Journal Description
Organics
Organics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on organic chemistry published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 12.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Synthesis of Novel Trisubstituted Olefin-Type Probe Molecules Containing N-Heterocycles and Their Application in Detection of Malononitrile
Organics 2024, 5(2), 46-58; https://doi.org/10.3390/org5020004 - 02 Apr 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►
Show Figures
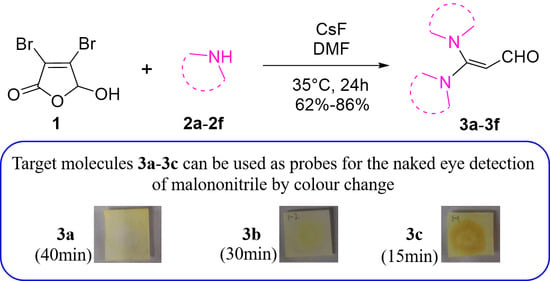
Recently, the construction of the trisubstituted olefin-type probe molecules has elicited the attention of many researchers. However, the synthesis of the trisubstituted olefin-type probes containing two N-heterocycles simultaneously has been rarely reported. In this study, starting from the inexpensive mucobromic acid 1
[...] Read more.
Recently, the construction of the trisubstituted olefin-type probe molecules has elicited the attention of many researchers. However, the synthesis of the trisubstituted olefin-type probes containing two N-heterocycles simultaneously has been rarely reported. In this study, starting from the inexpensive mucobromic acid 1 and N-heterocyclic compound 2, we first utilized a simple one-step reaction to synthesize a series of trisubstituted olefin-type compounds 3 simultaneously bearing with the structure of two N-heterocyclic rings in the absence of transition metal catalysts with a yield of 62–86%. The optimal reaction conditions were systematically explored, and the structure of the obtained compounds 3 were well characterized with 1H NMR, 13C NMR, X-ray single-crystal and HR-MS. The preliminary observation showed that, in the presence of base, mucobromic acid 1 reacts as its ring-opening structure, and the successive nucleophilic substitution reaction and Michael addition reaction can generate the target product 3. Considering that the aldehyde group in the molecular structure of the trisubstituted olefin-type compounds 3 may react with malononitrile, we carried out some relevant investigations so as to realize the visual detection of malononitrile. Interestingly, among the products, compounds 3a–3c can be prepared in portable test strips through a simple process and used to achieve the naked-eye detection of malononitrile in environmental systems as designed.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Supramolecular Catalysis with Chiral Mono- and Bis-(Thio)Urea-Derivatives
by
Veronica Iuliano, Paolo Della Sala, Carmen Talotta, Margherita De Rosa, Carmine Gaeta, Placido Neri and Annunziata Soriente
Organics 2024, 5(2), 32-45; https://doi.org/10.3390/org5020003 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chiral mono- and bis-(thio)urea supramolecular organocatalysts were studied in the enantioselective vinylogous addition reaction of 2-trimethylsilyloxyfuran (TMSOF) to carbonylic compounds; the corresponding chiral γ-hydroxymethyl-butenolides are obtained in good yields and with high enantiomeric excesses. The catalyst structure, as well as the reaction conditions,
[...] Read more.
Chiral mono- and bis-(thio)urea supramolecular organocatalysts were studied in the enantioselective vinylogous addition reaction of 2-trimethylsilyloxyfuran (TMSOF) to carbonylic compounds; the corresponding chiral γ-hydroxymethyl-butenolides are obtained in good yields and with high enantiomeric excesses. The catalyst structure, as well as the reaction conditions, strongly influence the efficiency of the reaction. The conformational features of mono(thio)urea catalysts 2 and 3 and bis(thio)urea catalysts 7 and 8 were investigated by DFT calculations along with the structure of their complexes with benzaldehyde. Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) and Non-Covalent Interaction (NCI) calculations provided useful information concerning the activating H-bonding interactions in the complexes.
Full article
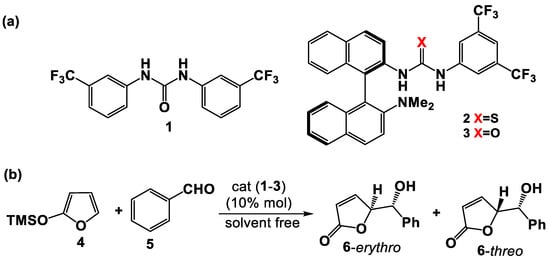
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis and Butyllithium-Induced Cyclisation of 2-Benzyloxyphenylphosphonamidates Giving 2,3-Dihydrobenzo[d][1,3]oxaphospholes
by
R. Alan Aitken, Khadija Ait Moulay, David B. Cordes, Ryan A. Inwood, Fraser G. Jamieson, Alexander J. B. Nelson and Aidan P. McKay
Organics 2024, 5(1), 12-31; https://doi.org/10.3390/org5010002 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
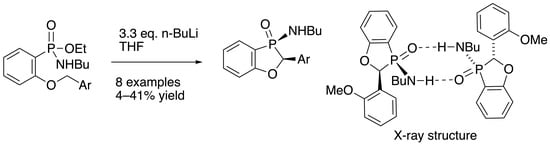
A series of fourteen O-ethyl-N-butylphenylphosphonamidates with benzyl ether substituents at the ortho position was prepared and fully characterised. Upon treatment with n-butyllithium in THF at RT, they underwent cyclisation in eight cases to give the novel 2,3-dihydrobenzo[d][1,3]oxaphospholes
[...] Read more.
