Journal Description
Reproductive Medicine
Reproductive Medicine
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on obstetrics and gynecology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), FSTA, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 29.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 10.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Defining the Limits of Postpartum Leukocytosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Reprod. Med. 2024, 5(2), 33-42; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed5020005 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
There are established reference ranges for many laboratory values during pregnancy. Fewer studies exist regarding the expected white blood cell (WBC) count after delivery. The aim of this study was to determine appropriate postpartum leukocytosis in a diverse patient cohort. Patients who delivered
[...] Read more.
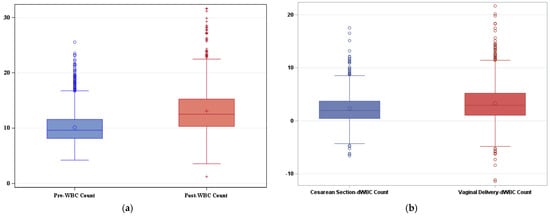
There are established reference ranges for many laboratory values during pregnancy. Fewer studies exist regarding the expected white blood cell (WBC) count after delivery. The aim of this study was to determine appropriate postpartum leukocytosis in a diverse patient cohort. Patients who delivered a live fetus at 37 weeks or later were retrospectively identified. Complete blood counts collected on hospital admission and postpartum day one were used to quantify the change in WBC count associated with delivery. A total of 2245 patients were included; of these patients, 1476 delivered vaginally and 769 delivered via cesarean section. The average change in WBC count was 2.99 × 103/mm3. A WBC count of 20.19 × 103/mm3 defined the 95th percentile. The average rise in WBC count was 3.31 × 103/mm3 after vaginal delivery and 2.34 × 103/mm3 after cesarean section (p < 0.001). Patients with chorioamnionitis or endometritis had an average postpartum WBC rise of 7.38 × 103/mm3 compared to 2.99 × 103/mm3 in controls (p < 0.001). There was no difference in WBC count rise with comorbid asthma, diabetes, or chronic hypertension. A greater WBC count rise was found in patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension. This study provides reference values for the average rise in WBC count after delivery and the 95th percentile postpartum WBC count in a diverse, medically complex patient population with and without delivery complications. Our findings further highlight maternal medical comorbidities that may contribute to the degree of postpartum leukocytosis.
Full article
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Rose et al. The Effect of In Vitro Maturation (IVM) Protocol Changes on Measures of Oocyte/Embryo Competence. Reprod. Med. 2023, 4, 65–73
by
Bruce I. Rose, Kevin Nguyen and Samuel E. Brown
Reprod. Med. 2024, 5(2), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed5020004 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
**Samuel E [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Pre-Operative Anxiety Related to Major Urogynecologic Surgery: Insights from Perioperative Survey Data in Maine
by
Nadi Nina Kaonga, Yanghee Courbron, Emmy Holmgren, Eliot Konzal, Whitney Williams, Mary Brandes and Caroline Foust-Wright
Reprod. Med. 2024, 5(1), 23-31; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed5010003 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Higher levels of pre-operative anxiety are associated with adverse outcomes according to the cardiothoracic and orthopedic literature on emergent surgeries. There are limited data on pre-operative anxiety levels in the gynecologic setting. This study sought to identify predictive variables for high pre-operative
[...] Read more.
Background: Higher levels of pre-operative anxiety are associated with adverse outcomes according to the cardiothoracic and orthopedic literature on emergent surgeries. There are limited data on pre-operative anxiety levels in the gynecologic setting. This study sought to identify predictive variables for high pre-operative anxiety levels in patients undergoing major urogynecologic surgery. Methods: Pre- and post-operative surveys that included demographic data, a modification of the Amsterdam Pre-Operative Anxiety and Information Scale, and open-ended questions regarding anxiety were administered. Descriptive, univariate and multivariate analyses were used to analyze the quantitative elements of the survey data. The qualitative components of the survey data were coded and analyzed using thematic analyses. Results: A total of 54 participants completed the pre-operative survey. The median age was 62 years old, and the majority were employed (n = 34, 60.7%). Roughly 1/3 had been diagnosed with a mental health condition (n = 19, 33.9%) and nearly all had other health conditions (n = 51, 91%). The baseline APAIS score ranged from 9 to 40, with higher scores reflecting higher levels of pre-operative anxiety. The median APAIS score was 24, with a score equal to or greater than 30 being in the highest tertile. Conclusion: No associations were made between the variables and pre-operative anxiety levels. However, useful insights into our patient population were made.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Diabetes Technology in Pregnant Women with Type 1 Diabetes—Distribution and Effects on Glycemic Regulation and Perinatal Outcomes
by
Sara Yalda Ghaur, Pernille Bundgaard Grinderslev, Magnus Leth-Møller, Per Glud Ovesen, Jens Fuglsang, Sanne Fisker, H. David McIntyre and Ulla Kampmann
Reprod. Med. 2024, 5(1), 12-22; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed5010002 - 07 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes (TID) are associated with an increased risk of obstetric and neonatal adverse outcomes. Optimal glycemic control prior to and through pregnancy is crucial to reduce complications. The use of diabetes technology is rapidly increasing. The aim of
[...] Read more.
Pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes (TID) are associated with an increased risk of obstetric and neonatal adverse outcomes. Optimal glycemic control prior to and through pregnancy is crucial to reduce complications. The use of diabetes technology is rapidly increasing. The aim of the study was to investigate the use and effects of diabetes technology in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes. A retrospective cohort study was conducted; 84 women were included in the analysis and were divided into subgroups according to their glucose monitoring method and insulin delivery method. HbA1c values declined during pregnancy in all subgroups with no significant difference between the subgroups. A difference was, however, found in birth weight z-scores. Women using a sensor and an insulin pump had larger babies compared to women without these treatment modalities. The results of the study indicate that diabetes technology, including insulin pumps and/or glucose sensors are not superior to self-monitoring blood glucose measurement and multiple daily injection insulin therapy, which is comforting in the light of the unequal access to health benefits.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Antenatal Secondhand Smoke (SHS) Exposure and the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products (RAGE)
by
Katrina L. Curtis, Kelsey M. Hirshi, Kary Tsai, Evan T. Clark, Brendan M. Stapley, Benjamin T. Bikman, Paul R. Reynolds and Juan Arroyo
Reprod. Med. 2024, 5(1), 1-11; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed5010001 - 30 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exposure to secondhand smoke (SHS) during fetal development results in negative postnatal effects, including altered organ development, changes in metabolism, and increased risk of respiratory illness. Previously, we found the induction of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) dependent on the expression of the receptor
[...] Read more.
Exposure to secondhand smoke (SHS) during fetal development results in negative postnatal effects, including altered organ development, changes in metabolism, and increased risk of respiratory illness. Previously, we found the induction of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) dependent on the expression of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) in mice treated with SHS. Furthermore, antenatal SHS exposure increases RAGE expression in the fetal lung. Our objective was to determine the postnatal effects of antenatal SHS treatment in 4- and 12-week-old offspring. Pregnant animals were treated with SHS via a nose-only delivery system (Scireq Scientific, Montreal, Canada) for 4 days (embryonic day 14.5 through 18.5), and offspring were evaluated at 4 or 12 weeks of age. Animal and organ weights were measured, and lungs were histologically characterized. Blood pressure and heart rates were obtained, and RAGE protein expression was determined in the lungs of control and treated animals. We observed the following: (1) significant decreases in animal, liver, and heart weights at 4 weeks of age; (2) increased blood pressure in 4-week-old animals; and (3) increased RAGE expression in the lungs of the 4-week-old animals. Our results suggest an improvement in these metrics by 12 weeks postnatally such that measures were not different regardless of RA or SHS exposure. Increased RAGE expression in lungs from 4-week-old mice antenatally treated with SHS suggests a possible role for this important smoke-mediated receptor in establishing adult disease following IUGR pregnancies.
Full article
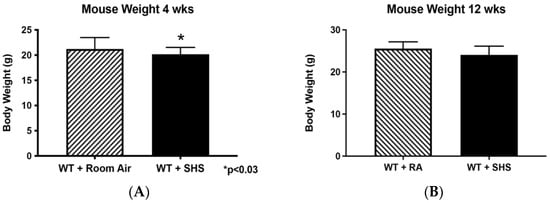
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exposure of Early Postnatal Oocytes to Chemotherapy Alters the Potential Ovarian Reserve, According to an Ex Vivo Mouse Model
by
Meghan C. H. Ozcan, Julienne Chaqour, Morgan F. Woodman-Sousa and Kathryn J. Grive
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(4), 248-258; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4040023 - 18 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Current safety data on chemotherapy during pregnancy are based on studies which focus on the mother and do not explore reproductive health and fecundity potential within the exposed offspring. We designed this randomized ex vivo animal study to evaluate the effect of chemotherapy
[...] Read more.
