Journal Description
Poultry
Poultry
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on poultry health, welfare and productivity, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 25.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Poultry is a companion journal of Agriculture.
Latest Articles
The Effect of Supplementation with Organic Acid and Oregano Oils in Drinking Water on Pekin Duck Growth and Welfare
Poultry 2024, 3(2), 95-106; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3020009 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study evaluated duck growth, health, and welfare in response to water supplementation with organic acid (OA) and oregano oils (OOs) in Pekin duck. The treatments used in this study included a control (CON) treatment with no water additives given, an OA treatment
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated duck growth, health, and welfare in response to water supplementation with organic acid (OA) and oregano oils (OOs) in Pekin duck. The treatments used in this study included a control (CON) treatment with no water additives given, an OA treatment (ProPhorce Exclusive NC®), and an OO treatment (Nubiotic 4X Concentrate®). The OA and OO improved the feed conversion ratio (FCR) and body weight (BW) (p < 0.01) compared to the control (CON). Both OA and OO showed differences (p < 0.05) in villus height and crypt depth compared to the CON. But only OA showed an increase (p < 0.01) in villus height and villus height/crypt depth ratio. On D 35, the total plasma corticosterone levels, heterophil-to-lymphocyte ratios, and asymmetry scores for OA and OO were decreased (p < 0.05) compared to CON, indicating lower stress susceptibility. The pH levels of OA ceca and jejunum were lower (p < 0.05) compared to CON. Tibia breaking strength was increased (p = 0.02) for OA compared to CON, while no differences were found with OO (p > 0.05). In conclusion, these experiments indicate that OA and OO can be used to improve duck growth, feed efficiency, stress susceptibility, and bird welfare.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Efficiency of Utilization of Metabolizable Energy for Carcass Energy Retention in Broiler Chickens Fed Maize, Wheat or a Mixture
by
Vasil Radoslavov Pirgozliev, Muhammad Hassan Hammandy, Stephen Charles Mansbridge, Isobel Margaret Whiting and Stephen Paul Rose
Poultry 2024, 3(2), 85-94; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3020008 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
The study aimed to quantify carcass fat and protein retention, and the efficiency of carcass energy utilization (Kre) resulting from feeding broiler chickens diets containing wheat, maize or mixtures of both as the major cereal ingredient. The apparent metabolizable energy (AME) of the
[...] Read more.
The study aimed to quantify carcass fat and protein retention, and the efficiency of carcass energy utilization (Kre) resulting from feeding broiler chickens diets containing wheat, maize or mixtures of both as the major cereal ingredient. The apparent metabolizable energy (AME) of the four cereal samples was determined in adult cockerels. There was a linear (p < 0.001) increase in AME with increasing amounts of maize within the four cereal mixtures, with analyses indicating that the AME of maize was 1.4 MJ/kg greater than that of wheat. A second bioassay with growing chickens was used to determine Kre in each cereal, measured as carcass fat and protein from 7 to 21d age. Increasing proportions of maize resulted in linear increases in carcass fat and energy retained from fat (p < 0.001). However, the carcass protein and energy retained from protein did not follow the same pattern as fat (p = 0.121), but rather decreased numerically (L = 0.032). The Kre tended (p = 0.060) to increase with greater proportion of maize in a linear fashion (L = 0.009). Although AME values of cereals were confirmed to be additive, this could not be confirmed for Kre. This data can be used for optimizing energy utilization models for growing broilers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers of Poultry)
Open AccessArticle
Black Soldier Meal in Feed Could Adversely Affect Organic Broiler Meat Quality When Used for the Total or Half Replacement of Diet Proteins
by
Maria Chiara La Mantia, Massimo Calì, Luigi Petrocchi Jasinski, Michela Contò, David Meo Zilio, Gianluca Renzi and Monica Guarino Amato
Poultry 2024, 3(2), 66-84; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3020007 - 22 Mar 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Organic poultry sector needs high-quality proteins sources to meet specific requirements. The EU’s organic regulation forbids synthetic amino acids; therefore, soybean, with its balanced essential amino acid content, has become the most used protein source, though much of it is imported from non-EU
[...] Read more.
Organic poultry sector needs high-quality proteins sources to meet specific requirements. The EU’s organic regulation forbids synthetic amino acids; therefore, soybean, with its balanced essential amino acid content, has become the most used protein source, though much of it is imported from non-EU countries, with sustainability and crop competition issues; therefore, it should be substituted with a high-protein-value alternative such as insect meal. In this study, 900 Aviagen Savanna broilers were fed with three different organic diets: soybean only (S100), 50% black soldier fly larvae meal (BSL) and 50% soybean (BSL50), and 100% BSL only (BSL100). Broiler performance, welfare, and fatty acids (FA) were analyzed. BSL50 and BSL100 negatively affected growth, while only BSL100 worsened all of the market-related performances. Meat showed a significant increase in saturated FA (SFA) (p < 0.000) and a corresponding decrease in polyunsaturated FA (PUFA), in BSL50 and BSL100, but α-linolenic acid was not affected by BSL50 treatment (p < 0.000). The SFA increase could represent a negative aspect for human health (e.g., cardiovascular diseases), but, as reported by other authors, medium chain SFA, (i.e., lauric acid), may show beneficial effects as well (i.e., antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties).
