dose of nanoparticles. The objective of the present study was to state whether the intracellular detection of nanodiamonds is possible by measuring the refractive index. Based on optical diffraction tomography of treated live cells, the results show that unlabeled nanoparticles can be detected and localized inside cells. The results were confirmed by fluorescence measurements. Optical diffraction tomography paves the way to measuring the true intracellular concentrations and the localization of nanoparticles which will improve the dose-response paradigm of pharmacology and toxicology in the field of nanomaterials.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
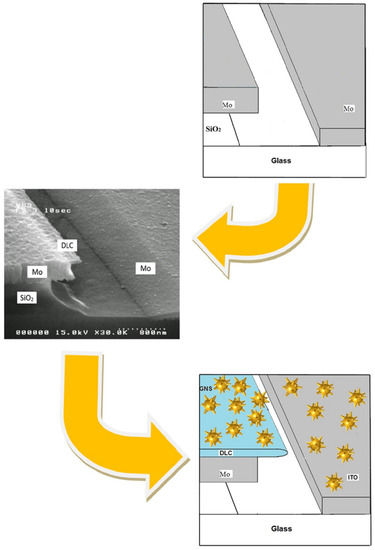
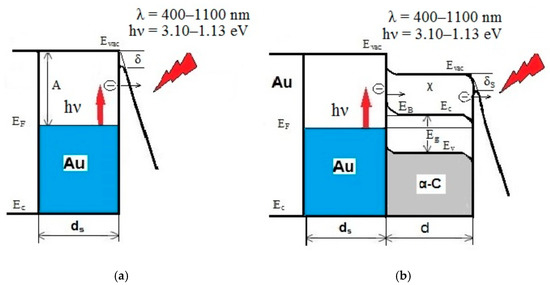
Modeling of Laser-Induced Plasmon Effects in GNS-DLC-Based Material for Application in X-ray Source Array Sensors
by
Alexander N. Yakunin, Sergey V. Zarkov, Yuri A. Avetisyan, Garif G. Akchurin, Nikolay P. Aban’shin and Valery V. Tuchin
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3187
Abstract
An important direction in the development of X-ray computed tomography sensors in systems with increased scanning speed and spatial resolution is the creation of an array of miniature current sources. In this paper, we describe a new material based on gold nanostars (GNS)
[...] Read more.
An important direction in the development of X-ray computed tomography sensors in systems with increased scanning speed and spatial resolution is the creation of an array of miniature current sources. In this paper, we describe a new material based on gold nanostars (GNS) embedded in nanoscale diamond-like carbon (DLC) films (thickness of 20 nm) for constructing a pixel current source with photoinduced electron emission. The effect of localized surface plasmon resonance in GNS on optical properties in the wavelength range from UV to near IR, peculiarities of localization of field and thermal sources, generation of high-energy hot electrons, and mechanisms of their transportation in vacuum are investigated. The advantages of the proposed material and the prospects for using X-ray computed tomography in the matrix source are evaluated.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
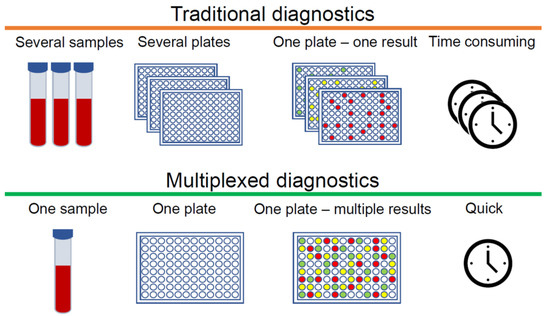
Multiplexed Nanobiosensors: Current Trends in Early Diagnostics
by
Greta Jarockyte, Vitalijus Karabanovas, Ricardas Rotomskis and Ali Mobasheri
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 5165
Abstract
The ever-growing demand for fast, cheap, and reliable diagnostic tools for personalised medicine is encouraging scientists to improve existing technology platforms and to create new methods for the detection and quantification of biomarkers of clinical significance. Simultaneous detection of multiple analytes allows more
[...] Read more.