Current safety data on chemotherapy during pregnancy are based on studies which focus on the mother and do not explore reproductive health and fecundity potential within the exposed offspring. We designed this randomized ex vivo animal study to evaluate the effect of chemotherapy on the developing ovarian reserve in the exposed offspring. Specimens (100 postnatal day zero C57BL/6 mouse ovaries) were randomized to control or chemotherapy drug exposure and maintained in a hanging well organ culture. Murine ovarian reserve establishment mirrors activity seen in the human fetus but with a significant time shift of the transition to meiotic arrest to the postnatal period. Exposures included: doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, paclitaxel, docetaxel, and cisplatin. Doxorubicin resulted in a significant loss of 95.2% (p < 0.0001) of oocyte density compared to controls. Cyclophosphamide also caused depletion of 50.5% (p < 0.0001) of oocyte density. Cisplatin, docetaxel, and paclitaxel all demonstrated unique phenotypical changes on the ovaries and their oocytes, without a significant decrease in oocyte density over a five-day exposure. Exposure to chemotherapy may result in profound loss of oogonia during the transition to mature oocytes.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Prenatal Evaluation of a Fetal Cystic Hygroma: An Unexpected Finding of a De Novo Fetal BRCA1 Deletion Case Report
by
Stephanie C. Laniewski, LauraAnne Hirschler, Anwar M. Iqbal and Neil S. Seligman
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(4), 242-247; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4040022 - 23 Oct 2023
Abstract
This case presents a novel occurrence of a de novo BRCA1 gene deletion in a fetus with a cystic hygroma. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) was performed for chromosome G-banding analysis, demonstrating a normal karyotype: 46, XX. Chromosome microarray analysis performed as a reflex
[...] Read more.
This case presents a novel occurrence of a de novo BRCA1 gene deletion in a fetus with a cystic hygroma. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) was performed for chromosome G-banding analysis, demonstrating a normal karyotype: 46, XX. Chromosome microarray analysis performed as a reflex test revealed an 80 kb deletion on 17q21.31, encompassing the BRCA1 gene. Follow-up FISH analysis performed on parental blood samples yielded negative results, confirming that the deletion was de novo in the fetus. Subsequent anatomic ultrasound evaluation showed no identifiable structural defects, and it was concluded that the microdeletion was unlikely to be the cause of the cystic hygroma. Regardless, it will be imperative that the patient’s daughter be appropriately counseled regarding the implications of carrying a BRCA1 deletion and the need for heightened surveillance in adulthood. As BRCA1 genetic testing is traditionally performed on adult patients with informed consent, this case report highlights the need for ongoing conversations and research in the management of incidental fetal diagnosis discovered during routine prenatal testing, as well as the care and counseling of these patients and their families.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Celebration of the Fourth Anniversary of the Founding of Reproductive Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
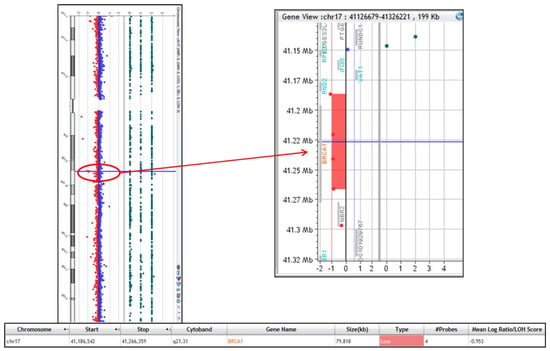
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can We Safely Decrease Early-Term Delivery and Cesarean Section Rate in Pregnancies Complicated by Fetal Transposition of Great Arteries?
by
Angel Chimenea, Lutgardo García-Díaz, Ana Méndez and Guillermo Antiñolo
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 233-241; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030021 - 14 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Transposition of the great arteries (TGA) is a common critical neonatal congenital heart defect. After birth, physiological shunts close rapidly, necessitating early treatment with prostaglandin infusion and balloon-atrial septostomy. Timing of delivery is challenging, balancing the risks and advantages of early-term delivery
[...] Read more.
Background: Transposition of the great arteries (TGA) is a common critical neonatal congenital heart defect. After birth, physiological shunts close rapidly, necessitating early treatment with prostaglandin infusion and balloon-atrial septostomy. Timing of delivery is challenging, balancing the risks and advantages of early-term delivery and specialized care. The aim of this study is to assess the safety of a full-term delivery policy in fetuses diagnosed with TGA. Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted of 17 women with a prenatal diagnosis of fetal TGA at Virgen del Rocío University Hospital between 2015 and 2021. Primary outcomes included: incidence of preterm, early-term, full-term, and late-term delivery, and rate of cesarean section. Secondary outcomes included: Saturday to Sunday admission and birth, and delivery between 0:00 a.m. and 8:00 a.m. Results: Full-term birth was achieved in 94.1%, reaching a low cesarean delivery rate (17.6%). A total of 82.4% of infants were born on weekdays, and only in three of the cases (17.6%) did delivery occur between 0 a.m. and 8 a.m. The median birth weight was 3300 g. Intravenous prostaglandins were administered in all cases, and 94.1% required balloon-atrial septostomy. Conclusions: In our study favoring full-term delivery, we reduce early-term deliveries and the cesarean section rate in prenatally diagnosed TGA.
