-
 Evaluation and Development of a Nutrition Model to Predict Intake and Growth of Suckling Calves
Evaluation and Development of a Nutrition Model to Predict Intake and Growth of Suckling Calves -
 Farm-Scale Effectiveness of Feed Additives Supplied through a Mineral Mix for Beef Cattle Grazing Tropical Pastures
Farm-Scale Effectiveness of Feed Additives Supplied through a Mineral Mix for Beef Cattle Grazing Tropical Pastures -
 A Survey of the Current Farming Practices and Perceptions on Adopting Orphan Lambs in the United Kingdom: How Do “Ewe” Do It?
A Survey of the Current Farming Practices and Perceptions on Adopting Orphan Lambs in the United Kingdom: How Do “Ewe” Do It?
Journal Description
Ruminants
Ruminants
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on ruminants, including cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Article processing charge (APC) discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Ruminants is a companion journal of Animals.
Latest Articles
Drinking Behaviour of Beef Cattle Subject to Water Medication in Various Environmental Conditions
Ruminants 2024, 4(2), 213-226; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4020015 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Two experiments were conducted to assess the effects of water medication technology on beef cattle behaviour and performance in tropical conditions. Experiment 1 involved 30 Droughtmaster yearling steers monitored over seven days in a controlled environment. Feed and water consumptions were monitored with
[...] Read more.
Two experiments were conducted to assess the effects of water medication technology on beef cattle behaviour and performance in tropical conditions. Experiment 1 involved 30 Droughtmaster yearling steers monitored over seven days in a controlled environment. Feed and water consumptions were monitored with Smart Feed Pro® systems, with three water treatments administered via uDOSE® technology. The results indicated an average water intake of 13.6 L/head/d. Experiment 2 had 120 yearling steers from four genetic groups grazing on an extensive pasture system. Throughout four 24-day periods, forage availability and chemical composition were measured once monthly. Experiment 2 revealed a variation in water intake, ranging from 16.2 L/head/d down to 4.75 L/head/d. Notably, the lower intake coincided with a rainfall event documented during the fourth experimental period. Overall, results from both experiments indicated that water medication did not alter cattle water preference. There was no preference for treated water sources in Experiment 1, while differences in Experiment 2 appeared to be influenced by external factors like weather and prior habits. These experiments demonstrate the feasibility of water medication for beef cattle without disruption of their natural behaviour.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Beef Cattle Production and Management)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Combining Embryo Transfer and Artificial Insemination to Achieve Twinning in Beef Cattle, and Effects of Different Twin Calf-Raising Methods on Neonatal Behavior and Growth
by
Eduarda M. Bortoluzzi, Kolton W. Aubuchon, Nicole D. Robben, Nicole Stafford, Mikayla J. Goering, Claiborn Bronkhorst, John A. Odde, Clay Breiner, Karol Fike, Lindsey E. Hulbert and Kenneth G. Odde
Ruminants 2024, 4(2), 201-212; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4020014 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
As the beef industry moves towards efficient animal production to improve sustainability in agriculture, new production and management approaches are emerging. Among the many facets of the beef industry, cow–calf operations have the most opportunity for efficiency improvement, including improvements in fertility. This
[...] Read more.
As the beef industry moves towards efficient animal production to improve sustainability in agriculture, new production and management approaches are emerging. Among the many facets of the beef industry, cow–calf operations have the most opportunity for efficiency improvement, including improvements in fertility. This project accounts for measures and methods of (1) twinning reproductive technologies and (2) twin calf perinatal care and pre-weaning rearing. The overall objective was to produce twin calves using two reproductive technologies—embryo transfer and artificial insemination. The subobjectives were to determine accuracy of twin pregnancies embryo/fetal losses using ultrasonography, evaluate parturition and dystocia, and determine the effects of different twin-raising methods on neonatal behavior and growth. A fixed-time artificial insemination (FTAI) protocol was applied to 77 multiparous Angus-cross cows from a commercial beef herd in northcentral South Dakota during the summer of 2019. Cows were assigned to two different treatments groups: only artificially inseminated (AI) or received an embryo transfer following artificial insemination (ET + AI). They were estrous-synchronized, artificially inseminated (AI) with black Angus semen at day 0, and received and embryo transfer (ET) at day 7. Ultrasound examination detected 56% pregnancy risk for both groups, with sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 75%, 100%, and 90.5%, respectively, for bilateral twin detection. Calves were born during spring 2020. Twin calves (n = 34) and singleton calves (n = 11) were assigned to one of three raising methods: (1) twin born and twin raised (TT; n = 16), (2) twin born and single raised (TS; n = 18), and (3) single born and single raised (S; n = 11). Neonatal nursing behavior and birth weights were recorded, and adjusted day 200 and day 280 were calculated measures of vitality and growth. Blood samples were collected at age 24 h for colostrum intake measures (total serum protein, IgG1, and IgM). Twin calves were born 20% (p < 0.05) lighter in body weight than singletons; however, weights did not differ at day 280 between TT and S calves. TS calves had the shortest average latency to stand, but immunoglobulin concentrations did not differ among treatments. At weaning, cows that had birthed and raised twins produced more kilograms of live weight per pregnancy than cows birthing and raising singletons. Using ET + AI proved to increase twinning rate, and growth was maintained when raising both twins with their dam.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Hot Iron Branding of Beef Cattle: Process Characterization, Implications for Animal Welfare, and Its Efficiency for Cattle Individual Identification
by
Jaira de Oliveira, Joseph Kaled Grajales-Cedeño, Mariana Parra Cerezo, Tiago S. Valente and Mateus J. R. Paranhos da Costa
Ruminants 2024, 4(2), 192-200; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4020013 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study aimed to characterize the hot iron branding (HIB) procedure by assessing its implications for animal welfare and its efficiency for cattle identification. The study was carried out in two stages: First, with 37 Nellore calves, by measuring the skin temperatures in
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to characterize the hot iron branding (HIB) procedure by assessing its implications for animal welfare and its efficiency for cattle identification. The study was carried out in two stages: First, with 37 Nellore calves, by measuring the skin temperatures in the place of HIB application (ONB) and 10 cm above it (OFFB) immediately after its application and during four consecutive days, the time required for application of each HIB digit and the occurrences of rebranding; second, with two batches of cows (N = 97 and N = 94, respectively, by measuring the time spent to read cattle ID and comparing the efficiency of HIB vs. EET (electronic ear tag) and visual ear tags (VET) vs. EET. Skin temperature was significantly affected by the interaction between the place where the skin temperatures were taken (on and 10 cm above the HIB) and assessment day, with temperatures in ONB on days d0 and d2 being higher than in OFFB (p < 0.05), and 86% of the calves required at least one rebranding. EET reading was faster than HIB and VET (p < 0.001), and fewer errors were made when reading EET than HIB (1/97 vs. 17/97) and VET (2/94 vs. 12/94). We concluded that HIB potentially compromises cattle welfare and has a lower efficiency for cattle identification than EET and VET.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Beef Cattle Production and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
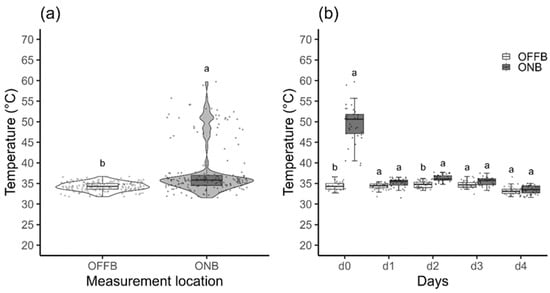
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
1H-NMR-Based Plasma Metabolomic Profiling of Crossbred Beef Cattle with Divergent RFI Phenotype
by
Godstime Taiwo, Modoluwamu Idowu, Taylor Sidney, Emily Treon, Deborah Ologunagba, Yarahy Leal, Samanthia Johnson, Rhoda Olowe Taiwo, Anjola Adewoye, Ephraim Ezeigbo, Francisca Eichie and Ibukun M. Ogunade
Ruminants 2024, 4(2), 182-191; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4020012 - 08 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study focused on exploring the metabolomic profiles of crossbred beef cattle with varying levels of residual feed intake (RFI), a measure of feed efficiency in beef cattle. Sixty-seven crossbred growing beef steers (BW = 277 ± 29.7 kg) were subjected to a
[...] Read more.