Full article
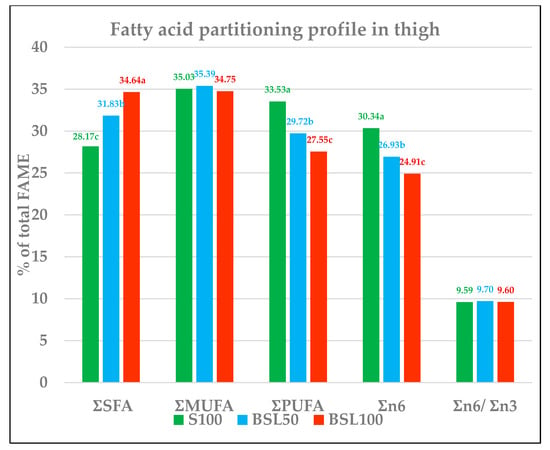
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating the Effects of Feeding a Concentrated Saccharomyces cerevisiae Fermentation Product on the Performance and Stress Susceptibility of Broiler Chickens
by
Zachary Heinsohn, Austin Brown, Eric Sobotik, Gabrielle House, Austin Stiewert, William Evan Chaney, Vivek Kuttappan and Gregory S. Archer
Poultry 2024, 3(1), 57-65; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3010006 - 11 Mar 2024
Abstract
This study evaluated the effect of a concentrated yeast fermentation product on the performance and stress response of broiler chickens. Day-old Cobb 500 male broiler chicks were randomly allocated to one of two dietary treatments: Control (CON) or concentrated yeast fermentation product (CSCFP,
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the effect of a concentrated yeast fermentation product on the performance and stress response of broiler chickens. Day-old Cobb 500 male broiler chicks were randomly allocated to one of two dietary treatments: Control (CON) or concentrated yeast fermentation product (CSCFP, 0.625 kg/MT). On d18, simultaneous feed withdrawal and heat stress challenges were performed for 12 h. Blood was analyzed for plasma corticosterone (CORT) and heterophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (HL) on d19 and d42. Performance parameters were collected throughout the trial: body weight (BW), feed consumption (FC), and feed conversion ratio (FCR). On d19, the CSCFP birds had lower (p ≤ 0.05) CORT (5320.3 ng/mL) and HL (0.14) than the CON birds (9049.6 ng/mL and 0.21). On d42, the CSCFP birds had lower (p ≤ 0.05) CORT (1623.8 ng/mL) and HL (0.74) than the CON birds (2920.2 ng/mL and 1.05). No differences were observed in mortality (p > 0.05). The CON birds had a higher (p ≤ 0.05) FCR than CSCFP throughout all phases. The CON birds consumed more feed than the CSCFP birds throughout all phases (p ≤ 0.05). In conclusion, CYFP reduced stress and improved feed conversion when compared to CON, making it a viable feed additive to improve welfare and production.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Rapid DNA Detection of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium and Heidelberg from Poultry Samples
by
Joana Bittencourt Mathias, Margarida Neves Souza, Diéssy Kipper, André Salvador Kazantzi Fonseca, Vagner Ricardo Lunge and Nilo Ikuta
Poultry 2024, 3(1), 47-56; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3010005 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
The Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium), Heidelberg (S. Heidelberg), and their monophasic variants (S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. 1,4,[5],12:r:- and S. 1,4,[5],12:-:1,2) are highly disseminated in poultry farming and can contaminate chicken meat, eggs, and other foods of avian origin. A time-consuming
[...] Read more.
The Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium), Heidelberg (S. Heidelberg), and their monophasic variants (S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. 1,4,[5],12:r:- and S. 1,4,[5],12:-:1,2) are highly disseminated in poultry farming and can contaminate chicken meat, eggs, and other foods of avian origin. A time-consuming bacteriological and serological analysis is usually required to identify serovars by traditional methods. Incomplete and inconclusive serological results are frequent in routine analysis, mainly due to the occurrence of bacterial isolates presenting similar antigenic profiles. Molecular biology assays have been developed to improve the detection of specific Salmonella serovars and strains. This study aimed to develop a multiplex real-time PCR (SHTAmp) for the rapid DNA detection of S. Typhimurium, S. Heidelberg, and their monophasic variants from poultry samples. The methodology was used in the analysis of 147 field isolates from Brazilian poultry flocks previously evaluated with serological analysis. The results demonstrated that it was able to specifically and rapidly detect 21 S. Typhimurium and 57 S. Heidelberg isolates with complete antigenic formulae. Furthermore, SHTAmp was able to differentiate nine S. Typhimurium and 44 S. Heidelberg isolates with incomplete serological formulae (monophasic and aphasic variants). The complete methodology was also successfully used to detect these bacteria directly from 34 poultry samples after pre-enrichment in buffered peptone water (BPW). In conclusion, SHTAmp is a fast and accurate method to detect the two frequent and concerning serovars S. Typhimurium and S. Heidelberg directly from poultry samples.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Egg Quality and Performance in Late-Lay Hens Fed Different Combinations of Copper, Manganese, and Zinc Complexed with Sulfate or Amino Acid Ion
by
Jill R. Domel, Gabrielle M. House, Eric B. Sobotik and Gregory S. Archer
Poultry 2024, 3(1), 36-46; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3010004 - 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
Dietary inclusion of copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) can improve egg shell quality through changing the membrane structure. This study aimed to compare the responses of egg shell to different mineral sources. In this study, 60-week-old laying hens (n = 378)
[...] Read more.
Dietary inclusion of copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) can improve egg shell quality through changing the membrane structure. This study aimed to compare the responses of egg shell to different mineral sources. In this study, 60-week-old laying hens (n = 378) were assigned to one of seven treatments with 18 replicates each in an RCBD. Treatments included the following: control (basal + sulfated minerals (CuSO4, MnSO4, and ZnSO4)), and basal + amino acid complexed (AAC) minerals (AAC Cu, AAC Mn, AAC Zn, AAC Cu + Mn, AAC Mn + Zn, AAC Zn + Cu). Trace minerals were added to a basal diet containing 20 ppm MnSO4 and 20 ppm ZnSO4 to achieve overall target concentrations of 20 ppm Cu, 60 ppm Mn, and 60 ppm Zn. The hens were fed the treatment diet for 15 weeks, and egg production and egg quality were assessed during weeks 5, 10, and 15 of the experiment. Egg shells, egg contents, and excreta were analyzed for Cu, Mn, Zn, Ca, and P during weeks 10 and 15. No treatment differences (p > 0.05) were observed for production or egg quality. Differences between excreta mineral content were observed. The mineral content of egg shells and egg contents did not differ (p > 0.05) at any time point. The mineral source did not affect egg mineral deposition and egg quality measures (p > 0.05). Some AAC trace minerals enhanced retention of zinc, calcium, and manganese, although AAC Cu increased Cu excretion. Taken together, feeding AAC trace minerals does not significantly affect egg production or egg quality during the late-lay period. More research is needed to demonstrate whether Cu excretion is increased when feeding AAC Cu due to increased bioavailability or other factors.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Effect of a Bacillus subtilis plus Yeast Cell Wall Synbiotic on Salmonella Enteritidis Colonization in Ceca of Layer Pullets
by
Miloud Araba, George Girgis, Hannah McBride and Troy Lohrmann
Poultry 2024, 3(1), 26-35; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3010003 - 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Salmonella Enteritidis (SE) is a major contamination concern in eggs and risk for Salmonellosis in humans. Strains of Bacillus subtilis and yeast cell wall can be used as substitutes for antibiotic substances in feed against Salmonella in poultry. The objective of this study
[...] Read more.