Full article
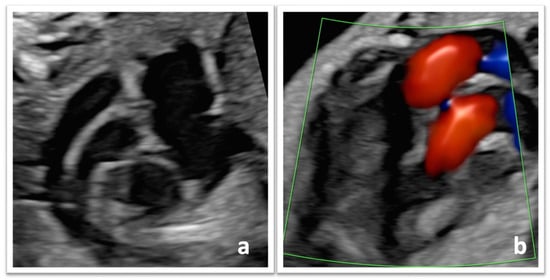
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Recent Developments in In Vitro Spermatogenesis and Future Directions
by
In Ki Cho and Charles A. Easley
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 215-232; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030020 - 11 Sep 2023
Abstract
Recent developments in stem cell technologies have made significant advancements in the field of in vitro gametogenesis. In vitro gametogenesis (IVG) is a promising technology where functional gametes (sperm or egg cells) can be generated from stem cells. Scientists have made continuous advancements
[...] Read more.
Recent developments in stem cell technologies have made significant advancements in the field of in vitro gametogenesis. In vitro gametogenesis (IVG) is a promising technology where functional gametes (sperm or egg cells) can be generated from stem cells. Scientists have made continuous advancements in the field and successfully derived fully functional sperm from stem cells in mice. Two recent papers generated excitement in IVG by generating bi-maternal and bi-paternal mice from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). IVG is a promising technology with potential applications that include infertility treatment, fertility preservation, same-sex reproduction, bypassing oocyte depletion in women with advanced age, conservation biology, genetic disorder prevention, and research into human germ cell development. In vitro spermatogenesis (IVS) is the attempt to recreate the process of spermatogenesis in a culture system. Spermatogenesis is essential for male fertility and reproductive health, but it can be impaired by various factors such as genetic defects, environmental toxicants, infections, aging, or medical therapies. Spermatogenesis is a complex and highly regulated process involving multiple cell proliferation, differentiation, and maturation stages. The main challenges of IVS are to provide a suitable microenvironment that mimics the testis in vivo, to support the survival and development of all the cell types involved in spermatogenesis, and to achieve complete and functional spermatogenesis. Therefore, there is a great interest in developing methods to study spermatogenesis in vitro, both for basic research and clinical applications. This review covers recent developments in in vitro spermatogenesis in the past two years. Advances in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have introduced techniques like ex vivo tissue culture and technologies such as bioreactors, microfluidic systems, and organoids. Bioreactors and microfluidic systems replicate physiological conditions for tissue and cell cultivation, while organoids model organ functionality. Meanwhile, scaffolds, made from various materials, provide essential structural support, guiding the growth and organization of cells into functional tissues.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Reviews on Reproductive Biology and Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
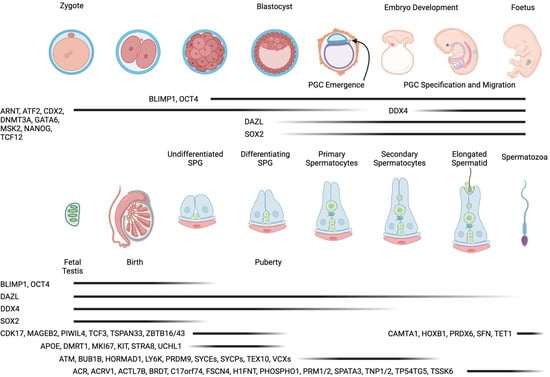
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Special Issue Featuring Papers for Celebrating the Third Year since the Founding of Reproductive Medicine
by
Stefano Palomba
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 210-214; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030019 - 06 Sep 2023
Abstract
It is a great pleasure to introduce this Special Issue celebrating the third year since the founding of Reproductive Medicine [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Relationship between Ovarian Reserve Markers and Body Mass Index in Infertile Women with and without Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
by
Luisa Casadei, Ilaria Nacci, Veronica Vicomandi, Roberto Pietro Sorge and Carlo Ticconi
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 198-209; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030018 - 17 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study, carried out on 94 women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and 176 controls without it, investigated the influence of body mass index (BMI) on serum levels of antimüllerian hormone (AMH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and 17ß-estradiol (E2) in
[...] Read more.