This study focused on exploring the metabolomic profiles of crossbred beef cattle with varying levels of residual feed intake (RFI), a measure of feed efficiency in beef cattle. Sixty-seven crossbred growing beef steers (BW = 277 ± 29.7 kg) were subjected to a high-forage total mixed ration for 64 days to determine their RFI phenotypes. At the end of the 64d feeding trial, beef steers were divided into two groups based on their RFI values: low (or negative)-RFI beef steers (n = 28; RFI = −1.08 ± 0.88 kg/d) and high (or positive)-RFI beef steers (n = 39; RFI = 1.21 ± 0.92 kg/d). Blood samples were collected, and plasma samples were analyzed using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy, resulting in the identification of 50 metabolites. The study found a distinct metabolomic signature associated with RFI status. Eight metabolites, including amino acids (tyrosine, glycine, valine, leucine, and methionine) and other compounds (dimethyl sulfone, 3-hydroxy isovaleric acid, citric acid, creatine, and L-carnitine), showed differential abundance between low- and high-RFI groups. Specifically, tyrosine, glycine, and dimethyl sulfone exhibited significant specificity and sensitivity, which produced a discriminatory model with an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of 0.7, making them potential markers for RFI. A logistic regression model incorporating these biomarkers effectively distinguished between high- and low-RFI steers, with a threshold cutoff point of 0.48, highlighting a distinctive metabolite profile associated with efficient nutrient utilization in low-RFI cattle. The logistic regression model, incorporating these biomarkers, holds promise for accurately categorizing RFI values, providing insights into the metabolic basis of feed efficiency in beef cattle.
Full article
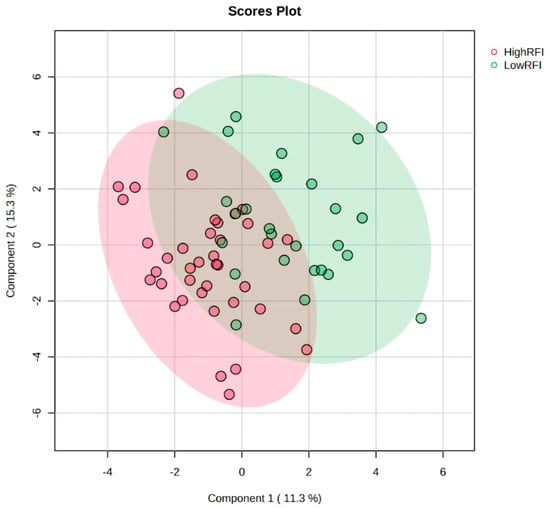
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Competing Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and Application of Their Regulatory Networks in Complex Traits and Diseases of Ruminants
by
Farzad Ghafouri, Vahid Dehghanian Reyhan, Mostafa Sadeghi, Seyed Reza Miraei-Ashtiani, John P. Kastelic, Herman W. Barkema and Masoud Shirali
Ruminants 2024, 4(2), 165-181; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4020011 - 01 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This manuscript summarizes information on the diverse range of RNA molecules and their role as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs). Moreover, it provides an overview of ceRNA regulatory networks and their applications in ruminant biology. Knowledge of co-expression networks has increased with microarrays, RNA-seq,
[...] Read more.
This manuscript summarizes information on the diverse range of RNA molecules and their role as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs). Moreover, it provides an overview of ceRNA regulatory networks and their applications in ruminant biology. Knowledge of co-expression networks has increased with microarrays, RNA-seq, and scRNA-seq characterizing molecular mediators across various biological scales, using sequences from numerous blood and tissue samples. By synthesizing existing knowledge, this study summarizes interactions between coding and non-coding RNAs through microRNA response elements (MREs), elucidating large-scale regulatory networks throughout the transcriptome that influence the expression and activities of various ceRNAs. Identification of non-coding RNAs with important regulatory functions will revolutionize understanding of RNA biology, shifting from an mRNA-centric model to a complex network of RNA crosstalk. The ceRNA networks offer a more comprehensive and arguably more realistic perspective compared to protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks and weighted gene co-expression networks (WGCN). These ceRNA regulatory networks can describe potential molecular regulatory mechanisms related to functional and economically important traits in ruminants, plus contribute to disease and pathology research, by elucidating pathogenesis and potential drug effects in disease and cancer models. Furthermore, they can provide insights into farm animal biology, e.g., reproductive traits in goats and sheep, regulation of fat metabolism in beef cattle, heat stress responses, and lactation regulation in dairy cattle, fertility and muscle characteristics in buffalo, and resistance to high-salt and water-deprivation conditions in camels. In conclusion, ceRNA and associated regulatory networks should promote a new understanding of molecular mechanisms and identify candidate genes and metabolic-signaling pathways in ruminants.
