Journal Description
Phycology
Phycology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on phycology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
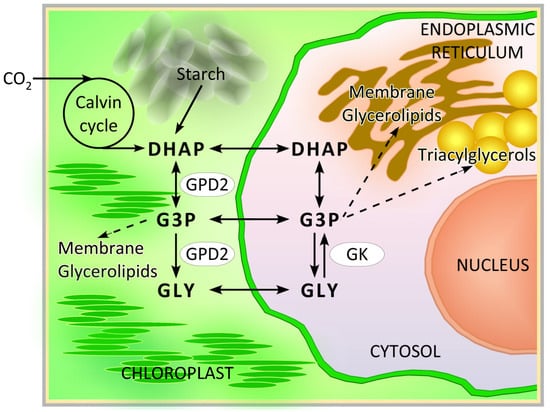
Post-Translational Regulation of a Bidomain Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Catalyzing Glycerol Synthesis under Salinity Stress in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Phycology 2024, 4(2), 213-234; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020012 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Core chlorophytes possess glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (GPDs) with an unusual bidomain structure, consisting of a glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase (GPP) domain fused to canonical GPD domains. These plastid-localized enzymes have been implicated in stress responses, being required for the synthesis of glycerol under high salinity and
[...] Read more.
Core chlorophytes possess glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (GPDs) with an unusual bidomain structure, consisting of a glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase (GPP) domain fused to canonical GPD domains. These plastid-localized enzymes have been implicated in stress responses, being required for the synthesis of glycerol under high salinity and triacylglycerols under nutrient deprivation. However, their regulation under varying environmental conditions is poorly understood. C. reinhardtii transgenic strains expressing constitutively bidomain GPD2 did not accumulate glycerol or triacylglycerols in the absence of any environmental stress. Although the glycerol contents of both wild type and transgenic strains increased significantly upon exposure to high salinity, cycloheximide, an inhibitor of cytoplasmic protein synthesis, abolished this response in the wild type. In contrast, GPD2 transgenic strains were still capable of glycerol accumulation when cultured in medium containing cycloheximide and NaCl. Thus, the pre-existing GPD2 protein appears to become activated for glycerol synthesis upon salt stress. Interestingly, staurosporine, a non-specific inhibitor of protein kinases, prevented this post-translational GPD2 protein activation. Structural modeling analyses suggested that substantial conformational rearrangements, possibly triggered by high salinity, may characterize an active GPD2 GPP domain. Understanding this mechanism(s) may provide insights into the rapid acclimation responses of microalgae to osmotic/salinity stress.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Global Chemical Characterization of Sargassum spp. Seaweeds from Different Locations on Caribbean Islands: A Screening of Organic Compounds and Heavy Metals Contents
by
Jérôme Bauta, Elliot Calbrix, Sophie Capblancq, Christine Cecutti, Jérôme Peydecastaing, Christine Delgado Raynaud, Antoine Rouilly, Valérie Simon, Guadalupe Vaca-Medina, Virginie Vandenbossche, Emeline Vedrenne and Pascale De Caro
Phycology 2024, 4(2), 190-212; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020011 - 13 Apr 2024
Abstract
Large-scale strandings of Sargassum spp. seaweeds occur annually on the beaches of the Caribbean islands and cause major environmental, health, and economic problems. In order to support an approach of valorisation of algae, an exhaustive characterisation of the composition of these seaweeds has
[...] Read more.
Large-scale strandings of Sargassum spp. seaweeds occur annually on the beaches of the Caribbean islands and cause major environmental, health, and economic problems. In order to support an approach of valorisation of algae, an exhaustive characterisation of the composition of these seaweeds has been performed by analysing the contents in alginates, structural carbohydrates (fucans and glucans), minerals, proteins, lipids, mannitol, polyphenols, and heavy metals. Nine batches were collected at different harvesting sites over the years 2021 and 2022, to estimate the spatial and temporal variation in Sargassum composition. A batch of floats was harvested and analysed to estimate the differences in composition between floats and whole algae. Samples collected during the same year (floats or entire plant, freshly collected or stored) showed no significant differences in composition. However, slight differences were observed between batches collected in the two years. Some samples showed significant amounts of heavy metals, especially arsenic. A detailed structural carbohydrates analysis was carried out and discussed with literature data. As the nitrogen content of algae is an interesting parameter for food or agronomic uses, protein analysis enabled us to calculate a new nitrogen–protein conversion factor, specific to these algae species.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sargassum Golden Tides, a Global Problem)
►▼
Show Figures
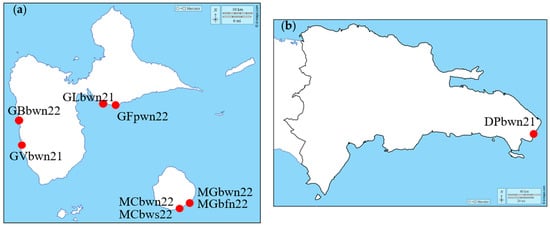
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea
by
Elena Bișinicu, Laura Boicenco, Elena Pantea, Florin Timofte, Luminița Lazăr and Oana Vlas
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 168-189; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010010 - 21 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In order to analyze how environmental factors affect planktonic organisms along the Romanian Black Sea coast, this study created semi-quantitative models of the causal relationships between phytoplankton, zooplankton, and physicochemical parameters by utilizing user-friendly modeling tools. Eleven years of time-series data (March–September 2008–2018)
[...] Read more.
