Journal Description
Onco
Onco
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the whole field of oncotargets and cancer therapies research published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Onco is a companion journal of Cancers.
Latest Articles
How Reliable Are Predictions of CD8+ T Cell Epitope Recognition? Lessons for Cancer
Onco 2024, 4(2), 68-76; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4020006 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Synthetic peptides derived from antigen sequences are essential reagents for the detection of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), in assays such as ELISPOT/ImmunoSpot®. Indeed, the combination of peptides and ImmunoSpot® has been widely used for immune monitoring in numerous
[...] Read more.
Synthetic peptides derived from antigen sequences are essential reagents for the detection of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), in assays such as ELISPOT/ImmunoSpot®. Indeed, the combination of peptides and ImmunoSpot® has been widely used for immune monitoring in numerous vaccine trials. Target antigens in pathogens or cancers may be large in size and multiple in number, often seemingly necessitating in silico peptide epitope predictions using algorithms and programs for certain HLA alleles to narrow down the numbers of required peptides. In this commentary, we discuss our data in the context of immune responses to viral and cancer antigens, concluding that systematic high-throughput immune monitoring of CD8+ T cells will provide more reliable insights on the host’s response to cancer than the reliance on select CD8+ T cell epitopes, no matter whether these are in silico predicted or even if they had been empirically established. We show the feasibility of large scale, high-throughput systematic CD8+ T cell epitope testing towards this goal.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Progress in Vaccination against Cancer - 2023 (PIVAC-23))
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Deficiency in DNA Damage Repair Proteins Promotes Prostate Cancer Cell Migration through Oxidative Stress
by
Philippa Lantwin, Adam Kaczorowski, Cathleen Nientiedt, Constantin Schwab, Martina Kirchner, Viktoria Schütz, Magdalena Görtz, Markus Hohenfellner, Anette Duensing, Albrecht Stenzinger and Stefan Duensing
Onco 2024, 4(2), 56-67; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4020005 - 28 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: DNA damage repair gene deficiency defines a subgroup of prostate cancer patients with early metastatic progression and unfavorable disease outcome. Whether deficiency in DNA damage repair genes directly promotes metastatic dissemination is not completely understood. Methods: The migratory behavior of prostate cancer
[...] Read more.
Introduction: DNA damage repair gene deficiency defines a subgroup of prostate cancer patients with early metastatic progression and unfavorable disease outcome. Whether deficiency in DNA damage repair genes directly promotes metastatic dissemination is not completely understood. Methods: The migratory behavior of prostate cancer cells was analyzed after siRNA-mediated knockdown of DNA damage repair and checkpoint proteins, including BRCA2, ATM, and others, using transwell migration assays, scratch assays and staining for F-actin to ascertain cell circularity. Cells deficient in BRCA2 or ATM were tested for oxidative stress by measuring reactive oxygen species (ROS). The effects of ROS inhibition on cell migration were analyzed using the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). The correlation between BRCA2 deficiency and oxidative stress was ascertained via immunohistochemistry for methylglyoxal (MG)-modified proteins in 15 genetically defined primary prostate cancers. Results: Prostate cancer cells showed a significantly increased migratory activity after the knockdown of BRCA2 or ATM. There was a significant increase in ROS production in LNCaP cells after BRCA2 knockdown and in PC-3 cells after BRCA2 or ATM knockdown. Remarkably, the ROS scavenger NAC abolished the enhanced motility of prostate cancer cells after the knockdown of BRCA2 or ATM. Primary prostate cancers harboring genetic alterations in BRCA2 showed a significant increase in MG-modified proteins, indicating enhanced oxidative stress in vivo. Conclusions: Our results indicate that DNA damage repair gene deficiency may contribute to the metastatic dissemination of prostate cancer through enhanced tumor cell migration involving oxidative stress.
Full article
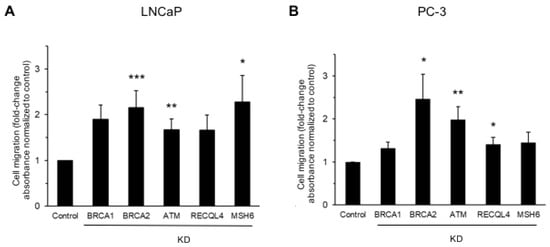
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Dendritic Cell Immunotherapy for Ovarian Cancer: An Overview of Our Achievements
by
Jiřina Bartůňková
Onco 2024, 4(1), 46-55; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4010004 - 21 Mar 2024
Abstract
Epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related death in women, largely reflecting the early dissemination of this malignant disease to the peritoneum. Due to its immunological features, EOC has poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), including a limited
[...] Read more.
Epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related death in women, largely reflecting the early dissemination of this malignant disease to the peritoneum. Due to its immunological features, EOC has poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), including a limited tumor mutational burden (TMB), poor infiltration by immune cells, and active immunosuppression. Thus, novel strategies are needed to overcome the frequent lack of pre-existing immunity in patients with EOC. We developed and tested an autologous dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccine (DCVAC), which has recently been shown to be safe and to significantly improve progression-free survival (PFS) in two independent randomized phase II clinical trials enrolling patients with EOC (SOV01, NCT02107937; SOV02, NCT02107950). In addition, our exploratory data analyses suggest that the clinical benefits of the DCVAC were more pronounced in patients with EOC with lower-than-median TMBs and reduced CD8+ T cell infiltration. Thus, the DC-based vaccine stands out as a promising clinical tool to jumpstart anticancer immunity in patients with immunologically “cold” EOC. Our findings underscore the need for personalized immunotherapy and the clinical relevance of potential tumor-related biomarkers within the immunotherapy field. Additional clinical trials are needed to address these strategies as well as the potential value of the TMB and immune infiltration at baseline as biomarkers for guiding the clinical management of EOC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Progress in Vaccination against Cancer - 2023 (PIVAC-23))
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessCommentary
When Therapy-Induced Cancer Cell Apoptosis Fuels Tumor Relapse
by
Razmik Mirzayans
Onco 2024, 4(1), 37-45; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4010003 - 04 Feb 2024
Abstract
Most therapeutic strategies for solid tumor malignancies are designed based on the hypothesis that cancer cells evade apoptosis to exhibit therapy resistance. This is somewhat surprising given that clinical studies published since the 1990s have demonstrated that increased apoptosis in solid tumors is
[...] Read more.
Most therapeutic strategies for solid tumor malignancies are designed based on the hypothesis that cancer cells evade apoptosis to exhibit therapy resistance. This is somewhat surprising given that clinical studies published since the 1990s have demonstrated that increased apoptosis in solid tumors is associated with cancer aggressiveness and poor clinical outcome. This is consistent with more recent reports demonstrating non-canonical (pro-survival) roles for apoptotic caspases, including caspase 3, as well as the ability of cancer cells to recover from late stages of apoptosis via a process called anastasis. These activities are essential for the normal development and maintenance of a healthy organism, but they also enable malignant cells (including cancer stem cells) to resist anticancer treatment and potentially contribute to clinical dormancy (minimal residual disease). Like apoptosis, therapy-induced cancer cell dormancy (durable proliferation arrest reflecting various manifestations of genome chaos) is also not obligatorily a permanent cell fate. However, as briefly discussed herein, compelling pre-clinical studies suggest that (reversible) dormancy might be the “lesser evil” compared to treacherous apoptosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Targeting of Tumor Dormancy Pathway)
►▼
Show Figures
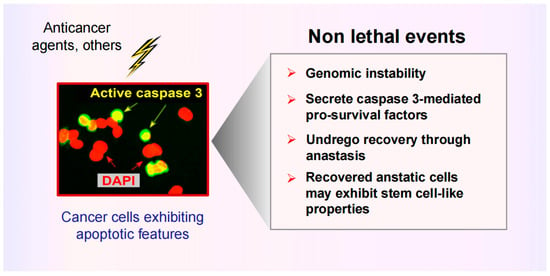
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Significance of PET/CT Imaging in Myeloma Assessment: Exploring Novel Applications beyond Osteolytic Lesion Detection and Treatment Response
by
Mahdi Zirakchian Zadeh
Onco 2024, 4(1), 15-36; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4010002 - 09 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In multiple myeloma (MM), specific cytokines produced by plasma cells disrupt the equilibrium between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. As a result, MM patients experience an increase in osteoclast activity and a decrease in osteoblast activity. This disparity is fundamental to the development of myeloma
[...] Read more.