Full article
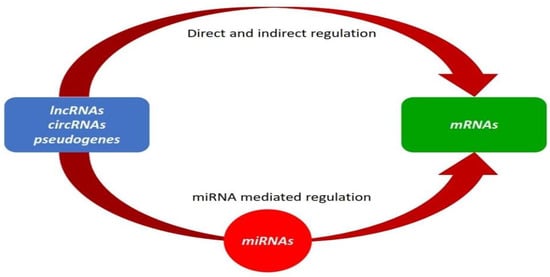
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Bibliometric Mapping of Academic Research Focusing on Animal Production and Climate Change in Association with Methane Emissions and Animal Productivity
by
Akeem Babatunde Sikiru, Olayinka John Makinde, Bossima Ivan Koura, Stephen Sunday Egena Acheneje, John Olushola Alabi, Maria Ndakula Tautiko Shipandeni and Oludayo Michael Akinsola
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 152-164; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010010 - 09 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Climate change is a pressing global challenge, and animal production is a major contributor to methane emissions. This study examines the academic landscape of research on CH4 emissions and animal productivity, with a focus on cattle, sheep, and goats. Using a bibliometric
[...] Read more.
Climate change is a pressing global challenge, and animal production is a major contributor to methane emissions. This study examines the academic landscape of research on CH4 emissions and animal productivity, with a focus on cattle, sheep, and goats. Using a bibliometric analysis of 2500 documents published between 1987 and 2023, the study finds that research on this topic has increased significantly over time, with a record high in 2022. The leading countries in terms of research output are the United States, China, Brazil, Canada, and Italy. The study identifies several key research themes, including the impact of CH4 emissions on animal productivity parameters, the development of mitigation strategies, and the assessment of trade-offs and synergies between CH4 emissions reduction and other sustainability goals. The study concludes by highlighting the importance of continued research on CH4 emissions and animal productivity to develop and implement effective mitigation strategies. This study has important implications for policymakers, researchers, and the livestock industry. Policymakers can use the findings to inform the development of policies and regulations that support the reduction of CH4 emissions from animal production. Researchers can use the findings to identify gaps in the existing knowledge base and to develop new research directions. The livestock industry can use the findings to develop more sustainable production practices. By working together, policymakers, researchers, and the livestock industry can develop and implement effective mitigation strategies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect the environment, and support sustainable food production.
Full article
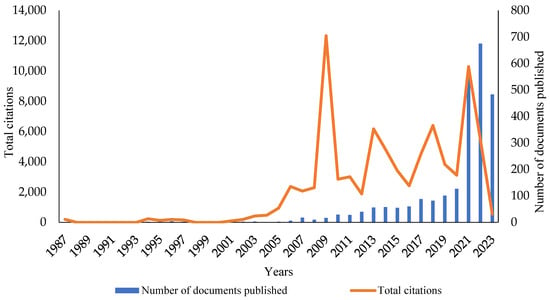
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Welfare in Transhumance Yak Hybrids (Chauris) in the Lower Himalayan Region of Nepal
by
Sujan Sapkota, Richard Laven, Shanker Raj Barsila, Nikki Kells, Kristina Ruth Mueller and Dhurba DC
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 136-151; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010009 - 08 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In order to develop a yak/chauri-specific welfare assessment protocol, we sent a set of 31 potential welfare measures to 120 Nepalese experts and asked them to identify the measures that they thought would be useful and propose additional useful measures. Eighty-three experts responded,
[...] Read more.
In order to develop a yak/chauri-specific welfare assessment protocol, we sent a set of 31 potential welfare measures to 120 Nepalese experts and asked them to identify the measures that they thought would be useful and propose additional useful measures. Eighty-three experts responded, with 13 measures being identified by >50% of respondents as likely to be useful. These thirteen measures plus one new measure (hematology) were included in an assessment protocol that was tested in the second phase of this study in five chauri herds in two districts in northern Nepal. Animal-based evaluations along with sampling for mastitis, intestinal parasites, and hematology were undertaken during or just after morning milking. Resource- and record-based measures were assessed through structured interviews, with verifications on-site where possible. No chauris exhibited poor body conditions, skin injuries, significant locomotion issues, or significant subclinical mastitis. Fecal testing suggested a high prevalence of intestinal parasites at the herd level, while blood testing suggested no evidence of hematological abnormalities. However, for both results, we need more data to use these effectively as measures of welfare. The resource-based assessment revealed significant challenges across all resources, and veterinary services were reported as being inadequate. A high estimated annual mortality rate (10–21%) needs further investigation. This protocol provided a useful start towards developing a welfare assessment protocol for yak/chauri and identified issues that need addressing to optimize chauri welfare.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Ultrasonography and Postmortem Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bilateral Ocular Disease in a Heifer
by
Takeshi Tsuka, Yuji Sunden, Takehito Morita, Md Shafiqul Islam and Osamu Yamato
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 125-135; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010008 - 08 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bovine ocular diseases are typically characterized by the concurrent appearances of both macroscopic and intraocular abnormalities. This study examines the diagnostic efficacy of a combination of ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the bilateral ocular disease observed in a 9-month-old Japanese Black
[...] Read more.
Bovine ocular diseases are typically characterized by the concurrent appearances of both macroscopic and intraocular abnormalities. This study examines the diagnostic efficacy of a combination of ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the bilateral ocular disease observed in a 9-month-old Japanese Black heifer. This case presented with bilateral strabismus and a white-colored lens structure in the right eye. A combination of ultrasonography and MRI revealed formations of corn-like and V-shaped membranous structures within the vitreous cavities of the left and right eyeballs, respectively. In the right eye, a cataract was suspected on both ultrasonogram and MRI. This case involved bilateral retinal detachments and strabismus similar to the signs of an autosomal recessive hereditary ocular disease; however, the cataract in the right eye differed from that hereditary disease. Finally, in genetic analysis, a known mutation of the WFDC1 gene was not detected. Ultrasonography is superior to MRI in demonstrating intraocular pathological changes. On the other hand, MRI is helpful for evaluating invasiveness of the ocular lesions to the peripheral structures. Thus, the combined use of these imaging modalities is recommended for diagnosing various bovine ocular diseases.
Full article
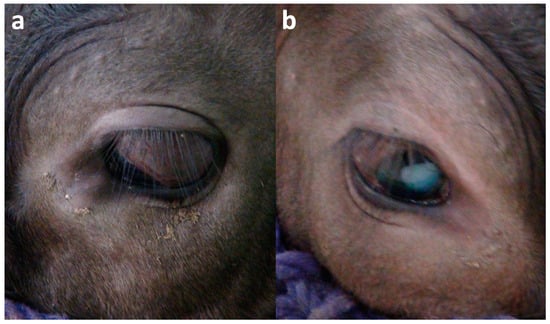
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Precision Ingredient Inclusion on Production Efficiency Responses in Finishing Beef Cattle
by
Santana R. Hanson, Erin. R. DeHaan, Forest L. Francis, Warren C. Rusche and Zachary K. Smith
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 112-124; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010007 - 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
Two randomized complete block design experiments evaluated the influence that varying degrees of ingredient inclusion accuracy in a finishing diet have on growth performance and carcass traits. Treatments included (1) normal inclusion tolerance with a 0.454 kg tolerance for all ingredients (CON) or
[...] Read more.