In order to analyze how environmental factors affect planktonic organisms along the Romanian Black Sea coast, this study created semi-quantitative models of the causal relationships between phytoplankton, zooplankton, and physicochemical parameters by utilizing user-friendly modeling tools. Eleven years of time-series data (March–September 2008–2018) were used to investigate the relationships between phytoplankton, zooplankton, and environmental factors (such as temperature, salinity, and nutrients). Variables such as marine reporting units and phytoplankton species and classes were used to identify developmental patterns, utilizing the Mental Modeler platform to consider interactions between the physicochemical parameters and phytoplankton, phytoplankton and zooplankton, and zooplankton and physicochemical parameters. Although the increase in the overall number of elements and linkages was uncertain in waters with variable salinity compared to marine ones, the semi-quantitative models created for the three marine reporting units along the Romanian Black Sea coast were comparable in terms of complexity. Across the typical and examined types of phytoplankton proliferation (normal, abundant, and blooms), the number of components and connections in the case of phytoplankton blooms substantially decreased as species- and growth-promoting variables increased.
Full article
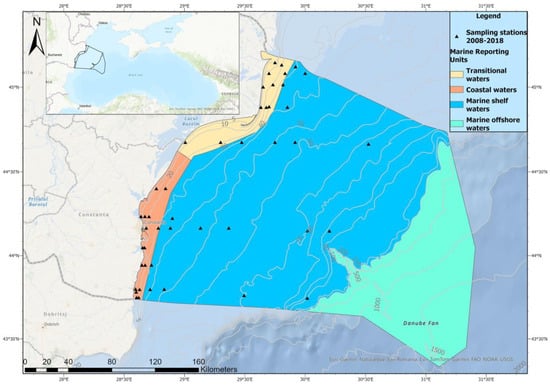
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Is Africa Ready to Use Phycoremediation to Treat Domestic Wastewater as an Alternative Natural Base Solution? A Case Study
by
Paul J. Oberholster, Yolandi Schoeman and Anna-Maria Botha
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 153-167; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010009 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review outlines the potential of phycoremediation as a natural, cost-effective solution for domestic wastewater treatment in Africa, particularly focusing on its application in less densely populated and rural areas. The urgency of improving sanitation access, a key objective in both the Millennium
[...] Read more.
This review outlines the potential of phycoremediation as a natural, cost-effective solution for domestic wastewater treatment in Africa, particularly focusing on its application in less densely populated and rural areas. The urgency of improving sanitation access, a key objective in both the Millennium Development Goals (2000–2015) and the Sustainable Development Goals (2015–2030), is underscored by the fact that half of Africa’s population suffers from diseases linked to inadequate water and sanitation facilities. South Africa, a focal point of this study, faces significant challenges in wastewater management. These include the limited capacity of wastewater treatment plants to handle the burgeoning wastewater volumes due to population growth, unregulated discharges causing fluctuating pollution levels, and high operational costs leading to improper sludge disposal and odor issues. Compounding these problems are frequent power outages, financial constraints impacting wastewater treatment plant operations and maintenance across Africa, and a lack of skilled personnel to manage these facilities.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pelagic Sargassum as a Potential Vector for Microplastics into Coastal Ecosystems
by
Dalila Aldana Arana, Tania P. Gil Cortés, Víctor Castillo Escalante and Rosa E. Rodríguez-Martínez
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 139-152; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010008 - 23 Feb 2024
Abstract
Macroalgal blooms are increasing globally, with those linked to pelagic Sargassum affecting over 30 nations since 2011. As Sargassum mats traverse the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, they entrap and transport plastic to coastal areas, intensifying pollution in diverse ecosystems. This research
[...] Read more.
Macroalgal blooms are increasing globally, with those linked to pelagic Sargassum affecting over 30 nations since 2011. As Sargassum mats traverse the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, they entrap and transport plastic to coastal areas, intensifying pollution in diverse ecosystems. This research assessed microplastics (MPs) within Sargassum fluitans III collected from the northern Mexican Caribbean coast (March 2021 to January 2022). The study employed a hydrogen peroxide protocol for macroalgae pretreatment to optimize MP extraction. All samples analyzed contained MPs at monthly mean concentrations that ranged from 3.5 to 15.3 MPs g−1 DW, with fibers constituting ≥90%. Fiber colors, mainly transparent, blue, and black, exhibited diverse sizes and wear stages. The study underscores the pervasive and consistent presence of MPs in pelagic Sargassum reaching the Mexican Caribbean. Considering the documented Sargassum influxes to this coast in recent years (2789–11,297 tons km−1 yr−1), potential annual MP influxes range from 0.1 × 109 to 17.3 × 109 km−1 yr−1. Efficiently removing beach-cast Sargassum and directing it to landfills could serve as a viable strategy for the simultaneous removal of attached MPs from the ocean and coastal waters, offering a promising mitigation strategy to combat plastic pollution in the examined marine environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sargassum Golden Tides, a Global Problem)
►▼
Show Figures
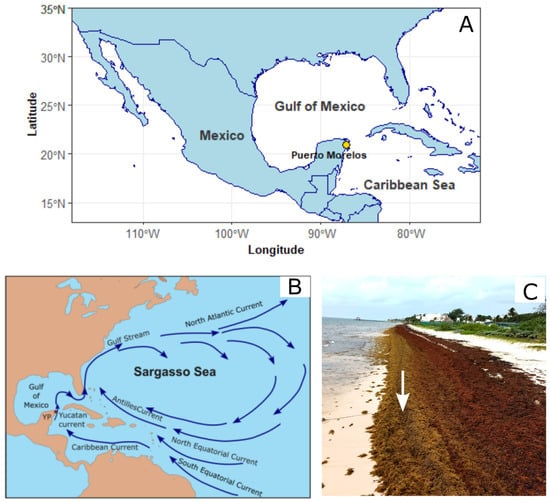
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Reciprocal Effects of Metal Mixtures on Phytoplankton
by
Ammara Nawaz, Pavlína Eliška Šotek and Marianna Molnárová
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 117-138; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010007 - 06 Feb 2024
Abstract
Several types of contaminants are anthropogenically introduced into natural aquatic ecosystems and interact with other chemicals and/or with living organisms. Although metal toxicity alone has been relatively well studied, the toxic metal ion effects in the mixture have been thoroughly studied only during
[...] Read more.
