-
 Quality and Nutraceutical Features of Cicer arietinum L. Stored under Nitrogen Atmosphere
Quality and Nutraceutical Features of Cicer arietinum L. Stored under Nitrogen Atmosphere -
 Geometric Analysis of Seed Shape Diversity in the Cucurbitaceae
Geometric Analysis of Seed Shape Diversity in the Cucurbitaceae -
 Exploring Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation in Allium fistulosum L. Seeds Exposed to Different Storage Conditions
Exploring Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation in Allium fistulosum L. Seeds Exposed to Different Storage Conditions -
 Chemopreventive Potential of Oils Extracted from Seeds of Three Annona Species
Chemopreventive Potential of Oils Extracted from Seeds of Three Annona Species
Journal Description
Seeds
Seeds
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on seed science and technology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 29.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Seeds is a companion journal of Agronomy.
Latest Articles
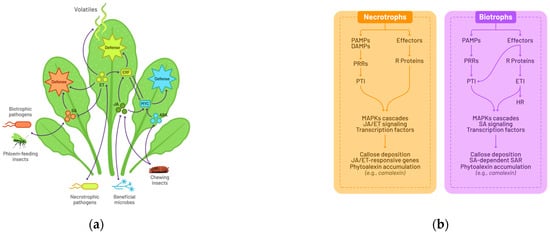
Fungal Necrotrophic Interaction: A Case Study of Seed Immune Response to a Seed-Borne Pathogen
Seeds 2024, 3(2), 216-227; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3020017 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Seeds play a vital role in the perpetuation of plant species, both in natural environments and agriculture. However, they often face challenges from biotic stresses, such as seed-borne pathogenic fungi. The transgenerational transmission of these seed-borne fungi, along with their dissemination during seed
[...] Read more.
Seeds play a vital role in the perpetuation of plant species, both in natural environments and agriculture. However, they often face challenges from biotic stresses, such as seed-borne pathogenic fungi. The transgenerational transmission of these seed-borne fungi, along with their dissemination during seed commercialization, can contribute to the emergence of global epidemic diseases, resulting in substantial economic losses. Despite the recognized impact of seed-borne pathogens on agriculture, our understanding of seed–pathogen interactions remains limited. This review establishes parallels between the current state of knowledge regarding seed responses to pathogen interactions and well-established plant defense models, primarily derived from typical physiological conditions observed during leaf infections. Examining fragmented results from various pathosystems, this review seeks to offer a comprehensive overview of our current understanding of interactions during seed development and germination. The necrotrophic interactions in Brassicaceae are described using recent transcriptomic and genetic studies focused on the Arabidopsis/Alternaria pathosystem, which illustrates original response pathways in germinating seeds that markedly differ from the general concept of plant–pathogen interactions. The co-existence of regulatory mechanisms affecting both seed resistance and susceptibility, potentially promoting fungal colonization, is examined. The vulnerable response during germination emerges as a crucial consideration in the context of sustainable plant health management in agriculture.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Marquandomyces marquandii SGSF043 on Maize Growth Promotion and Soil Enzyme Activity
by
Xu Zheng, Bo Zhang, Feng Shi, Yuanlong Chen and Xiumei Zhao
Seeds 2024, 3(2), 203-215; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3020016 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In order to further clarify the growth-promoting effect of the non-core Metarhizium sp. Marquandomyces marquandii on plants, M. marquandii SGSF043, which was obtained via pre-screening in the laboratory, was selected as a test strain and the seed soaking method was adopted. The effects
[...] Read more.
In order to further clarify the growth-promoting effect of the non-core Metarhizium sp. Marquandomyces marquandii on plants, M. marquandii SGSF043, which was obtained via pre-screening in the laboratory, was selected as a test strain and the seed soaking method was adopted. The effects of a fermentation broth obtained from this strain on the seed germination, seedling growth, and rhizosphere soil enzyme activity of maize were studied. The results were as follows: In seed germination tests, M. marquandii SGSF043 fermentation liquid had a certain inhibitory effect on corn seed germination, and the germination rate was only 15%. When the fermentation solution was diluted 10 times, the germination rate reached 97%. After the germination test, the growth of maize plumules was promoted in the groups treated with 10-times and 1000-times dilutions. In the field community experiment, based on the comprehensive evaluation of seedling biomass indicators, the solution diluted 100 times had the best growth-promoting effect. The aboveground fresh weight was increased by 127.13% compared with the control group. The results show that M. marquandii SGSF043 has the potential to promote the growth of maize and improve the soil environment, which provides a theoretical basis for the research on and the application of M. marquandii in farmland.
Full article
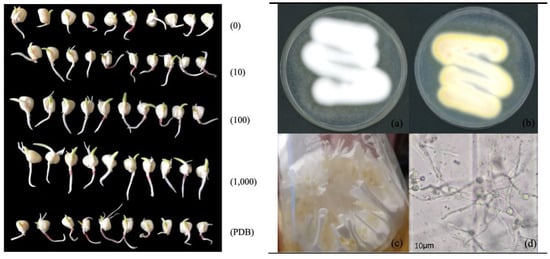
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Germination Kinetics of Ferula communis L. Seeds, a Potentially Multipurpose-Use Wild Species
by
Miriam Distefano, Giovanni Avola, Stefano Berti and Ezio Riggi
Seeds 2024, 3(2), 196-202; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3020015 - 14 Apr 2024
Abstract
Despite exhibiting intriguing features associated with its multipurpose applications and drought tolerance, Ferula communis remains a wild and uncultivated species, with limited experimental research on its biology, starting from seed germination and extending to its ecology. The purpose of this study was to
[...] Read more.