Two randomized complete block design experiments evaluated the influence that varying degrees of ingredient inclusion accuracy in a finishing diet have on growth performance and carcass traits. Treatments included (1) normal inclusion tolerance with a 0.454 kg tolerance for all ingredients (CON) or (2) variable inclusion tolerance where each ingredient was randomly increased or decreased but the targeted as-fed quantity for the daily delivery was met (VAR). In Experiment. 1, black Angus heifers (n = 60; initial shrunk BW = 460 ± 26.2 kg) were used in a 112 d experiment. Ten pens in total (5 pens/treatment, 6 heifers/pen) were used. The targeted diet (DM basis) consisted of high-moisture ear corn (75%), dried distiller’s grains (20%), and a liquid supplement (5%). As-fed inclusion rates for DDGS and LS varied from formulated targets by −20, −15, −10, −5, 0, +5, +10, +15 or +20%. The HMEC inclusion was adjusted so that the targeted as-fed amount of the diet was delivered daily. Treatment did not alter ADG, DMI, G:F, HCW, dressing percentage, rib-eye area, rib fat, USDA marbling score, KPH, yield grade, retail yield, empty body fat, or body weight at 28% estimated EBF, nor liver abscess prevalence or severity (p ≥ 0.15). In Exp. 2, Charolais–Angus cross steers (n = 128; initial shrunk BW = 505 ± 32.1 kg) were used in a 94 d experiment. Steers were assigned to pens (8 pens/treatment; 8 steers/pen) and one of the two management strategies used in Exp. 1 was employed. Ractopamine HCl was fed (300 mg per head daily) during the final 28 d. Diets consisted of (DM basis) dry-rolled corn (63%), dried distiller’s grains plus solubles (15%), liquid supplement (5%), grass hay (7%), and corn silage (10%). Ingredient inclusions were randomized in the same manner as Exp. 1, except LS inclusion was held constant. Corn silage inclusion was adjusted so that the targeted as-fed amount of the diet was delivered each day. Steers from VAR had increased (p = 0.01) DMI, but similar (p = 0.75) ADG resulting in reduced (p ≤ 0.02) G:F and growth-performance-predicted Net Energy for maintenance and gain. Treatment did not influence (p ≥ 0.38) HCW, dressing percentage, rib-eye area, rib fat, KPH, yield grade, retail yield, empty body fat, or body weight at 28% estimated EBF. A tendency for an increased USDA marbling score (p = 0.08) was noted in VAR. Under the conditions of this experiment, randomly altering ingredient proportions can impact growth performance and efficiency measures depending upon the type of finishing diet fed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Precision Feeding and Management of Farm Animals, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
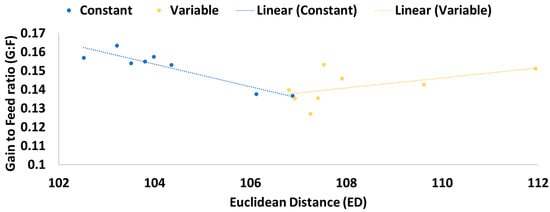
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Use of Interactive Visualizations for Tracking Haplotypic Inheritance in Livestock
by
Alana Selli, Stephen P. Miller and Ricardo V. Ventura
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 90-111; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010006 - 21 Feb 2024
Abstract
Our objective was to harness the power of interactive visualizations by utilizing open-source tools to develop an efficient strategy for visualizing Single Nucleotide Polymorphism data within a livestock population, focusing on tracking the transmission of haplotypes. To achieve this, we simulated a realistic
[...] Read more.
Our objective was to harness the power of interactive visualizations by utilizing open-source tools to develop an efficient strategy for visualizing Single Nucleotide Polymorphism data within a livestock population, focusing on tracking the transmission of haplotypes. To achieve this, we simulated a realistic beef cattle population in order to obtain phased haplotypes and generate the necessary inputs for creating our visualizations. The visualization tool was built using Python and the Plotly library, which enables interactivity. We set out to explore three scenarios: trio comparison, visualization of grandparents, and half-sibling evaluation. These scenarios enabled us to trace the inheritance of genetic segments, identify crossover events, and uncover common regions within related and unrelated animals. The potential applications of this approach are significant, particularly for improving genomic selection in smaller breeding programs and farms, and it provides valuable insights for guiding more in-depth genomic region analysis. Beyond its practical applications, we believe this strategy can be a valuable educational tool, helping educators clarify complex concepts like Mendelian sampling and haplotypic diversity. Furthermore, we hope it will encourage livestock producers to adopt advanced technologies like genotyping and genomic selection, thereby contributing to the advancement of livestock genetics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Beef Cattle Production and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
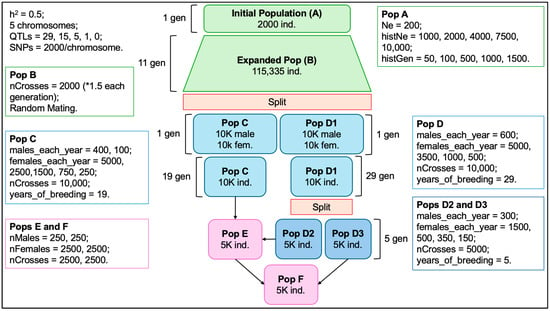
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Liver Abscesses on Performance and Carcass Traits in Beef Cattle: A Meta-Analysis Study
by
Rodrigo de Nazaré Santos Torres, David Attuy Vey da Silva, Luis Arthur Loyola Chardulo, Welder Angelo Baldassini, Rafael Assis Torres de Almeida, Marco Tulio Costa Almeida, Rogério Abdallah Curi, Guilherme Luis Pereira, Jon Patrick Schoonmaker and Otavio Rodrigues Machado Neto
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 79-89; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010005 - 12 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The use of high-grain diets in feedlots is associated with the development of acidosis and ruminitis, which can lead to the occurrence of liver abscesses (LAs). However, the effect of LA on carcass traits is not well known. This study assessed the effects
[...] Read more.