Several types of contaminants are anthropogenically introduced into natural aquatic ecosystems and interact with other chemicals and/or with living organisms. Although metal toxicity alone has been relatively well studied, the toxic metal ion effects in the mixture have been thoroughly studied only during the last decades. This review focuses on the published reciprocal effects of different metals on different species of algae, together with describing their toxic effects on studied parameters. Phytoplankton as a bioindicator can help to estimate the reciprocal metal risk factor. Many methodologies have been developed and explored, such as the biotic ligand model (BLM), concentration addition (CA), independent action (IA), sensitivity distribution of EC50 species sensitivity distribution (SSD curves), and others, to study reciprocal metal toxicity and provide promising results, which are briefly mentioned too. From our review, we can commonly conclude the following: Zn acted antagonistically with most heavy metals (Al, Cu, Cd, and Ni). The Cu interaction with Cd, Fe, and Pb was mostly antagonistic. Cd showed synergistic behaviour with Hg, Cu, Zn, and Pb and antagonistic behaviour with Co and Fe in many cases. Methods and techniques need to be developed and optimised to determine reciprocal metal toxicity so that the ecotoxicological predictions made by using phytoplankton can be more accurate and related to real-time toxic metals risks to the aquatic ecosystem. This is the main objective of ecotoxicological tests for risk assessment. Understanding how metals enter algal cells and organelles can help to solve this challenge and was one of the main parts of the review.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Helicoid Morphology of Arthrospira platensis NIES-39 Confers Temperature Compensation in the Longitudinal Movement Velocity of Its Trichomes
by
Hideaki Shiraishi, Mari Sasase and Ayano Sakaida Nakashima
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 104-116; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010006 - 03 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The velocity of the gliding movement of filamentous cyanobacteria on a solid surface usually has a strong temperature dependency, and the higher the temperature, the faster the speed. Former studies on this phenomenon were conducted using filamentous cyanobacteria with straight morphology. We examined
[...] Read more.
The velocity of the gliding movement of filamentous cyanobacteria on a solid surface usually has a strong temperature dependency, and the higher the temperature, the faster the speed. Former studies on this phenomenon were conducted using filamentous cyanobacteria with straight morphology. We examined the velocity of the gliding movement of Arthrospira platensis NIES-39 along its longitudinal axis to see if the same was true for this cyanobacterium with helicoid trichomes. Experimental results showed little temperature dependency in the velocity in a wide temperature range in this cyanobacterium. However, when we examined the velocity using mutants with straight trichomes, their velocity was strongly affected by temperature, like other formerly analyzed filamentous cyanobacteria. This result indicates that the helicoid morphology of A. platensis trichomes confers temperature compensation to their migration velocity, enabling them to keep a relatively constant velocity under various temperatures. Migration of wild-type trichomes is considerably suppressed compared to the straight-trichome mutants on solid media. The temperature compensation in the locomotion of this organism appears to be established as part of such a suppression. It was also found that the velocity of this cyanobacterium depended on the trichome length when they were atypically short (<250 µm); the shorter the trichomes, the slower the gliding movement tended to be. This result indicates that the coordinated action of a high number of cells constituting the trichome is required for efficient gliding movement.
Full article
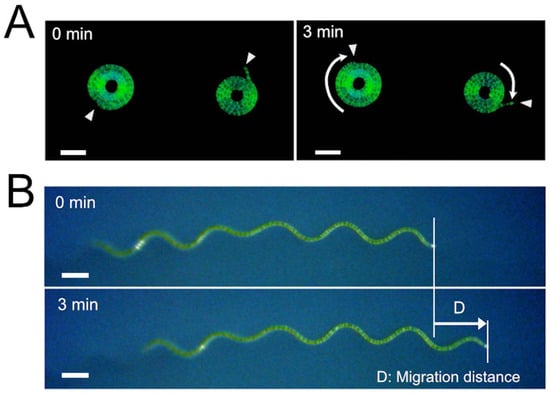
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Cell Rupture Techniques for the Extraction of Proteins from the Microalgae Tetradesmus obliquus
by
César Augusto Sodré da Silva, Karen Vanessa Marimón Sibaja, Sabrina de Ramos Cizilio, José Roberto Miranda Júnior, Rejane de Castro Santana, Marcio Arêdes Martins, Maurício de Oliveira Leite, Eduardo Basílio de Oliveira and Jane Sélia dos Reis Coimbra
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 87-103; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010005 - 30 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The high protein content of several microalgal species makes them attractive and unconventional candidates for use in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Due to the robust cell walls of microalgae, cell rupture is necessary to improve the extraction of intracellular proteins. Thus, choosing
[...] Read more.
The high protein content of several microalgal species makes them attractive and unconventional candidates for use in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Due to the robust cell walls of microalgae, cell rupture is necessary to improve the extraction of intracellular proteins. Thus, choosing a suitable cell-breaking treatment before protein extraction is a vital downstream processing step. Additionally, it is necessary to use an effective technique for monitoring and measuring the impact of rupture treatments on microalgal cell walls. In our study, Tetradesmus obliquus cells were disrupted using three different mechanical rupture methods: high-pressure homogenization (HPH), ultrasound (US), and ball milling (BM). The ruptured biomass cells were counted, and soluble proteins were extracted and quantified. The cell-counting technique did not detect any differences between intact and damaged cells after BM treatment because the dye (erythrosine B) did not permeate the microalgal biomass accurately. The US treatment promoted the highest yield of total protein extraction (19.95%), while the highest yields in the HPH and BM treatments were 15.68% and 14.11%, respectively. Since the cell breakage method affects protein extraction from microalgal biomass, protein release can be used as a central indicator of the degree of cell disruption.