This study, carried out on 94 women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and 176 controls without it, investigated the influence of body mass index (BMI) on serum levels of antimüllerian hormone (AMH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and 17ß-estradiol (E2) in infertile patients. Patients were assigned to four subgroups according to age (<35 or ≥35 years) and BMI (<25 kg/m2 or ≥25 kg/m2). Significant differences between PCOS-affected and control women were observed with respect to most of the parameters of interest. In both PCOS-affected and control women, age was inversely correlated with AMH. In the control patients, age was directly correlated with FSH and LH. In women affected by PCOS, no correlation was found between BMI and serum levels of AMH, E2, and LH, except FSH. No correlation was found between BMI and markers of ovarian reserve in control women. BMI was not correlated with AMH in any of the four subgroups considered regardless of the presence of PCOS. An inverse correlation was found only in PCOS-affected women aged ≥35 years between a BMI < 25/FSH and a BMI ≥ 25/LH. The possible association between BMI and ovulation disorder (OD) was investigated in 96 control women aged ≤37 years. In women with OD, the BMI values were significantly higher and FSH and E2 levels were lower than those of patients without OD. Taken together, our data suggest that BMI is not related to hormonal parameters of ovarian reserve, irrespective of the presence of PCOS, and could influence ovulation disorder rather than cause a decrease in ovarian reserve.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Celebration of the Fourth Anniversary of the Founding of Reproductive Medicine)
Open AccessReview
The Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease during Reproductive Years: An Updated Narrative Review
by
Nariman Hossein-Javaheri, Michael Youssef, Yaanu Jeyakumar, Vivian Huang and Parul Tandon
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 180-197; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030017 - 03 Aug 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) frequently affects women of childbearing age and often coincides with pregnancy. With an increased incidence of IBD, gastroenterologists and obstetricians are more frequently involved in caring for women of reproductive age. While the development of novel therapies has allowed
[...] Read more.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) frequently affects women of childbearing age and often coincides with pregnancy. With an increased incidence of IBD, gastroenterologists and obstetricians are more frequently involved in caring for women of reproductive age. While the development of novel therapies has allowed for successful conception and pregnancy outcomes, many patients may hesitate to conceive due to concerns for presumed adverse IBD effects on maternal and fetal health. As such, a noticeable percentage of patients may choose voluntary childlessness. Indeed, active IBD carries a greater risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including a loss of pregnancy, preterm delivery, and emergent C-sections. However, those with a quiescent disease tend to have fewer pregnancy complications. Therefore, it is essential to achieve remission prior to conception to optimize pregnancy outcomes. Dedicated IBD and pregnancy clinics can greatly assist in improving patient knowledge and attitudes towards pregnancy; through individualized pre-conception counseling, education, and medication adherence, the risks of poor pregnancy outcomes can be minimized. Furthermore, it is important for healthcare providers to have a sufficient understanding of the medication safety and tools to measure the disease activity, while counseling patients during gestation and breastfeeding periods. This review article aims to provide the most recent evidence-based management methods for IBD during pregnancy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Reviews on Reproductive Biology and Medicine)
Open AccessArticle
Travel during Pregnancy: A Web-Based Survey of People Who Have Been Pregnant within the Past 10 Years
by
Lada H. Nechval and Kathleen M. Antony
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 166-179; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030016 - 28 Jul 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Travel is frequent among many populations, including pregnant people. The focus of this online survey was to better understand the travel practices of people who have been pregnant within the last ten years. An online survey was conducted for three months through social
[...] Read more.
Travel is frequent among many populations, including pregnant people. The focus of this online survey was to better understand the travel practices of people who have been pregnant within the last ten years. An online survey was conducted for three months through social media posts on Facebook and Twitter. Previously pregnant people were asked questions about where they traveled, if they cancelled any travel plans, and travel-related discussions with their obstetric provider. During the three months the survey was open, 469 participants completed the survey. A total of 390 (83.2%) participants traveled domestically, while 114 (24.3%) traveled internationally or between non-contiguous states within the United States of America (USA). Of these respondents, 170 (44.2%) of the domestic travelers and 69 (61.1%) of the international travelers reported discussing travel plans with their OB provider. Additionally, 49 (10.5%) participants cancelled at least one domestic trip and 30 (6.41%) cancelled at least one international trip. Regarding travel discussions, 6 (3.6%) participants who traveled domestically and 2 (2.9%) who traveled internationally reported that their OB provider initiated the conversation. Many pregnant people choose to travel domestically and internationally. However, it is also clear that not all travelers discuss plans with their OB provider, and in few cases does the provider initiate the conversation. Given the frequency with which people travel, pregnant people and their OB providers should have conversations regarding travel to minimize potential risks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Duration of Menstrual Blood Loss: Historical to Current Understanding
by
Marwan Habiba and Giuseppe Benagiano
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 145-165; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030015 - 26 Jul 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
Most published research focuses on the amount of menstrual blood loss and, to a lesser extent, on cyclicity. Little attention has been paid to the duration of bleeding, the factors that enable its cessation within a ‘normal’ timeframe, or to patterns that entail
[...] Read more.