Despite exhibiting intriguing features associated with its multipurpose applications and drought tolerance, Ferula communis remains a wild and uncultivated species, with limited experimental research on its biology, starting from seed germination and extending to its ecology. The purpose of this study was to investigate potential germination and kinetics in F. communis seeds in response to four cold stratification periods (0, 15, 45, and 90 days at a constant temperature of 5 °C) and four temperatures (5, 10, 15, and 20 °C) under continuous darkness. F. communis exhibited a pronounced germination potential exceeding 90%, with the optimal temperature for germination falling within the range of 5 °C to 15 °C, without necessitating cold stratification. A dramatic drop of the germination percentage was observed at 20 °C (<10%), suggesting a form of conditional dormancy attributed to the higher temperature tested.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Parameters of Seed Germination in Wild Plant Species)
►▼
Show Figures
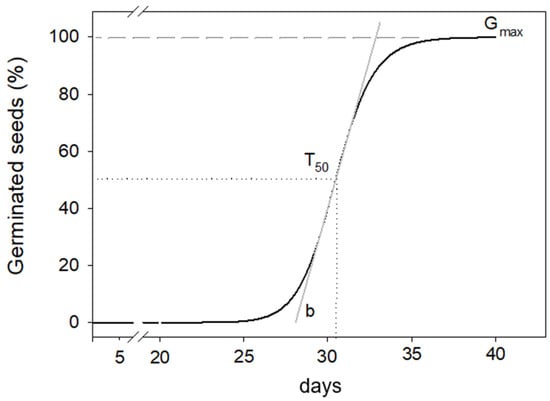
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Variations in Seed Dormancy Occurrence and Their Classifications in Thirteen Actinidia Species
by
Azadeh Esfandiari, Cara Norling, Ryohei Kaji, Andrew McLachlan, Liya Mathew, Margaret Fleming, Ed Morgan and Jayanthi Nadarajan
Seeds 2024, 3(2), 179-195; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3020014 - 22 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As differences in seed dormancy between Actinidia species have not been reported previously, in this study we characterized the variation in the dormancy of seeds in 13 kiwifruit species that originated from different regions of China and Taiwan, and for which mature plants
[...] Read more.
As differences in seed dormancy between Actinidia species have not been reported previously, in this study we characterized the variation in the dormancy of seeds in 13 kiwifruit species that originated from different regions of China and Taiwan, and for which mature plants are now growing in New Zealand orchards. Dormancy-breaking treatments, including cold-moist stratification, seed coat scarification and soaking in water and gibberellic acid (GA3), were tested for their efficacy in alleviating dormancy and improving final germination and germination rates. In addition, we assessed seed viability using RNA integrity analysis to distinguish dead seeds from dormant seeds. This study identified that dormancy type in Actinidia seeds is species-specific and can be morphological, morphophysiological or a combination of physiological and physical, and that seed RNA integrity is a useful metric to incorporate into seed dormancy studies. Our results also suggest that species originating from colder climates that experience large differences between winter minimum and summer maximum temperatures exhibit physiological dormancy and require cold-moist stratification, contrasting with species originating in milder climates. Interestingly, although not all seeds from all the species were dormant, the proportion of dormant seeds in each species did not correlate to the climatic data of the region from which they originated. These findings provide new insights into mechanisms of seed dormancy in kiwifruit.
Full article
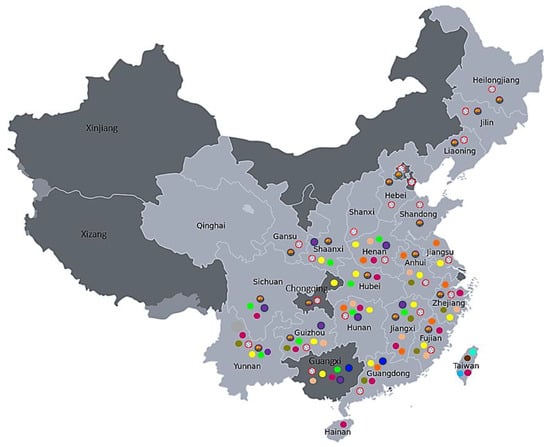
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Magneto-Priming of Seeds Decreases the Saline Effect of Wastewater Irrigation on Broccoli Germination and Seedling Growth
by
Julio Gutierrez, Francisco Alonso, Jose Alvarez, María Victoria Carbonell, Elvira Martinez, Mercedes Florez, María del Mar Delgado, Brenda Katherine Franco and Claudia Hernandez-Aguilar
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 169-178; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010013 - 18 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Crop plant varieties exhibit diverse reactions when subjected to wastewater irrigation in terms of seed germination, seedling development, and overall productivity. Magneto-priming, which involves treating seeds with an appropriate magnetic field, is gaining popularity as the preferred technique due to its effectiveness and
[...] Read more.
Crop plant varieties exhibit diverse reactions when subjected to wastewater irrigation in terms of seed germination, seedling development, and overall productivity. Magneto-priming, which involves treating seeds with an appropriate magnetic field, is gaining popularity as the preferred technique due to its effectiveness and environmentally friendly characteristics for improving seed vigour, growth, and plant yield. In this study, magneto-primed and non-primed broccoli seeds were irrigated with distilled or wastewater and kept under observation for a 10-day period to record seedling growth. A laboratory study was conducted to evaluate the impact of magneto-priming on broccoli seeds with a homogeneous stationary magnetic-field strength of 5.9 mT for 1 h. They were irrigated with two types of water: distilled and wastewater. Another test was performed to evaluate the effect of 1-h and 2-h magneto-priming on seed germination when seeds were irrigated with wastewater. From the results, the broccoli seedlings irrigated with distilled water grew higher and heavier than the ones irrigated with wastewater, probably due to the significant amounts of salts in organic wastewater. Nonetheless, the saline effect of wastewater was ameliorated when seeds were previously magneto-primed. All the germination parameters of broccoli seeds irrigated with wastewater were significantly reduced when seeds were magneto-primed for both periods.