Full article
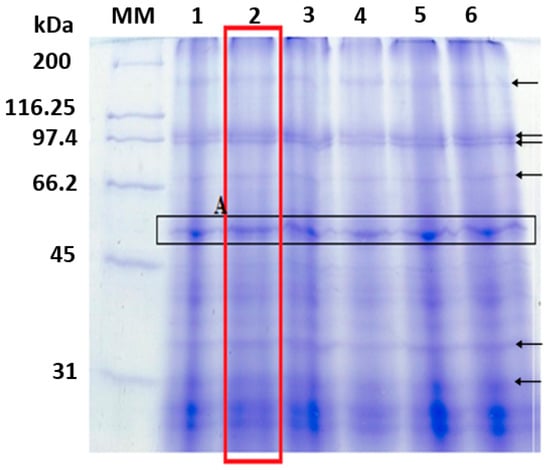
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
DNA Barcode-Assisted Inventory of the Marine Macroalgae from the Azores, Including New Records
by
Daniela Gabriel, William E. Schmidt, Joana Micael, Mónica Moura and Suzanne Fredericq
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 65-86; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010004 - 19 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Up to the present study, only 8.5% of the 522 macroalgal species reported at the Azores have sequences deposited in GenBank and BOLD public repositories. The sequences of four genetic markers (cox1, rbcL, UPA, tufA) were obtained for recently
[...] Read more.
Up to the present study, only 8.5% of the 522 macroalgal species reported at the Azores have sequences deposited in GenBank and BOLD public repositories. The sequences of four genetic markers (cox1, rbcL, UPA, tufA) were obtained for recently collected samples from two Azorean islands. DNA barcode-assisted identification was conducted on newly generated and unpublished sequences from public repositories. A literature review of recently published studies, including the molecular identifications of Azorean macroalgae, was also performed. The results confirm the occurrence of 51 species (including subspecific ranks) and provide four new records, namely, three cryptogenic species (Olokunia boudouresquei, Padina gymnospora, and Ulva lacinulata) and one introduced species (Ulva australis). This study contributes 23 DNA barcodes generated for the first time to the Azores, which now has 10.5% of its marine flora represented in public repositories. Additionally, UPA sequences were generated for the first time for the five taxa.
Full article
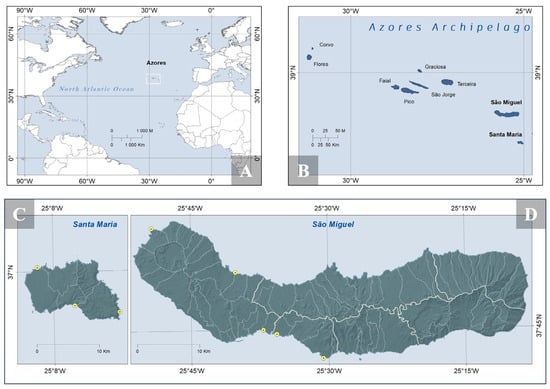
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accessing the Efficacy of Sargassum-Based Aqueous Phase Products Derived from Hydrothermal Carbonisation and Hydrothermal Liquefaction on Plant Growth
by
James Smith, Amy Pilsbury, Vinod Kumar, Eleni E. Karamerou, Christopher J. Chuck, Leopoldo Herrera-Rodriguez, Julio V. Suarez and Michael J. Allen
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 53-64; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010003 - 18 Jan 2024
Abstract
Mass Sargassum inundations have created opportunities for readily available biomass to be used as a crop enrichment application. However, the heavy metal contents of Sargassum pose serious concerns for crop administration and subsequent human consumption. Hydrothermal processing can break the feedstock components, allowing
[...] Read more.
Mass Sargassum inundations have created opportunities for readily available biomass to be used as a crop enrichment application. However, the heavy metal contents of Sargassum pose serious concerns for crop administration and subsequent human consumption. Hydrothermal processing can break the feedstock components, allowing heavy metals to be partitioned, through the utilisation of high temperatures and pressures. As a result, seemingly nutrient-rich phases can be produced. Elemental analyses showed that Sargassum-derived fractions contain important macro- and micronutrients for plants, particularly ammonium, orthophosphate, and potassium, making them potential nutrient sources for plant growth. To date, no research has investigated the plant growth potential of hydrothermally processed Sargassum products from a bioavailability or biotoxicity perspective. We seek to determine if the aqueous phase products derived following Sargassum processing by hydrothermal carbonisation and liquefaction are toxic to higher plants, and if they can support plant growth. Aqueous phase products in ≥1% concentrations inhibit root growth and lateral root formation in Arabidopsis plants, likely from the presence of inhibitory compounds. However, aqueous phase products in ≤0.1% concentrations paired with an established nutrient mix may provide improved leaf and root growth. Both HTC and HTL were capable of eliciting improved foliage growth, while only HTC induced improved root growth. Conclusively, aqueous phase products lack nutrient potency to allow high dilutions for fertiliser application on their own and may contain inhibitory compounds that deter plant growth at high concentrations. However, they might have a purpose as an additive extract. The recovery of important elements needed for plant growth draws a promising path for future applications of hydrothermal processing with different feedstocks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sargassum Golden Tides, a Global Problem)
►▼
Show Figures
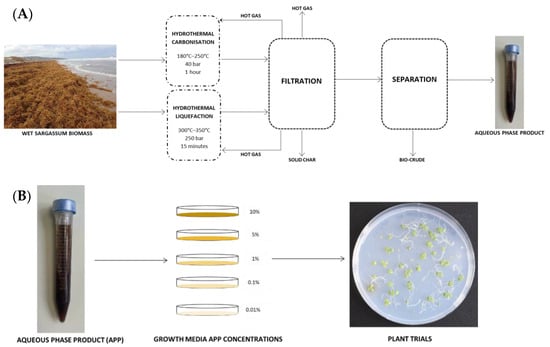
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Production of the Macroalgae Ulva lactuca Integrated with the Shrimp Penaeus vannamei in a Biofloc System: Effect of Total Suspended Solids and Nutrient Concentrations
by
Andrezza Carvalho, Ítalo Braga, Florencia Chaar, Alessandro Pereira Cardozo, José María Monserrat, Juan Rafael Buitrago Ramírez, Wilson Wasielesky, Jr. and Luís H. Poersch
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 37-52; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010002 - 31 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study focused on evaluating the effect of different concentrations of nutrients and total suspended solids on the removal rate of nutrients and biocompounds from the macroalgae U. lactuca in an integrated system with the shrimp Penaeus vannamei in biofloc. The experiment lasted
[...] Read more.