Salmonella Enteritidis (SE) is a major contamination concern in eggs and risk for Salmonellosis in humans. Strains of Bacillus subtilis and yeast cell wall can be used as substitutes for antibiotic substances in feed against Salmonella in poultry. The objective of this study was to assess the effect of BacPack® (Quality Technology International, Inc., Elgin, IL, USA) Q1+1 (BPQ11), a feed additive combination of a Bacillus subtilis strain and Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall, on SE cecal colonization in Lohmann LSL pullets. A control group (CON) and a test group (BPQ) were each randomly assigned 100-day-old chicks. CON was fed a corn–soybean meal-based vegetarian mash diet, and BPQ was fed the control diet supplemented with BPQ11 for the duration of the study. At 8 days of age, chicks were orally challenged with a nalidixic acid-resistant SE strain at a dose of 6.3 × 107 colony forming units (CFUs) per bird. At 7, 11, 15, and 19 days post-challenge (DPC), 25 birds per group were euthanized, and their cecal contents were collected and analyzed for SE. SE counts were 6.88, 7.98, 7.79, and 7.50 in CON and 7.18, 7.31, 6.35, and 6.30 log10 CFU/g in BPQ at 7, 11, 15, and 19 DPC, respectively. SE did not differ between CON and BPQ at 7 DPC; however, BPQ had lower (p < 0.0001) SE at 11 (−0.67), 15 (−1.45), and 19 (−1.20 log10 CFU/g) DPC. Results indicate that synbiotic BPQ11 may be a useful dietary pre-harvest tool for SE management in layer birds.
Full article
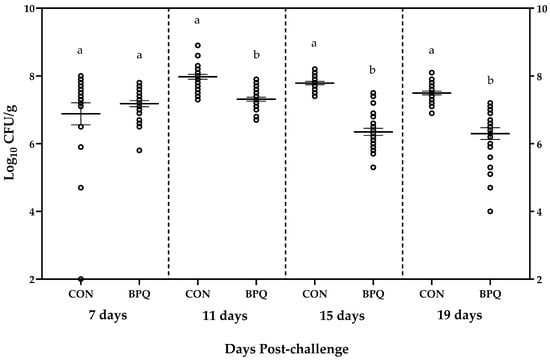
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reduction of Bacterial Load on Broiler Carcasses Using Low-Volume Fluidic Nozzles in Combination with 60 °C Water at 450 Psi Pressure
by
Douglas E. Cosby, Michael D. McIntyre, Josh DeVoll, Aaron Jordan, Johnna K. Garrish, Mark E. Berrang and Elizabeth McMillan
Poultry 2024, 3(1), 15-25; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3010002 - 26 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the changing regulations in poultry processing, increased pressure is placed on integrators to reduce the number of human enteropathogenic bacteria on the final carcass and/or parts. Reducing the total number of bacteria on broiler carcasses before entering the evisceration side of the
[...] Read more.
With the changing regulations in poultry processing, increased pressure is placed on integrators to reduce the number of human enteropathogenic bacteria on the final carcass and/or parts. Reducing the total number of bacteria on broiler carcasses before entering the evisceration side of the processing plant is projected to reduce the number of bacteria on the carcasses after chilling. This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of a prototype wash cabinet using low volume, fluidic nozzles in combination with high pressure (450 psi) and hot water (60 °C) to remove bacteria from pre-scald, post-scald, or post picked carcasses. Carcasses (n = 5) from each location were obtained from a commercial processing plant, placed into individual sterile sample bags, placed into an insulated container, and transported to the U.S. National Poultry Research Center Pilot Plant within 30 min of collection. Carcasses were hung in standard shackles and sampled pre-wash with pre-moistened, cellulose swabs. All carcasses were washed in the prototype wash cabinet with 60 °C water at 450 psi at a line speed of 52 birds/minute on 15.24 cm centered shackles. Post-wash breast sponge samples were collected identical to pre-wash swabs. Buffered peptone water (BPW) was added, sponges stomached and serially diluted before plating onto total aerobic count (TAC), Enterobacteriaceae (ENT) and Escherichia. coli (EC) Petrifilm® cards. All PetriFilm® cards were incubated at 37 °C for 24 ± 2 h. After incubation, bacterial counts were recorded and converted to log10 CFU/swab. Samples were processed for Campylobacter species using the Tempo® CAM protocol. Four replications were conducted on separate dates. Paired t-tests were used to compare numbers recovered from breast swabs collected before and after the wash cabinet, significance reported at p < 0.05. Pre-scald samples had significant reductions of 2.50, 2.01, and 1.73 log10 colony-forming units/carcass (CFU/carcass) for TAC, Ent, and EC Petrifilm®, respectively, and a 2.21 CFU/mL reduction of Campylobacter species using Tempo® CAM. Post-scald, there were significant reductions of 2.09, 1.23, and 0.90 CFU/carcass for TA, Ent, and EC Petrifilm®, respectively, and a 1.14 CFU/mL reduction of Campylobacter species using Tempo® CAM. Post-pick, significant reductions of 0.73, 1.53, and 0.99 CFU/carcass for TA, Ent, and EC Petrifilm®, respectively, and a 0.86 CFU/carcass reduction of Campylobacter species using Tempo® CAM were reported. These data indicate that hot water at high pressure can reduce total bacterial load on carcasses and reduce pathogenic bacteria on carcasses prior to evisceration.