A series of fourteen O-ethyl-N-butylphenylphosphonamidates with benzyl ether substituents at the ortho position was prepared and fully characterised. Upon treatment with n-butyllithium in THF at RT, they underwent cyclisation in eight cases to give the novel 2,3-dihydrobenzo[d][1,3]oxaphospholes in moderate to low yield as a single diastereomer, for which the relative configuration was determined by X-ray diffraction in one case.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
How an Internal Supramolecular Interaction Determines the Stereochemistry of a Metal Center
by
Maxime Steinmetz, Christophe Gourlaouen and David Sémeril
Organics 2024, 5(1), 1-11; https://doi.org/10.3390/org5010001 - 04 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
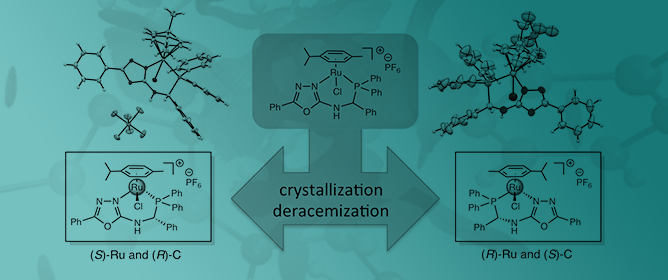
The chloro-P,N-{diphenylphosphanyl-[(5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylamino)phenyl-me- thyl]}(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate complex (4) was obtained in two steps from diphenylphosphanyl-[(5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylamino)phenyl-methyl] borane (2). In the first step, the oxadiazole ring coordinated with the ruthenium atom, resulting in the formation of the
[...] Read more.
The chloro-P,N-{diphenylphosphanyl-[(5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylamino)phenyl-me- thyl]}(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate complex (4) was obtained in two steps from diphenylphosphanyl-[(5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylamino)phenyl-methyl] borane (2). In the first step, the oxadiazole ring coordinated with the ruthenium atom, resulting in the formation of the dichloro-N-{diphenylphosphanyl-[(5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylamino)phenyl-methyl]borane}(p-cymene) ruthenium(II) complex (3). During the crystallization of the P,N-chelate ruthenium complex, the formation of conglomerate crystals was revealed by X-ray structure analysis. Only two stereoisomers were obtained with (S)-Ru and (R)-C configurations in the first complex and with (R)-Ru and (S)-C configurations in the second. This deracemization during crystallization is due to the formation of a hydrogen bond between the P,N-ligand and the chlorine atom (CH•••Cl). This supramolecular interaction allows the transfer of the ligand chirality to the metal center and decrees the stereochemistry of the ruthenium atom.
Full article
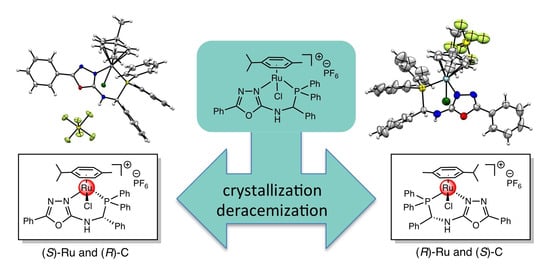
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
4-Hydroxy-2-pyrones: Synthesis, Natural Products, and Application
by
Vladislav V. Fedin, Dmitrii L. Obydennov, Sergei A. Usachev and Vyacheslav Y. Sosnovskikh
Organics 2023, 4(4), 539-561; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4040037 - 15 Dec 2023
Abstract
4-Hydroxy-2-pyrones are of interest as potential biorenewable molecules for a sustainable transition from biomass feedstock to valuable chemical products. This review focuses on the methodologies for the synthesis of 4-hydroxy-2-pyrones published over the last 20 years. These pyrones as polyketides are widespread in
[...] Read more.
4-Hydroxy-2-pyrones are of interest as potential biorenewable molecules for a sustainable transition from biomass feedstock to valuable chemical products. This review focuses on the methodologies for the synthesis of 4-hydroxy-2-pyrones published over the last 20 years. These pyrones as polyketides are widespread in Nature and possess versatile bioactivity that makes them an attractive target for synthesis and modification. Biosynthetic paths of the pyrones are actively developed and used as biotechnological approaches for the construction of natural and unnatural polysubstituted 4-hydroxy-2-pyrones. The major synthetical methods are biomimetic and are based on the cyclization of tricarbonyl compounds. Novel chemical methods of de novo synthesis based on alkyne cyclizations using transition metal complexes and ketene transformations allow for straightforward access to 4-hydroxy-2-pyrones and have been applied for the construction of natural products. Possible directions for further pyrone ring modification are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Modern Trends in Organic Synthesis, including PASE and Green Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
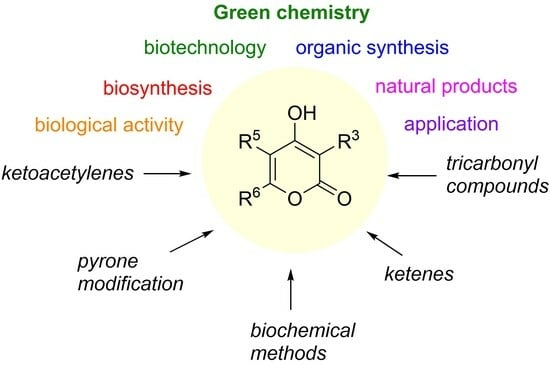
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Synthesis of 2-Substituted Benzimidazole Derivatives as a Platform for the Development of UV Filters and Radical Scavengers in Sunscreens
by
Kameliya K. Anichina and Nikolai I. Georgiev
Organics 2023, 4(4), 524-538; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4040036 - 28 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The modern trend in sunscreen products is towards the development of UV filters with multi-functional properties, to provide a broad shielding against ultraviolet radiation, antioxidant activity, and the prevention of skin cancer. Additionally, they should also be safe for humans as well as
[...] Read more.
The modern trend in sunscreen products is towards the development of UV filters with multi-functional properties, to provide a broad shielding against ultraviolet radiation, antioxidant activity, and the prevention of skin cancer. Additionally, they should also be safe for humans as well as the environment. The benzimidazole heterocycle is a suitable platform for the development of such multifunctional molecules with potential application in cosmetic formulations, due to their ability to act as both UV protectors and reactive pharmacophores. This review presents for the first time the progress in the synthesis and optimization of benzimidazole compounds as UV sunscreen filters. The modifications to the substitution pattern of the lead compound and structure–activity relationships are discussed, as well as the synthetic approaches for the preparation of 2-substituted benzimidazoles. These aggregated data will be useful in future in the development of modern benzimidazole-based sunscreen.
Full article
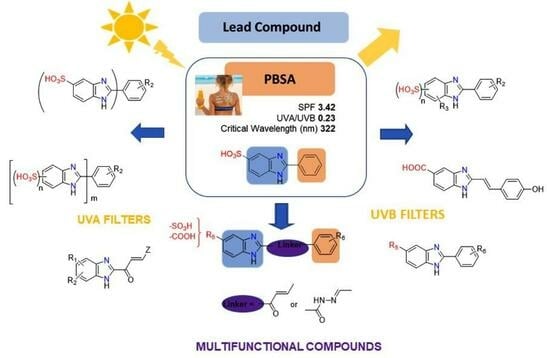
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Synthesis of Antifungal Heterocycle-Containing Mannich Bases: A Comprehensive Review
by
Diego Quiroga and Ericsson Coy-Barrera
Organics 2023, 4(4), 503-523; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4040035 - 09 Nov 2023
Abstract
Mannich bases are a class of organic compounds usually obtained by the condensation reaction between an amine, a compound with active hydrogens, and an aldehyde. They are versatile intermediates in organic synthesis, and those compounds containing this motif find applications in pharmaceutical, agrochemical,
[...] Read more.
Mannich bases are a class of organic compounds usually obtained by the condensation reaction between an amine, a compound with active hydrogens, and an aldehyde. They are versatile intermediates in organic synthesis, and those compounds containing this motif find applications in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and even material fields since they are widely known for their wide range of biological activities, including antimicrobial properties. Thus, as part of our interest in antifungal agents, this narrative review aimed to gather information from the literature on the synthesis of various representative Mannich-base-containing compounds, particularly centered on those exhibiting antifungal properties. In this context, the compilation indicated that Mannich bases could be considered as a relevant toxophore/pharmacophore by incorporating heterocyclic moieties to be implemented for the design of new antifungal agents, given its proven efficacy against phytopathogens, other opportunistic human pathogens, and some dermatophytic fungal species, which can be further exploited as agrochemical agents or in medicinal applications to treat fungal infections. The antifungal effect exhibited by Mannich bases conjugated with oxa and/or aza-heterocycles suggests that compounds that have a heterocyclic system attached to the β-amino core are attractive alternatives oriented to the synthesis of novel and helpful antifungal agents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Heterocyclic Compounds and Their Derivatives: Synthesis and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
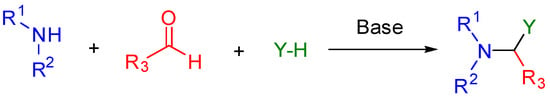
Scheme 1
Open AccessArticle
Absorption Spectra of Protonated Corroles: Two Distinct Patterns Due to Peripheral Substitution Architecture
by
Lev L. Gladkov, Dmitry V. Klenitsky and Mikalai M. Kruk
Organics 2023, 4(4), 490-502; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4040034 - 09 Oct 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
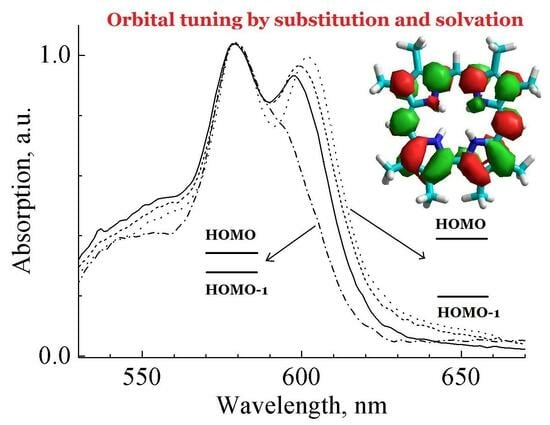
The origin of individual features in the ground state absorption spectra of two protonated corroles differing in the architecture of peripheral substitution (either Cm-aryl or Cb-alkyl) have been studied in detail with the ground state absorption spectroscopy and density
[...] Read more.
The origin of individual features in the ground state absorption spectra of two protonated corroles differing in the architecture of peripheral substitution (either Cm-aryl or Cb-alkyl) have been studied in detail with the ground state absorption spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations. The geometry optimization, molecular orbitals and absorption spectra calculation have been carried out. It was found that protonation leads to the saddle type macrocycle conformation in contrast with the wave type conformation known for the parent-free base corroles. The mean plane deviation parameter Δ23 for the macrocycle, pyrrole tilting angles and the degree of pyramidalization λ2 of all four pyrrole nitrogens was found to depend on the peripheral substitution architecture. Macrocycle conformation of the protonated forms has distinct asymmetrical features which are reflected by the sets of values of the tilting angles and values of pyramidalization degree. The pair of pyrroles B and C has smaller tilting angles and higher pyramidalization degree values, whereas the opposite trend was found for the pair of pyrroles A and D. Electronic effects and structural differences induced by substitution lead to the pronounced shifts of the molecular orbitals. In the Cb-alkylated corrole, almost-degenerated HOMO and HOMO-1 molecular orbitals lead to enhancement of the configuration interaction. As a result, the Qx transition oscillator strength goes down, becoming comparable to that of the Qy one. A large HOMO-HUMO-1gap in the Cm-aryl corrole minimizes the configuration interaction, giving rise to Qx band domination in the visible range spectrum.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Application of Alkoxy Radical in Organic Synthesis
by
Munsaf Ali, Shi Sewell, Juncheng Li and Ting Wang
Organics 2023, 4(4), 459-489; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4040033 - 28 Sep 2023
Abstract
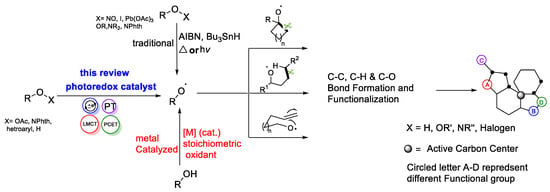
Alkoxy radicals have been identified as versatile intermediates in synthetic chemistry in the last few decades. Over the last decade, various catalytic processes for the in situ generation of alkoxy radicals have been explored, leading to the development of new synthetic methodologies based
[...] Read more.
Alkoxy radicals have been identified as versatile intermediates in synthetic chemistry in the last few decades. Over the last decade, various catalytic processes for the in situ generation of alkoxy radicals have been explored, leading to the development of new synthetic methodologies based on alkoxy radicals. In this review, we provided a comprehensive review of recent developments in the utilization of alkoxy radicals in diverse organic transformations, natural product synthesis, and the late-stage modification of bioactive molecules through the implementation of the photoredox methodology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Development of New Organic Synthetic Methods and Techniques)
►▼
Show Figures
Scheme 1
Open AccessArticle
Stimuli-Sensitive Pyrenylated Hydrogels as Optical Sensing Platform for Multiple Metal Ions
by
Dipen Biswakarma, Nilanjan Dey and Santanu Bhattacharya
Organics 2023, 4(3), 447-458; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030032 - 04 Sep 2023
Abstract
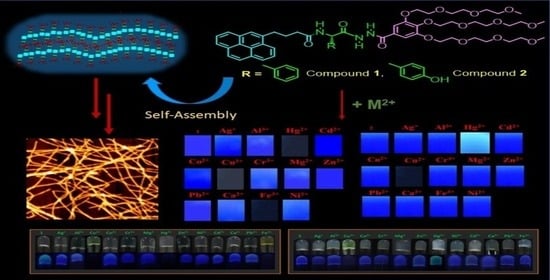
In the present work, we report a thermoresponsive hydrogel formed by the self-assembly of compounds 1 and 2 Milli Q water. Both hydrogels showed thixotropic behavior. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) studies confirm the fiber-like microstructure of compounds 1 and 2, but denser fibers
[...] Read more.
In the present work, we report a thermoresponsive hydrogel formed by the self-assembly of compounds 1 and 2 Milli Q water. Both hydrogels showed thixotropic behavior. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) studies confirm the fiber-like microstructure of compounds 1 and 2, but denser fibers were observed in the case of compound 1. The hydrogel formed by compound 1 detected Cu2+, Fe3+, and Hg2+, whereas the hydrogel of 2 showed a change in the optical signal, specifically upon adding Cu2+ and Hg2+. Mechanistically, adding metal ions to the hydrogel resulted in the formation of a (1:1) complex with Fe3+ and Hg2+ and (2:1) with Cu2+. The detection of metal ions has also been achieved in real-life samples, such as in tap water. Low-cost portable gel-coated paper strips have also been developed for the onsite detection of these metal ions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aromatic Heterocycles: A Wonderful Pool of Organic Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
Synthesis and Structure of 6-Acetyl-2-Arylhydrazone Derivatives of Thiazolo[3,2-a]Pyrimidine
by
Artem S. Agarkov, Dilyara O. Mingazhetdinova, Anna A. Nefedova, Alexander S. Ovsyannikov, Andrey K. Shiryaev, Igor A. Litvinov, Svetlana E. Solovieva and Igor S. Antipin
Organics 2023, 4(3), 438-446; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030031 - 11 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidine is one of the promising structural fragments for the development of drugs, including anticancer drugs. This work is devoted to the synthesis of a number of new 2-arylhydrazone derivatives of thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine, which are synthetic precursors for triazolo[4,3-a
[...] Read more.
Triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidine is one of the promising structural fragments for the development of drugs, including anticancer drugs. This work is devoted to the synthesis of a number of new 2-arylhydrazone derivatives of thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine, which are synthetic precursors for triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidines. The crystal structure of 6-acetyl-7-methyl-5-phenyl-2-(2-phenylhydrazineylidene)-5H-thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidin-3(2H)-one was established by SCXRD. In the reduction reaction of the compound, the following system was used: vanadium(V) oxide, and sodium borohydride in ethanol at room temperature, which led to the formation of only one pair of diastereomers (1R*)-1-((5S*,6R*,7R*)-(1-(hydroxymethyl)-7-methyl-1,5-diphenyl-1,5,6,7-tetrahydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)ethan-1-ol.
Full article
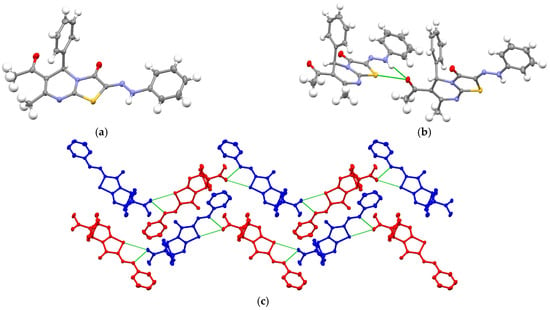
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Bispidine-Based Macrocycles: Achievements and Perspectives
by
Aleksei V. Medved’ko, Savelii V. Gaisen, Mikhail A. Kalinin and Sergey Z. Vatsadze
Organics 2023, 4(3), 417-437; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030030 - 24 Jul 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review presents all currently known macroheterocyclic compounds that include a bispidine (3,7-diazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane) fragment in their structure. A classification of bispidine-containing macroheterocycles, which is based on the ring size and the nature of bispidinic nitrogen atoms, is suggested. Synthetic approaches to the studied
[...] Read more.
This review presents all currently known macroheterocyclic compounds that include a bispidine (3,7-diazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane) fragment in their structure. A classification of bispidine-containing macroheterocycles, which is based on the ring size and the nature of bispidinic nitrogen atoms, is suggested. Synthetic approaches to the studied compounds are classified and considered. The features of the crystal structures and solution behavior of bispidine macroheterocycles are analyzed. Prospects for the development of these organic receptors are proposed.
Full article
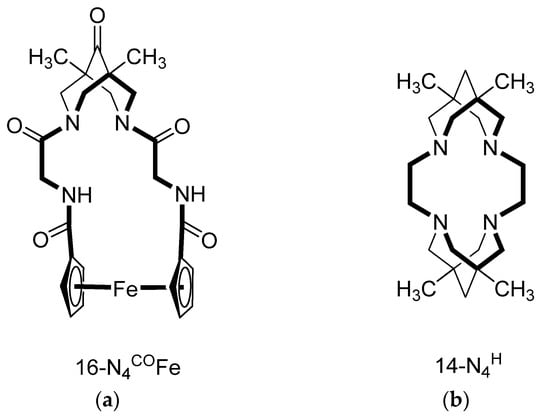
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of an Electrodeficient Dipyridylbenzene-like Terdentate Ligand: Cyclometallating Ligand for Highly Emitting Iridium(III) and Platinum(II) Complexes
by
Pierre-Henri Lanoë, Christian Philouze and Frédérique Loiseau
Organics 2023, 4(3), 403-416; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030029 - 14 Jul 2023
Abstract
Cyclometallated iridium(III) and platinum(II) complexes are intensely used in optoelectronics for their photophysical properties and ability to convert excitons from singlet to triplet state, thus improving the device efficiency. In this contribution, we report the multi-steps synthesis of an electrodeficient dipyridylbenzene-like terdentate ligand
[...] Read more.
Cyclometallated iridium(III) and platinum(II) complexes are intensely used in optoelectronics for their photophysical properties and ability to convert excitons from singlet to triplet state, thus improving the device efficiency. In this contribution, we report the multi-steps synthesis of an electrodeficient dipyridylbenzene-like terdentate ligand [N^C^N], namely 2′,6′-dimethyl-2,3′:5′,2″-terpyridine (6), with 18% overall yield. Compound 6 has been employed to synthesize two phosphorescent complexes of platinum(II) and iridium(III), namely compounds 7 and 8, respectively. Both complexes have been characterized by NMR and high resolution mass spectrometry, and demonstrate high luminescence quantum yields in a deaerated solution at room temperature, with 18% and 61% for 7 and 8, respectively. If the iridium(III) complex displays similar emission properties to [Ir(dpyx)(ppy)Cl] (dpyx = 3,5-dimethyl-2,6-dipyridylbenzene and ppy = 2- phenylpyridine), the platinum(II) derivative, with λem = 470 nm, is a rare example of a fluorine atom-free blue emitting [N^C^N]PtCl complex.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advanced Research Papers in Organics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
An Overview of Some Reactive Routes to Flame-Retardant Fibre-Forming Polymers: Polypropylene and Polyacrylonitrile
by
Svetlana Tretsiakova-McNally, Malavika Arun, Maurice Guerrieri and Paul Joseph
Organics 2023, 4(3), 386-402; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030028 - 12 Jul 2023
Abstract
The thermal degradation and flammability characteristics of some common fibre-forming polymers, such as polypropylene (PP) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN), are described in this review paper. The flame retardance of these polymers is principally affected by reactive routes that were primarily developed in our laboratories.
[...] Read more.
The thermal degradation and flammability characteristics of some common fibre-forming polymers, such as polypropylene (PP) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN), are described in this review paper. The flame retardance of these polymers is principally affected by reactive routes that were primarily developed in our laboratories. The modifying groups that are incorporated into polymeric chains include phosphorus- or phosphorus/nitrogen-containing moieties in different chemical environments. The degradation characteristics and extent of flame retardance were mainly evaluated using routine thermal and calorimetric techniques. Elements of flame-retardant mechanisms occurring in the condensed and vapour phases were also identified. Furthermore, we also explored the effects of molecularly dispersed β-cyclodextrin, including its physical mixtures, on the thermal and combustion characteristics of PAN. Given that both types of polymers are often used in the form of fibres, and that the aspect ratio of fibrous materials is relatively high, even nominal enhancements in their fire retardance are highly welcomed. Hence, the preliminary results of our research on chemically modified PAN incorporating molecularly dispersed β-cyclodextrin are encouraging in terms of their enhanced fire retardance, and hence this field warrants further exploration.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Progress in Synthesis and Applications of Phosphorus-Containing Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Substituted Fused Dipyranoquinolinones
by
Evangelia-Eirini N. Vlachou, Eleni Pontiki, Dimitra J. Hadjipavlou-Litina and Konstantinos E. Litinas
Organics 2023, 4(3), 364-385; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030027 - 10 Jul 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
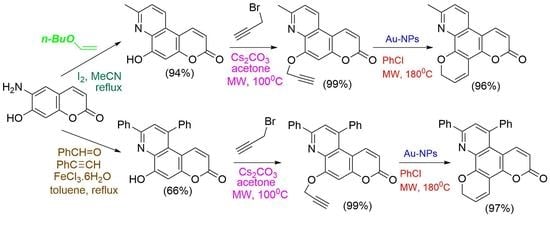
New methyl-substituted, and diphenyl-substituted fused dipyranoquinolinones are prepared in excellent yields via the triple bond activation and 6-endo-dig cyclization of propargyloxycoumarin derivatives by gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2 in chlorobenzene under microwave irradiation. In the absence of gold nanoparticles, the methyl-substituted propargyloxycoumarin
[...] Read more.
New methyl-substituted, and diphenyl-substituted fused dipyranoquinolinones are prepared in excellent yields via the triple bond activation and 6-endo-dig cyclization of propargyloxycoumarin derivatives by gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2 in chlorobenzene under microwave irradiation. In the absence of gold nanoparticles, the methyl-substituted propargyloxycoumarin derivatives resulted in fused furopyranoquinolinones through Claisen rearrangement and 5-exo-dig cyclization. The intermediate propargyloxy-fused pyridocoumarins are prepared by propargylation of the corresponding hydroxy-fused pyridocoumarins. The methyl-substituted derivatives of the latter are synthesized in excellent yield by the three-component reaction of amino hydroxycoumarin with n-butyl vinyl ether under iodine catalysis. The diphenyl-substituted derivatives of hydroxy-fused pyridocoumarins are obtained, also, by the three-component reaction of amino hydroxycoumarin with benzaldehyde and phenyl acetylene catalyzed by iron (III) chloride. Preliminary biological tests of the title compounds indicated lipoxygenase (LOX) (EC 1.13.11.12) inhibitory activity (60–100 μM), whereas compound 28a, with IC50 = 10 μM, was found to be a potent LOX inhibitor and a possible lead compound. Only compounds 10b and 28b significantly inhibited lipid peroxidation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advanced Research Papers in Organics)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Indole-Based Macrocyclization by Metal-Catalyzed Approaches
by
Subba Rao Cheekatla, Debashis Barik, Geethanjali Anand, Rakhi Mol K. M. and Mintu Porel
Organics 2023, 4(3), 333-363; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030026 - 04 Jul 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
This review is dedicated to the different varieties of macrocycles synthesis bearing indole units in their architecture by metal-catalyzed strategies. The progress of the new macrocyclization approaches is persisted be a keen area of research. Macrocycles contain a wide variety of molecules, and
[...] Read more.
This review is dedicated to the different varieties of macrocycles synthesis bearing indole units in their architecture by metal-catalyzed strategies. The progress of the new macrocyclization approaches is persisted be a keen area of research. Macrocycles contain a wide variety of molecules, and among those, heteroaryl motifs are valuable constituents that provide an attractive feature to macrocyclic systems. Indole represents one of the privileged pharmacophores against a variety of targets with various biological applications. Among the nitrogen-based heterocycles, indole plays a prominent role in organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, pharmaceuticals, natural products synthesis, agrochemicals, dye and fragrances, and drug design. These scaffolds are widely distributed in several bioactive natural products and synthetic macrocycles constructed against a specific biochemical target and the most common constituents of naturally occurring molecules. Due to its immense importance, the progress of novel approaches for the synthesis of indole-based scaffolds has increased steadily. The majority of the macrocycles synthesis proceeds through the macrolactamization and macrolactonization, as well as the C–C bond macrocyclization process described by metal-catalyzed ring-closing metathesis (RCM) and coupling reactions. Among macrocyclizations, metal-catalyzed approaches are considered one of the most powerful tools for synthetic chemists in the design of a variety of macrocycles. This review aims to give a comprehensive insight into the synthesis of varieties of macrocycles bearing indole scaffold catalyzed by various transition metals that emerged in the literature over the last two decades. We hope that this review will persuade synthetic chemists to search for novel strategies for the C–C bond macrocyclization by metal-catalyzed protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advanced Research Papers in Organics)
►▼
Show Figures
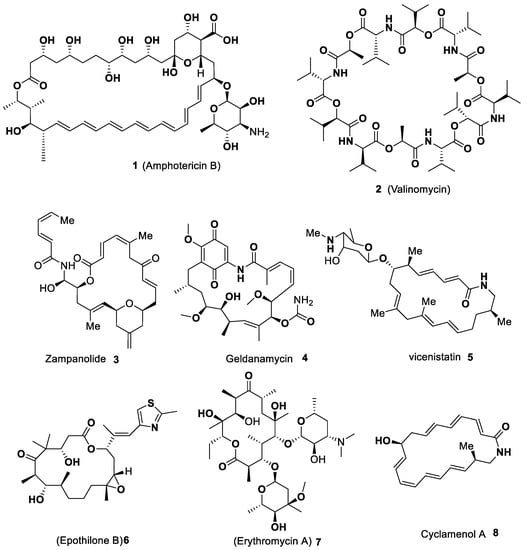
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Consecutive Four-Component Coupling-Addition Aza-Anellation Pictet–Spengler Synthesis of Tetrahydro-β-Carbolines: An Optimized Michael Addition and Computational Study on the Aza-Anellation Step
by
Kai Ries, Françoise A. Aouane and Thomas J. J. Müller
Organics 2023, 4(3), 313-332; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030025 - 28 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Starting from acid chlorides, alkynes, tryptamines, and acryloyl chloride, 21 densely substituted tetrahydro-β-carbolines were prepared in a four-component, one-pot reaction. In this study, the aza-Michael addition step to generate intermediate enaminones was optimized in the presence of ytterbium triflate. Moreover,
[...] Read more.
Starting from acid chlorides, alkynes, tryptamines, and acryloyl chloride, 21 densely substituted tetrahydro-β-carbolines were prepared in a four-component, one-pot reaction. In this study, the aza-Michael addition step to generate intermediate enaminones was optimized in the presence of ytterbium triflate. Moreover, apart from acryloyl chloride, all reactants could be deployed in almost equimolar ratios, which increases the atom economy of the sequence. For mechanistic rationalization, the concluding aza-anellation was investigated by DFT calculations on potential intermediates and corresponding activation energies, revealing that the aza-anellation proceeds via ene reaction rather than via electrocyclization.
Full article
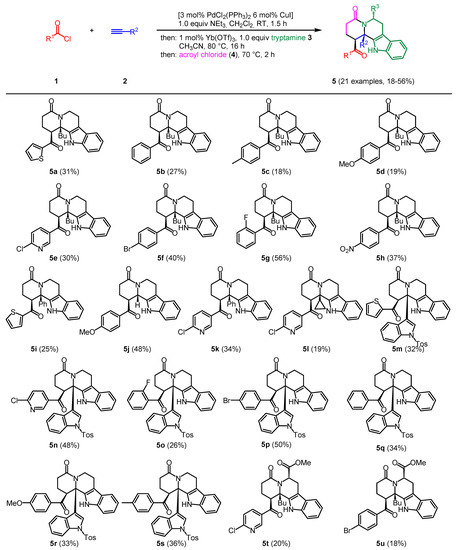
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Structural and Dynamic Behaviour of Heterocycles Derived from Ethylenediamines with Formaldehyde: 1,3,5-Triazinanes and Bis(imidazolidinyl)methanes
by
Raúl Colorado-Peralta, Sonia Araceli Sánchez-Ruiz and Angelina Flores-Parra
Organics 2023, 4(2), 297-312; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020024 - 15 Jun 2023
Abstract
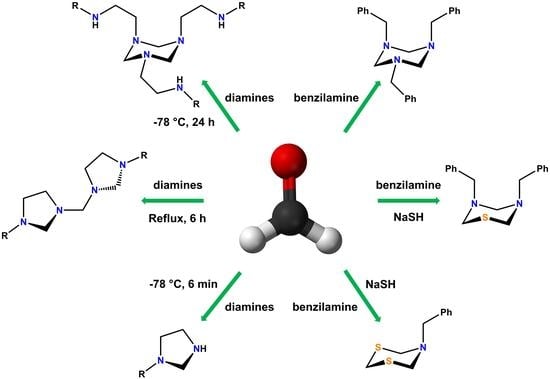
Formaldehyde is a simple chemical compound that is used as a building block in obtaining a wide range of products. The versatility of formaldehyde in chemical synthesis becomes evident when it is reacted with N-alkylethylenediamines. Therefore, this paper reports the structure and
[...] Read more.
Formaldehyde is a simple chemical compound that is used as a building block in obtaining a wide range of products. The versatility of formaldehyde in chemical synthesis becomes evident when it is reacted with N-alkylethylenediamines. Therefore, this paper reports the structure and reactivity of a series of compounds derived from easily accessible molecules, such as formaldehyde, sodium hydrosulphide, and N-alkylethylenediamines. The 1,3,5-triazines (1a-1d) and bis(3-alkyl-imidazolidin-1-yl)methanes (2a-2d) were obtained by simple reaction conditions. Additionally, different proportions of sodium hydrosulphide and formaldehyde were used with N-benzylamine to obtain N-benzyltriazinane (3), N-benzylthiadiazinane (4) and N-benzyldithiazinane (5). All these compounds were characterized by analytical, spectroscopic, and spectrometric techniques, such as melting point, solubility, one-dimensional and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (13C, 1H, 15N, COSY, HETCOR, NOESY, COLOC), elemental analysis, high- and low-resolution mass spectrometry, among others. The structures of compounds 4 and 5 were obtained by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The results show that small variations in the stoichiometry and the reaction conditions significantly influence the products obtained.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advanced Research Papers in Organics)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
Palladium Catalyzed Allylic C-H Oxidation Enabled by Bicyclic Sulfoxide Ligands
by
Yuming Wen, Jianfeng Zheng, Alex H. Evans and Qiang Zhang
Organics 2023, 4(2), 289-296; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020023 - 13 Jun 2023
Abstract
The activation of C-H bonds is a potent tool for modifying molecular structures in chemistry. This article details the steps involved in a novel ligand bearing a bicyclic [3.3.1]-nonane framework and bissulfoxide moiety. A palladium catalyzed allylic C-H oxidation method enables a direct
[...] Read more.
The activation of C-H bonds is a potent tool for modifying molecular structures in chemistry. This article details the steps involved in a novel ligand bearing a bicyclic [3.3.1]-nonane framework and bissulfoxide moiety. A palladium catalyzed allylic C-H oxidation method enables a direct benzyl-allylic functionalization with the bissulfoxide ligand. Bissulfoixde ligand possesses a rapidly constructed bicyclic [3.3.1] framework and it proved to be effective for enabling both N- and C-alkylation. A total of 13 C-H activation productions were reported with good to excellent yields. This report validated that it is necessary to include bissulfoxide as a ligand for superior reactivities. Naftifine was produced utilizing developed C-H functionalization methodology in good overall yields.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Development of New Organic Synthetic Methods and Techniques)
►▼
Show Figures
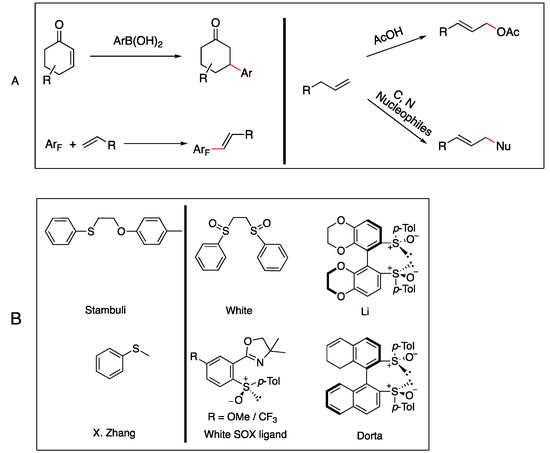
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hydrogen-Bonding Secondary Coordination Sphere Effect on CO2 Reduction
by
Anamarija Briš and Davor Margetić
Organics 2023, 4(2), 277-288; https://doi.org/10.3390/org4020022 - 05 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Great efforts of the scientific community are focused on the development of catalysts for the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) to useful molecules such as carbon monoxide, formic acid, methanol, ethanol, methane, ethylene, or acetate. Various metal porphyrin complexes were synthesized
[...] Read more.
Great efforts of the scientific community are focused on the development of catalysts for the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) to useful molecules such as carbon monoxide, formic acid, methanol, ethanol, methane, ethylene, or acetate. Various metal porphyrin complexes were synthesized and studied to develop highly active and selective catalysts. While the substituents on the porphyrin core (the primary coordination sphere) determine the reactivity of the metal, the introduction of the secondary coordination is important for the binding and activation of CO2. In this review, selected examples of iron porphyrin catalysts with a secondary coordination sphere capable of stabilizing intermediates of the CO2 reduction process by hydrogen bonding are presented.
Full article
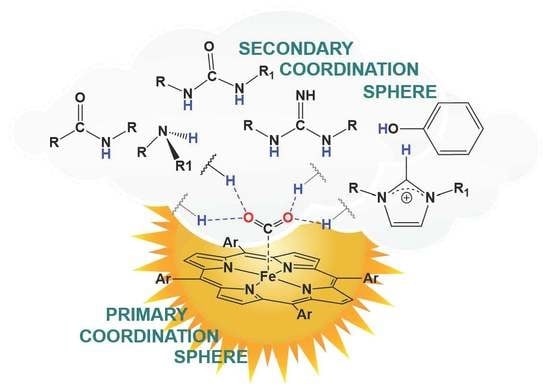
Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Organics
The Modern Trends in Organic Synthesis, including PASE and Green Chemistry
Guest Editors: Denis N. Bazhin, Yulia S. KudyakovaDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Organics
Heterocyclic Compounds and Their Derivatives: Synthesis and Applications
Guest Editor: Xiaoyu HaoDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Organics
Aromatic Heterocycles: A Wonderful Pool of Organic Materials
Guest Editor: Filip BurešDeadline: 31 July 2024
Special Issue in
Organics
Design and Development of New Organic Synthetic Methods and Techniques
Guest Editors: Ting Wang, Li XiaoDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Organics
Advanced Research Papers in Organics
Collection Editors: Wim Dehaen, Michal Szostak, Huaping Xu