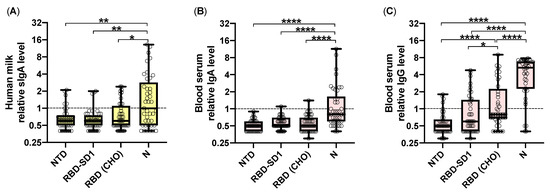
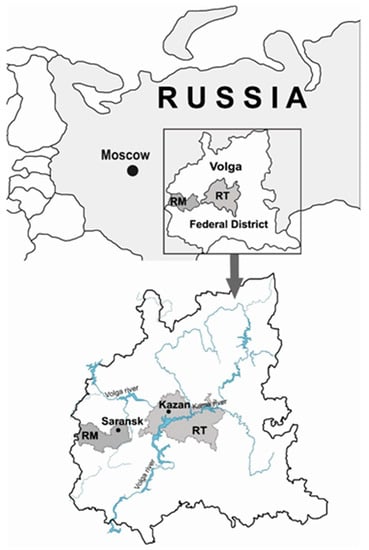
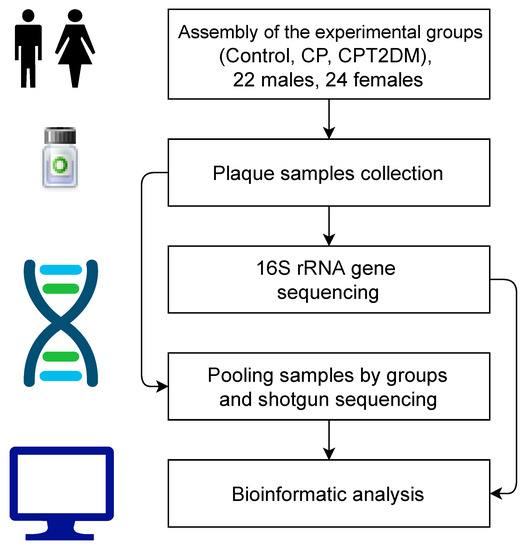
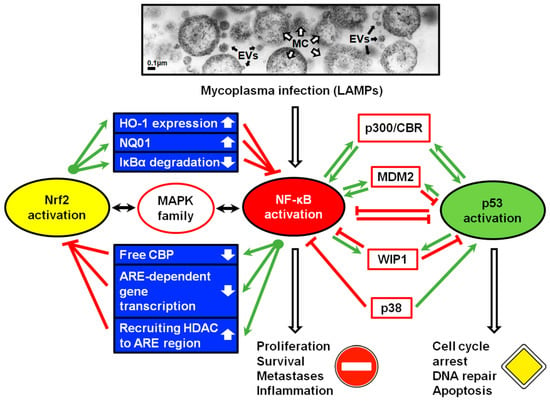
Biomarkers and Pathogenesis of Infectious and Autoimmune Diseases (Closed)
A topical collection in Pathogens (ISSN 2076-0817). This collection belongs to the section "Immunological Responses and Immune Defense Mechanisms".
Viewed by 42959Editor
Interests: multi-omics medicine; precision medicine; regenerative medicine; gene and cell therapy; molecular neurobiology; molecular virology; cancer diagnostics and therapy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Infections and autoimmunity combined represent the group of diseases with highest challenge to the health system in the world. Emerging and re-emerging infections are registered globally putting the large populations at risk of getting seriously ill or death. Climate change, human activities, pathogen evolution and socio-economical status as well as human interactions with animals could contribute to infectious disease emergence and transmission. Immune response to infectious agent is essential to restore the health and establish long term protection. However, in some cases, the immune response could lead to autoagression, when leukocytes fail to properly process the antigen, leading to autoimmunity.
This collection is aimed to summarize the current knowledge on infectious and autoimmune diseases with the main emphasis to reveal biomarkers (old and novel) which could help to facilitate diagnosis, treatment and protection against infectious disease as well as autoimmune conditions.
We invite authors to contribute original manuscripts, case reports, clinical trials as well as reviews focused on infectious disease and autoimmunity.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
- Recent discoveries in infectious pathogens (genetic, proteomic, etc)
- In vitro and in vivo studies aimed to identify mechanisms of infectious disease;
- Biomarkers for diagnosis and therapy of infectious disease and autoimmune conditions;
- Transcriptome and proteome analysis of infectious pathogens and autoimmune conditions;
- Bioinformatics approaches to characterize infectious pathogens related to clinical presentation, treatment efficacy and prognosis of various cancers;
- Novel therapeutic approaches for treatment of infectious disease and autoimmune conditions;
- Mechanisms of the immune system, evasion and development of autoimmunity
Prof. Dr. Albert Rizvanov
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pathogens is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.