Full article
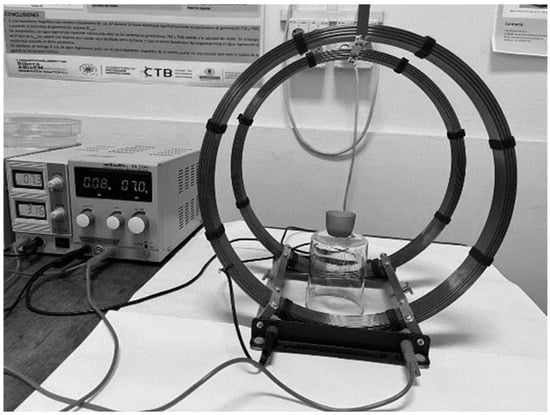

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic Parameters in Mesocotyl Elongation and Principal Components for Corn in High Valleys, Mexico
by
Antonio Villalobos-González, Ignacio Benítez-Riquelme, Fernando Castillo-González, Ma. del Carmen Mendoza-Castillo and Alejandro Espinosa-Calderón
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 149-168; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010012 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Corn germplasm with different mesocotyl elongation was characterized for High Valleys in Mexico by estimating the general combinatory aptitude (GCA), specific combinatory aptitude (SCA), heterosis (H), inbreeding depression (ID) and principal component aptitude (PCA), with the purpose of directing the improvement for deep
[...] Read more.
Corn germplasm with different mesocotyl elongation was characterized for High Valleys in Mexico by estimating the general combinatory aptitude (GCA), specific combinatory aptitude (SCA), heterosis (H), inbreeding depression (ID) and principal component aptitude (PCA), with the purpose of directing the improvement for deep sowing. The hypothesis was that the parents and crosses of mesocotyl present variability in seedling and adult plant traits based on deep sowing. The 36 F1 and F2 crosses—derived from nine parents, three with short mesocotyl (S), three medium (M) and three long (L), obtained through Griffing diallel II—plus the parents were planted in sand beds and polyethylene bags in a greenhouse during the spring–summer cycles of 2021 and 2022. The following traits were measured: length of mesocotyl (LM), length of coleoptile, total seedling dry matter and 10 cob traits in addition to total dry matter. In 11 of the 14 traits, there was a positive and significant correlation (p ≤ 0.05) between the GCA of the parents and their LM. The highest SCA, H and ID (p ≤ 0.05) were for crosses L × L for all the traits measured. When comparing the GCA/SCA proportions, this relation varied from 0.76 to 0.97, which points to practically equal additive effects with those of dominance; however, in parents and L × L crosses, this relation was on average 0.94, 1.07 in M × M, 0.22 in S × S and 0.36 in L × S. In both F1 and F2, the variation was explained by two principal components: 89.5% for GCA and 73.4% for SCA. In both generations, the parents with higher GCA were H-48, HS-2 and Promesa, the three with long mesocotyl, while those with the highest GCA were crosses between these three hybrids.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Soybean Seed Coat Cracks and Green Seeds—Predisposing Conditions, Identification and Management
by
Ernane Miranda Lemes and Hugo César Rodrigues Moreira Catão
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 133-148; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010011 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Seed coat cracking and green seeds threaten soybean crop production. Seed coat cracking results from a complex interplay of genetic factors, environmental stresses, and crop management practices. Green seeds, linked to water deficit, nutritional deficiencies, and environmental stresses, exhibit reduced quality and viability.
[...] Read more.
Seed coat cracking and green seeds threaten soybean crop production. Seed coat cracking results from a complex interplay of genetic factors, environmental stresses, and crop management practices. Green seeds, linked to water deficit, nutritional deficiencies, and environmental stresses, exhibit reduced quality and viability. The intricate relationships between seed coat integrity and seed permeability, influenced by the lignin content, porosity, and color, play a pivotal role in seed germination, storage potential, and resistance to field stresses. These issues reverberate through the soybean agricultural supply chain. Strategic interventions are crucial to address these abnormalities and ensure soybean productivity. Seed germination and vigor are reduced due to seed coat cracking and green seeds, undermining food security and necessitating additional resources for disease management. The occurrence and identification of green seeds and seeds with cracks in the seed coat were also reported by identifying the genes and QTLs (quantitative trait loci) associated with these characteristics. Herbicides, commonly used in weed management, may offer a strategic approach to mitigating seed coat cracking and green seed occurrence. Understanding the complex interactions between the genetics, environmental factors, and management practices influencing seed abnormalities is essential as global climate change intensifies. This review emphasizes the need for integrated strategies, balanced plant nutrition, and cohesive phytosanitary management to mainly alleviate seed coat cracking and greenish occurrences in soybeans and other plant species.