This study focused on evaluating the effect of different concentrations of nutrients and total suspended solids on the removal rate of nutrients and biocompounds from the macroalgae U. lactuca in an integrated system with the shrimp Penaeus vannamei in biofloc. The experiment lasted 45 days and included five treatments with three replicates each, with percentages of 0 (control), 25, 50, 75, and 100% biofloc inoculum (73.3 ± 5.7 and 325.0 ± 21.2 mg L−1 initial nitrate and solids, respectively, in the 100% inoculum), from a shrimp farm, resulting in different concentrations of solids and nutrients. The macroalgae were introduced into 280 L tanks at a density of 0.88 kg m−2, along with 200 shrimp m−3. The algae were separated by a floating structure. Water quality parameters were measured, and the nutrient removal rate was evaluated. The treatment with 75% inoculum showed a removal rate of 55.0 ± 4.0 and 31.0 ± 10.0% of nitrate and phosphate, respectively. There was no difference in macroalgae growth between the treatments; however, macroalgae grown in 75% inoculum had higher protein, chlorophyll-a, and lower ash values compared with the control. The use of macroalgae in integrated production with shrimp under the conditions of the treatment with 75% biofloc inoculum proved to be viable and sustainable.
Full article
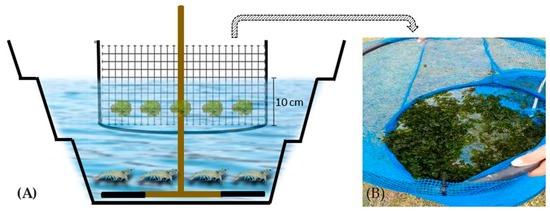
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Phytohormones and Pheromones in the Phycology Literature: Benchmarking of Data-Set and Developing Critical Tools of Biotechnological Implications for Commercial Aquaculture Industry
by
Sachin G. Rathod, Satej Bhushan and Vaibhav A. Mantri
Phycology 2024, 4(1), 1-36; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010001 - 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Plant hormones and pheromones are natural compounds involved in the growth, development, and reproductive processes. There is a plethora of studies on hormones and pheromones in terrestrial plants, but such investigations are few in the phycological literature. There are striking similarities between the
[...] Read more.
Plant hormones and pheromones are natural compounds involved in the growth, development, and reproductive processes. There is a plethora of studies on hormones and pheromones in terrestrial plants, but such investigations are few in the phycological literature. There are striking similarities between the chemical diversity, biosynthetic processes, roles, and actions of hormones and pheromones in both higher angiospermic plants and algae. However, there are substantial knowledge gaps in understanding the genes responsible for hormone biosynthesis and regulation in algae. Efforts have focused on identifying the genes and proteins involved in these processes, shedding light on lateral gene transfer and evolutionary outcomes. This comprehensive review contributes to benchmarking data and essential biotechnological tools, particularly for the aquaculture industry where seaweed is economically crucial. Advanced techniques in plant hormones and pheromones can revolutionize commercial aquaculture by using synthetic analogs to enhance growth, yield, and reproductive control, thereby addressing seasonal limitations and enabling sustainable seedling production. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive review that focuses on biosynthetic pathways and modes of action (of five plant hormones and five pheromones), roles (of 11 hormones and 29 pheromones), and extraction protocols (of four hormones and six pheromones) reported in the phycological domain.
Full article
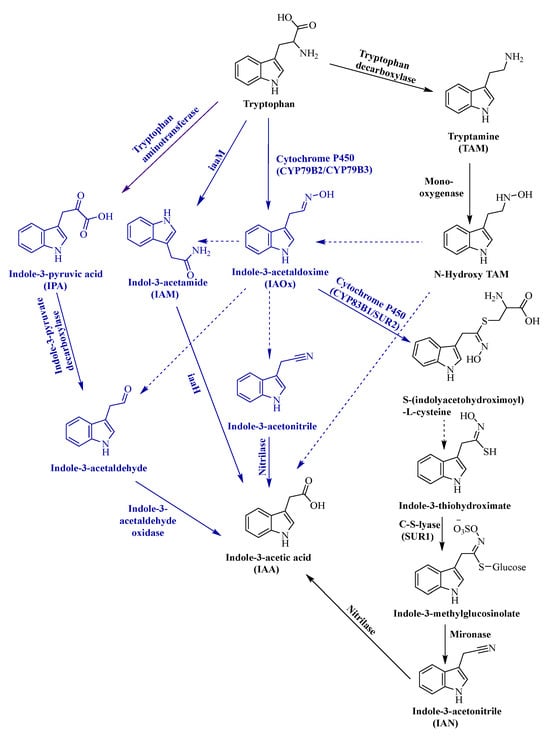
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preliminary Examinations of Phenotypical Changes in Land-Based Long-Term Tumble Culture of Palmaria palmata
by
Stefan Sebök, Martina Strittmatter, Claire M. M. Gachon and Dieter Hanelt
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 503-519; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040034 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Within the last decade, the red alga P. palmata gained increasing interest as a food additive in Europe. Traditionally, P. palmata is harvested from wild stocks, but higher biomass demands request a shift towards industrial cultivation of this species. Using a land-based tumble
[...] Read more.
