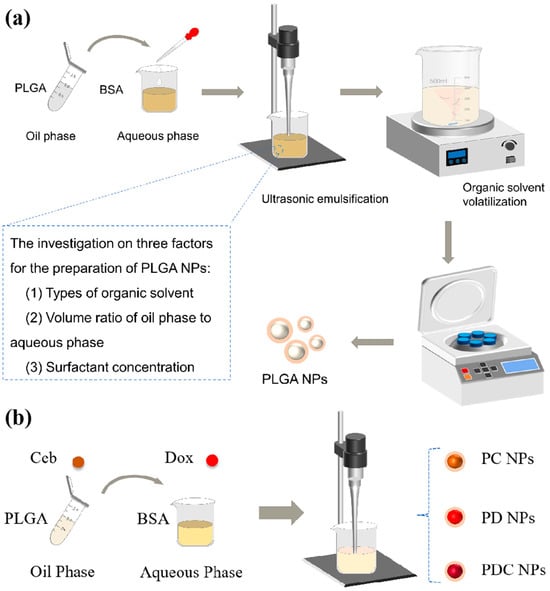
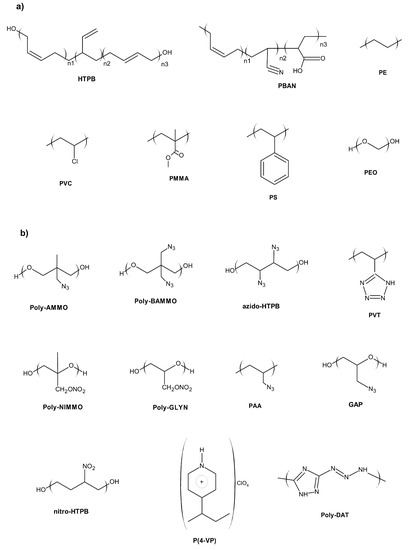
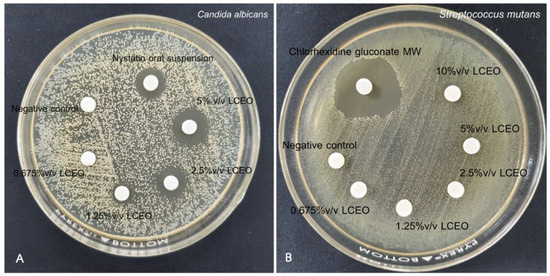
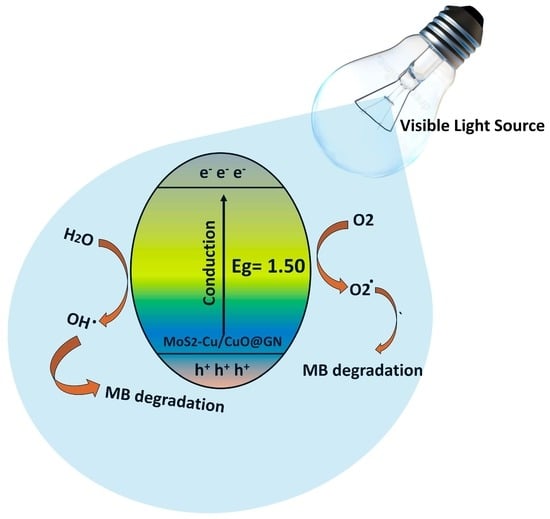
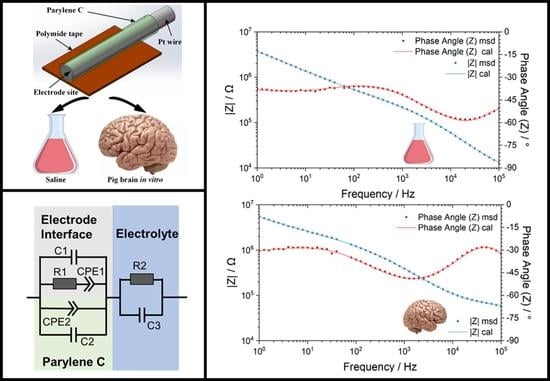
Progress in Polymer Applications
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Applications".
Viewed by 105907Editors
Interests: polymer synthesis; catalyst; polymer membranes; fuel cells; electrochemical sensors
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This collection from the open-access journal Polymers aims at collecting reviews on the topic of Polymer Applications. All kinds of applications (from fuel cell electrodes to membranes, from sensors to actuators, from biomedical engineering to space engineering, and from macro scale down to nano scale) with polymeric materials, proof of concept, structural/system design, performance verification and characterization, are included. Submission of manuscripts should be falling the following hot fields:
- Polymer materials for energy storage and conversion devices
- Polymers for chemosensing and electrochemical sensors applications
- Polymer-based materials for environmental applications
- Functional polymeric membranes
- Polymers for drug delivery
- Polymers for tissue engineering
- Polymer materials for adsorption applications
- Innovative functional textiles
- Polymers for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial activity of polymeric materials
- Flame retardancy of polymeric materials
- Polymeric self-healing materials
- Polymers for food applications
- Functional carbon fiber reinforced polymer
- Polymer composites for 3D/4D printing
Prof. Dr. Dong Jin Yoo
Dr. Mohanraj Vinothkannan
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Polymer materials for energy storage and conversion devices
- Polymers for chemosensing and electrochemical sensors applications
- Polymer-based materials for environmental applications
- Functional polymeric membranes
- Polymers for drug delivery
- Polymers for tissue engineering
- Polymer materials for adsorption applications
- Innovative functional textiles
- Polymers for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial activity of polymeric materials
- Flame retardancy of polymeric materials
- Polymeric self-healing materials
- Polymers for food applications
- Functional carbon fiber reinforced polymer
- Polymer composites for 3D/4D printing