Full article
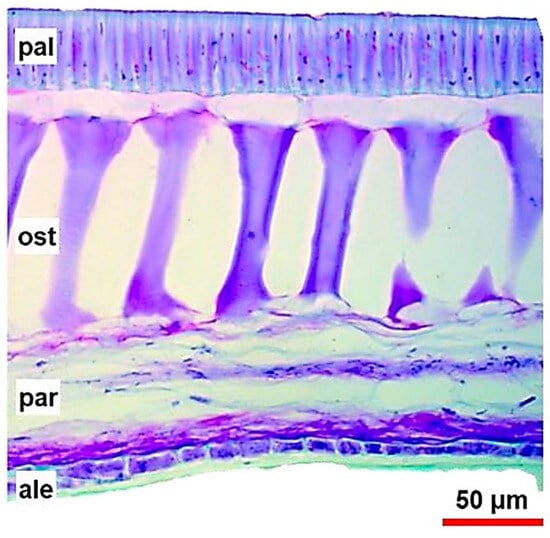
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation in Allium fistulosum L. Seeds Exposed to Different Storage Conditions
by
Gregorio Padula, Anca Macovei, Adriano Ravasio, Andrea Pagano, Conrado Jr Dueñas, Xianzong Xia, Roman Hołubowicz and Alma Balestrazzi
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 123-132; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010010 - 09 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The purpose of this work was to investigate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Allium fistulosum seeds stored under different conditions. Optimized seed storage conditions are essential to maintain seed viability, otherwise accumulation of ROS-induced oxidative damage can lead to seed
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this work was to investigate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Allium fistulosum seeds stored under different conditions. Optimized seed storage conditions are essential to maintain seed viability, otherwise accumulation of ROS-induced oxidative damage can lead to seed aging. The A. fistulosum seed lots used in this study have been selected based on their breeding background and reproduction site. Seed samples were stored up to 22 months under six different conditions of temperature (25, 10, and 7.5 °C) and relative humidity (RH) (25% and 45% RH). A germination test and ROS quantification assay were performed on the samples collected after 12 and 22 months of storage, respectively. Within a time-window of 10 months, the tested seed lots evidenced a decrease in the germination rate associated with increased ROS levels. Correlation analysis also showed that ROS production was influenced by genotype. The reported data showed that ROS accumulation was dependent on the storage condition and genotype. Some of the tested seed lots appeared to be prone to ROS accumulation, independent of storage conditions. On the other hand, specific condition storages (25 °C, 25% RH; 25 °C, 45% RH; 10 °C, 25% RH; 7.5 °C, 25% RH) resulted in a lower impact on seed aging.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Chemopreventive Potential of Oils Extracted from Seeds of Three Annona Species
by
Prabash Attanayake, Dinesha Rupasinghe, Ashoka Gamage, Terrence Madhujith and Othmane Merah
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 105-122; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010009 - 07 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Annona fruit, leaves, seeds, roots, and bark have been conventionally used in many countries for medical treatments as they are considered ideal sources of pharmacologically active compounds, but Annona remains an underutilized fruit in many countries. The fruit of these plants is delicately
[...] Read more.
Annona fruit, leaves, seeds, roots, and bark have been conventionally used in many countries for medical treatments as they are considered ideal sources of pharmacologically active compounds, but Annona remains an underutilized fruit in many countries. The fruit of these plants is delicately flavored and is used in industrial products such as ready-to-serve beverages, wine, jellies, jam, and fruit-butter preserve, while the seeds generally go to waste. Annona seed oil contains numerous health-benefiting factors such as vitamins, minerals, bioactive compounds, fatty acids, antioxidants, and phenolic compounds, which are responsible for various biological activities, including antibacterial, antioxidant, and antitumor activities. Cancer is a worldwide major health problem that remains unresolved. Even though the current treatments can manage to reduce tumor growth, there is an urgent need to investigate more efficient but less expensive novel techniques to overcome some of the restrictions in treating tumors. Annona might offer an indispensable choice besides chemotherapy and radiotherapy, especially for terminally ill patients, as the Annona genus contains secondary metabolites in nearly every component of Annona plants. Research has shown that many Annona species contain promising components that could potentially exhibit anticancer activity, but the information available is scarce and inconsistent. Annona muricata (Soursop, “Katuanoda”), Annona squamosa (Sweetsop, “Seenianoda”), and Annona reticulata (Custard apple, “Welianoda”) are three commonly cultivated edible Annona species in Sri Lanka. The main objective of the review was to present an updated comprehensive literature analysis of the putative chemopreventive functions against cancer cell lines/the anticancer effect on cancers, phytochemical properties, and antioxidant properties possessed by the seed oils of three selected common Annona species. Although there are some in vitro and in vivo experimental investigations supporting the benefits of Annona seed oils, clinical investigations are still needed to explore concealed areas, determine the effects on the human body, determine the safest concentration, and determine health-contributing benefits before they are submitted to clinical trials.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Seeds: What Happened in 2023?
by
José Antonio Hernández, Pedro Díaz-Vivancos and Gregorio Barba-Espín
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 103-104; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010008 - 29 Jan 2024
Abstract
As Editor-in-Chief of Seeds, I would like to thank the Authors, Reviewers, Editorial Board Members, Academic Editors, Assistant Editors and all the Staff involved in Seeds for their effort and dedication, which has helped to establish Seeds as a scientific journal in
[...] Read more.