In multiple myeloma (MM), specific cytokines produced by plasma cells disrupt the equilibrium between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. As a result, MM patients experience an increase in osteoclast activity and a decrease in osteoblast activity. This disparity is fundamental to the development of myeloma bone disease. Lytic lesions, which are a feature of MM, can result in pathologic fractures and excruciating pain. For many years, whole-body X-ray radiography has been the standard imaging method for identifying lytic lesions. However, its sensitivity is limited because it can only detect lesions once the bone mass has been reduced by 30% to 50%. Hence, utilizing advanced and sensitive imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET) fused with computed tomography (CT), is crucial for the early detection of osteolytic lesions. Among radiotracers used in PET imaging, 1⁸F-fluorodeoxyglucose ([18F]FDG) is the most commonly employed in the field of oncology. Currently, most guidelines include [18F]FDG PET/CT in the assessment of myeloma patients, particularly for detecting osteolytic lesions, evaluating treatment response, and assessing extramedullary and residual disease. Nonetheless, in recent years, new applications of PET/CT for evaluating myeloma have been investigated. These include assessing aspects such as bone turnover, dual-time-point imaging (early and delayed scans), the impact of chemotherapy on the brain (commonly known as ‘chemo brain’), innovative PET radiotracers, and the use of artificial intelligence technology. This article aims to provide a comprehensive review of both conventional and innovative uses of PET/CT in evaluating multiple myeloma.
Full article
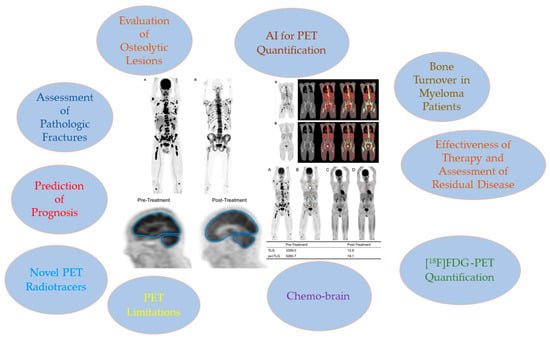
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Predictors of Complete Pathological Response with Chemoimmunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
by
Arya Mariam Roy, Supritha Chintamaneni, Sabah Alaklabi, Hassan Awada, Kristopher Attwood and Shipra Gandhi
Onco 2024, 4(1), 1-14; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4010001 - 28 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have investigated the impact of adding checkpoint inhibitors to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients. However, there is a lack of biomarkers that can help identify patients who would benefit from combination therapy. Our research
[...] Read more.
Background: Multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have investigated the impact of adding checkpoint inhibitors to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients. However, there is a lack of biomarkers that can help identify patients who would benefit from combination therapy. Our research identifies response predictors and assesses the effectiveness of adding immunotherapy to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for TNBC patients. Methods: We identified eligible RCTs by searching PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, Embase, and oncological meetings. For this meta-analysis, we obtained odds ratios using the standard random effects model. To assess the heterogeneity of the study outcomes, the I2 statistic was obtained. Potential bias was assessed using a funnel plot and the corresponding Egger’s test. Results: In total, 1637 patients with TNBC were included from five RCTs. Neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy significantly improved pCR when compared to neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone. In the subgroup analysis, neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy showed higher pCR rates in both Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)-positive and PD-L1-negative TNBC patients. An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score (PS) of 0 correlated with increased pCRs (OR = 1.9, p < 0.001) in neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy vs. neoadjuvant chemotherapy, but no benefit was observed for patients with ECOG PS 1. Nodal positivity was significantly associated with pCR (OR = 2.52, p < 0.001), while neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy did not benefit patients with negative lymph nodes. Conclusions: Checkpoint inhibition and neoadjuvant chemotherapy significantly increased pCRs in TNBC patients, regardless of their PDL-1 status. Additional checkpoint inhibitors improved pCR rates, mainly for patients with ECOG PS 0 and lymph node-positive disease.