The ever-growing demand for fast, cheap, and reliable diagnostic tools for personalised medicine is encouraging scientists to improve existing technology platforms and to create new methods for the detection and quantification of biomarkers of clinical significance. Simultaneous detection of multiple analytes allows more accurate assessment of changes in biomarker expression and offers the possibility of disease diagnosis at the earliest stages. The concept of multiplexing, where multiple analytes can be detected in a single sample, can be tackled using several types of nanomaterial-based biosensors. Quantum dots are widely used photoluminescent nanoparticles and represent one of the most frequent choices for different multiplex systems. However, nanoparticles that incorporate gold, silver, and rare earth metals with their unique optical properties are an emerging perspective in the multiplexing field. In this review, we summarise progress in various nanoparticle applications for multiplexed biomarkers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessLetter
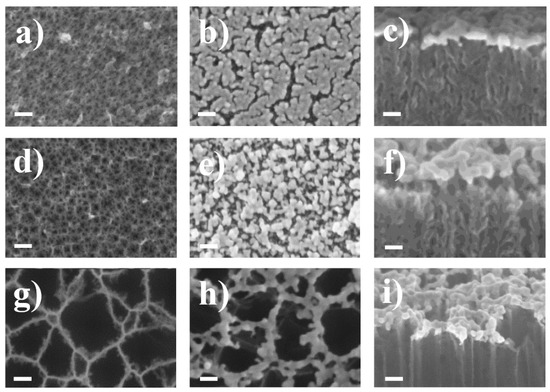
Raman Signal Enhancement Tunable by Gold-Covered Porous Silicon Films with Different Morphology
by
Svetlana N. Agafilushkina, Olga Žukovskaja, Sergey A. Dyakov, Karina Weber, Vladimir Sivakov, Jürgen Popp, Dana Cialla-May and Liubov A. Osminkina
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 2598
Abstract
The ease of fabrication, large surface area, tunable pore size and morphology as well surface modification capabilities of a porous silicon (PSi) layer make it widely used for sensoric applications. The pore size of a PSi layer can be an important parameter when
[...] Read more.
The ease of fabrication, large surface area, tunable pore size and morphology as well surface modification capabilities of a porous silicon (PSi) layer make it widely used for sensoric applications. The pore size of a PSi layer can be an important parameter when used as a matrix for creating surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) surfaces. Here, we evaluated the SERS activity of PSi with pores ranging in size from meso to macro, the surface of which was coated with gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). We found that different pore diameters in the PSi layers provide different morphology of the gold coating, from an almost monolayer to 50 nm distance between nanoparticles. Methylene blue (MB) and 4-mercaptopyridine (4-MPy) were used to describe the SERS activity of obtained Au/PSi surfaces. The best Raman signal enhancement was shown when the internal diameter of torus-shaped Au NPs is around 35 nm. To understand the role of plasmonic resonances in the observed SERS spectrum, we performed electromagnetic simulations of Raman scattering intensity as a function of the internal diameter. The results of these simulations are consistent with the obtained experimental data.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
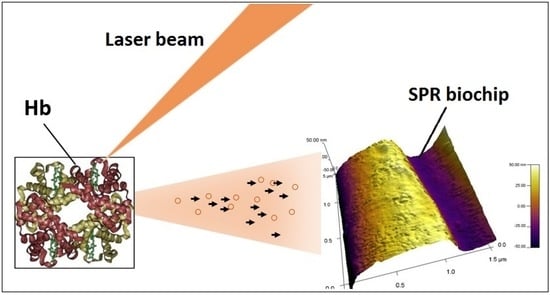
A Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Based on Directly Immobilized Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
by
Georgi Dyankov, Ekaterina Borisova, Evdokia Belina, Hristo Kisov, Ivan Angelov, Alexander Gisbrecht, Velichka Strijkova and Nikola Malinowski
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2588
Abstract
Immobilization of proteins on a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) transducer is a delicate procedure since loss of protein bioactivity can occur upon contact with the untreated metal surface. Solution to the problem is the use of an immobilization matrix having a complex structure.