As Editor-in-Chief of Seeds, I would like to thank the Authors, Reviewers, Editorial Board Members, Academic Editors, Assistant Editors and all the Staff involved in Seeds for their effort and dedication, which has helped to establish Seeds as a scientific journal in the field of Seed Biology and Technology [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Hydro, Mechanical, and Chemical Treatments to Seed for Germination and Seedling Growth of Saraca asoca (Roxb. De Wilde)
by
Abha Manohar Kandileri, Gopal Shukla, Libin T. Louis, Anil Raj Kizha, Azamal Husen and Sumit Chakravarty
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 88-102; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010007 - 10 Jan 2024
Abstract
It has been noticed that Saraca asoca (Roxb. de Wilde) populations are drastically declining in the wild. Conserving such populations is crucial because of the numerous ecological, cultural, and economic values. The purpose of our study was to determine if germination and seedling
[...] Read more.
It has been noticed that Saraca asoca (Roxb. de Wilde) populations are drastically declining in the wild. Conserving such populations is crucial because of the numerous ecological, cultural, and economic values. The purpose of our study was to determine if germination and seedling growth could be improved for globally vulnerable Ashoka populations. The study analyzed the effect of various hydro, mechanical, and chemical pre-sowing treatments on the germination and one-year growth of Ashoka seedlings. Our results demonstrated that mechanical (exposing the seed cotyledons) and soaking of seeds in hot water treatments (60 °C) were better than all other water- and chemical-based pre-sowing treatments used in the study of enhancing germination. Nevertheless, chemical treatments were better for the growth and survival of the seedlings. This methodology offers to restore the scattered populations of Ashoka that are facing the risk of extinction in the wild while successfully meeting the commercial demand for this medicinal tree.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Sesame Germination Dynamics: Unravelling Sesame’s Response to Salinity and Temperature Variability
by
Majid Gholamhoseini and Aria Dolatabadian
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 76-87; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010006 - 10 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sesame (Sesamum indicum), a highly valued oilseed, faces challenges in cultivation, especially in regions susceptible to environmental stressors. This study investigates the interactive effects of salinity and temperature on sesame seed germination. Two cultivars, Darab 1 and Oltan, were subjected to
[...] Read more.
Sesame (Sesamum indicum), a highly valued oilseed, faces challenges in cultivation, especially in regions susceptible to environmental stressors. This study investigates the interactive effects of salinity and temperature on sesame seed germination. Two cultivars, Darab 1 and Oltan, were subjected to various salinity levels (−3 to −12 bars) and temperatures (15 °C, 20 °C, and 25 °C). Results revealed that at 15 °C, salinity levels beyond -3 bars significantly reduced germination, while at 25 °C, 40% and 62% germination rates were recorded even at −12 bars for Darab 1 and Oltan, respectively. This study highlights the importance of temperature in mitigating the inhibitory effects of salinity on germination. Germination speed exhibited a decline with increasing salinity, particularly at lower temperatures. Shoot and root lengths and dry weights decreased with rising salinity, but Oltan demonstrated greater tolerance than Darab 1. The research emphasises the species-specific nature of temperature-salinity interactions and the intraspecific variability among sesame cultivars. Notably, Oltan, adapted to arid regions with elevated temperatures, displayed increased tolerance to salinity stress. These findings contribute to understanding sesame’s resilience to environmental stressors, aiding in developing resilient cultivars for challenging agricultural landscapes. Overall, temperature is pivotal in influencing sesame seed germination and early seedling growth under salinity stress, offering insights for optimised cultivation practices.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Effects of Storage Conditions on Seed Deterioration and Ageing: How to Improve Seed Longevity
by
Françoise Corbineau
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 56-75; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010005 - 09 Jan 2024
Abstract
Seeds are classified as either: orthodox, seeds that tolerate dehydration; recalcitrant, seeds that are high in moisture content and cannot withstand intensive desiccation; or intermediate, seeds that survive dehydration but die during dry storage at low temperatures. Seed lifespan depends on the seed
[...] Read more.
Seeds are classified as either: orthodox, seeds that tolerate dehydration; recalcitrant, seeds that are high in moisture content and cannot withstand intensive desiccation; or intermediate, seeds that survive dehydration but die during dry storage at low temperatures. Seed lifespan depends on the seed category and also varies from one species to another. The rate of loss of vigor and viability of orthodox seeds depends mainly on temperature and seed moisture content (MC); the lower the MC and storage temperature, the longer the longevity. Ultimately, storage in liquid nitrogen or seed ultra-drying by well-adapted processes should allow for long-term storage. The ageing of orthodox seeds is associated with numerous forms of cellular and metabolic damage (membrane integrity, energy metabolism, and the impairment of DNA, RNA, and proteins) in which reactive oxygen species play a prominent role. Interestingly, priming treatment can reinvigorate aged seeds by restoring the antioxidant systems. The storage of recalcitrant seeds is very difficult since they must be placed in a wet medium to avoid dehydration and at temperatures low enough to prevent germination but warm enough to avoid chilling injury. A better understanding of the mechanisms involved in ageing is necessary to identify markers in order to estimate seed longevity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Technologies to Improve the Yield and Storage of Seeds for Different Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Geometric Analysis of Seed Shape Diversity in the Cucurbitaceae
by
José Javier Martín-Gómez, Diego Gutiérrez del Pozo, José Luis Rodríguez-Lorenzo, Ángel Tocino and Emilio Cervantes
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 40-55; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010004 - 31 Dec 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
The Cucurbitaceae is a monophyletic family with close to 1000 species of climbers, including important agronomic species and varieties characterized by tendrils and pepo fruits. The seed’s morphology is varied, and the development and structure of the seed coat have been described in
[...] Read more.