Full article
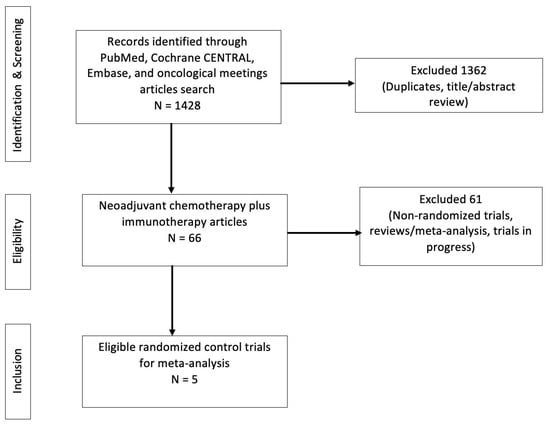
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anticancer Effects of Fucoxanthin in a PDX Model of Advanced Stage Pancreatic Cancer with Alteration of Several Multifunctional Molecules
by
Masaru Terasaki, Sally Suzuki, Takuji Tanaka, Hayato Maeda, Masaki Shibata, Kazuo Miyashita, Yasuhiro Kuramitsu, Junichi Hamada, Tohru Ohta, Shigehiro Yagishita, Akinobu Hamada, Yasunari Sakamoto, Susumu Hijioka, Chigusa Morizane and Mami Takahashi
Onco 2023, 3(4), 217-236; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3040016 - 24 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most fatal cancers, and there is an urgent need to develop new anticancer agents with fewer side effects for the treatment of this condition. A patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mouse model transplanted with cancer tissue from patients
[...] Read more.
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most fatal cancers, and there is an urgent need to develop new anticancer agents with fewer side effects for the treatment of this condition. A patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mouse model transplanted with cancer tissue from patients is widely accepted as the best preclinical model for evaluating the anticancer potential of drug candidates. Fucoxanthin (Fx) is a highly polar carotenoid contained in edible marine brown algae and possesses anticancer activity. However, there is a lack of data on the effects of Fx in PDX models. We investigated the anticancer effects of Fx in PDX mice transplanted with cancer tissues derived from a patient with PC (PC-PDX) using comprehensive protein expression assay. Fx administration (0.3%Fx diet) ad libitum for 27 days significantly abrogated tumor development (0.4-fold) and induced tumor differentiation in PC-PDX mice, as compared to those in the control mice. Fx significantly upregulated the expression of non-glycanated DCN (2.4-fold), tended to increase the expressions of p-p38(Thr180/Tyr182) (1.6-fold) and pJNK(Thr183/Tyr185) (1.8-fold), significantly downregulated IGFBP2 (0.6-fold) and EpCAM (0.7-fold), and tended to decrease LCN2 (0.6-fold) levels in the tumors of the PC-PDX mice, as compared to those in the control mice. Some of the protein expression patterns were consistent with the in vitro experiments. That is, treatment of fucoxanthinol (FxOH), a prime metabolite derived from dietary Fx, enhanced non-glycanated DCN, p-p38(Thr180/Tyr182), and pJNK(Thr183/Tyr185) levels in human PC PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells.These results suggested that Fx exerts anticancer and differentiation effects in a PC-PDX mice through alterations of some multifunctional molecules.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Organization of Contemporary Biobanks for Translational Cancer Research
by
Vasiliki Gkioka, Olga Balaoura, Maria Goulielmaki and Constantin N. Baxevanis
Onco 2023, 3(4), 205-216; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3040015 - 22 Sep 2023
Abstract
Cancer biobanks have a crucial role in moving forward the field of translational cancer research and, therefore, have been promoted as indispensable tools for advancing basic biomedical research to preclinical and clinical research, ultimately leading to the design of clinical trials. Consequently, they
[...] Read more.
Cancer biobanks have a crucial role in moving forward the field of translational cancer research and, therefore, have been promoted as indispensable tools for advancing basic biomedical research to preclinical and clinical research, ultimately leading to the design of clinical trials. Consequently, they play an essential role in the establishment of personalized oncology by combining biological data with registries of detailed medical records. The availability of complete electronic medical reports from individualized patients has led to personalized approaches for diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction. To this end, identifying risk factors at early time points is important for designing more effective treatments unique for each patient. Under this aspect, biobanking is essential for accomplishing improvements in the field of precision oncology via the discovery of biomarkers related to cellular and molecular pathways regulating oncogenic signaling. In general terms, biological samples are thought to reflect the patient’s disease biology, but under certain conditions, these may also represent responses to various biological stresses. Divergent collection, handling, and storage methods may significantly change biosamples’ inherent biological properties. The alteration or loss of biological traits post-collection would lead to the discovery of nonreliable biomarkers and, consequently, to irreproducible results, thus constituting a formidable obstacle regarding the successful translation of preclinical research to clinical approaches. Therefore, a necessary prerequisite for successful biobanking is that the stored biological samples retain their biological characteristics unchanged. The application of quality standards for biospecimen collection and storage could be useful for generating encouraging preclinical data leading to the successful translation to clinical treatment approaches. Herein, we aim to comprehensively review the issues linked to biobank implementation for promoting cancer research.