The use of high-grain diets in feedlots is associated with the development of acidosis and ruminitis, which can lead to the occurrence of liver abscesses (LAs). However, the effect of LA on carcass traits is not well known. This study assessed the effects of LA on the performance and carcass traits of beef cattle. Nine peer-reviewed publications with forty-seven treatment means were included in the data set. The effects of the LA were evaluated by examining the weighted mean difference (WMD) between LA (animal with LA) and control treatment (animal without LA). Heterogeneity was explored by meta-regression, followed by a subgroup analysis of the scores and percentages of liver abscess and concentrate level in the feedlot diet. Animals affected by LA showed a reduction in dry matter intake (−1.03%) and feed efficiency (−1.82%). Animals with an LA score of “A” (one or two small abscesses) exhibited a decrease in carcass weight (WMD = 3.41 kg; p = 0.034) and ribeye area (WMD = −1.37 cm2; p = 0.019). When assessing the impact of LA on carcass traits, the most reliable finding indicates a 1.21% reduction in the ribeye area, with no adverse effects observed on subcutaneous fat thickness or the marbling score in the carcass.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
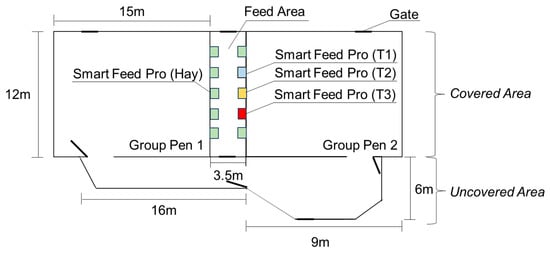
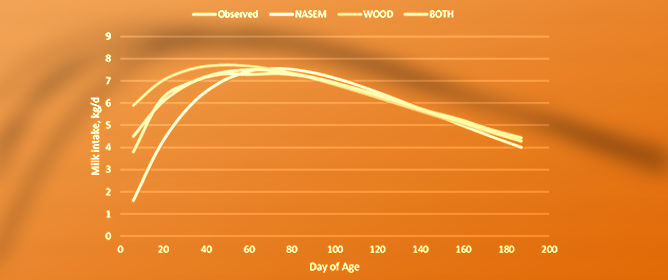
Evaluation and Development of a Nutrition Model to Predict Intake and Growth of Suckling Calves
by
Geovana Camila Baldin, Caleb Hildebrand, Robert L. Larson and Phillip A. Lancaster
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 47-78; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010004 - 28 Jan 2024
Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate and develop equations to predict forage intake and growth of calves throughout the suckling period of beef calves grazing on forage or dairy calves fed harvested forage. Milk and forage intake and body weight data
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to evaluate and develop equations to predict forage intake and growth of calves throughout the suckling period of beef calves grazing on forage or dairy calves fed harvested forage. Milk and forage intake and body weight data for individual animals were collected from published theses (one using bottle-fed dairy calves and one using suckling beef calves). A nutrition model was constructed using milk and forage intake equations and growth equations. Additional datasets were compiled from the literature to develop equations to adjust the original nutrition model for forage digestibility, milk composition, and growth. In general, the original nutrition model predicted the forage intake and body weight of dairy calves with moderate-to-high precision (CCC = 0.234 to 0.929) and poor accuracy (MB = −341.16 to −1.58%). Additionally, the original nutrition model predicted forage intake and body weight in beef calves with poor-to-moderate precision (CCC = 0.348 to 0.766) and accuracy (MB = 6.39 to 57.67%). Adjusted nutrition models performed better with the best model precisely (CCC = 0.914) predicting forage intake and precisely (CCC = 0.978) and accurately (MB = 2.83%) predicting body weight in dairy calves. The best adjusted nutrition model predicted forage intake and body weight with high precision (CCC = 0.882 and 0.935) and moderate accuracy (MB = −7.01 and −7.34) in beef calves. Nutrition models were able to adequately predict the forage intake and growth of calves with adjustments made to standard milk energy concentrations and growth equations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Beef Cattle Production and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
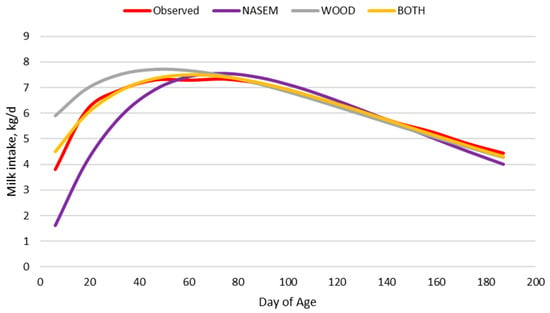
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Enhancing Animal Production through Smart Agriculture: Possibilities, Hurdles, Resolutions, and Advantages
by
Moammar Dayoub, Saida Shnaigat, Radi A. Tarawneh, Azzam N. Al-Yacoub, Faisal Al-Barakeh and Khaled Al-Najjar
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 22-46; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010003 - 26 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Smart livestock farming utilizes technology to enhance production and meet food demand sustainably. This study employs surveys and case studies to gather data and information, subsequently analyzing it to identify opportunities and challenges. The proposed solutions encompass remote sensing, technology integration, farmer education,
[...] Read more.
Smart livestock farming utilizes technology to enhance production and meet food demand sustainably. This study employs surveys and case studies to gather data and information, subsequently analyzing it to identify opportunities and challenges. The proposed solutions encompass remote sensing, technology integration, farmer education, and stakeholder engagement. The research delves into smart technologies in animal production, addressing opportunities, challenges, and potential solutions. Smart agriculture employs modern technology to improve efficiency, sustainability, and animal welfare in livestock farming. This includes remote monitoring, GPS-based animal care, robotic milking, smart health collars, predictive disease control, and other innovations. Despite the great promise of smart animal production, there are existing challenges such as cost, data management, and connectivity. To overcome these challenges, potential solutions involve remote sensing, technology integration, and farmer education. Smart agriculture provides opportunities for increased efficiency, improved animal welfare, and enhanced environmental conservation. A well-planned approach is crucial to maximize the benefits of smart livestock production while ensuring its long-term sustainability. This study confirms the growing adoption of smart agriculture in livestock production, with the potential to support the sustainable development goals and deliver benefits such as increased productivity and resource efficiency. To fully realize these benefits and ensure the sustainability of livestock farming, addressing cost and education challenges is essential. Therefore, this study recommends promoting a positive outlook among livestock stakeholders and embracing smart agriculture to enhance farm performance.
Full article
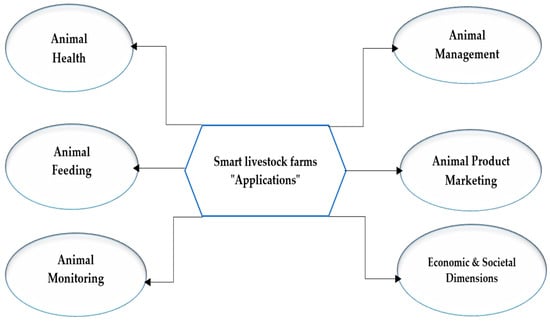
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Different Anthelmintic Drugs on the Development and Efficacy of Duddingtonia flagrans
by
Sara Zegbi, Federica Sagües, Carlos Saumell, Laura Ceballos, Paula Domínguez, Inés Guerrero, Milagros Junco, Lucía Iglesias and Silvina Fernández
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 10-21; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010002 - 11 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nematophagous fungi are a biological control tool used against gastrointestinal nematodes in livestock. These fungi prey on free-living larvae in faeces and could be affected by active drugs excreted post-treatment. This study aimed to determine in vitro and under environmental conditions the effect
[...] Read more.