The Cucurbitaceae is a monophyletic family with close to 1000 species of climbers, including important agronomic species and varieties characterized by tendrils and pepo fruits. The seed’s morphology is varied, and the development and structure of the seed coat have been described in detail on some species. Overall description of the seed shape is based on terms comparing it with geometric figures, but quantitative methods are lacking in the literature. Here we apply a general morphological analysis to seeds of representative genera of the Cucurbitaceae, followed by curvature analysis in the poles and symmetry analysis. These methods are useful for the quantitative description of seed shape and the comparison between species and varieties. Differences between species were found for most morphological measurements, as well as for symmetry and curvature values. The comparison between three species of Cucumis (Cucumis sativus, C. myriocarpus and C. melo) and two varieties of C. melo reveals differences between species and varieties both in curvature and symmetry. The results obtained from both methods, curvature and symmetry analysis, form similar groupings in a cluster analysis. The methods described here were applied for the identification of agronomic varieties and the quantitative description of seed shape in taxonomy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Imaging and Artificial Intelligence in Seed Research)
►▼
Show Figures
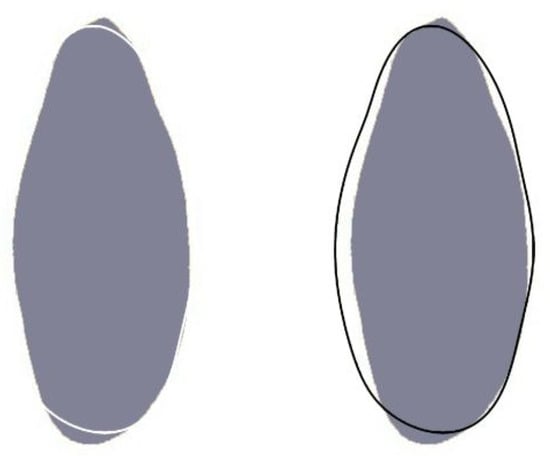
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Physical Conditions That Limit Chickpea Root Growth and Emergence in Heavy-Textured Soil
by
Wendy H. Vance, Richard W. Bell and Chris Johansen
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 26-39; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010003 - 30 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The tillage method determines several soil physical parameters that affect the emergence of post-rice chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) in the Indo-Gangetic Plain of South Asia. Mechanised row-sowing with minimum soil disturbance and crop residue retention in medium-to-heavy-textured soils will alter the seedbed
[...] Read more.
The tillage method determines several soil physical parameters that affect the emergence of post-rice chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) in the Indo-Gangetic Plain of South Asia. Mechanised row-sowing with minimum soil disturbance and crop residue retention in medium-to-heavy-textured soils will alter the seedbed when compared to that prepared after traditional full tillage and broadcast sowing. Whilst minimum soil disturbance and timely sowing may alleviate the soil water constraint to crop establishment, other soil physical properties such as soil strength, bulk density, and aggregate size may still inhibit seedling emergence and root elongation. This study’s objective was to determine the limitations to chickpea crop establishment with increasing bulk density and soil strength, and different aggregate sizes below and above the seed. In two growth cabinet studies, chickpea seed was sown in clay soil with (i) a bulk density range of 1.3–1.9 Mg m−3 (Experiment 1) and (ii) the combination of bulk densities (1.3 and 1.8 Mg m−3) and aggregate sizes (<2 mm and >4 mm) above and below the seed (Experiment 2). Root length was significantly reduced with increasing bulk density (>1.4 Mg m−3), and soil strength impeded early root growth at >1 MPa. Where main root growth was impeded due to high bulk density and soil strength, a greater proportion of total root growth was associated with the elongation of lateral roots. The present study suggests that the soil above the seed needs to be loosely compacted (<1.3 Mg m−3) for seedling emergence to occur. Further research is needed to determine the size of the soil aggregates, which optimise germination and emergence. We conclude that soil strength values typical of field conditions in the Indo-Gangetic Plain at sowing will impede the root growth of chickpea seedlings. This effect can be minimised by changing tillage operations to produce seedbed conditions that are within the limiting thresholds of bulk density and soil strength.
Full article
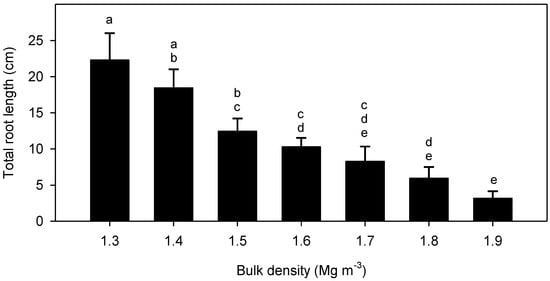
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quality and Nutraceutical Features of Cicer arietinum L. Stored under Nitrogen Atmosphere
by
Lorenzo Moncini, Gea Guerriero, Gabriele Simone, Chiara Vita and Roberto Berni
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 16-25; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010002 - 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
Cicer arietinum L. (chickpea, or garbanzo bean) is one of the most consumed legumes worldwide. It is a rich source of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, minerals and vitamins with very low cholesterol. From a nutritional point of view, despite the low content of fats,
[...] Read more.