Full article
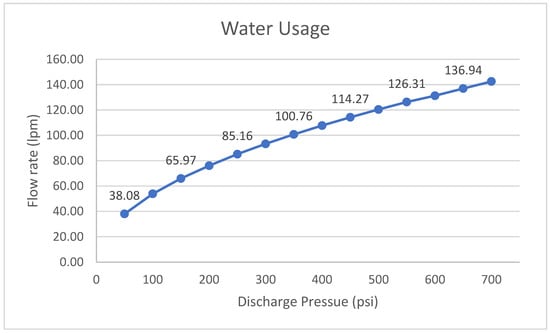
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Varying Concentrations of Eimeria Challenge on the Intestinal Integrity of Broiler Chickens
by
Giovana Camargo de Souza, Giovanna Fernandes Esteves, Franciana Aparecida Volpato, Rovian Miotto, Marcos Antônio Zanella Mores, Adriana Mércia Guaratini Ibelli and Ana Paula Bastos
Poultry 2024, 3(1), 1-14; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry3010001 - 25 Jan 2024
Abstract
The objective of the current investigation was to evaluate several Eimeria challenges and the resulting alterations in intestinal permeability, intestinal morphology, and intestinal lesion scores in broiler chickens. This study included four groups with ten replicate cages per treatment, in which each group
[...] Read more.
The objective of the current investigation was to evaluate several Eimeria challenges and the resulting alterations in intestinal permeability, intestinal morphology, and intestinal lesion scores in broiler chickens. This study included four groups with ten replicate cages per treatment, in which each group received a different treatment dosage of Eimeria, characterizing high, medium-high, and medium-low challenges. Five days after the challenge, intestinal lesions and permeability were assessed. The results showed that the increase in Eimeria challenge led to a considerable decrease in the height of intestinal villosities, in the ratio between villosity size and crypt depth, and in goblet cells. Moreover, after the challenge, there was a considerable increase in intestinal permeability. In conclusion, the medium-low, medium-high, and high-challenge models can be utilized for experimental infection. In the context of clinical studies, it has been observed that the administration of medium-high and high-challenge doses has proven to be adequate. However, it is advisable to utilize a medium-low challenge level to develop a subclinical challenge model for forthcoming investigations that aim to evaluate nutritional recommendations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Poultry Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
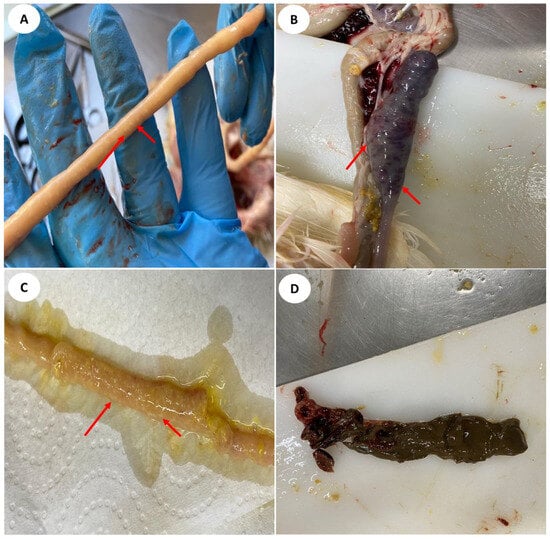
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Attenuation of a Field Strain of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus in Primary Chicken Culture Cells and Adaptation to Secondary Chicken Embryo Fibroblasts
by
Victor A. Palomino-Tapia, Guillermo Zavala, Sunny Cheng and Maricarmen Garcia
Poultry 2023, 2(4), 516-530; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040038 - 18 Dec 2023
Abstract
The establishment of commercial infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) live-modified vaccines has relied on serial passaging in chicken embryo (CEO) and tissue culture (TCO) for attenuation. The objective of this study was to attenuate and adapt a virulent CEO-related ILTV field strain (6340) in
[...] Read more.
The establishment of commercial infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) live-modified vaccines has relied on serial passaging in chicken embryo (CEO) and tissue culture (TCO) for attenuation. The objective of this study was to attenuate and adapt a virulent CEO-related ILTV field strain (6340) in immortalized cells (LMH), primary chicken embryo kidney cells (CEK), chicken embryo liver cells (CEL), and chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEF). CEFs were refractory to parent ILTV, LMH cells produced low virus yields (~2.5 log10 TCID50 per mL), while CEK and CEL cells produced higher viral titers (≥log10 6.0 TCID50 per mL). After 52 passages in CELs, the cytopathic effect (CPE) was observed not only in hepatocytes but also in CEL fibroblasts. Once CPE was evident in CEL fibroblasts, 20 further passages in CEFs with viral titers reaching yields of ~4.4–5.5 log10 TCID50 per mL were performed. The attenuation of CEF-adapted viruses was evaluated after intra-tracheal and conjunctival inoculation in 28-day-old broilers by assessing clinical signs at five days post-inoculation (DPI). Virus CEL cells passages 80, 90, and 100, and CEF passages 10 and 20 were significantly attenuated compared to the parental strain. This is the first report of the attenuation of a virulent field CEO-related ILTV strain (RFLP Group V) in CEF cells—a cell type from a different embryonic germ layer (mesoderm) than ILTV target cells—the respiratory epithelium (endoderm). This finding underscores the potential use of CEF adaptation for the development of a live-attenuated ILTV vaccine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Poultry Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
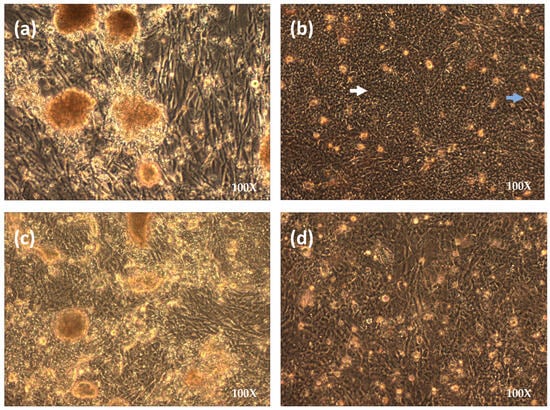
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nutritional Balance Matters: Assessing the Ramifications of Vitamin A Deficiency on Poultry Health and Productivity
by
Yauheni Shastak and Wolf Pelletier
Poultry 2023, 2(4), 493-515; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040037 - 01 Dec 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Vitamin A, a critical micronutrient, plays a vital role in maintaining poultry health and maximizing productivity. This comprehensive review paper conducts a thorough analysis of the consequences of vitamin A deficiency in domestic fowl. It delves into the physiological functions of vitamin A
[...] Read more.