Within the last decade, the red alga P. palmata gained increasing interest as a food additive in Europe. Traditionally, P. palmata is harvested from wild stocks, but higher biomass demands request a shift towards industrial cultivation of this species. Using a land-based tumble culture approach, we have successfully grown P. palmata via vegetative propagation over a 2-year period. One year after the initial setup, phenotypic changes represented in the formation of randomly shaped, mostly circular galls and homogeneous greenish–white spots with significantly reduced photosynthetic activity were observed on the algal thalli. With progressing time, galls increased into large flat or sunken structures, whereas the tissue in the center of the greenish–white spots weakened. In later stages, the weakened tissue is disrupted, forming holes in the thallus. In this study, we present observations, microscopy analysis, PAM results, and biotechnological approaches to describe a possible infection of P. palmata. Test results showed that light quantity might be the most important factor for the propagation behavior of the infection, whereas the pH level might be secondary, and the nutrient level and biomass density might be of minor relevance. Similarly, changes in light quality could also influence the occurrence of pathological changes in P. palmata.
Full article
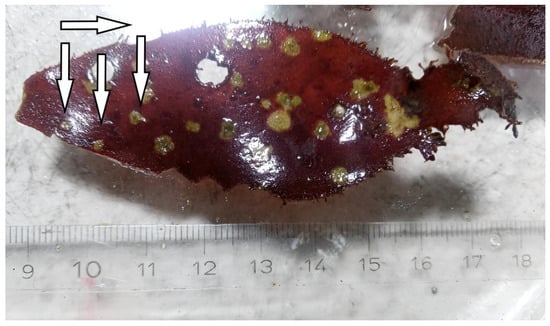
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploration of Microalgae-Activated Sludge Growth Performance in Lab-Scale Photobioreactors under Outdoor Environmental Conditions for Wastewater Biotreatment
by
Abraham O. James, Abayomi O. Bankole, Caroline M. E. Pompei, Gustavo A. S. A. Dantas, Graziele Ruas and Gustavo H. R. Silva
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 484-502; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040033 - 17 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Increasing the volume of untreated and inadequately treated municipal wastewater undermines the circular economy potential of wastewater resources, particularly in low-income regions. This present study focused on and evaluated the performance of native microalgae-activated sludge (MAS) growth for tertiary treatment of anaerobically digested
[...] Read more.
Increasing the volume of untreated and inadequately treated municipal wastewater undermines the circular economy potential of wastewater resources, particularly in low-income regions. This present study focused on and evaluated the performance of native microalgae-activated sludge (MAS) growth for tertiary treatment of anaerobically digested wastewater from an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) in an outdoor lab-scale photobioreactor (2.2 L). Three conditions with distinct MAS inoculum concentrations alongside three controls were operated in batch mode for 5 days hydraulic retention time (HRT) at 11.5:12.5 photo-hours. The MAS inoculum concentration influenced the treatment outcome. The best performance was observed when the MAS concentration was 0.10/0.20 g L−1, and the cell density was 1.60 × 107 cells mL−1, total biomass productivity of 0.10 g TSS L−1 d−1, total phosphorus uptake of 85.1%, and total nitrogen uptake of 66.1%. Logarithmic removal (Log-Re) of bacterial pathogens (water quality indicators) showed Log-Re 3.4 for total coliforms (1.37 × 102 CFU 100 mL−1) and 4.7 for Escherichia coli (0.00 × 100 CFU 100 mL−1). The results revealed optimum remediation performance and nutrient recovery potential with appropriate inoculum concentration, in admiration to advancing the science of circular economy.
Full article
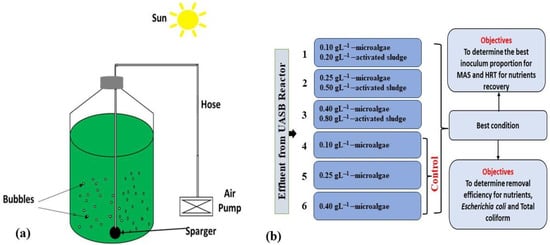
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cultivation of Cyanobacteria on Sustainable Dried Luffa cylindrica
by
Jonas Kollmen, Judith Stiefelmaier, Ramtin Mofrad and Dorina Strieth
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 472-483; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040032 - 08 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cyanobacteria are promising organisms for the sustainable production of various biotechnological interesting products. Due to their energy production via photosynthesis, the cultivation of cyanobacteria expands the CO2 cycle. Most cyanobacteria form biofilms on surfaces in their natural environment by surrounding the cells
[...] Read more.
Cyanobacteria are promising organisms for the sustainable production of various biotechnological interesting products. Due to their energy production via photosynthesis, the cultivation of cyanobacteria expands the CO2 cycle. Most cyanobacteria form biofilms on surfaces in their natural environment by surrounding the cells with a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) that hold the cells together. These special growth properties need special reactors for cultivation. By immobilizing cyanobacteria on carriers, systems currently established in industry could also be used for biofilm formers. Various artificial carriers for immobilized growth of cyanobacteria and microalgae have already been described in the literature. However, the use of waste materials or natural biodegradable carriers would be more sustainable and is, therefore, the focus of this study. Dried Luffa cylindrica, zeolite, and corn stalks were investigated for their use as carriers for cyanobacteria. L. cylindrica was shown to be an excellent natural carrier for (i) Anabaena cylindrica, (ii) Nostoc muscorum 1453-12a, and (iii) Nostoc muscorum 1453-12b. Higher or at least similar growth rates were achieved when cyanobacteria were cultivated with L. cylindrica compared to submerged cultivation. Additionally, the production of EPS and C-phycocyanin was increased at least 1.4 fold in all strains by culturing on L. cylindrica. The improved growth could be explained on the one hand by the high surface area of L. cylindrica and its properties, and, on the other hand, by the release of growth-promoting nutrients from L. cylindrica to the medium.