Cicer arietinum L. (chickpea, or garbanzo bean) is one of the most consumed legumes worldwide. It is a rich source of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, minerals and vitamins with very low cholesterol. From a nutritional point of view, despite the low content of fats, the seeds contain various unsaturated acids, such as linoleic and oleic acids, as well as bioactive compounds, like antioxidants, with reactive oxygen species-scavenging activities. It is known that long periods of storage can drastically affect the preservation of these compounds in seeds. For this reason, in the last few years, different methods have been tested with the aim of increasing the shelf life of economically relevant beans, seeds and cereals. A promising and eco-friendly alternative to traditional storage is the use of a controlled atmosphere, represented by N2-pressurized silos. The present study aims at evaluating the content of different compounds, e.g., fatty acids, proteins, vitamins, and molecules of nutraceutical interest, in chickpeas stored at ambient temperature in N2-pressurized silos (98.5 ± 0.5% (v/v)) and control ones (standard storage) in long-term kinetics (1 year). The results show the stable content of most compounds during the kinetics. However, vitamin E decreased in samples stored under both standard and controlled atmosphere conditions, with a more pronounced and significant decrease under standard conditions as compared to the controlled atmosphere. Additionally, samples stored under a controlled atmosphere show a total higher content of quinic, indole butyric and benzoic acid, as well as their derivates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Technologies to Improve the Yield and Storage of Seeds for Different Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
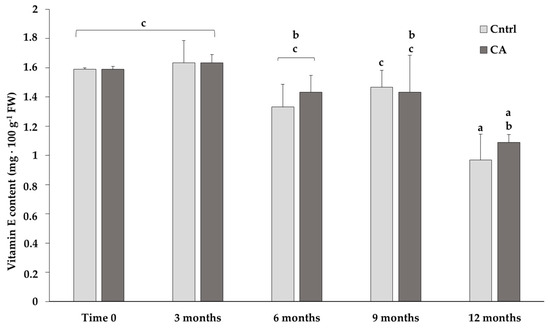
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Altitudinal Genetic Variation of Pinus oocarpa Seedling Emergence in the Southern Mountains, Oaxaca, Mexico
by
Mario Valerio Velasco-García and Adán Hernández-Hernández
Seeds 2024, 3(1), 1-15; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010001 - 20 Dec 2023
Abstract
Pinus oocarpa is the most important conifer for resin production in Mexico, so superior resin trees were selected in the Southern Mountains of Oaxaca, Mexico. The objective was to determine the variation and differences among provenances and among trees according to the parameters
[...] Read more.
Pinus oocarpa is the most important conifer for resin production in Mexico, so superior resin trees were selected in the Southern Mountains of Oaxaca, Mexico. The objective was to determine the variation and differences among provenances and among trees according to the parameters of seedling emergence and the number of cotyledons, and their relationship with elevation and climatic variables. The seedling emergence of four replicates of 20 seeds from 80 trees was counted daily. For the emergence parameters, provenance contributed 42.02% to the total variance, tree 29.19% and error 28.79%. Only tree (11.71%) and error (88.29%) contributed to the total variance of the cotyledon number. The effect of provenance (p ≤ 0.0006) and tree (p ≤ 0.0001) was significant for all variables evaluated. Higher-elevation provenances and trees had higher emergence values. The emergence parameters were positively associated with tree elevation. Climatic variables related to precipitation and temperature were negatively related to the emergence parameters. The results allow for the selection of phenotypes without emergence problems to establish seed orchards.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Parameters of Seed Germination in Wild Plant Species)
►▼
Show Figures
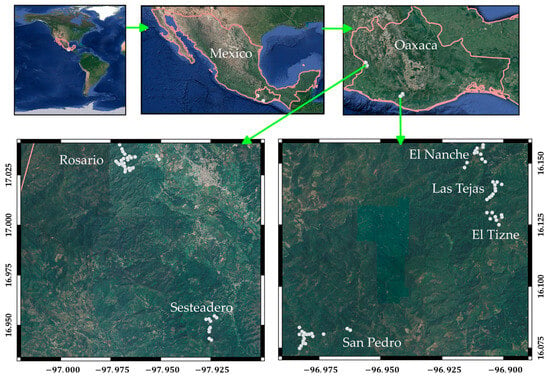
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seed Characterization and Evaluation of Pre-Germinative Barriers in the Genus Alstroemeria (Alstroemeriaceae)
by
Danilo Aros, Paulina Barraza, Álvaro Peña-Neira, Christina Mitsi and Ricardo Pertuzé
Seeds 2023, 2(4), 474-495; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2040035 - 28 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The genus Alstroemeria originates from South America, and Chile is one of the countries showing the highest number of taxa (49), of which 40 are endemic. However, anthropogenic and environmental factors are affecting the survival of these species; therefore, the conservation of their
[...] Read more.
The genus Alstroemeria originates from South America, and Chile is one of the countries showing the highest number of taxa (49), of which 40 are endemic. However, anthropogenic and environmental factors are affecting the survival of these species; therefore, the conservation of their genetic variability is of great importance, and can be achieved through seed propagation. Seeds of this genus normally show dormancy, which prevents their germination under favorable conditions. The objective of this work was to understand the pre-germinative barriers to develop a seed propagation protocol for native alstroemerias and to determine the best method to break their dormancy. Seeds from 10 Alstroemeria species native to Chile were collected from the Coquimbo Region to Maule Region, and 5 pre-germination treatments combining scarification and stratification methods were evaluated. Moreover, a morphological and biochemical evaluation of the seeds was performed. The results showed a positive and significant effect on the percentage of emergence using seed soaking in water and cold stratification at 13 °C, obtaining the best results in A. pelegrina and A. angustifolia subsp. angustifolia (98.33% and 91.67%, respectively) after 30 days. The morphological characterization of seeds showed a wide range of size (diameter), from 2.18 mm (A. pulchra subsp. pulchra) up to 3.43 mm (A. pelegrina), and different shapes (pseudospherical and angular) and textures (rough and smooth). The highest phenol and tannin concentrations were observed in A. hookeri subsp. maculata with values of 4.71 and 30.95 mg g−1 of seeds, respectively. A bigger size of the seed and a higher concentration of phenols could be related to a higher % of emergence of alstroemeria seeds.