Most published research focuses on the amount of menstrual blood loss and, to a lesser extent, on cyclicity. Little attention has been paid to the duration of bleeding, the factors that enable its cessation within a ‘normal’ timeframe, or to patterns that entail interruption and resumption of blood loss. The definition of what constitutes normal remains arbitrary and there is no therapy specifically designed to shorten the duration of bleeding. Here, we critically review the literature that addresses the duration of bleeding and the factors that trigger endometrial breakdown and repair. Available reports used population averages which mask inter- and intra-individual variations. The duration of bleeding is not necessarily linked to the amount of loss but may be influenced by age, ethnicity, habitus, region and altitude of residence, dieting and stress. The onset of bleeding has been linked to declining steroid production by the corpus luteum. There remains considerable controversy around the extent of endometrial shedding at menstruation. This is likely to vary within and between women. The significance of a change from previous patterns, very short or prolonged bleeding, days of light loss or spotting before or after days of bleeding, or of bleed-free days that punctuate flow, remain poorly understood.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Predicting the Need for Insulin Treatment: A Risk-Based Approach to the Management of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
by
Anna S. Koefoed, H. David McIntyre, Kristen S. Gibbons, Charlotte W. Poulsen, Jens Fuglsang and Per G. Ovesen
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(3), 133-144; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4030014 - 10 Jul 2023
Abstract
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes including large for gestational age infants. Individualizing the management of women with GDM based on the likelihood of needing insulin may improve pregnancy outcomes. The aim of this study is to identify characteristics
[...] Read more.
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes including large for gestational age infants. Individualizing the management of women with GDM based on the likelihood of needing insulin may improve pregnancy outcomes. The aim of this study is to identify characteristics associated with a need for insulin in women with GDM, and to develop a predictive model for insulin requirement. A historical cohort study was conducted among all women with GDM in a singleton pregnancy at Aarhus University Hospital from 2012 to 2017. Variables associated with insulin treatment were identified through multivariable logistic regression. The variables were dichotomized and included in a point scoring system aiming to predict the likelihood of needing insulin. Seven variables were associated with needing insulin: family history of diabetes, current smoker, multiparity, prepregnancy body mass index, gestational age at the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), 2-h glucose value at the OGTT and hemoglobin A1c at diagnosis. A risk score was calculated assigning one point to each variable. On ROC analysis, a cut-off value of ≥3 points optimally predicted a requirement for insulin. This prediction model may be clinically useful to predict requirement for insulin treatment after further validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Pregnancy-Related Complications)
►▼
Show Figures
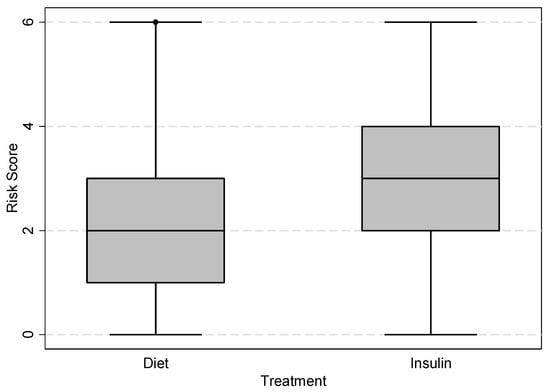
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hypo-Osmotic Swelling Test and Male Factor
by
Jerome H. Check, Diane L. Check and Aniela Bollendorf
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(2), 118-132; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4020013 - 12 Jun 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
For over 30 years, defects of the functional integrity of the sperm membrane, as evidenced by a low hypo-osmotic swelling test when evaluating the semen analysis, are not only associated with male infertility (even with sperm that otherwise seem normal), but unless corrected,
[...] Read more.