Nematophagous fungi are a biological control tool used against gastrointestinal nematodes in livestock. These fungi prey on free-living larvae in faeces and could be affected by active drugs excreted post-treatment. This study aimed to determine in vitro and under environmental conditions the effect of the following anthelmintics on the fungus Duddingtonia flagrans: ivermectin, levamisole, albendazole, fenbendazole and ricobendazole. The in vitro effect of anthelmintics on fungal growth and predatory capacity was assessed in corn meal agar and coprocultures, respectively. Ivermectin (1, 2 and 10 ppm), fenbendazole (0.027, 0.054 and 1 ppm) and albendazole (1 ppm) significantly affected fungal development. The fungal efficacy against L3 was high in the control and levamisole coprocultures but decreased significantly in the presence of albendazole, fenbendazole, ricobendazole and ivermectin. The impact of levamisole on D. flagrans was further assessed under environmental conditions in autumn and winter; the fungal efficacy measured in faecal pats and the surrounding herbage was not affected by levamisole at any time. This study shows that using albendazole, fenbendazole, ricobendazole or ivermectin may compromise fungal activity, as these drugs affect the free-living stages of nematodes in faeces, but levamisole can be safely considered in parasite control strategies involving D. flagrans and anthelmintic treatments.
Full article
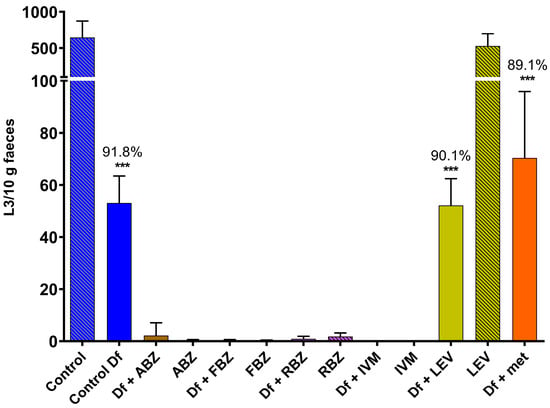
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Chemical Composition and In Vitro Nutritive Evaluation of Pomegranate and Artichoke Fractions as Ruminant Feed
by
Trinidad de Evan, Carlos N. Marcos and María Dolores Carro
Ruminants 2024, 4(1), 1-9; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4010001 - 02 Jan 2024
Abstract
The aim of this work was to assess the chemical composition and in vitro ruminal fermentation of samples (n = 3) of pomegranate (peels (PPs) and seeds (PSs)) and artichoke (hearts (AHs) and stems (ASs)) wastes. Dried orange pulp (DOP) and tomato pomace
[...] Read more.
The aim of this work was to assess the chemical composition and in vitro ruminal fermentation of samples (n = 3) of pomegranate (peels (PPs) and seeds (PSs)) and artichoke (hearts (AHs) and stems (ASs)) wastes. Dried orange pulp (DOP) and tomato pomace (TP) were used as reference feeds. All wastes had low dry matter (DM; lower than 33.0 and 12.0% for pomegranate and artichoke, respectively). The DM of pomegranate fractions was rich in sugars (>42.0%) and contained low protein (<8.0%) and neutral detergent fiber (NDF; <27.0%), whereas that of both artichoke fractions had high protein (>18.0%) and NDF (>36.0%) and low sugars content (<9.2%). Pomegranate seeds were more rapidly and extensively fermented in vitro than PPs, but both were less degradable and contained less metabolizable energy (ME) than DOP (7.43, 11.0 and 12.5 MJ ME/kg DM, respectively). Although AHs were more rapidly fermented and produced more volatile fatty acids (VFAs) than ASs, both had lower ME content than TP (9.50, 7.25 and 12.5 MJ ME/kg DM). The analyzed wastes had lower ME content than other by-products, but they were extensively fermented by ruminal microorganisms and could be used as ruminant feeds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ruminal Microbiota, Fermentation Process, Enteric Methane Emissions, and Animal Performance)
Open AccessArticle
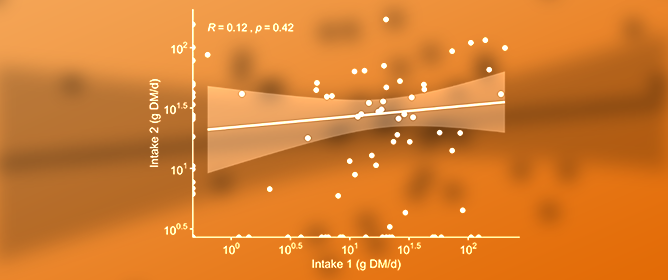
Farm-Scale Effectiveness of Feed Additives Supplied through a Mineral Mix for Beef Cattle Grazing Tropical Pastures
by
Ricardo Cazerta Duarte Goulart, Diogo Fleury Azevedo Costa, Tiago Alves Corrêa Carvalho da Silva, Guilhermo Francklin de Souza Congio, Rodrigo da Silva Marques and Moacyr Corsi
Ruminants 2023, 3(4), 483-494; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040039 - 13 Dec 2023
Abstract
The effectiveness of feed additives delivered through free-choice mineral mixtures (MMs) to grazing cattle remains unclear. Two farm-scale and one in vitro experiment (Exp.) were conducted to investigate the effects of salinomycin and virginiamycin, delivered through an MM, on growing bulls grazing tropical
[...] Read more.
The effectiveness of feed additives delivered through free-choice mineral mixtures (MMs) to grazing cattle remains unclear. Two farm-scale and one in vitro experiment (Exp.) were conducted to investigate the effects of salinomycin and virginiamycin, delivered through an MM, on growing bulls grazing tropical pastures. In Exp. 1, 316 zebu (Bos indicus) Nellore bulls (225 ± 26.7 kg liveweight (LW)) were randomly allocated to four treatments: (1) MM no additives (CON), (2) MM with salinomycin at 1950 mg/kg (SLI), (3) MM with salinomycin at 780 mg/kg (SHI), and (4) MM with virginiamycin at 1950 mg/kg (VGN). Over 123 days, these bulls grazed tropical grasses on pastures of guinea grass, palisade grass, or Bermuda grass. No significant treatment effects were observed for oocyst eggs or ruminal parameters. Bulls fed VGN had higher average daily gain (ADG) compared to CON (p = 0.02) and SLI (p = 0.03) but similar compared to SHI (p = 0.07). In Exp. 2, 308 zebu cross bulls (237 ± 23.0 kg LW) grazed Bermuda grass paddocks and were allocated into two treatments: (1) MM with no additives (CON) and (2) MM containing virginiamycin at 2522 mg/kg (VGN). Cattle fed VGN had a significantly higher ADG (p = 0.007). Exp. 3 tested salinomycin’s effectiveness in vitro at different exposure times to MM, revealing no impact of exposure time on short-chain fatty acid production. In conclusion, virginiamycin delivered through free-choice MM can increase grazing beef bulls’ ADG by 12% compared with CON, with no clear link to rumen fermentation or coccidiostat effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Beef Cattle Production and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Survey of the Current Farming Practices and Perceptions on Adopting Orphan Lambs in the United Kingdom: How Do “Ewe” Do It?