Full article
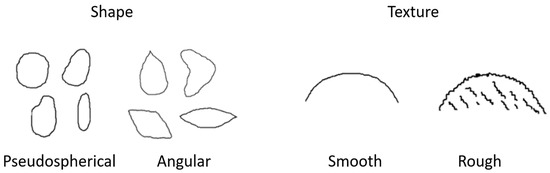
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Elongation of the Mesocotyl-Coleoptile and Biomass in Parents and Crosses of Corn Seedlings of the High Valleys of Mexico
by
Antonio Villalobos González, Ignacio Benítez Riquelme, Fernando Castillo González, Ma. del Carmen Mendoza Castillo and Alejandro Espinosa Calderón
Seeds 2023, 2(4), 449-473; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2040034 - 22 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
The elongation of the mesocotyl and the coleoptile and other seedling traits were analyzed from 16 hybrids of two seed sizes, five varieties and a control. Sowing was conducted in sand beds during the S-F 2020 cycle, where nine genotypes were identified that
[...] Read more.
The elongation of the mesocotyl and the coleoptile and other seedling traits were analyzed from 16 hybrids of two seed sizes, five varieties and a control. Sowing was conducted in sand beds during the S-F 2020 cycle, where nine genotypes were identified that differed in the elongation of the mesocotyl: long (H-48, HS-2 and Promesa); medium (H-44-H-52 and H-70); and short (H-49 AE, H-40 and H-32). A total of 36 possible crosses were obtained between these nine parents, which were established in the S-S 2021 cycle, and on sand beds. Results show that seed size affected (p< 0.05) the speed and percentage of emergence, the elongation of mesocotyl–coleoptile, the biomass and the heterosis in parents and their crosses. The H-48 hybrid presented greater speed and percentage of emergence and elongation of the mesocotyl and the coleoptile with both seed sizes. The highest dry weight of mesocotyl, coleoptile, roots, and leaves was found in the hybrids Promesa and H-48. The crosses between parents with contrasting mesocotyl presented superior elongation and dry weight (p ≤ 0.05) compared to their parents, with the long × long (1 × 2, 1 × 3 and 2 × 3) crosses standing out for all the traits measured. A strong positive association was obtained (p ≤ 0.01) between the elongation of the mesocotyl–coleoptile, the percentage of emergence, and the production of total dry matter in parents and their crosses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Seed Priming Approaches That Achieve Environmental Stress Tolerance)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seaweed Extract Components Are Correlated with the Seeds Germination and Growth of Tomato Seedlings
by
Rosalba Mireya Hernández-Herrera, Mario Felipe González-González, Ana Paulina Velasco-Ramírez, Sandra Fabiola Velasco-Ramírez, Fernando Santacruz-Ruvalcaba and Juan Francisco Zamora-Natera
Seeds 2023, 2(4), 436-448; https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2040033 - 22 Nov 2023
Abstract
Seaweeds are used in traditional agriculture practices because of their beneficial effects. Recently, the rising demand for organically grown foods has amplified the use of organic fertilizers such as seaweed extracts. Despite their beneficial effects, few studies have reported information about compounds in
[...] Read more.
Seaweeds are used in traditional agriculture practices because of their beneficial effects. Recently, the rising demand for organically grown foods has amplified the use of organic fertilizers such as seaweed extracts. Despite their beneficial effects, few studies have reported information about compounds in seaweed extracts that are responsible for these benefits. Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the potential relationships between the components and secondary metabolites in four seaweed liquid extracts from Eisenia arborea, Macrocystis pyrifera, Padina caulescens, and Sargassum horridum and their biostimulant activity through changes in the germination, growth, and protein content of tomato seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum). The E. arborea and S. horridum extracts showed similar compositions (ash, organic carbon, bicarbonates, and chlorides), minerals (Ca, Fe, and Cu) and secondary metabolites (triterpenes and saponins), albeit with different component concentrations. The chemical composition of the P. caulescens extract was significantly different from those of the other extracts; it was characterized by high levels of total nitrogen, phenols, and carbohydrates. Almost all seaweed extracts had beneficial effects on seed germination and seedling length, except the S. horridum extract that inhibits germination. The hierarchical clustering plots and principal component analysis indicated that germination and protein content are related to the presence of sterol. Shoot length was closely related to mineral levels (K, Zn, B, Na) and the C:N ratio, whereas radicle length was closely related to the content of nitrogen, carbohydrates, phenols, and flavonoids in the seaweed extracts. However, the underlying mechanisms are still unclear and require further studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Technologies to Improve the Yield and Storage of Seeds for Different Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
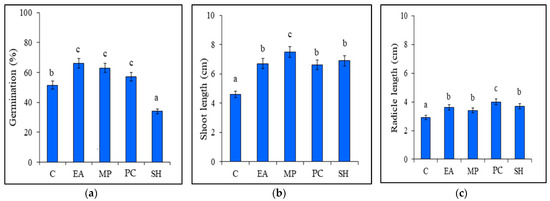
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agronomy, Agriculture, Crops, Seeds
Advances in Industrial Crops Physioecology and Sustainable Cultivation
Topic Editors: Wei Hu, Zhiguo Zhou, Wenqing ZhaoDeadline: 30 April 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Seeds
Seed Germination Ecophysiology of Invasive Species
Guest Editor: Lina PoddaDeadline: 15 October 2024
Special Issue in
Seeds
Parameters of Seed Germination in Wild Plant Species
Guest Editor: Božena ŠeráDeadline: 31 October 2024