Vitamin A, a critical micronutrient, plays a vital role in maintaining poultry health and maximizing productivity. This comprehensive review paper conducts a thorough analysis of the consequences of vitamin A deficiency in domestic fowl. It delves into the physiological functions of vitamin A and investigates how hypovitaminosis A impacts growth, immune function, reproduction, and overall poultry performance. Additionally, the review explores effective strategies for preventing and managing vitamin A deficiency, such as dietary adjustments and supplementation, while addressing the specific requirements for vitamin A intake. The implementation of these strategies holds immense importance in optimizing poultry management practices and achieving peak performance in poultry production. A profound understanding of the prevalence and factors contributing to clinical and subclinical vitamin A deficiency in domestic fowl is essential for ensuring the efficiency of poultry farming operations. Recognizing the pivotal role of vitamin A and applying the appropriate measures empowers poultry farmers to enhance the health outcomes and overall performance of their flocks.
Full article
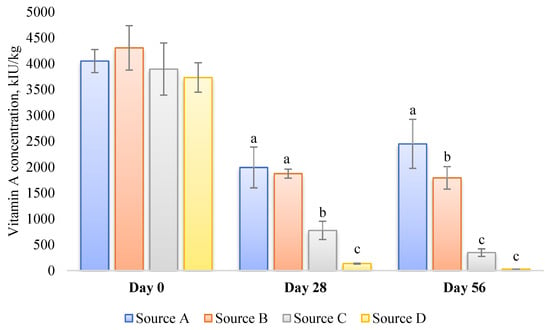
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Metabolizable Energy Intake and Body-Weight Restriction on Layer Pullets: 1-Growth, Uniformity, and Efficiency
by
Thiago L. Noetzold, Jo Ann Chew, Douglas R. Korver, René P. Kwakkel, Laura Star and Martin J. Zuidhof
Poultry 2023, 2(4), 475-492; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040036 - 13 Nov 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to determine the effects of dietary energy and body-weight (BW) restriction on layer pullets’ growth, uniformity, and feed efficiency. Two experiments were conducted using a precision feeding (PF) system (Experiment 1) and a conventional feeding (CON) system (Experiment 2). Experiment
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to determine the effects of dietary energy and body-weight (BW) restriction on layer pullets’ growth, uniformity, and feed efficiency. Two experiments were conducted using a precision feeding (PF) system (Experiment 1) and a conventional feeding (CON) system (Experiment 2). Experiment 1 consisted of a 2 × 4 factorial arrangement (eight treatments) with two feed allocation (FA) levels: meal every visit (MEV) or restricted to the lower boundary of Lohmann Brown-Lite pullets; and three dietary metabolizable energy (ME) levels: Low, Standard (Std), and High (2600, 2800, and 3000 kcal/kg, respectively); the fourth treatment enabled birds to choose from the three diets (Choice). Experiment 2 consisted of a 2 × 3 factorial arrangement (six treatments): two FA levels (ad libitum or restricted) and three dietary ME levels (Low, Std, and High). In each experiment, BW, coefficient of variation (CV), average daily feed intake (ADFI), average daily metabolizable energy intake (MEI), and feed conversion ratio (FCR) were recorded. Diet ADFI preferences and feeding motivation were determined only in the PF experiment. ANOVA was conducted on each experiment with the two main effects as fixed factors (FA and dietary ME), and age or period as the sources of variation. Differences were reported at p ≤ 0.05. MEV (PF experiment) and ad libitum-fed (CON experiment) pullets had greater BW compared to restricted-fed pullets (p < 0.05). The lowest CV was observed in the restricted-fed pullets from the PF experiment (p < 0.05). ADFI was greater in pullets fed the Low ME diet in the PF experiment compared to all the other groups, and the lower the dietary ME, the greater the ADFI in the CON experiment (p < 0.05). Choice-feeding pullets preferred feed with greater ME content in the PF experiment (p < 0.05). The lower the dietary ME, the greater the FCR in the CON experiment (p < 0.05). Restricted-fed pullets had greater daily visits, and lower daily meals, meal size, and successful visits to the PF system (p < 0.05). In conclusion, the results of this trial indicated that lower dietary ME increased FCR and ADFI, whereas feed restriction decreased BW and increased feeding motivation. Future steps after this trial will include examining the effects of dietary energy and feed restriction on carcass composition and sexual maturation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Poultry Nutrition)
►▼
Show Figures
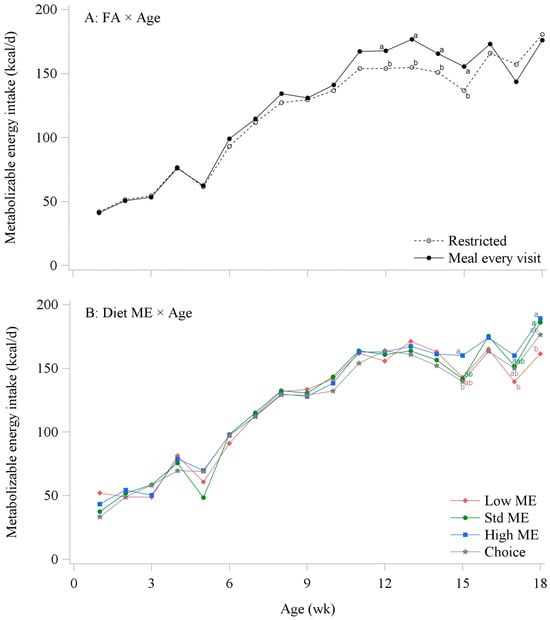
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Addition of Humicola Grisea Cellulase to Broiler Chicken Rations for a 21-Day Period
by
Dênia Oliveira de Souza, Cirano José Ulhoa, Weslane Justina da Silva, Denise Russi Rodrigues, Nadielli Pereira Bonifácio, Fabiana Ramos dos Santos, Fabiano Guimarães Silva and Cibele Silva Minafra
Poultry 2023, 2(4), 463-474; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040035 - 13 Nov 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the addition of liquid cellulose, produced by Humicola grisea, in 21-day-old broiler chickens’ diets. The treatments comprised control rations of corn and soybean meal and rations to which 500 mL/t and 1000 mL/t of cellulase were added. A