by
Louise Whatford, Benedict Delahaye Chivers, Megan Rowe and Nicola Blackie
Ruminants 2023, 3(4), 468-482; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040038 - 05 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fostering orphan lambs is common in the United Kingdom and therefore it is important to understand more about these practices to support sustainable sheep farming. Data were collected on current approaches to adopting lambs and the perceived success of these methods using an
[...] Read more.
Fostering orphan lambs is common in the United Kingdom and therefore it is important to understand more about these practices to support sustainable sheep farming. Data were collected on current approaches to adopting lambs and the perceived success of these methods using an online survey. Of the 543 responses, 93.7% reported that they attempt to foster lambs with the most common reasons reported as high litter size and ewes with little to no milk production. Although respondents reported that the best method was wet, non-tethering techniques, the most commonly used methods were tethered (restraint of the ewe) followed by untethered (birth fluids and skins from dead lambs). Other techniques included disguising the smell of the lamb. There was a significant association between increased flock size and using tethered methods as well as increased numbers of methods used and orphan lambs (p ≤ 0.001). However, larger flocks were also associated with decreased lamb survival rates (p ≤ 0.001). Time and patience were mentioned as important tips for fostering and could be a factor in which method is chosen. Research on the impacts of these methods is warranted as some may be stressful, affecting long-term flock performance, survival, welfare and health.
Full article
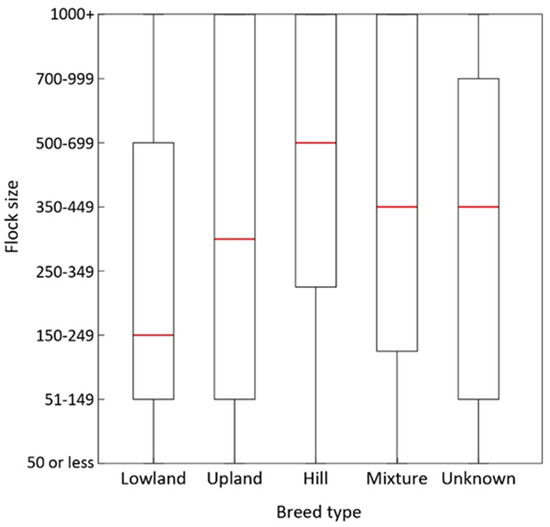
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Creep Feeding Supplementation on Growth Performance and Metabolic Characteristics of Nellore Heifers
by
Robert T. da Paixão, Edenio Detmann, Marcos I. Marcondes, Jarbas M. da Silva Júnior and Claudia B. Sampaio
Ruminants 2023, 3(4), 457-467; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040037 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
The objective of this paper is to evaluate the effects of creep feeding supplementation during the preweaning phase on the growth performance and metabolic characteristics of Nellore heifers. Forty-two female Nellore calves (age = 100 ± 25 d; initial body weight (BW) =
[...] Read more.
The objective of this paper is to evaluate the effects of creep feeding supplementation during the preweaning phase on the growth performance and metabolic characteristics of Nellore heifers. Forty-two female Nellore calves (age = 100 ± 25 d; initial body weight (BW) = 113.4 ± 16.6 kg) were randomly assigned to the following treatments: control, where calves received mineral mix supplementation (n = 21); supplemented in creep feeding, where calves received 6 g/kg BW of a concentrate supplement (n = 21) during a period of 140 d. In the postweaning phase, all heifers received 6 g/kg BW of a concentrate supplement during a period of 210 d. Supplemented heifers had a greater average daily gain (ADG) than control heifers during the preweaning phase and, consequently, were heavier at weaning and at the end of the growing phase (p < 0.05). However, preweaning supplementation did not influence (p > 0.05) the body measurements or BW at the end of the growing period. Greater (p < 0.05) rib fat was observed in supplemented heifers. Concentrations of metabolites were not affected by preweaning supplementation (p > 0.05). Thus, supplementing heifers in the preweaning phase improved growth performance of weaning and body adiposity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Beef Cattle Production and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
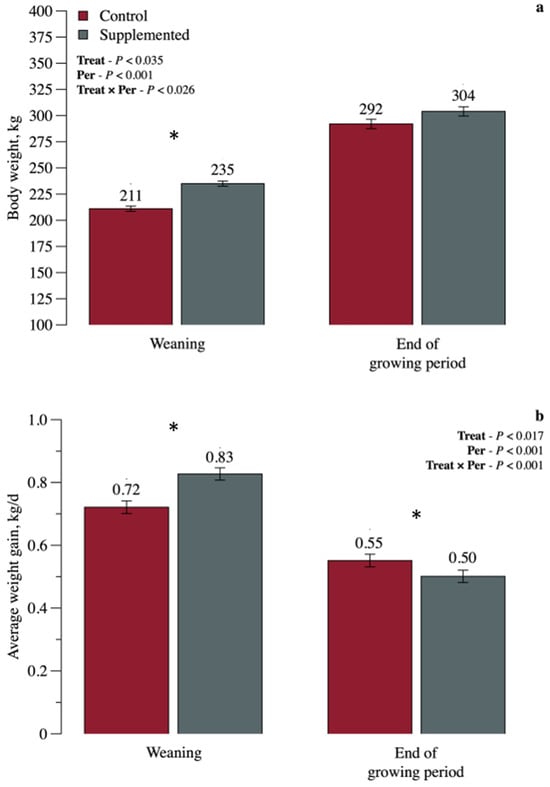
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Short-Term Glycerin Supplementation on Follicle Dynamics and Pregnancy Rate in Goats
by
Caroline Pessoa da Silva, César Carneiro Linhares Fernandes, Juliana Paula Martins Alves, Felipe Brener Bezerra de Oliveira, Aline Maia Silva, Francisco Carlos de Souza, Camila Muniz Cavalcante, Alfredo José Ferreira Conde, Anibal Coutinho do Rego and Davide Rondina
Ruminants 2023, 3(4), 445-456; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040036 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
We investigated the effects of short-term glycerin supplementation on follicular dynamics and pregnancy rates. Twenty-five goats with synchronized estrus and follicular waves with three injections of a prostaglandin analog every 7 days were used. Two days after the second injection, 13 goats were
[...] Read more.
