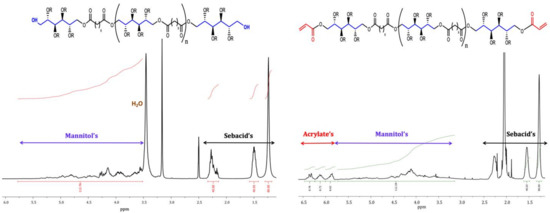
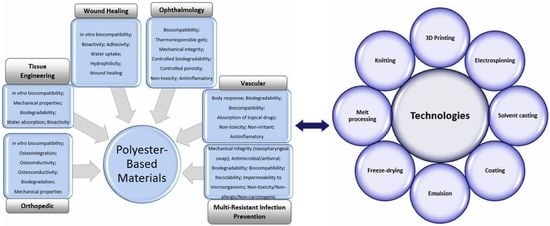
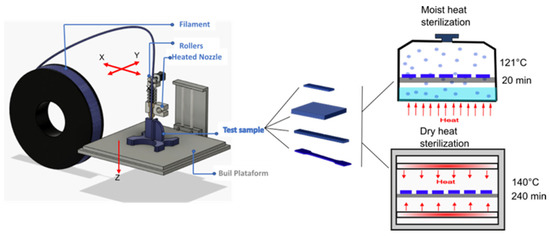
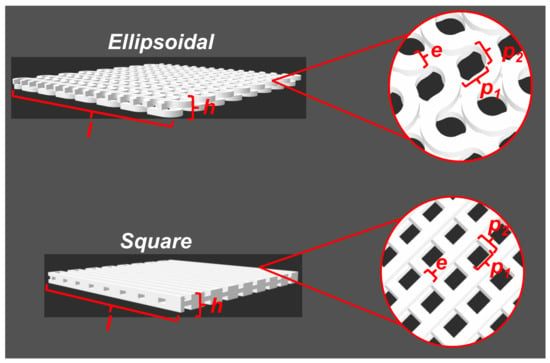
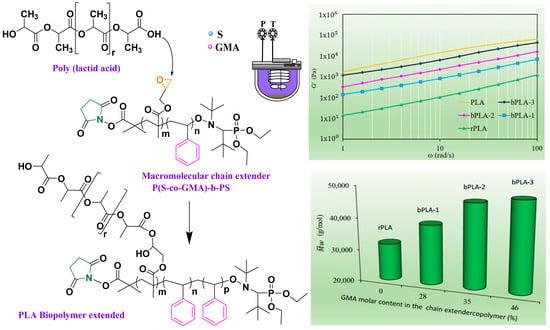
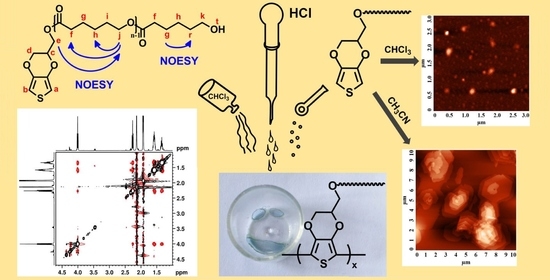
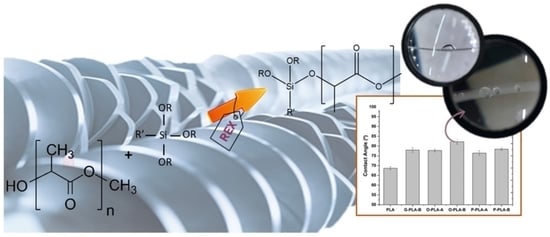
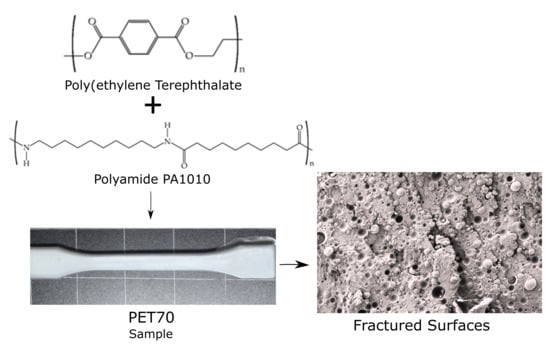
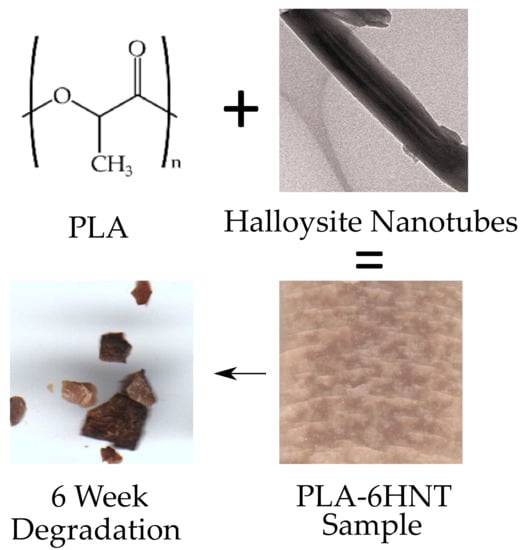
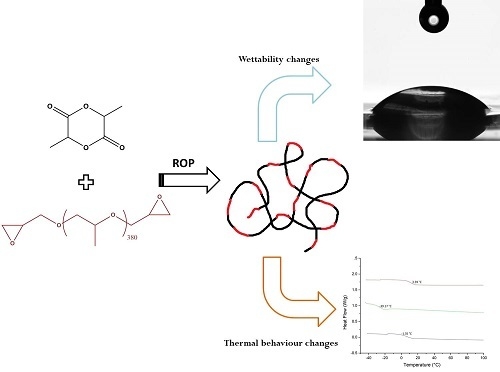
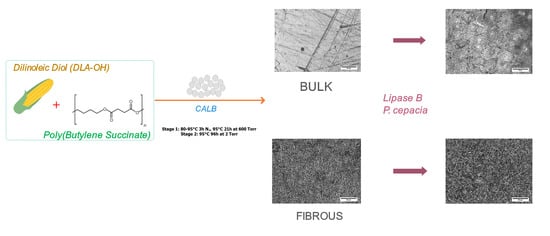
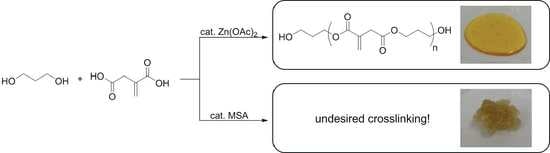
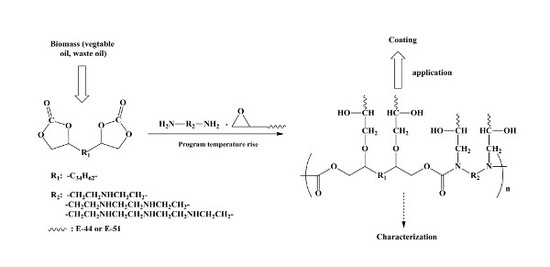
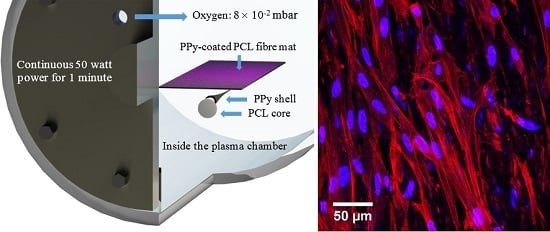
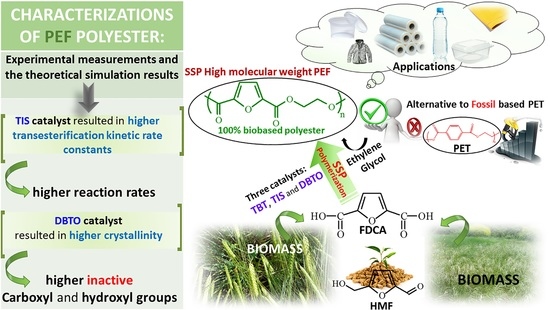
Polyesters
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Chemistry".
Viewed by 21656Editors
Interests: manufacturing; polymer analysis; thermal characterization; biopolyesters; biodegradation; film processing; nanoparticle functionalization; manufacturing of composites; thermosetting resins
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: aliphatic polyesters; blends; compatibilization; advanced characterization; functional additives; unsaturated polyester resins; composites
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: polymer processing; biobased and biodegradable polymers; wood plastic composites; mechanical and thermal characterization; biodegradation; green composites; advanced characterization; functional additives
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: food packaging; biobased and/or biodegradable polymers; nanocomposites; active materials; waste valorization; mechanical recycling; compostability.