[...] Read more.
Immobilization of proteins on a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) transducer is a delicate procedure since loss of protein bioactivity can occur upon contact with the untreated metal surface. Solution to the problem is the use of an immobilization matrix having a complex structure. However, this is at the expense of biosensor selectivity and sensitivity. It has been shown that the matrix-assisted pulsed laser evaporation (MAPLE) method has been successfully applied for direct immobilization (without a built-in matrix) of proteins, preserving their bioactivity. So far, MAPLE deposition has not been performed on a gold surface as required for SPR biosensors. In this paper we study the impact of direct immobilization of heme proteins (hemoglobin (Hb) and myoglobin (Mb)) on their bioactivity. For the purpose, Hb and Mb were directly immobilized by MAPLE technique on a SPR transducer. The bioactivity of the ligands immobilized in the above-mentioned way was assessed by SPR registration of the molecular reactions of various Hb/Mb functional groups. By SPR we studied the reaction between the beta chain of the Hb molecule and glucose, which shows the structural integrity of the immobilized Hb. A supplementary study of films deposited by FTIR and AFM was provided. The experimental facts showed that direct immobilization of an intact molecule was achieved.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessLetter
Determination of the pH Gradient in Hair Follicles of Human Volunteers Using pH-Sensitive Melamine Formaldehyde-Pyranine Nile Blue Microparticles
by
Dennis Kaden, Lars Dähne, Fanny Knorr, Heike Richter, Jürgen Lademann, Martina C. Meinke, Alexa Patzelt, Maxim E. Darvin and Sora Jung
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2589
Abstract
Nanoparticles can be applied to the hair follicles, which can serve as reservoirs for triggered drug release. A valid measurement method for the determination of the pH within the hair follicle in vivo has not been shown yet. Here, melamine formaldehyde particles up
[...] Read more.
Nanoparticles can be applied to the hair follicles, which can serve as reservoirs for triggered drug release. A valid measurement method for the determination of the pH within the hair follicle in vivo has not been shown yet. Here, melamine formaldehyde particles up to 9 µm in size were applied on 40 freshly plucked scalp hairs of eight individuals to determine the pH along the hair shaft down to the root area of the hair. For fluorescent pH indicators, pyranine and Nile blue were incorporated into the particles. Measurements were conducted using confocal laser scanning microscopy. A pH decay gradient could be found from the hair sheath towards the external hair shaft (
p = 0.012) with pH values at the hair sheath of 6.63 ± 0.09, at the hair sheath end at 6.33 ± 0.11, and at the external hair shaft at 6.17 ± 0.09 (mean ± SE). The pH difference between the hair sheath end and the external hair shaft was found to be significant (
p = 0.036). The results might be comparable with the pH within the hair follicle in vivo indicating a pH increase towards the hair root.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design of Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Nanosensor Array
by
Yaakov Mandelbaum, Raz Mottes, Zeev Zalevsky, David Zitoun and Avi Karsenty
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3358
Abstract
An advanced Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Nanosensor Array, dedicated to serve in the future as a pH imager for the real-time detection of chemical reaction, is presented. The full flow of elementary steps—architecture, design, simulations, fabrication, and preliminary experimental results of structural characterization
[...] Read more.