We investigated the effects of short-term glycerin supplementation on follicular dynamics and pregnancy rates. Twenty-five goats with synchronized estrus and follicular waves with three injections of a prostaglandin analog every 7 days were used. Two days after the second injection, 13 goats were randomly chosen to receive an oral drench of 200 mL of glycerin (glycerin group [GG], n = 13) for 6 days, whereas the remaining 12 animals received an oral drench of saline (control group [CG], n = 12). At 24 and 48 h after the third injection, the goats mated. The animals were kept in a collective stall and received the same diet. The GG had higher blood glucose levels during the supplementation period than the CG (76.4 ± 1.9 vs. 50.3 ± 0.7 mg/dL; p < 0.01). The glycemic peak was recorded 4 h after the glycerin administration (102.3 ± 5.1 mg/dL) and remained higher than that in the CG 8 and 12 h later. The GG goats had a higher rectal temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate than the CG goats and showed an increase in these parameters 4, 8, and 12 h after glycerin drenching. The GG animals also exhibited increased stress, urination, and drinking behaviors and reduced rumination. The ultrasonographic analysis showed a higher number of follicles with a diameter >4 mm (p < 0.05) and a greater follicular diameter (p < 0.01) in the waves before and after ovulation induction. The pregnancy and twinning rates and litter size at parturition were not different between the groups. Short-term supplementation with glycerin positively affects ovarian stimulation but has no effect on the reproductive response after mating.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Reproductive Management of Ruminants)
►▼
Show Figures
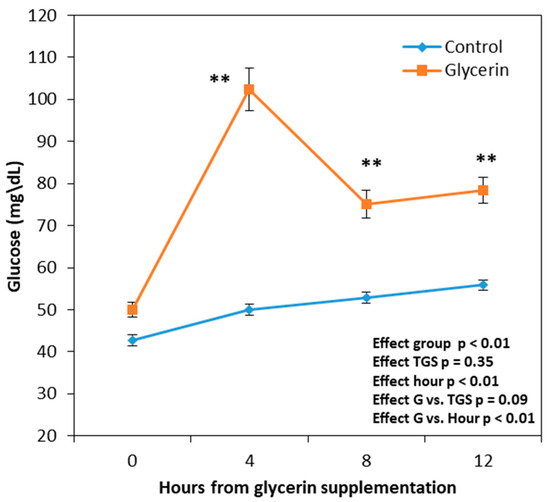
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Effect of Different Additives on the Quality of Rehydrated Corn Grain Silage: A Systematic Review
by
Luciana Viana Diogénes, José Morais Pereira Filho, Ricardo Loiola Edvan, Juliana Paula Felipe de Oliveira, Romilda Rodrigues do Nascimento, Edson Mauro Santos, Elisvaldo José Silva Alencar, Pedro Henrique Soares Mazza, Ronaldo Lopes Oliveira and Leilson Rocha Bezerra
Ruminants 2023, 3(4), 425-444; https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040035 - 01 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review aimed to analyze the effects of additives in producing silage from rehydrated corn grains for ruminants. The control treatment studies used in this analysis involved corn grain rehydrated with water only. To be included in the review, the studies needed to
[...] Read more.
This review aimed to analyze the effects of additives in producing silage from rehydrated corn grains for ruminants. The control treatment studies used in this analysis involved corn grain rehydrated with water only. To be included in the review, the studies needed to follow standardized criteria, including the absence of additives in the control treatment and the silage evaluation of the in animals such as cattle, goats, and sheep. A total of fifteen publications between 2014 and 2023 were included in the final dataset. The PROC ANOVA of SAS was used to compare the results, which included a random effect of comparison within the study, performing a paired comparison. It was observed that additives did not influence the chemical composition, pH, organic acid, ethanol content, microbial population, fermentative losses, aerobic stability, and dry matter in vitro digestibility of rehydrated corn grain silage (p > 0.05). Using additives in corn silage is a promising practice that can significantly benefit silage fermentation. Moisture silage additives mitigate high mycotoxin levels, enhance aerobic stability, improve cell wall digestibility, and increase the efficiency of utilization of silage nitrogen by ruminants. Using fermentation-stimulating additives (Lactobacillus buchneri) can improve the quality of rehydrated corn grain silage. There are still a few studies and more research to elucidate the best additives and the ideal amount to be added to ground corn grain silage.
Full article
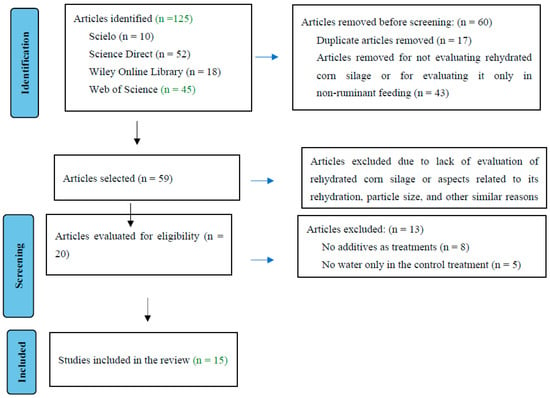
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Dairy, Ruminants, Veterinary Sciences
Practical Methods for Accommodating Behavioral Needs and Improving the Wellbeing of Both Farm Animals
Topic Editors: Temple Grandin, Kurt VogelDeadline: 20 June 2024
Topic in
Foods, Poultry, Ruminants
Carcass Characteristics and Meat Quality in Farm Animals
Topic Editors: Sergio Ghidini, Madalena Vieira-Pinto, Raffaella BranciariDeadline: 30 July 2024
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Poultry, Ruminants
Precision Feeding and Management of Farm Animals, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Manuel Gonzalez-Ronquillo, Marta I. Miranda Castañón, Einar Vargas-Bello-PérezDeadline: 31 August 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Ruminants
Dairy Cow Husbandry, Behaviour and Welfare
Guest Editor: Nicola BlackieDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Ruminants
Ruminal Microbiota, Fermentation Process, Enteric Methane Emissions, and Animal Performance
Guest Editors: Ana Isabel Roca-Fernández, Magdalena Arévalo-TurrubiarteDeadline: 31 August 2024
Special Issue in
Ruminants
Reproductive Management of Ruminants
Guest Editors: Vittoria Barile, Olimpia BarbatoDeadline: 30 September 2024
Special Issue in
Ruminants
Beef Cattle Production and Management
Guest Editors: Juliana Ranches, Alice P. BrandaoDeadline: 15 October 2024