For over 30 years, defects of the functional integrity of the sperm membrane, as evidenced by a low hypo-osmotic swelling test when evaluating the semen analysis, are not only associated with male infertility (even with sperm that otherwise seem normal), but unless corrected, successful intrauterine pregnancies will rarely ensue. This defect, interestingly, does not impair fertilization of the oocyte, but instead, prevents a normal-appearing embryo from successfully implanting. The frequency in infertile couples increases with advancing age of the male, ranging from 5% in younger males to 25% in men in their late forties or early fifties. It seems to be related to a toxic protein added to the sperm as they traverse the ejaculatory ducts. The defect is very correctable, either by treating the sperm with the protein digestive enzyme chymotrypsin prior to intrauterine insemination and avoidance of unprotected sex prior to ovulation, or in vitro fertilization with intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Unfortunately, this very inexpensive, easy-to-perform test is rarely performed by the large majority of physicians treating infertility. The purpose of this manuscript is to hopefully rekindle interest within the infertility community to add this test to the standard semen analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers for Celebrating the 3rd Founding Year of Reproductive Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
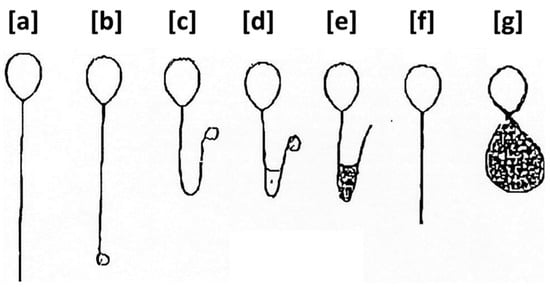
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Machine Learning Algorithm Predicting Infant Psychomotor Developmental Delay Using Medical and Social Determinants
by
David Waynforth
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(2), 106-117; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4020012 - 05 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Psychomotor developmental delay in infants includes failure to acquire abilities such as sitting, walking, grasping objects and communication at the ages when most infants have acquired these abilities. Known risk factors include a large number of aspects of family environment, socioeconomic position, problems
[...] Read more.
Psychomotor developmental delay in infants includes failure to acquire abilities such as sitting, walking, grasping objects and communication at the ages when most infants have acquired these abilities. Known risk factors include a large number of aspects of family environment, socioeconomic position, problems in pregnancy and birth and maternal health. It is clinically useful to be able to screen for developmental delay so that healthcare interventions can be considered. The present research used machine learning (random forest) to create an algorithm predicting psychomotor delay in 9-month-old infants using information ascertainable at birth and in early infancy. The dataset was the UK longitudinal Millennium Cohort study. In total, 53 predictors measuring socioeconomic indicators, paternal, family and social support for the mother, beliefs about good parenting, maternal health, pregnancy and birth were included in the initial algorithm. Feature reduction showed that of the 53 variables, birthweight, gestational age at birth, pre-pregnancy BMI, family income and parents’ ages had the highest feature importance scores and could alone correctly predict developmental delay with over 99% sensitivity and 100% specificity. No features measuring aspects of early infant care or environment meaningfully added to algorithm performance. The relationships between delay and some of the predictors, particularly income, were nonlinear and complex. The results suggest that the risk of psychomotor developmental delay can be identified in early infancy using machine learning, and that the best predictors are factors present prior to and at birth.
Full article
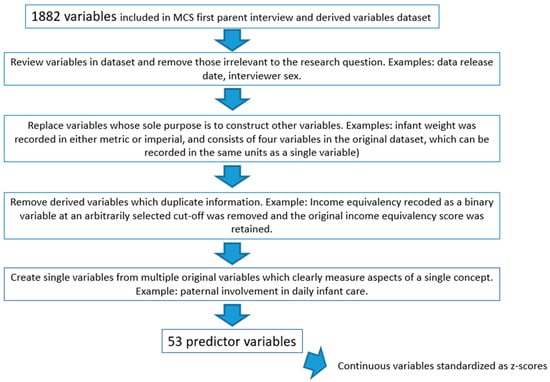
Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
Should Endometriosis-Associated Ovarian Cancer Alter the Management of Women with an Intact Endometrioma in the Reproductive Age?
by
Johnny S. Younis
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(2), 100-105; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4020011 - 24 May 2023
Abstract
Endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer (EAOC) is an evolving clinical entity believed to develop from ovarian endometriosis. Continuous efforts are nowadays invested in exploring its pathogenesis and causality. Since endometrioma is a widespread sub-type of the disease, malignant transformation to EAOC during reproductive age may
[...] Read more.
Endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer (EAOC) is an evolving clinical entity believed to develop from ovarian endometriosis. Continuous efforts are nowadays invested in exploring its pathogenesis and causality. Since endometrioma is a widespread sub-type of the disease, malignant transformation to EAOC during reproductive age may cause much concern and affect its management. The summary relative risk of developing EAOC in women with endometriosis is 1.93-fold compared to women without endometriosis, but its lifetime risk is relatively low, equivalent to 2.1%. EAOC is an age-dependent disease with a mean age of 51.64 ± 3.24 years at diagnosis; 30.68% of patients are below 50, presumably premenopausal. Only 2.10% and 0.017% of cases are below 45 and 40 years, apparently in reproductive age. The evidence is reassuring and implies that managing an intact endometrioma should not be altered in most women of reproductive age. Particular attention should be focused on sporadic cases with an enlarging endometrioma, atypical findings on transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS), and characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Infertility Treatment and Hypertension in Pregnancy: The Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study
by
Mami Ishikuro, Taku Obara, Keiko Murakami, Fumihiko Ueno, Aoi Noda, Tomomi Onuma, Fumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Kikuya, Zen Watanabe, Naomi Shiga, Masahito Tachibana, Noriyuki Iwama, Hirotaka Hamada, Masatoshi Saito, Junichi Sugawara, Hirohito Metoki, Nobuo Yaegashi and Shinichi Kuriyama
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(2), 89-99; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4020010 - 18 Apr 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Infertility treatment is a possible factor in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP). Identifying the characteristics of pregnant women who have undergone infertility treatment and have a potential risk for HDP is valuable for its prevention and treatment. Using data from 12,456 pregnant Japanese
[...] Read more.
Infertility treatment is a possible factor in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP). Identifying the characteristics of pregnant women who have undergone infertility treatment and have a potential risk for HDP is valuable for its prevention and treatment. Using data from 12,456 pregnant Japanese women from the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study, the association between infertility treatment and HDP was analyzed. A multiple logistic regression model showed an association between infertility treatment and HDP (odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.05–1.72). In vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection were also associated with HDP. Moreover, these associations were observed even among women who were not overweight and did not smoke. The application of infertility treatment should be carefully considered, even among women with low modifiable risk factors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Genomic Insults and their Redressal in the Eutopic Endometrium of Women with Endometriosis
by
Itti Munshi and Geetanjali Sachdeva
Reprod. Med. 2023, 4(2), 74-88; https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed4020009 - 15 Apr 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Endometrium, a highly dynamic tissue, is known for its remarkable ability to regenerate, differentiate, and degenerate in a non-conception cycle and transform into a specialized tissue to nurture and protect the embryo in a conception cycle. This plasticity of the endometrium endows the
[...] Read more.
Endometrium, a highly dynamic tissue, is known for its remarkable ability to regenerate, differentiate, and degenerate in a non-conception cycle and transform into a specialized tissue to nurture and protect the embryo in a conception cycle. This plasticity of the endometrium endows the uterus to execute its major function, i.e., embryo implantation. However, this boon becomes a bane, when endometrium- or endometrium-like cells adhere, grow, and invade extrauterine sites, leading to endometriosis. Endometrial deposits at the extrauterine site lead to severe pelvic pain, painful menstruation, and infertility in endometriosis. Although benign, endometriotic lesions share several traits with cancerous cells, excessive proliferation, adhesion, invasion, and angiogenesis make endometriotic lesions analogous to cancer cells in certain aspects. There exists evidence to support that, akin to the cancer cell, endometriotic lesions harbor somatic mutations. These lesions are known to experience higher proliferative stress, oxidative stress, and inflammation, which may contribute to somatic mutations. However, it would be of more interest to establish whether in the eutopic endometriosis also, the mutational burden is higher or whether the DNA Damage Response (DDR) is compromised in the eutopic endometrium, in endometriosis. Such investigations may provide more insights into the pathobiology of endometriosis and may also unravel cellular events associated with the origin of the disease. This review compiles inferences from the studies conducted to assess DNA damage and DDR in endometriosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Endometrial Physiology and Pregnancy Success)
►▼
Show Figures
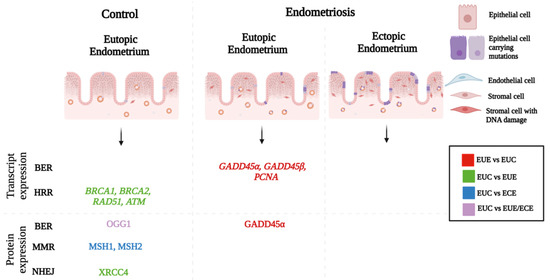
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, CIMB, Endocrines, IJMS, JMP, Life, Reprod. Med.
Pathogenesis of Pregnancy-Related Complications 2.0
Topic Editors: Ilona Hromadnikova, Katerina KotlabovaDeadline: 31 August 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Reprod. Med.
Reviews on Reproductive Biology and Medicine
Guest Editors: Giulia Guerriero, Kamla Kant ShuklaDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Reprod. Med.
Recent Advances in Preeclampsia
Collection Editor: Berthold Huppertz
Topical Collection in
Reprod. Med.
Reproductive Medicine in Europe
Collection Editor: Simone Ferrero