Full article
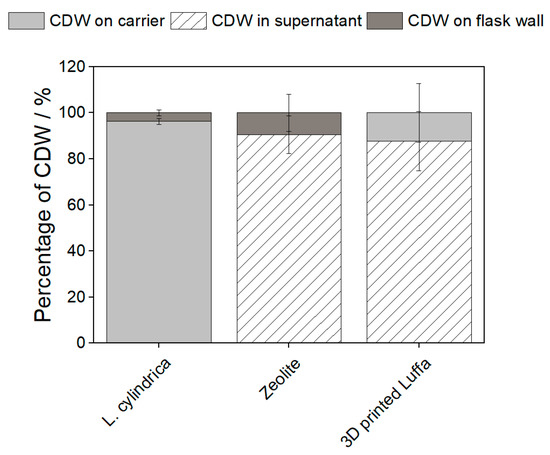
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Harnessing Symbiotic Mixotrophic Microalgal–Bacterial Biofilms for N and P Elimination
by
Mahshid Sedghi, John Fagan, Soheil Sedghi, Frithjof C. Küpper and Ricardo Amils
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 459-471; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040031 - 09 Oct 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Symbiotic microalgal–bacterial biofilms can be very attractive for potato wastewater treatment. Microalgae remove nitrogen and phosphorus and simultaneously produce the oxygen that is required for the aerobic, heterotrophic degradation of organic pollutants. In this study, symbiotic microalgal–bacterial biofilms were grown in flow cells
[...] Read more.
Symbiotic microalgal–bacterial biofilms can be very attractive for potato wastewater treatment. Microalgae remove nitrogen and phosphorus and simultaneously produce the oxygen that is required for the aerobic, heterotrophic degradation of organic pollutants. In this study, symbiotic microalgal–bacterial biofilms were grown in flow cells with ammonium and phosphate, and with acetate as a simulated biodegradable organic pollutant. The symbiotic biofilms removed acetate without an external oxygen or carbon dioxide supply, but ammonium and phosphate could not be completely removed. The biofilm was shown to have a considerable heterotrophic denitrification capacity. The symbiotic relationship between microalgae and aerobic heterotrophs was proven by subsequently removing light and acetate. In both cases, this resulted in the cessation of the symbiosis and in increasing effluent concentrations of both acetate and the nutrients ammonium and phosphate.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrative Literature Analysis of Holopelagic Sargassum (Sargasso) in the Western Atlantic (2011–2022): Status, Trends, and Gaps
by
Julianna T. Arita, Lowell Andrew R. Iporac, Natalie K. Bally, Mutue T. Fujii and Ligia Collado-Vides
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 447-458; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040030 - 09 Oct 2023
Abstract
Since 2011, the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico coasts have been receiving massive influxes of holopelagic sargasso algae composed of Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans. This phenomenon has been causing several negative local impacts, such as ecological disturbances and socioeconomic and health
[...] Read more.
Since 2011, the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico coasts have been receiving massive influxes of holopelagic sargasso algae composed of Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans. This phenomenon has been causing several negative local impacts, such as ecological disturbances and socioeconomic and health concerns of communities in impacted areas. This work aimed to assess the status of scientific knowledge related to pelagic sargasso, including trends, emphases, and gaps. A literature review was conducted on publications and reports from 2011 to 2022, of which 251 articles were collected based on an inclusion–exclusion criteria. Aspects of each article were quantified, including location, description of sargasso, the type of study, and research theme. A region-wide research emphasis on ecology, remote sensing, and valorization was observed. Areas first affected by the inundations composed a higher percentage of sargasso studies than other locations, and the distribution of studies varied among subregions. Topics requiring further investigation include sargasso’s growth and mortality rates and drivers, taxonomic and physiologic differences among morphotypes, and real-time forecasting resolution at local scales both on and offshore. This research emphasized efforts from the scientific community on research and mitigation initiatives.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sargassum Golden Tides, a Global Problem)
►▼
Show Figures
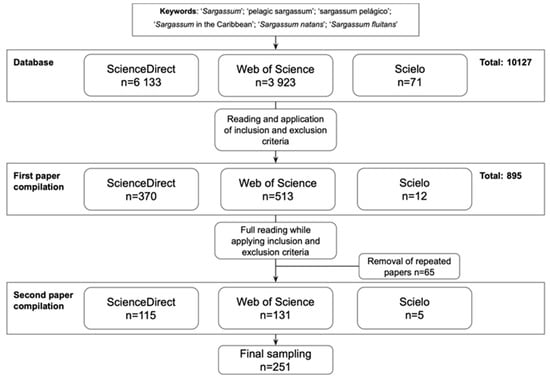
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Green Microalgae: A New Potential Drug for Thrombolytic Therapy?
by
Yanara Alessandra Santana Moura, Ariadne Tennyle Vieira De Souza, Páblo Eugênio Da Costa e Silva, Marllyn Marques Da Silva, Ana Lúcia Figueiredo Porto and Raquel Pedrosa Bezerra
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 436-446; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040029 - 05 Oct 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Thrombosis is characterized by the pathological formation of fibrin clots within a blood vessel, leading to the obstruction of blood flow. Fibrinolytic enzymes from microorganisms have been shown to be more efficient and safer in dissolving clots. Then, this study aimed to evaluate
[...] Read more.
Thrombosis is characterized by the pathological formation of fibrin clots within a blood vessel, leading to the obstruction of blood flow. Fibrinolytic enzymes from microorganisms have been shown to be more efficient and safer in dissolving clots. Then, this study aimed to evaluate the cell growth and fibrinolytic enzyme production of Tetradesmus obliquus under different cultivation conditions. T. obliquus grew under autotrophic and mixotrophic conditions using different concentrations of corn steep liquor (0.25 ≤ CSL ≤ 4.00%). The cells were concentrated and lysed via two different methods (sonication or homogenization) to trigger the release of the enzyme. It was precipitated via acetone or ammonium sulfate additions and purified using ion exchange chromatography. The highest biomass productivity (Px = 130 ± 12.8 mg∙L−1day−1), specific growth rate (µmax = 0.17 ± 0.00 day−1), and fibrinolytic activity (391 ± 40.0 U∙mg−1) was achieved on a mixotrophic cultivation at a 0.25% CSL concentration. The results showed that the homogenizing method had better performance in the release of enzyme, and the precipitation with acetone obtained the highest fibrinolytic activity (567 ± 49.3 U∙mg−1). The purified enzyme showed a specific activity of 1221 ± 31 U∙mg−1 and a molecular mass of 97 kDa. So, the fibrinolytic enzyme from T. obliquus had higher activity when compared to the other fibrinolytic enzymes, being a potential source for the development of therapeutic agents in thrombosis treatment. Additional studies are needed to investigate the biochemical properties and biological profile of this enzyme.