An advanced Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Nanosensor Array, dedicated to serve in the future as a pH imager for the real-time detection of chemical reaction, is presented. The full flow of elementary steps—architecture, design, simulations, fabrication, and preliminary experimental results of structural characterization (Focused Ion Beam (FIB), TEM and SEM)—show an advanced SERS pixel array that is capable of providing spatially resolved measurements of chemical pH in a fluid target that became more than desirable in this period. Ultimately, the goal will be to provide real-time monitoring of a chemical reaction. The pixels consist of a nanostructured substrate composed of an array of projections or cavities. The shape of the nanostructures and the thickness of the metallic (Ag or Au) layer can be tuned to give maximal enhancement at the desired wavelength. The number and arrangement of nanostructures is optimized to obtain maximal responsivity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
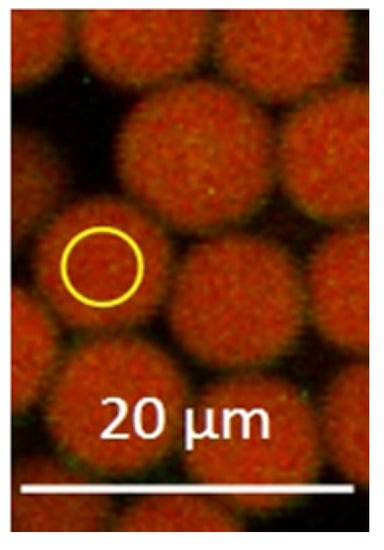
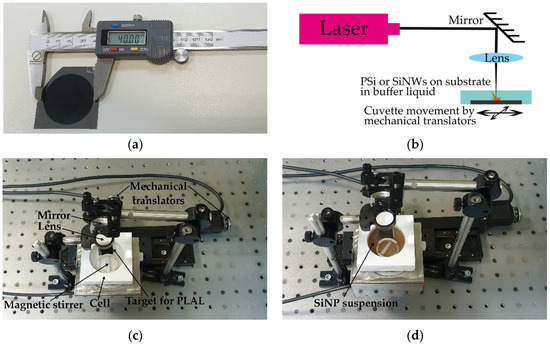
Nanoparticles Produced via Laser Ablation of Porous Silicon and Silicon Nanowires for Optical Bioimaging
by
Stanislav V. Zabotnov, Anastasiia V. Skobelkina, Ekaterina A. Sergeeva, Daria A. Kurakina, Aleksandr V. Khilov, Fedor V. Kashaev, Tatyana P. Kaminskaya, Denis E. Presnov, Pavel D. Agrba, Dmitrii V. Shuleiko, Pavel K. Kashkarov, Leonid A. Golovan and Mikhail Yu. Kirillin
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 2964
Abstract
Modern trends in optical bioimaging require novel nanoproducts combining high image contrast with efficient treatment capabilities. Silicon nanoparticles are a wide class of nanoobjects with tunable optical properties, which has potential as contrasting agents for fluorescence imaging and optical coherence tomography. In this
[...] Read more.
Modern trends in optical bioimaging require novel nanoproducts combining high image contrast with efficient treatment capabilities. Silicon nanoparticles are a wide class of nanoobjects with tunable optical properties, which has potential as contrasting agents for fluorescence imaging and optical coherence tomography. In this paper we report on developing a novel technique for fabricating silicon nanoparticles by means of picosecond laser ablation of porous silicon films and silicon nanowire arrays in water and ethanol. Structural and optical properties of these particles were studied using scanning electron and atomic force microscopy, Raman scattering, spectrophotometry, fluorescence, and optical coherence tomography measurements. The essential features of the fabricated silicon nanoparticles are sizes smaller than 100 nm and crystalline phase presence. Effective fluorescence and light scattering of the laser-ablated silicon nanoparticles in the visible and near infrared ranges opens new prospects of their employment as contrasting agents in biophotonics, which was confirmed by pilot experiments on optical imaging.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
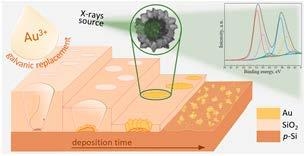
Morphology and Microstructure Evolution of Gold Nanostructures in the Limited Volume Porous Matrices
by
Dzmitry V. Yakimchuk, Victoria D. Bundyukova, Jon Ustarroz, Herman Terryn, Kitty Baert, Artem L. Kozlovskiy, Maxim V. Zdorovets, Soslan A. Khubezhov, Alex V. Trukhanov, Sergei V. Trukhanov, Larissa V. Panina, Grigory M. Arzumanyan, Kahramon Z. Mamatkulov, Daria I. Tishkevich, Egor Y. Kaniukov and Vladimir Sivakov
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3110
Abstract
The modern development of nanotechnology requires the discovery of simple approaches that ensure the controlled formation of functional nanostructures with a predetermined morphology. One of the simplest approaches is the self-assembly of nanostructures. The widespread implementation of self-assembly is limited by the complexity
[...] Read more.