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: high-performance polymers; nanoparticle additives for plastic formulations; biodegradation of polymers; polymer composites; biopolyesters; advanced manufacturing; composites
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
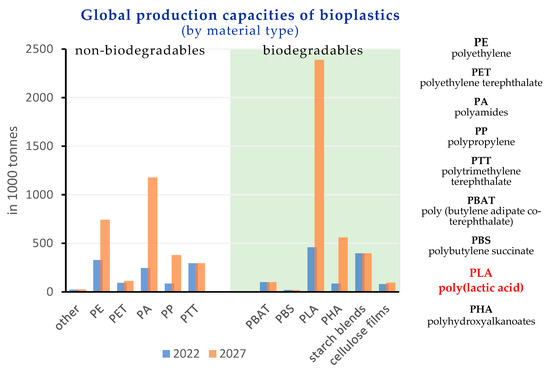
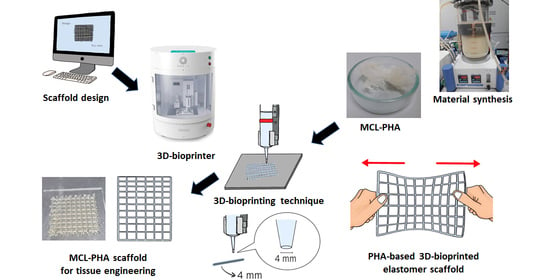
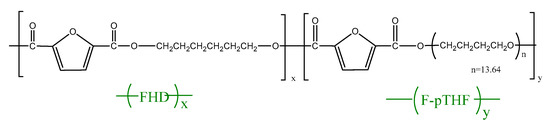
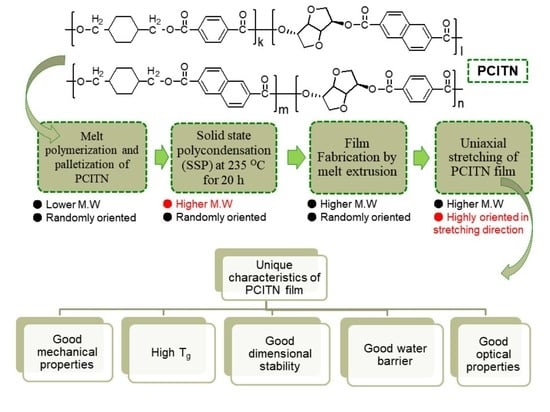
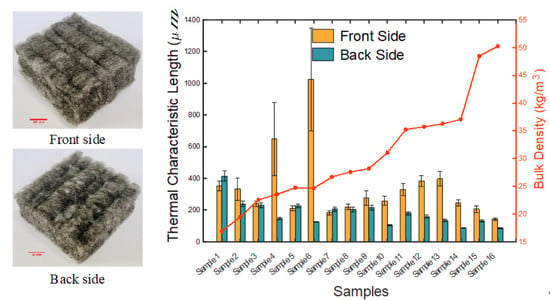
Recent decades have seen a remarkable growth in the use of polyesters. Polyester-type polymers include both thermoplastic and thermosetting materials, which offer a broad range of applications in a wide range of sectors. With regard to thermoplastic polyesters, aromatic polyesters such as poly(ethylene terephthalate)-PET or poly(butylene terephthalate)-PBT are well known and used in technical applications. Recently, with the increasing concern of our society about the environment, a great interest in aliphatic polyesters such as poly(lactide)-PLA, bacterial polyesters or poly(hydroxyalkanoates)-PHAs and others, has been detected. On the other hand, unsaturated polyester (UP) resins are widely used as matrices in high-performance composite materials. Recent trends in polyester-based thermosetting include the development of totally or partially biobased polyester resins for technical applications. This collection covers all topics related to the science and technology of polyesters, including synthesis, copolymerization, characterization, final applications, life cycle assessment, manufacturing techniques, and industrial blends, among other topics. Research on polyesters in the form of films, parts, fibers, nanofibers, and reinforcements is considered in this topic collection with the main aim of sharing a collection of cutting-edge technology research related to thermoplastic and thermosetting polyesters.
Prof. Dr. Octavio Ángel Fenollar Gimeno
Prof. Dr. Rafael Antonio Balart Gimeno
Dr. Luís Quiles Carrillo
Dr. Marina Patricia Arrieta Dillon
Dr. Franco Dominici
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- aromatic polyesters
- aliphatic polyesters
- synthesis
- copolymerization
- additives
- nanoparticles
- manufacturing
- composites
- functionalization
- blends
- characterization
- technical applications
- fibers
- films
- biodegradable polyesters
- bacterial polyesters
- chemical structure
- thermoplastic polyesters
- thermosetting polyesters
Related Special Issues
- Biodegradable and Biobased Polyesters in Polymers (25 articles - displayed below)
- Advances in Manufacturing and Characterization of Functional Polyesters in Polymers (14 articles - displayed below)
- Polyester-Based Materials in Polymers (9 articles - displayed below)