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to evaluate the addition of liquid cellulose, produced by Humicola grisea, in 21-day-old broiler chickens’ diets. The treatments comprised control rations of corn and soybean meal and rations to which 500 mL/t and 1000 mL/t of cellulase were added. A total of 180 male broiler chickens were used, distributed in a completely randomized design, with three treatments and six replicates. Broiler chicken performance was monitored during the period from 1 to 21 days old. Significant effects were detected for digestibility only between four and seven days old, when a reduced dry matter nitrogen intake was recorded, and for nitrogen digestibility in the broilers fed cellulase-supplemented rations at a dose of 1000 m/L. Among the analyzed digestive organs, only the biometrics of the large intestine were affected significantly at seven days old. The absolute weights of the liver and pancreas and the activities of amylase, alkaline phosphatase, and transaminases were not affected significantly, indicating that cellulase did not affect the metabolism of these organs. No significant effect was detected in the serum for electrolytes, total protein, or alkaline phosphatase. So, the addition of liquid cellulase produced by Humicola grisea did not affect performance and metabolism in 21-day-old broiler chickens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Poultry Nutrition)
Open AccessArticle
Supplementation of Japanese Quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) Breeders with Tagetes erecta Flower Extract and Vitamin E Improves the Oxidative Status of Embryos and Chicks
by
Lenilson Fonseca Roza, Evandro Menezes de Oliveira, Lidiane Staub, Tainara Ciuffi Euzébio Dornelas, Paula Toshimi Matumoto Pintro, Danielle Aparecida Munhos Hermoso, Emy Luiza Ishii Iwamoto, Alice Eiko Murakami and Tatiana Carlesso Santos
Poultry 2023, 2(4), 449-462; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040034 - 24 Oct 2023
Abstract
The effects of Tagetes erecta flower extract (TFE) and increasing levels of vitamin E (VE) in the diet of Japanese quail breeders on progeny performance and oxidative status were studied. Methods: 480 Japanese quail breeders were distributed in a completely randomized design with
[...] Read more.
The effects of Tagetes erecta flower extract (TFE) and increasing levels of vitamin E (VE) in the diet of Japanese quail breeders on progeny performance and oxidative status were studied. Methods: 480 Japanese quail breeders were distributed in a completely randomized design with five treatments and twelve replications of six females and two males each. A control diet (25 mg/kg VE) and four diets supplemented with TFE (3 g/kg) and VE (25, 100, 175, or 250 mg/kg) were used. Fresh yolk samples and the yolk sac and liver from embryos (11 and 15 days) and chicks (hatch and 3 days) were analysed. Data were subjected to ANOVA, a regression linear model, and contrast tests and the level of significance was set at p < 0.05. Results: TF and VE in the maternal diet improved the amount of alfa-tocopherol and total carotenoid content in the yolk. TFE + VE reduced lipid peroxidation and improved the oxidative status in the fresh yolk, in the embryo and chick yolk, and in the liver. Liver superoxide dismutase activity in hatched chicks increased linearly with the VE level and was not altered by TFE. Maternal diets did not influence progeny performance (1 to 28 days) or the relative expression of superoxide dismutase or glutathione peroxidase genes in the liver of chicks. Conclusions: TFE is an effective antioxidant in fresh eggs and supplementation of 3 g/kg TFE and high levels of VE in quail breeders improves the oxidative status of embryos and newly hatched chicks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Basic and Applied Aspects of Incubation Oriented to the Needs of the Embryos)
►▼
Show Figures
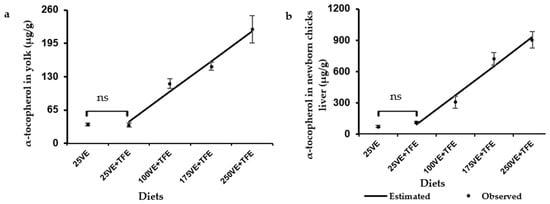
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Vitamin Compatibility with the Marek’s Disease Vaccine
by
Seyed Abolghasem Fatemi, Christopher J. Williams, Joshua Deines and Edgar David Peebles
Poultry 2023, 2(4), 442-448; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2040033 - 25 Sep 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In ovo injection of the Marek’s disease (MD) vaccine (MDV) has been widely practiced in commercial US hatcheries. However, the MDV is very sensitive and may not be compatible with some nutrients when administered together by in ovo injection. When individually administered by
[...] Read more.
In ovo injection of the Marek’s disease (MD) vaccine (MDV) has been widely practiced in commercial US hatcheries. However, the MDV is very sensitive and may not be compatible with some nutrients when administered together by in ovo injection. When individually administered by in ovo injection, L-Ascorbic acid (L-AA) and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25OHD3) have previously exhibited very promising results on the post-hatch physiological and immunological characteristics of broilers subjected to stressful commercial conditions. However, the compatibility of the MDV with these vitamins has not been previously explored. Their compatibility must first be established before their combined administration by in ovo injection can be considered. Therefore, the objective in this study was to determine the compatibility of the MDV with various levels of 25OHD3 or L-AA. The treatments employed were MDV-alone, MDV in combination with 0.6 (low) or 2.4 (high) μg doses of 25OHD3, or MDV in combination with 1.2 (low) or 12 (high) mg doses of L-AA. The live and dead ratio of primary chick embryo fibroblast cells infected by the MD virus (CEF-MDV) in each treatment was determined every 30 min for 2 h. The L-AA at both the low and high doses resulted in a 70% death of CEF-MDV within 1 h, but either dose of the 25OHD3 exhibited only an approximate 5% lower CEF-MDV survival as compared to those in the MDV-alone treatment. Therefore, it is suggested that the two designated doses of 25OHD3 have the potential to be effectively combined with the MDV for subsequent administration by in ovo injection.