Full article
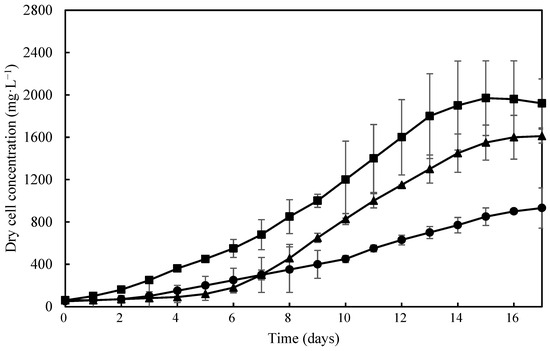
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Revealing Interactions between Temperature and Salinity and Their Effects on the Growth of Freshwater Diatoms by Empirical Modelling
by
T. T. Yen Le, Alina Becker, Jana Kleinschmidt, Ntambwe Albert Serge Mayombo, Luan Farias, Sára Beszteri and Bánk Beszteri
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 413-435; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040028 - 22 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Salinization and warming are of increasing concern for freshwater ecosystems. Interactive effects of stressors are often studied in bifactorial, two-level experimental setups. The shape of environmental reaction norms and the position of the “control” conditions along them, however, can influence the sign and
[...] Read more.
Salinization and warming are of increasing concern for freshwater ecosystems. Interactive effects of stressors are often studied in bifactorial, two-level experimental setups. The shape of environmental reaction norms and the position of the “control” conditions along them, however, can influence the sign and magnitude of individual responses as well as interactive effects. We empirically model binary-stressor effects in the form of three-dimensional reaction norm surfaces. We monitored the growth of clonal cultures of six freshwater diatoms, Cymbella cf. incurvata, Nitzschia linearis, Cyclotella meneghiniana, Melosira varians, Ulnaria acus, and Navicula gregaria at various temperature (up to 28 °C) and salinity (until the growth ceased) shock treatments. Fitting a broad range of models and comparing them using the Akaike information criterion revealed a large heterogeneity of effects. A bell-shaped curve was often observed in the response of the diatoms to temperature changes, while their growth tended to decrease with increasing electrical conductivity. C. meneghiniana was more tolerant to temperature, whilst C. incurvata and C. meneghiniana were the most sensitive to salinity changes. Empirical modelling revealed interactive effects of temperature and salinity on the slope and the breadth of response curves. Contrasting types of interactions indicates uncertainties in the estimation by empirical modelling.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
Temporal Changes in the Composition of Beached Holopelagic Sargassum spp. along the Northwestern Coast of Cuba
by
Eduardo Gabriel Torres-Conde, Brigitta I. van Tussenbroek, Rosa E. Rodríguez-Martínez and Beatriz Martínez-Daranas
Phycology 2023, 3(4), 405-412; https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040027 - 22 Sep 2023
Abstract
Since 2011, the distribution, abundance, and composition of holopelagic Sargassum spp. (sargasso) have changed by the emergence of the Great Atlantic Sargasso Belt (GASB) in the northern tropical Atlantic. We expected that the north of the Cuban coast would receive sargasso from both
[...] Read more.
Since 2011, the distribution, abundance, and composition of holopelagic Sargassum spp. (sargasso) have changed by the emergence of the Great Atlantic Sargasso Belt (GASB) in the northern tropical Atlantic. We expected that the north of the Cuban coast would receive sargasso from both the original Sargasso Sea and the GASB. We systematically monitored six beaches on the NW coast of Cuba to assess changes in sargasso composition from June 2019 to June 2021. During landing months, mean Sargasso wet biomass was at 1.54 kg/m2 (SE: 0.7), which was considerably lower than the sargasso on the Atlantic coasts directly impacted by GASB. Eleven out of 13 landings occurred in the autumn-winter seasons 2019–2020 and 2020–2021, with a dominance of S. natans I (accounting for 41–63% of total biomass), followed by S. fluitans III (25–36%) and S. natans VIII (12–31%). This composition is similar to those observed on the Sargasso Sea. During this season, dominant winds (≥14 km/h) came from northern (N), eastern (E), and east-northeastern (ENE) directions. In May and August 2020 (spring-summer season), S. fluitans III dominated (52–56%), followed by S. natans VIII (33–43%) and S. natans I (5–12%). This composition is similar to those observed on GASB-impacted Atlantic coasts in the spring-summer seasons (April to September). During this season, dominant winds (≥20 km/h) came from eastern (E) and east-northeastern (ENE) directions. Thus, the NW Cuba’s morphotype composition suggests that landings have different origin sources depending on season and specific meteorological and oceanographic conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sargassum Golden Tides, a Global Problem)
►▼
Show Figures
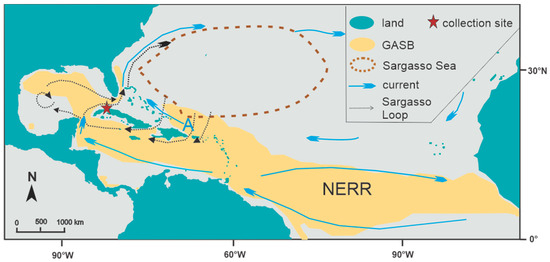
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Diversity, Life, Microorganisms, Plants, Water, Phycology, Toxins
Advances and New Insights into Diversity of Cyanobacteria
Topic Editors: Esther Berrendero Gómez, M. Ángeles Muñoz Martín, Elvira Perona UrízarDeadline: 31 October 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Phycology
Sargassum Golden Tides, a Global Problem
Collection Editors: Anne Desrochers, John Milledge