The modern development of nanotechnology requires the discovery of simple approaches that ensure the controlled formation of functional nanostructures with a predetermined morphology. One of the simplest approaches is the self-assembly of nanostructures. The widespread implementation of self-assembly is limited by the complexity of controlled processes in a large volume where, due to the temperature, ion concentration, and other thermodynamics factors, local changes in diffusion-limited processes may occur, leading to unexpected nanostructure growth. The easiest ways to control the diffusion-limited processes are spatial limitation and localized growth of nanostructures in a porous matrix. In this paper, we propose to apply the method of controlled self-assembly of gold nanostructures in a limited pore volume of a silicon oxide matrix with submicron pore sizes. A detailed study of achieved gold nanostructures’ morphology, microstructure, and surface composition at different formation stages is carried out to understand the peculiarities of realized nanostructures. Based on the obtained results, a mechanism for the growth of gold nanostructures in a limited volume, which can be used for the controlled formation of nanostructures with a predetermined geometry and composition, has been proposed. The results observed in the present study can be useful for the design of plasmonic-active surfaces for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy-based detection of ultra-low concentration of different chemical or biological analytes, where the size of the localized gold nanostructures is comparable with the spot area of the focused laser beam.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Advantages of Highly Spherical Gold Nanoparticles as Labels for Lateral Flow Immunoassay
by
Nadezhda A. Byzova, Anatoly V. Zherdev, Boris N. Khlebtsov, Andrey M. Burov, Nikolai G. Khlebtsov and Boris B. Dzantiev
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 5216
Abstract
The use of lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs) for rapid on-site testing is restricted by their relatively high limit of detection (LoD). One possible way to decrease the LoD is to optimize nanoparticle properties that are used as labels. We compare two types of
[...] Read more.
The use of lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs) for rapid on-site testing is restricted by their relatively high limit of detection (LoD). One possible way to decrease the LoD is to optimize nanoparticle properties that are used as labels. We compare two types of Au nanoparticles: usual quasispherical gold nanoparticles (C-GNPs), obtained by the Turkevich–Frens method, and superspherical gold nanoparticles (S-GNPs), obtained by a progressive overgrowth technique. Average diameters were 18.6–47.5 nm for C-GNPs and 20.2–90.4 nm for S-GNPs. Cardiomarker troponin I was considered as the target analyte. Adsorption and covalent conjugation with antibodies were tested for both GNP types. For C-GNPs, the minimal LoD was obtained with 33.7 nm nanoparticles, reaching 12.7 ng/mL for covalent immobilization and 9.9 ng/mL for adsorption. The average diameter of S-GNPs varied from 20.2 to 64.5 nm, which resulted in a decrease in LoD for an LFIA of troponin I from 3.4 to 1.2 ng/mL for covalent immobilization and from 2.9 to 2.0 ng/mL for adsorption. Thus, we obtained an 8-fold decrease in LoD (9.9 to 1.2 ng/mL) by using S-GNPs. This effect can be related to more effective antibody immobilization and improved S-GNP optical properties. The obtained results can improve LFIAs for various practically significant analytes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures