Journal Description
Pharmacoepidemiology
Pharmacoepidemiology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on high-quality epidemiological, clinical research across the fields of clinical pharmacology and epidemiology, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 34.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Pharmacoepidemiology is a companion journal of Pharmaceuticals.
Latest Articles
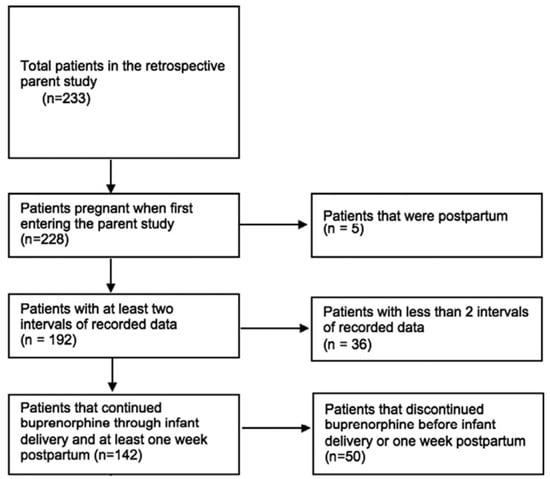
Association of Receipt of Opioid Prescription for Acute Post-Delivery Pain Management with Buprenorphine Discontinuation among Postpartum People with Opioid Use Disorder
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(2), 198-207; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3020012 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Buprenorphine is a safe and effective medication to treat opioid use disorder (OUD) in pregnant patients and is intended to be continued throughout pregnancy, delivery, and at least the one-year postpartum period. However, delivery often involves the need for acute pain management with
[...] Read more.
Buprenorphine is a safe and effective medication to treat opioid use disorder (OUD) in pregnant patients and is intended to be continued throughout pregnancy, delivery, and at least the one-year postpartum period. However, delivery often involves the need for acute pain management with opioid medications, such as after a cesarean section. For patients receiving buprenorphine, the provision of prescription opioids may negatively impact OUD treatment outcomes; however, not optimally managing acute pain may also impede OUD treatment benefit. Evidence is needed to disentangle the impacts of opioid prescription provision and methods of pain management in the immediate postpartum period on OUD treatment trajectories, ultimately to inform clinical guidelines tailored to the unique needs of pregnant and postpartum people receiving buprenorphine. Accordingly, this study took an initial step towards this goal to conduct a secondary analysis of a retrospective cohort of pregnant patients taking buprenorphine for OUD at the time of delivery (n = 142) to determine whether receipt of an opioid prescription at birth hospitalization discharge was associated with the time of buprenorphine discontinuation within the 12 months following delivery. Among the sample, 26% (n = 37) were prescribed an opioid at the time of birth hospitalization discharge. The number of weeks post-delivery until buprenorphine discontinuation occurred was shorter amongst patients who were prescribed an opioid (median 11 weeks) compared to patients who were not prescribed an opioid (median 39 weeks; p < 0.001 by Mann–Whitney U test). However, a Cox regression model reported that receipt of an opioid prescription following delivery did not significantly increase the hazard ratio for buprenorphine discontinuation. In other words, OUD patients not prescribed an opioid at birth hospitalization discharge continued their buprenorphine for a longer median duration after delivery compared to their counterparts who received prescription opioids; yet, this finding did not reach statistical significance when taking into account additional clinical variables. The findings indicate how further research is warranted to inform evidence-based post-delivery pain practices for postpartum OUD treatment patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Affordability of Paediatric Oral Anti-Infective Medicines in a Selected District, Sri Lanka
by
Malith Kumarasinghe and Manuj C. Weerasinghe
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 183-197; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010011 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this cross-sectional descriptive study conducted in the Ratnapura district, Sri Lanka, we assessed the affordability of oral pediatric anti-infective medicines (OPAIMs). Using a modified WHO/HAI medicinal price methodology, we examined the availability, median price ratios (MPRs), mean percentage difference, and affordability of
[...] Read more.
In this cross-sectional descriptive study conducted in the Ratnapura district, Sri Lanka, we assessed the affordability of oral pediatric anti-infective medicines (OPAIMs). Using a modified WHO/HAI medicinal price methodology, we examined the availability, median price ratios (MPRs), mean percentage difference, and affordability of the standard treatment of the originator brand (OB) and lowest-priced generic (LPG) OPAIMs in 30 private and 2 state-owned pharmacies. The study revealed disparities in availability, with only 50% of private pharmacies offering all 11 medicinal drugs in their generic form. The MPRs of OPAIMs for OB and LPG varied, with three drugs exceeding the financially acceptable MPR of 2 (albendazole, amoxicillin, and erythromycin). The standard treatment with LPGs costs between 0.17 and 0.85 and between 0.06 and 0.28 days’ wages for the lowest daily salary of the private sector and unskilled public employees, respectively. We identified erythromycin and albendazole as having less than 50% availability in their generic form in private pharmacies. To address these findings, we recommend frequent pricing revisions based on exchange rates and associated costs, coupled with the establishment of a transparent scientific criterion to subsidize essential medicines deemed “unaffordable.” Failure to implement such measures amidst economic crises may adversely impact financial access to essential medications.
Full article
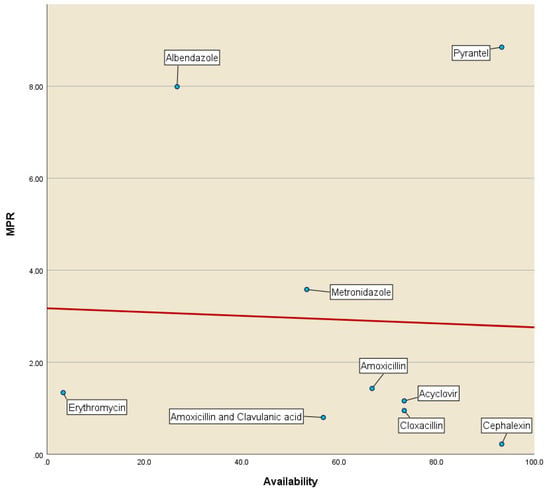
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pioneering Arterial Hypertension Phenotyping on Nationally Aggregated Electronic Health Records
by
Jing Wei Neo, Qihuang Xie, Pei San Ang, Hui Xing Tan, Belinda Foo, Yen Ling Koon, Amelia Ng, Siew Har Tan, Desmond Teo, Mun Yee Tham, Aaron Yap, Nicholas Ng, Celine Wei Ping Loke, Li Fung Peck, Huilin Huang and Sreemanee Raaj Dorajoo
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 169-182; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010010 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Hypertension is frequently studied in epidemiological studies that have been conducted using retrospective observational data, either as an outcome or a variable. However, there are few validation studies investigating the accuracy of hypertension phenotyping algorithms in aggregated electronic health record (EHR) data.
[...] Read more.
Background: Hypertension is frequently studied in epidemiological studies that have been conducted using retrospective observational data, either as an outcome or a variable. However, there are few validation studies investigating the accuracy of hypertension phenotyping algorithms in aggregated electronic health record (EHR) data. Methods: Utilizing a centralized repository of inpatient EHR data from Singapore for the period of 2019–2020, a new algorithm that incorporates both diagnostic codes and medication details (Diag+Med) was devised. This algorithm was intended to supplement and improve the diagnostic code-only model (Diag-Only) for the classification of hypertension. We computed various metrics (sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV)) to assess the algorithm’s effectiveness in identifying hypertension on 2813 chart-reviewed records. This pool was composed of two patient cohorts: a random sampling of all inpatient admissions (Random Cohort) and a targeted group with atrial fibrillation diagnoses (AF Cohort). Results: The Diag+Med algorithm was more sensitive at detecting hypertension patients in both cohorts compared to the Diag-Only algorithm (83.8 and 87.6% vs. 68.2 and 66.5% in the Random and AF Cohorts, respectively). These improvements in sensitivity came at minimal costs in terms of PPV reductions (88.2 and 90.3% vs. 91.4 and 94.2%, respectively). Conclusion: The combined use of diagnosis codes and specific antihypertension medication exposure patterns facilitates a more accurate capture of patients with hypertension in a database of aggregated EHRs from diverse healthcare institutions in Singapore. The results presented here allow for the bias correction of risk estimates derived from observational studies involving hypertension.
Full article
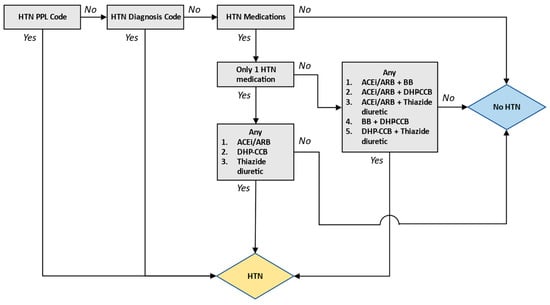
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond Statins: Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
by
Teimur Kayani, Bachar Ahmad, Rachel S. Chang, Frank Qian, Melis Sahinoz, Muhammad Waqar Rehan, Antonio Giaimo, Erica S. Spatz and Jiun-Ruey Hu
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 117-168; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010009 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Although statins have served as the cornerstone for pharmacological lowering of lipid levels in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk reduction, many patients are unable to achieve target doses of statin medication due to side effects or target levels of cholesterol reduction on statin
[...] Read more.
Although statins have served as the cornerstone for pharmacological lowering of lipid levels in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk reduction, many patients are unable to achieve target doses of statin medication due to side effects or target levels of cholesterol reduction on statin monotherapy. The landscape of lipid-lowering strategies has expanded in recent years, with the emergence of therapies that make use of small interfering RNA (siRNA) and antisense oligonucleotides, in addition to traditional small-molecule agents. Non-statin therapies that have shown promising results in randomized controlled trials include adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase inhibitors, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9)-inhibiting antibodies and siRNA, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and lipoprotein(a) gene-inhibiting siRNA and ASOs, in addition to older therapies such as ezetimibe. In contrast, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors have shown less promising results in randomized trials. The purpose of this narrative review is to summarize the evidence for these medications, with a focus on phase III randomized trials.
Full article
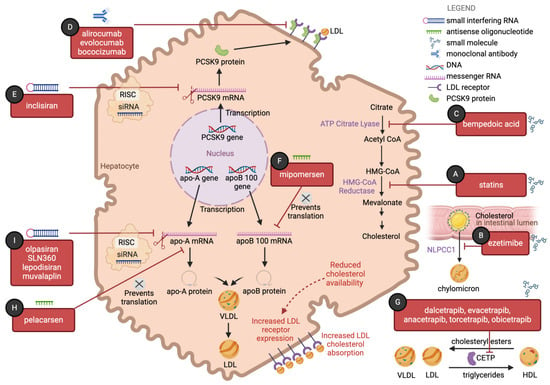
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Treatment Patterns, Effectiveness, and Safety of Originator Insulin Glargine versus Insulin Glargine-yfgn within the Veterans Health Administration
by
Samantha Walczuk, Francesca E. Cunningham, Xinhua Zhao, Diane Dong, Peter A. Glassman, Donald R. Miller, Deborah Khachikian, Anthony Au, Cedric Salone, Kelly Bryan, Qoua Her and Sherrie L. Aspinall
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 103-116; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010008 - 01 Mar 2024
Abstract
We described insulin glargine (originator) and insulin glargine-yfgn (biosimilar) treatment patterns, assessed effectiveness and safety outcomes, and identified reasons for switching back to the originator product from the biosimilar. This retrospective study included 328,463 Veterans 18 years of age and older who received
[...] Read more.
We described insulin glargine (originator) and insulin glargine-yfgn (biosimilar) treatment patterns, assessed effectiveness and safety outcomes, and identified reasons for switching back to the originator product from the biosimilar. This retrospective study included 328,463 Veterans 18 years of age and older who received one or more outpatient prescriptions for insulin glargine and/or insulin glargine-yfgn between 1 June 2021 and 31 December 2022. Patients were assigned to subgroups based on the initial prescription during the study period, prevalent versus incident use for originator insulin glargine, and prior versus no prior use of the originator before the biosimilar (i.e., prevalent originator non-switcher (n = 189,734), originator switch to biosimilar (n = 81,010), incident originator non-switcher (n = 49,401), and incident biosimilar (n = 8318)). There were no differences in the outcome of mean HbA1c (7.9% for all subgroups). There were also no differences in the unadjusted rates of hospitalization and/or emergency room visits for hyper- and hypoglycemia between the prevalent originator non-switcher and originator switched to biosimilar subgroups (p = 0.09 and 0.38, respectively) or the incident originator non-switcher and incident biosimilar subgroups (p = 0.054 and 0.61, respectively). Finally, none of the HbA1c or hyperglycemia outcomes adjusted for baseline characteristics were statistically different. Adjusted analyses for rates of hospitalization and/or emergency room visits for hypoglycemia could not be performed due to the low number of events. Overall, patients who received insulin glargine-yfgn had similar effectiveness and safety outcomes as patients who received the originator.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers of Pharmacoepidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures
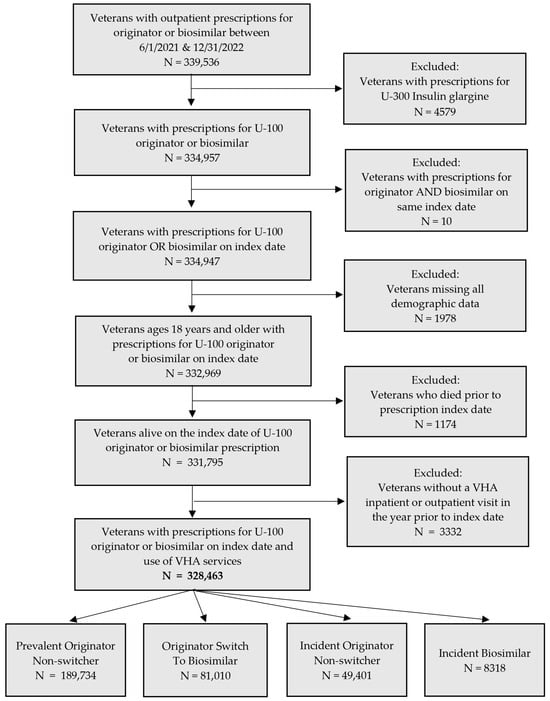
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Opioid Prescribing for Noncancer Patients—Issues of Drug Therapy Safety: Results from a German Study Based on Routine Data
by
Veronika Lappe, Daniel Grandt, Ursula Marschall and Ingrid Schubert
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 94-102; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010007 - 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
Opioids are highly effective drugs but need close monitoring to avoid harm to patients. The aim of this study was to analyze how guideline recommendations are met for (i) the avoidance of the concomitant use of anxiolytics, hypnotics, or sedatives; (ii) the prescribing
[...] Read more.
Opioids are highly effective drugs but need close monitoring to avoid harm to patients. The aim of this study was to analyze how guideline recommendations are met for (i) the avoidance of the concomitant use of anxiolytics, hypnotics, or sedatives; (ii) the prescribing of laxatives in long-term opioid treatment; (iii) the co-prescribing of drugs to control the emetic effect of opioids; (iv) pretreatment with non-opioids; and (v) screening for depression when initiating opioids. The results are based on a routine data analysis of a large German health insurance fund. Different study populations of noncancer patients (18+ years old) treated with opioids were analyzed: 10.4% of the opioid recipients in 2021 received at least one concomitant prescription with anxiolytics, hypnotics, or sedatives; 69.3% of those with long-term opioid treatment received at least one laxative prescription. Of those with first-time opioid prescriptions, 4.8% received an antiemetic drug; 47.3% of those with a newly initiated opioid therapy received a non-opioid prescription within three months before the start of the opioid therapy; and 22.0% of patients with incident opioid prescription had at least one documentation of a depression diagnosis within three months of the first prescription. There is an urgent need to improve opioid prescribing to avoid risky combinations and adverse effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacoepidemiology and Addiction)
►▼
Show Figures
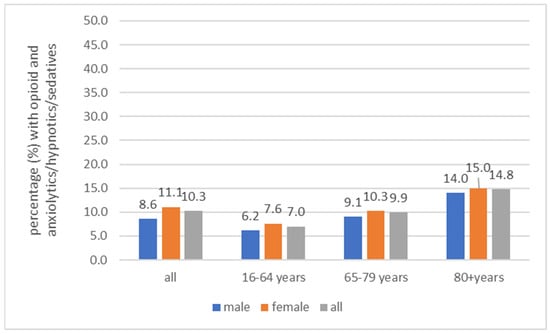
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Crises in Antimicrobial Stewardship: Misuse of Clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori Therapy
by
David Y. Graham
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 82-93; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010006 - 20 Feb 2024
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori is a class I carcinogen that infects more than 100 million individuals in the United States. Antimicrobial therapy for H. pylori has typically been prescribed empirically rather than based on susceptibility testing. Until recently, therapeutic recommendations have generally ignored the principles
[...] Read more.
Helicobacter pylori is a class I carcinogen that infects more than 100 million individuals in the United States. Antimicrobial therapy for H. pylori has typically been prescribed empirically rather than based on susceptibility testing. Until recently, therapeutic recommendations have generally ignored the principles of antibiotic stewardship. A combination of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), amoxicillin, and clarithromycin (triple therapy) remains popular despite increasing clarithromycin resistance and poor cure rates. Concomitant therapy (a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole) is recommended and widely used despite all patients receiving at least one unneeded antibiotic. In 2020, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin triple therapy, which administers unneeded clarithromycin to >90% of patients (i.e., ~6 tons of unneeded clarithromycin/million treatments). In the late 1980s, the infectious disease community functionally transferred responsibility for the management of H. pylori to gastroenterology, which has managed the infection as another common gastrointestinal disease such as constipation. In 2022, both traditional and noninvasive molecular-based susceptibility testing for H. pylori became available in the United States. In order to reduce and prevent antibiotic misuse, the infectious disease community should reclaim responsibility for the management of this important infectious disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers of Pharmacoepidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures
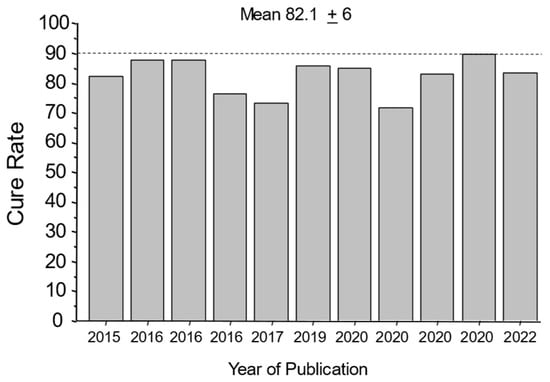
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Remdesivir and the Liver: A Concise Narrative Review of Remdesivir-Associated Hepatotoxicity in Patients Hospitalized Due to COVID-19
by
Alireza FakhriRavari and Mazyar Malakouti
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 69-81; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010005 - 13 Feb 2024
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has infected millions of people, but about 20% of infected individuals do not develop symptoms. COVID-19 is an inflammatory disease that affects a portion of individuals infected with the virus and it is associated with liver injury
[...] Read more.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has infected millions of people, but about 20% of infected individuals do not develop symptoms. COVID-19 is an inflammatory disease that affects a portion of individuals infected with the virus and it is associated with liver injury and other complications, leading to hospitalization, critical illness, and death. Remdesivir is an antiviral agent used for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve the time to recovery, reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation, decrease the need for supplemental oxygen, and decrease the risk of mortality. Remdesivir-associated hepatotoxicity has been observed as increased transaminases more than five times the upper limit of normal in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, but causality has not been proven. It is generally difficult to distinguish between remdesivir-associated hepatotoxicity and COVID-19-induced hepatotoxicity. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the evidence for remdesivir-associated hepatotoxicity. Current evidence suggests that elevated liver enzymes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients are more likely to be due to the infection than remdesivir, and a 5-day course of remdesivir seems to be safe in regard to hepatotoxicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anti-Infectives: Pharmacoepidemiology and Clinical Pharmacology)
►▼
Show Figures
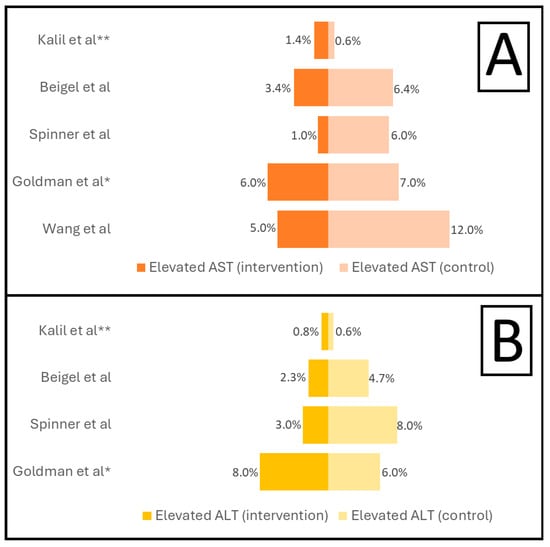
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
“My Addiction Doesn’t Define Me”—Experiences of Stigma among Mothers with Opioid Use Disorder
by
Christine Bakos-Block, Andrea Yatsco, A. Sarah Cohen, Francine Vega and Tiffany Champagne-Langabeer
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 57-68; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010004 - 29 Jan 2024
Abstract
Opioid use in women has increased by 300% since 1999, and opioid use disorder among pregnant women has quadrupled. The stigma of substance use disorder is a significant barrier to treatment, especially among women. The purpose of this study was to explore the
[...] Read more.
Opioid use in women has increased by 300% since 1999, and opioid use disorder among pregnant women has quadrupled. The stigma of substance use disorder is a significant barrier to treatment, especially among women. The purpose of this study was to explore the experiences and perceptions of stigma among mothers and the underlying themes. (1) Background: To understand the stigmatization of women with substance use disorders, we interviewed mothers in recovery from opioid use disorder. (2) Methods: Qualitative methods and descriptive analysis was used to extrapolate themes related to the experienced stigma. (3) Results: A total of 20 mothers in recovery from opioid use disorder were interviewed and three main themes emerged from the data: internal stigma, external stigma, and healing from stigma. (4) Conclusion: The examination of stigma is important in reducing its effect on all individuals with substance use disorders, and it is important to understand gender inequities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacoepidemiology and Addiction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients on Tofacitinib for Alopecia Areata or Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
by
Sarah Choe, Abhinav Birda, Jesse Salas, Olive Anagu and Natasha Mesinkovska
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 51-56; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010003 - 29 Jan 2024
Abstract
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) that is used off-label for the treatment of alopecia areata (AA). Its boxed warning includes an increased risk of serious adverse events (SAEs) based on the results of a safety trial in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients
[...] Read more.
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) that is used off-label for the treatment of alopecia areata (AA). Its boxed warning includes an increased risk of serious adverse events (SAEs) based on the results of a safety trial in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients taking the medication. The purpose of this study was to investigate the differences in patients’ characteristics and SAEs profiles between RA and AA populations taking tofacitinib. The cohorts were constructed using the TrinetX database to identify the patients who were prescribed tofacitinib for RA or AA between October 2012 and October 2023. A total of 22,873 patients were included in this analysis, with 21,080 individuals in the RA cohort and 1793 individuals in the AA cohort. After matching for age, sex, and race, each cohort had a sample size of 1482. Data on the patients’ sex, age, race, comorbidities, concomitant medications, and associated SAEs were collected. The cohorts were compared by calculating the odds ratios and tested for significance associations using Fisher’s Exact Tests. Both the RA and AA cohorts were predominantly female (RA 79%, AA 70%), with mean ages of 61 ± 14 years and 38 ± 19 years (p-value < 0.0001), respectively. Both the groups showed similar racial distributions. The RA cohort had increased rates of hypertension, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and nicotine dependence compared to those of the AA cohort (p-value < 0.0001). With the exception of cyclosporine and azathioprine, the percentage of concomitant medication use was higher in all the categories in the RA cohort than those in the AA cohort (p-value < 0.0001). Higher rates of adverse events were seen in the RA cohort across all the categories, except myocardial infarction, stroke, and lymphomas/hematopoietic malignancies. Our findings show that the SAEs on the boxed warning of tofacitinib should be strongly considered when being used off-label for the treatment of AA. Clinicians must carefully assess the individual patient factors when determining the appropriateness of tofacitinib use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Safety and Effectiveness in the Real World)
Open AccessArticle
Rescue Therapy for Supratherapeutic Concentrations of Calcineurin Inhibitors Using Potent Cytochrome P450 Inducers
by
Seth Duwor, Katharina Enthofer, Christoph Ganter, Prabin Poudel, Anna Svarin and Gerd A. Kullak-Ublick
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 33-50; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010002 - 29 Jan 2024
Abstract
Introduction: Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs), ciclosporin and tacrolimus, are utilized primarily in organ transplantation and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Since patients depend on these drugs over long periods, they face a potential risk of intoxication. This risk increases substantially when patients are overdosed
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs), ciclosporin and tacrolimus, are utilized primarily in organ transplantation and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Since patients depend on these drugs over long periods, they face a potential risk of intoxication. This risk increases substantially when patients are overdosed or inadvertently exposed to cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 inhibitors. Objectives: To analyze the utility of CYP inducers as a plausible treatment modality for acute CNI intoxication using real-world data from the WHO global pharmacovigilance database (VigiBase™) and supporting evidence from published data. Methodology: We explored all individual case safety reports (ICSRs) regarding CNI intoxications registered in VigiBase™. The queries “overdose” or “drug intoxication” were applied against the active ingredients “ciclosporin” and “tacrolimus”. Regarding the utility of CYP inducers, an extensive literature analysis was undertaken. We also report an index clinical case of a 60-year-old liver transplant patient that developed severe tacrolimus intoxication with multiple organ dysfunction at a peak concentration of 33.1 μg/L after a single dose of intravenous fluconazole. Results: Out of 143,710 documented ICSRs reported in VigiBase™ since 1992, 0.26% and 0.02% were registered as CNI overdoses and intoxications, respectively. The main etiological factor for CNI intoxication was the interaction with CYP 3A4 inhibitors (40.0% vs. case reports: 50.0%). The most commonly reported manifestation was acute kidney injury (36.7% vs. case reports: 46.3%). A total of 16.7% of intoxications led to fatal outcomes after drug withdrawal or dose reduction; however, in 43.0% of cases the exact actions undertaken were not reported. In peer-reviewed reports, 34 distinct clinical cases were treated with CYP inducers. Diverse pharmacoenhancement strategies with phenobarbital (5), phenytoin (23) and rifampicin (6) were described with a mean time of achieving the therapeutic target after 2.7 (±0.7), 3.1 (±0.5) and 4.6 (±1.0) days, respectively. In the index case, a therapeutic concentration of 4.9 [4–6 μg/L] was achieved after a 3-day regimen of rifampicin. Conclusion: In addition to general supportive treatment, the administration of phenobarbital, phenytoin, or rifampicin to reverse acute CNI intoxication is a viable treatment modality. The relatively long half-life of phenobarbital coupled with its exclusive renal elimination are potential pitfalls to reckon with. In spite of the favorable pharmacokinetic advantages of rifampicin, phenytoin offers a competitive pharmacodynamic advantage that is indisputable in patients with overt neurotoxicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers of Pharmacoepidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures
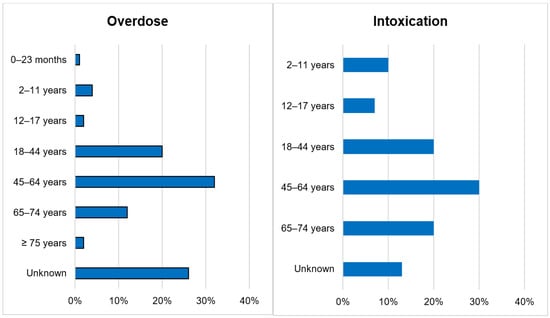
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Direct Oral Anticoagulants’ Consumption and Expenditure in the COVID-19 Pandemic in Russia and Clinical Practice Guidelines for Their Use
by
Elena A. Baybulatova, Mikhail S. Chenkurov, Elina A. Korovyakova, Sergey K. Zyryanov and Liliya Eugenevna Ziganshina
Pharmacoepidemiology 2024, 3(1), 1-32; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma3010001 - 29 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The coronavirus pandemic has led to the creation of clinical guidelines by a large number of professional medical communities. However, the quality and methodology of development of Russian clinical guidelines has been little studied. The continued relevance of studying the use of
[...] Read more.
Background: The coronavirus pandemic has led to the creation of clinical guidelines by a large number of professional medical communities. However, the quality and methodology of development of Russian clinical guidelines has been little studied. The continued relevance of studying the use of DOACs (Direct oral anticoagulants) in patients with COVID-19 was the basis for conducting this study. Aim: The objective of this study was to assess DOAC consumption and expenditure in the Russian Federation during the COVID-19 pandemic and to analyze whether it was supported by the domestic evidence base for the use of DOACs in COVID-19 patients through identifying all publicly available Russian-produced CPGs (Clinical practice guidelines) for the treatment of COVID-19 and assessing their quality as the source of recommendations for the use of oral anticoagulants for the prevention of thrombotic complications in COVID-19 patients. We searched Russian databases for CPGs, published between 2020 and 2023. We identified seven relevant documents that met our inclusion criteria. Three authors analyzed Russian clinical guidelines using an AGREE II questionnaire. We calculated DOAC DDD (defined daily dose) consumption according to Russian clinical guidelines and DDD consumption in patients with COVID-19 for the period 2020–2022. Results: Seven clinical CPGs were analyzed with the AGREE II tool. It was revealed that experts gave the highest scores for the sections on scope and purpose (from 62.98% to 100%), and clarity of presentation (from 96.30% to 100%). The lowest scores were given for the sections on stakeholder involvement (33.33% to 64.81%), rigour of development (from 0% to 49.31%), applicability (from 23.61% to 50%), and editorial independence (from 0% to 50%). When comparing the total score, it was found that two clinical guidelines received the highest scores—ROPNIZ (Livzan), and ROPNIZ (Drapkina). The minimum score was registered with the NIIOZMM (Khripun) clinical guideline. No guideline received a total score of more than 70%. According to clinical recommendations, the consumption of apixaban and rivaroxaban is 15 DDD (30-day course of therapy), or 22.5 DDD (45-day course of therapy). Consumption of apixaban in the Russian Federation in 2020 and 2021 corresponds to the indicators presented in clinical recommendations (in 2020—26.59 DDD per patient with COVID-19; in 2021—15.75 DDD per patient with COVID-19), and in 2022—10.67 DDD, which is below the recommended values. In 2020, consumption of rivaroxaban in the Russian Federation was 26.59 which corresponds to data from clinical recommendations; in 2021, consumption decreased to 7.87 DDD; in 2022 it decreased to 5.48 DDD, which is 2.74 times less than recommended. Conclusions: Analysis of seven clinical recommendations revealed that such sections of clinical recommendations as scope, purpose, and clarity of presentation had the highest degree of assessment in accordance with AGREE II. The lowest scores were given for the sections on stakeholder involvement, rigour of development, applicability, and editorial independence. When comparing the total score, it was found that two clinical guidelines received the highest scores—the Russian Society for the Prevention of Non-communicable Diseases (Livzan), and the Russian Society for the Prevention of Non-communicable Diseases (Drapkina). The minimum score was registered with the Research Institute for Healthcare Organization and Medical Management of Moscow Healthcare Department clinical guideline. No guideline received a total score of more than 70%. During the pandemic, the highest DDD consumption of DOACs was in 2020, which exceeded the DOACs’ recommended DDD by Russian clinical guidelines. DOAC consumption had decreased by 2022. There was a decrease in the consumption of rivaroxaban, with an increase in apixaban’s share in the structure of DOAC consumption during the coronavirus pandemic. Obtained data indicate that in 2021 the apixaban consumption in the Russian Federation corresponded to the recommended DDD in the national guidelines, which indicates the most correct use of apixaban according to Russian GPGs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Helpful, Unnecessary, or Harmful: A Systematic Review of the Effects of Prescription Drug Monitoring Program Use on Opioid Prescriptions
by
Nina Z. Y. Smith, J. Douglas Thornton, Susan H. Fenton, Debora Simmons and Tiffany Champagne-Langabeer
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 350-365; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040030 - 15 Dec 2023
Abstract
Prescription drug misuse is a global problem, especially in the United States (US). Clinician involvement is necessary in this crisis, and prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) are a recommended tool for the prevention, recognition, and management of prescription opioid misuse. However, because of
[...] Read more.
Prescription drug misuse is a global problem, especially in the United States (US). Clinician involvement is necessary in this crisis, and prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) are a recommended tool for the prevention, recognition, and management of prescription opioid misuse. However, because of the plethora of differences between different PDMPs, research on their effects is mixed. Yet, despite varied evidence, policy on PDMP use is trending stricter and more comprehensive. We aimed to identify patterns in the research to inform clinicians and policy. Through a systematic review of four literature databases (CINAHL, Cochrane Database, Embase, and Medline/OVID), we found 56 experimental and quasi-experimental studies published between 2016 and 2023 evaluating PDMP effects on clinician behavior. To address study heterogeneity, we categorized studies by type of intervention and study outcome. The review suggests that more comprehensive PDMP legislation is associated with decreases in the number of opioid prescriptions overall and the number of risky prescriptions prescribed or dispensed. However, this review shows that much is still unknown, encourages improvements to PDMPs and policies, and suggests further research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacoepidemiology and Addiction)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Literature Review of Safety Event Reporting in Observational Studies: Challenges Extrapolating across Comparable Products
by
Heather A. Ward, Bao-Anh Nguyen-Khoa and Robert Massouh
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 338-349; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040029 - 05 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (PAXLOVIDTM, Pfizer) is an anti-infective inhibiting CYP3A4 indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults at increased risk of severe COVID-19. As a newly approved product, PAXLOVID has limited safety information regarding rare events and serious adverse events (SAEs). This
[...] Read more.
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (PAXLOVIDTM, Pfizer) is an anti-infective inhibiting CYP3A4 indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults at increased risk of severe COVID-19. As a newly approved product, PAXLOVID has limited safety information regarding rare events and serious adverse events (SAEs). This review describes the characterization of the real-world safety profile of products with similar pharmacological properties to PAXLOVID and aims to understand the impact of any drug interaction on the concomitantly prescribed products. A literature search of articles in PubMed published between 2018 and 2023 was conducted to assess the real-world frequency of safety outcomes of interest, specifically those meeting the criteria of serious adverse reaction. The review was restricted to observational, noninterventional studies and included CYP3A4 inhibitors prescribed for short-term treatment of infections in the outpatient setting. Twenty-one articles were included in the review. Most focused on a small, predefined list of safety outcomes and did not provide insight into the broader range of safety outcomes that might occur for the evaluated products with similar pharmacological properties to PAXLOVID or the impact of any interaction on the concomitant product. The findings highlight the challenges in obtaining proxy safety outcomes characteristics via a review of products with comparable pharmacological properties and underscore the need to have large, rapidly accessible data sources that can contribute to the safety profile of newly authorized products in the real world.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Retrospective Review of COVID-19 Medicines Information Queries in a Quaternary Hospital with Unique COVID-19 Border Controls
by
Jeanie Misko and Matthew D. M. Rawlins
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 328-337; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040028 - 10 Nov 2023
Abstract
Background: Medicines information (MI) is a specialist area of pharmacy that provides evidence-based answers to often complex medication queries, utilising resources such as textbooks and databases. With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a need to change the way COVID-19-related queries
[...] Read more.
Background: Medicines information (MI) is a specialist area of pharmacy that provides evidence-based answers to often complex medication queries, utilising resources such as textbooks and databases. With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a need to change the way COVID-19-related queries were answered due to the rapid evolution of information on vaccination, treatment and prevention. Methods: Medicines information queries were retrospectively reviewed utilising the centre’s medicines information database from January 2020 through December 2022 using the COVID-19 keyword to retrieve relevant queries. Information was collected on the enquirer’s role, query category, time taken to complete the query, relevant keywords and references accessed. Keywords and references were analysed further to determine the types of queries asked and which references were helpful. Results: The centre received 214 COVID-19-related queries, predominantly in 2022. Most queries were from pharmacy staff (95.8%) and related to vaccination (n = 95, 44.4%) or treatment (n = 87, 40.7%). Government and specialist organisation websites were used most commonly as reference sources (24.6% and 16.5%, respectively) for their currency with COVID-19-specific resources (such as national guidelines, COVID-19 treatment interaction checkers) and textbooks/databases used less commonly. Conclusions: MI pharmacists have demonstrated their ability to obtain reliable COVID-19-related information, utilising and interpreting information from less traditional sources.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Safety and Effectiveness in the Real World)
Open AccessArticle
Analyzing Black Market Sales of the Second-Line ADHD Medication Atomoxetine
by
Sophie A. Roe, Dayna S. DeSalve and Brian J. Piper
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 320-327; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040027 - 07 Nov 2023
Abstract
Research Question and Objective: While the number of pharmacoepidemiological studies on stimulant-based ADHD medications has expanded rapidly in recent years, likely due to the stimulant shortage, few studies have analyzed non-stimulant ADHD medications from a pharmacoepidemiological perspective. Such research is important because a
[...] Read more.
Research Question and Objective: While the number of pharmacoepidemiological studies on stimulant-based ADHD medications has expanded rapidly in recent years, likely due to the stimulant shortage, few studies have analyzed non-stimulant ADHD medications from a pharmacoepidemiological perspective. Such research is important because a significant number of individuals with ADHD have medical or psychiatric conditions that preclude stimulant use. Furthermore, no studies, to our knowledge, have analyzed atomoxetine exchanges on the black market. In this report, we seek to fill both these gaps in the research by analyzing black market diversions of atomoxetine, a non-stimulant medication for ADHD. As ADHD medication diversion is a growing issue, we also hypothesize the pharmacoepidemiologic contributors to and implications of such diversion. Method: This study analyzed black market atomoxetine purchases entered on the web-based platform StreetRx between January 2015 and July 2019. Data included the generic drug name, dosage, purchase price, date, and location in the United States. The mean price per milligram was determined and a heatmap was generated. Results: The average price per milligram of 113 diverted atomoxetine submissions was USD 1.35 (±USD 2.76 SD) (Median = USD 0.05, Min = USD 0.01, Max = USD 20.00). The states with the most submissions included Michigan (11), Pennsylvania (9), Indiana (8), and Ohio (8). Conclusion: The cost per milligram of atomoxetine on the black market is over 50 times the cost per milligram of the generic prescribed form. Future qualitative studies should investigate reasons why individuals are motivated to purchase atomoxetine, a non-stimulant medication, on the black market (recreational vs. nootropic vs. other clinical uses).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacoepidemiology and Addiction)
►▼
Show Figures
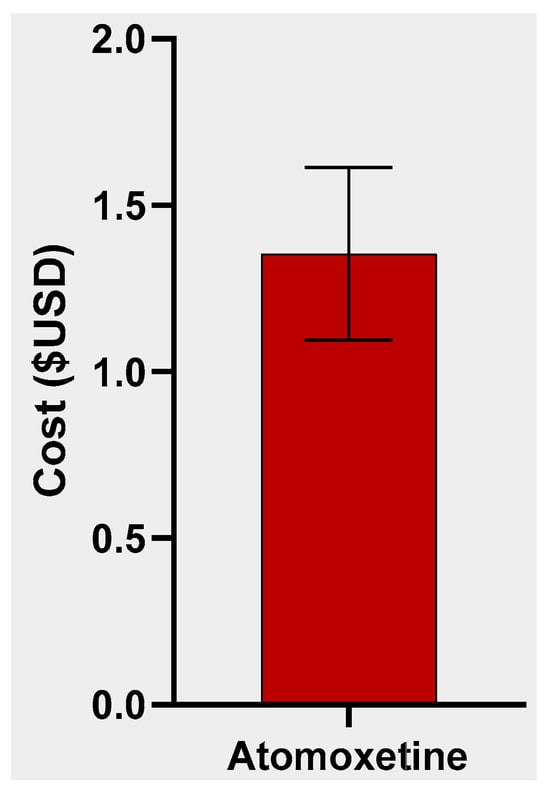
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Blood Pressure Control in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente (DIALECT): The Role of Patient Adherence and Physician’s Follow-Up Action
by
Simone L. Dam, Heleen M. Masselink-Haverkate, Christina M. Gant, Stephan J. L. Bakker, Roos M. Nijboer, Willemien J. Kruik-Kollöffel and Gozewijn D. Laverman
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 307-319; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040026 - 30 Oct 2023
Abstract
We studied the role of adherence to antihypertensive drug therapy (AHT) in blood pressure (BP) control in a type 2 diabetes (T2D) population treated in secondary care in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente-1 (DIALECT-1). In addition, intensification of AHT was assessed. Adherence
[...] Read more.
We studied the role of adherence to antihypertensive drug therapy (AHT) in blood pressure (BP) control in a type 2 diabetes (T2D) population treated in secondary care in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente-1 (DIALECT-1). In addition, intensification of AHT was assessed. Adherence was determined by using the medication possession ratio (MPR), calculated with pharmacy dispensing data for a period of two years following baseline. Adherence was defined as an MPR ≥ 80%. The proportion of adherent patients was compared between patients who had BP-on target (BP-OT) and BP-not on target (BP-NOT). Of the 385 patients included, 56% achieved their BP target. The proportion of adherent patients did not differ between BP-OT and BP-NOT (96% vs. 96%; p = 0.91). Intensification of AHT, including ‘increase in dosage’ and ‘start of a new drug’, was assessed in the two years following baseline. In only 37% of patients with uncontrolled BP during follow-up was AHT intensified. To conclude, adherence to AHT was high and there does not seem to be a relationship between adherence and BP control. There is an opportunity to improve AHT in patients who do not reach their BP target.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Safety and Effectiveness in the Real World)
►▼
Show Figures
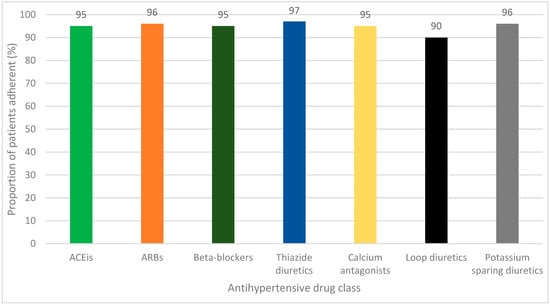
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Impact of Antibiotic De-Escalation on Antibiotic Consumption, Length of Hospitalization, Mortality, and Cost: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Abeer Alanazi, Reem Almuhaya, Mohammad Almohaimeed, Nada Alahmari, Noor Abdulrahim, Marouj Basyouni, Farah Althikrallah, Jumanah Al Badwyi, Abdulrahman Khallaf, Khalid Albalawi, Amal Almalki, Khalid Alsaedi, Fatima Bakarman, Fatimah Alotaibi and Mohammed Kanan
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 289-306; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040025 - 13 Oct 2023
Abstract
Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and pose a significant threat due to adverse drug reactions, increased healthcare costs, and poor patient outcomes. Antibiotic stewardship programs, including antibiotic de-escalation, aim to optimize antibiotic use and to
[...] Read more.
Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and pose a significant threat due to adverse drug reactions, increased healthcare costs, and poor patient outcomes. Antibiotic stewardship programs, including antibiotic de-escalation, aim to optimize antibiotic use and to reduce the development of antibiotic resistance. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to fill the gap by analyzing the current literature on the implications of antibiotic de-escalation in patients on antibiotic use, duration of hospital stay, mortality, and cost; to update clinical practice recommendations for the proper use of antibiotics; and to offer insightful information about the efficacy of antibiotic de-escalation. Based on the PRISMA 2020 recommendations, a comprehensive literature search was conducted using electronic databases and reference lists of identified studies. Eligible studies were published in English, conducted in humans, and evaluated the impact of antibiotic de-escalation on antibiotic consumption, length of hospitalization, mortality, or cost in hospitalized adult patients. Data were extracted using a standardized form, and the quality of included studies was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. The data from 25 studies were pooled and analyzed using the Revman-5 software, and statistical heterogeneity was evaluated using a chi-square test and I2 statistics. Among the total studies, seven studies were conducted in pediatric patients and the remaining studies were conducted in adults. The studies showed a wide range of de-escalation rates, with most studies reporting a rate above 50%. In some studies, de-escalation was associated with a decrease in antimicrobial utilization and mean length of stay, but the impact on overall cost was mixed. Our pooled analysis for mortality reported that a significant difference was observed between the de-escalation group and the non-de-escalation group in a random effect model (RR = 0.67, 95% CI 0.52–0.86, p = 0.001). The results suggest that de-escalation therapy can be applied in different healthcare settings and patient populations. However, the de-escalation rate varied depending on the study population and definition of de-escalation. Despite this variation, the results of this systematic review support the importance of de-escalation as a strategy to optimize antibiotic therapy and to reduce the development of subsequent antibiotic resistance. Further studies are needed to evaluate the impact of de-escalation on patient outcomes and to standardize the definition of de-escalation to allow for better comparison of studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anti-Infectives: Pharmacoepidemiology and Clinical Pharmacology)
►▼
Show Figures
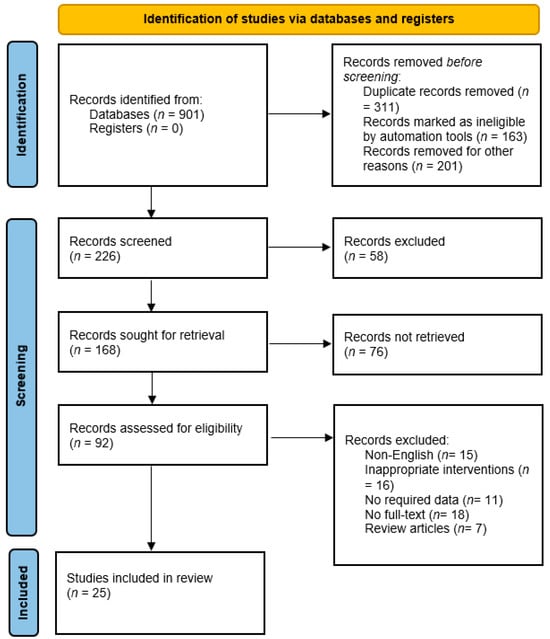
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Detectable Vancomycin Stool Concentrations in Hospitalized Patients with Diarrhea Given Intravenous Vancomycin
by
Taryn A. Eubank, Chenlin Hu, Anne J. Gonzales-Luna and Kevin W. Garey
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(4), 283-288; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2040024 - 28 Sep 2023
Abstract
Vancomycin is not appreciably passaged via the colonic membrane to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in persons with an intact gut epithelium due to its large chemical structure. However; hospitalized patients with diarrhea often have a disrupted GI tract. The aim of this study
[...] Read more.
Vancomycin is not appreciably passaged via the colonic membrane to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in persons with an intact gut epithelium due to its large chemical structure. However; hospitalized patients with diarrhea often have a disrupted GI tract. The aim of this study was to determine the frequency of detectable vancomycin concentrations in the stool of patients with antibiotic-associated diarrhea receiving IV vancomycin. This was a multicenter cohort study of hospitalized patients with stool samples collected for Clostridioides difficile testing. Leftover stool samples were collected from patients who had received at least 3 days of IV vancomycin. Fecal vancomycin was quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography. The study cohort included 33 unique patients, majority female (54.5%) aged 60 years (range 23–84). Eighteen of thirty-three patients (54.5%) tested positive for C. difficile toxins. The average duration of systemic vancomycin administration prior to stool collection was 3.5 (range 2–15) days. Three of 33 (9%) stool samples had a detectable vancomycin concentration (range 1.2–13.2 mcg/mL). These concentrations may promote the development of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus or van mutations in C. difficile, leading to vancomycin resistance. Further studies on implications are warranted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anti-Infectives: Pharmacoepidemiology and Clinical Pharmacology)
Open AccessArticle
Depression Events Associated with Proton-Pump Inhibitors in Postmarketing Drug Surveillance Data
by
Tigran Makunts, Haroutyun Joulfayan, Kenneth Ta and Ruben Abagyan
Pharmacoepidemiology 2023, 2(3), 272-282; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma2030023 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Proton-pump inhibitors, PPIs, are widely prescribed and are available over the counter for prolonged reduction of stomach acid production and related disorders. PPIs irreversibly inhibit the hydrogen/potassium ATPase in gastric parietal cells. Recent retrospective studies have described an association between PPI use and
[...] Read more.
Proton-pump inhibitors, PPIs, are widely prescribed and are available over the counter for prolonged reduction of stomach acid production and related disorders. PPIs irreversibly inhibit the hydrogen/potassium ATPase in gastric parietal cells. Recent retrospective studies have described an association between PPI use and depression. However, there is conflicting evidence that PPI therapy improves depressive symptoms. Considering the widespread use and over-the-counter availability of these drugs, further investigation into depression adverse event was warranted with a larger-scale postmarketing set of reports. Here we analyzed over 125,923 reports from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System consisting of PPI and histamine-2 receptor antagonist monotherapy records and found a statistically significant association between use of PPIs and depression. Additionally, we analyzed each of the six currently marketed PPIs individually and observed the association with the depression adverse reaction for all of them.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Safety and Effectiveness in the Real World)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacoepidemiology
Advance in Cancer Pharmacoepidemiology
Topic Editors: Shih-Chieh Shao, Edward Chia-Cheng LaiDeadline: 20 February 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pharmacoepidemiology
Bridging Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics for Better Healthcare Outcomes
Guest Editor: Hao HuDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Pharmacoepidemiology
Anti-Infectives: Pharmacoepidemiology and Clinical Pharmacology
Guest Editors: Lee Nguyen, Jason YamakiDeadline: 31 July 2024
Special Issue in
Pharmacoepidemiology
Herbal Pharmacoepidemiology: Exploring the Application of Pharmacoepidemiology Principles in Herbal Medicinal Products by Advancing Evidence-Based Medicine
Guest Editor: Christos KontogiorgisDeadline: 30 November 2024