Full article
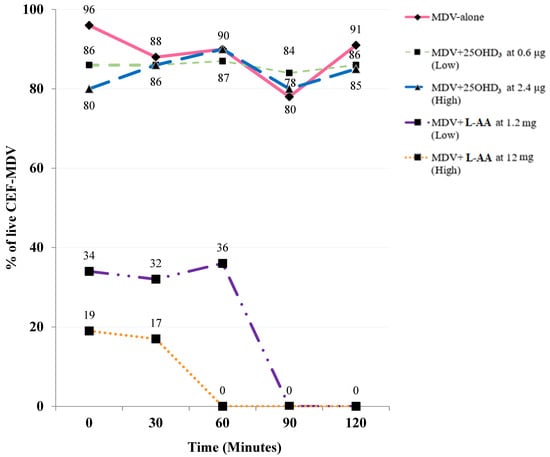
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Defatted Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal as an Alternative to Soybean Meal for Broiler Chickens
by
Sashka Chobanova, Nikolay Karkelanov, Stephen Charles Mansbridge, Isobel Margaret Whiting, Antonija Simic, Stephen Paul Rose and Vasil Radoslavov Pirgozliev
Poultry 2023, 2(3), 430-441; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2030032 - 20 Sep 2023
Abstract
The production of soybean meal (SBM) has a substantial impact on the environment and reducing its inclusion in poultry diets by using alternative protein sources, such as insect meal, is an important challenge for nutritionists. This study aimed to compare the productive performance
[...] Read more.
The production of soybean meal (SBM) has a substantial impact on the environment and reducing its inclusion in poultry diets by using alternative protein sources, such as insect meal, is an important challenge for nutritionists. This study aimed to compare the productive performance of broiler chickens fed one of two isonitrogenic (195 g/kg CP) and isocaloric (12.91 MJ/kg) diets. The first diet contained SBM as the main protein source, whereas SBM was completely replaced by defatted meal from Black Soldier Fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.; BSFL) in the second diet. Compared to the BSFL diet, the final body weight (BW) and weight gain (WG) of birds fed the SBM diet was ~17% greater and feed was utilised 19% more efficiently (p < 0.05). The differences in WG and FCR were supported by improved energy metabolism metrics, fat digestibility and digestibility of acid detergent fibres (ADFD) (p < 0.05). The present study shows that a complete replacement of dietary SBM with BSFL meal must be achieved with care, ensuring that all other factors (e.g., insect processing technology, feed additive supplementation, non-protein nitrogen accounting, mineral balance, fatty acid profile, amino acid supplementation) have been considered.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers of Poultry)
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Stocking Densities on the Microbiota of the Cloaca, Eggshell, and Egg Content of White Egg Layers in Colony Cages
by
Benjamin N. Alig, Kenneth E. Anderson, Ramon D. Malheiros, Justin H. Lowery and Lin L. Walker
Poultry 2023, 2(3), 418-429; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2030031 - 19 Sep 2023
Abstract
Food safety is a major concern for commercial poultry producers and consumers. Currently, there is also pressure from retailers and legislators to increase the space per hen in cages. Five different density treatments consisting of six (208 in2/bird), nine (139 in
[...] Read more.
Food safety is a major concern for commercial poultry producers and consumers. Currently, there is also pressure from retailers and legislators to increase the space per hen in cages. Five different density treatments consisting of six (208 in2/bird), nine (139 in2/bird), twelve (104 in2/bird), fifteen (83 in2/bird), and eighteen birds (69 in2/bird) per cage were examined in colony cage environments. Microbiological tests were performed at 39, 55, and 68 weeks of age. The populations of total aerobic bacteria; E. coli/coliform; Enterobacteriaceae; and yeasts and molds from an eggshell rinse, egg content, and cloacal swabs were enumerated. The prevalence of Salmonella spp. in these samples was also monitored. Overall, no bacteria were detected in any of the egg content, and there were no differences (p > 0.05) between treatments for the shell rinse. Stocking density did not influence the eggshell microbiota of the hens. Hens housed at 104 in2 per hen showed higher levels of total aerobic bacterial counts from the cloaca compared to hens at 208 in2 and 69 in2 per hen. Hens housed at 139 in2 per hen had the highest level of cloacal molds. This research demonstrates that stocking density does not influence eggshell microbiota or Salmonella contamination of the eggshell or cloaca, thereby indicating that allowing more space per hen will not positively or negatively affect the prevalence or concentration of foodborne pathogen-associated bacteria in or on the eggs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers of Poultry)
Open AccessCommunication
Bacitracin Supplementation as a Growth Promoter Down-Regulates Innate and Adaptive Cytokines in Broilers’ Intestines
by
Gabriela C. Dal Pont, Annah Lee, Cristiano Bortoluzzi, Yuhua Z. Farnell, Christos Gougoulias and Michael H. Kogut
Poultry 2023, 2(3), 411-417; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2030030 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the past decade, the withdrawal of antibiotics used as growth promoters (AGP) has increased some poultry industry challenges, such as the rise of intestinal diseases. Experts advocate that AGPs improve performance due to the modulation of the intestinal microbiota, with resulting anti-inflammatory
[...] Read more.
In the past decade, the withdrawal of antibiotics used as growth promoters (AGP) has increased some poultry industry challenges, such as the rise of intestinal diseases. Experts advocate that AGPs improve performance due to the modulation of the intestinal microbiota, with resulting anti-inflammatory effects. However, the impact and interactions of AGPs with the host intestinal immune system are still unknown, which represents issues in developing effective alternatives for AGPs. Therefore, this study was aimed at better understanding the potential mechanism of action of bacitracin used as AGP and its impacts on the intestinal immune system. Ninety day-of-hatch chickens were randomly assigned to two treatments with three repetitions of fifteen birds, a control (CNT) group with a corn/soybean meal standard diet, and a control diet supplemented with 50 g/ton of feed of bacitracin (BMD). The cytokines’ and chemokines’ production (IFN-α, IFN-γ, IL-16, IL-10, IL-21, IL-6, M-CSF, MIP-3α, MIP-1β, VEGF and CCL-5) were assessed in the jejunum and ileum at 14, 21, 28 and 36 days of age by using a chicken-specific cytokine/chemokine peptide ELISA array. Broilers with BMD supplementation were found to have a lower production of IL-16, IFN-γ, M-CSF, IL-21, MIP-1β and VEGF in the jejunum at 14 d. However, from 21 through 36 days, the effect of BMD on cytokine production in the jejunum was negligible except for CCL-5, which was reduced at D36. In the ileum, BMD effects on the cytokine profile started at 28 d, when BMD-supplemented broilers showed a reduced IL-6 production level. At day 36, BMD reduced IL-16 and MIP-3α production but increased VEGF concentration in the ileum tissue. The present study demonstrated that the use of bacitracin as an AGP modulates the small intestine immune system, especially in the first phase of the broiler’s life (up to 14 days). Moreover, BMD anti-inflammatory effects include not only innate immunity but also seemed to influence the development of the adaptive immune response as seen by the decreased production of IL-21 and IL-16. These results demonstrate that a commonly used AGP in broiler feed had a local anti-inflammatory effect.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Poultry Future and Options: Research into the Environmental, Physiological, Wellbeing, and Health Challenges Facing Our Industry)
►▼
Show Figures
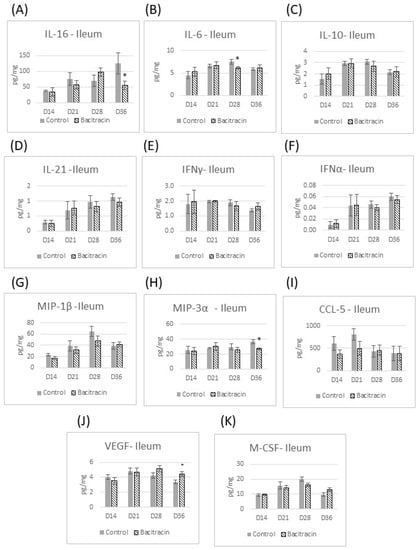
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Impact of COVID-19 and the Associated Lockdown on the Production, Distribution, and Consumption of Poultry Products in Gujarat, India: A Qualitative Study
by
Pallavi Mishra, Akash Golaviya, Ketankumar Panchal, Ankit Hinsu, Kavita Yadav, Guillaume Fournié, Tony Barnett, Prakash Koringa, Haidar Ul Iman Paleja and Rajib Dasgupta
Poultry 2023, 2(3), 395-410; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2030029 - 16 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The poultry industry in India, estimated to be worth about one trillion INR, was severely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study was conducted in Gujarat, India to unpack the processes through which COVID-19-related factors affected the poultry production and distribution network
[...] Read more.
Background: The poultry industry in India, estimated to be worth about one trillion INR, was severely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study was conducted in Gujarat, India to unpack the processes through which COVID-19-related factors affected the poultry production and distribution network and explore the impacts on the relevant actors. Methods: An exploratory qualitative study was conducted among 34 poultry stakeholders using semi-structured interviews. The data were thematically analyzed by adopting an interpretative phenomenological approach. Results: Convincing evidence emerged that the lockdown and the pandemic significantly impacted the production, distribution, and consumption of poultry products. Movement restrictions during the first lockdown disrupted the supply of inputs and the distribution of poultry and poultry products. Between March and June 2020, rumors contributed to a substantial decrease in the consumption of poultry products. Consumption picked up following the reopening after the lockdown and the prices and availability of poultry products. The profits, however, failed to compensate for the losses that had been incurred. Conclusions: The experience and impacts of the first COVID-19 lockdown on the poultry industry unraveled several short- and medium-term challenges in the poultry sector in India that need to be addressed to make it more resilient to similar shocks.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Intestinal Permeability Methods in Broilers over a 6-Week Growth Period
by
Maddison L. Wiersema, Brian J. Kerr and Dawn A. Koltes
Poultry 2023, 2(3), 383-394; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry2030028 - 04 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The adoption of methods detecting intestinal permeability in poultry has been slow due to the lack of urine availability in avian species. The objective of this study was to examine intestinal permeability assays in broilers using serum. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FITC-D) and lactulose/mannitol/sucralose (LMS),
[...] Read more.
The adoption of methods detecting intestinal permeability in poultry has been slow due to the lack of urine availability in avian species. The objective of this study was to examine intestinal permeability assays in broilers using serum. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FITC-D) and lactulose/mannitol/sucralose (LMS), indigestible sugars, were used to detect intestinal permeability across two fed states (fed or fasted) and four sugar treatments (Control, FITC-D, LMS, or FITC-D+LMS). Broilers housed in pens were assigned one of eight treatments and sampled on 14, 28, and 42 days of age. Data were analyzed using PROC Glimmix for fed state, sugar treatment, age, and all interactions. Serum lactulose and FITC-D increased in fasted compared to fed birds (p < 0.006), whereas mannitol increased in fed compared to fasted birds (p < 0.001). Serum lactulose and FITC-D decreased on day 28 compared to other timepoints (p < 0.003). Serum FITC-D only had a significant sugar by fed state interaction (p < 0.05) with elevated concentrations in fasted and fed birds that received FITC-D. Serum lactulose was significant for all interactions with elevated concentrations in broilers provided lactulose and fasted (p < 0.001). The ability to detect a three-way interaction with serum lactulose suggests an increased sensitivity; however, additional studies are needed.
Full article
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Animals, Fishes, Poultry
Sustainable Development of Natural Bioactive Compounds/Products in Animal Resource and Agriculture Science: Volume II
Topic Editors: In Ho Kim, Balamuralikrishnan Balasubramanian, Shanmugam SureshkumarDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Foods, Poultry, Ruminants
Carcass Characteristics and Meat Quality in Farm Animals
Topic Editors: Sergio Ghidini, Madalena Vieira-Pinto, Raffaella BranciariDeadline: 30 July 2024
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Poultry, Ruminants
Precision Feeding and Management of Farm Animals, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Manuel Gonzalez-Ronquillo, Marta I. Miranda Castañón, Einar Vargas-Bello-PérezDeadline: 31 August 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Poultry
Feature Papers of PoultryGuest Editors: Ilias Giannenas, Michael HessDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Poultry
Current Research and Key Issues in Poultry Immunology
Guest Editors: Dieter Liebhart, Christine JansenDeadline: 31 March 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Poultry
Basic and Applied Aspects of Incubation Oriented to the Needs of the Embryos
Collection Editor: Barbara Tzschentke