Full article
Open AccessReview
ROS1-Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinoma: From Molecular Genetics to Target Therapy
by
Ugo Testa, Germana Castelli and Elvira Pelosi
Onco 2023, 3(3), 189-204; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3030014 - 22 Aug 2023
Abstract
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a heterogeneous group of diseases accounting for 80–85% of lung cancers. A molecular subset of NSCLC (1–2.5%) harboring molecular rearrangements of the tyrosine kinase gene ROS1 is defined as ROS1-positive and is almost exclusively diagnosed in patients with
[...] Read more.
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a heterogeneous group of diseases accounting for 80–85% of lung cancers. A molecular subset of NSCLC (1–2.5%) harboring molecular rearrangements of the tyrosine kinase gene ROS1 is defined as ROS1-positive and is almost exclusively diagnosed in patients with lung adenocarcinoma histology, predominantly nonsmokers. ROS1 is constitutively activated by molecular rearrangements and acts as a main driver of lung carcinogenesis. These findings have provided a strong rationale for the clinical use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors that target ROS1; these inhibitors block ROS1-positive NSCLC and provide clinical benefit. Crizotinib was introduced as a first-line treatment for ROS1-positive NSCLCs, with 75–80% of patients responding and a PFS of about 20 months. More recently developed ROS1-TKIs, such as entrectinib, lorlatinib, taletrectinib, repotrectinib and NVL-520, are active against some resistant ROS1 mutants appearing during crizotinib therapy and more active against brain metastases, frequent in ROS1-positive NSCLC. The development of resistance mechanisms represents a great limitation for the targeted treatment of ROS1-positive NSCLCs with TKIs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Challenge and Future Advances for Lung Cancer: Genetics, Instrumental Diagnosis and Treatment 2.0)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning-Based Model Helps to Decide which Patients May Benefit from Pancreatoduodenectomy
by
Emanuel Vigia, Luís Ramalhete, Edite Filipe, Luís Bicho, Ana Nobre, Paulo Mira, Maria Macedo, Catarina Aguiar, Sofia Corado, Beatriz Chumbinho, Jorge Balaia, Pedro Custódio, João Gonçalves and Hugo P. Marques
Onco 2023, 3(3), 175-188; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3030013 - 10 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is an invasive tumor with similar incidence and mortality rates. Pancreaticoduodenectomy has morbidity and mortality rates of up to 60% and 5%, respectively. The purpose of our study was to assess preoperative features contributing to unfavorable 1-year survival prognosis. Study
[...] Read more.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is an invasive tumor with similar incidence and mortality rates. Pancreaticoduodenectomy has morbidity and mortality rates of up to 60% and 5%, respectively. The purpose of our study was to assess preoperative features contributing to unfavorable 1-year survival prognosis. Study Design: Retrospective, single-center study evaluating the impact of preoperative features on short-term survival outcomes in head PDAC patients. Forty-four prior features of 172 patients were tested using different supervised machine learning models. Patient records were randomly divided into training and validation sets (80–20%, respectively), and model performance was assessed by area under curve (AUC) and classification accuracy (CA). Additionally, 33 patients were included as an independent revalidation or holdout dataset group. Results: Eleven relevant features were identified: age, sex, Ca-19-9, jaundice, ERCP with biliary stent, neutrophils, lymphocytes, lymphocyte/neutrophil ratio, neoadjuvant treatment, imaging tumor size, and ASA. Tree regression (tree model) and logistic regression (LR) performed better than the other tested models. The tree model had an AUC = 0.92 and CA = 0.85. LR had an AUC = 0.74 and CA = 0.78, allowing the development of a nomogram based on absolute feature significance. The best performance model was the tree model which allows us to have a decision tree to help clinical decisions. Discussion and conclusions: Based only on preoperative data, it was possible to predict 1-year survival (91.5% vs. 78.1% alive and 70.9% vs. 76.6% deceased for the tree model and LR, respectively). These results contribute to informed decision-making in the selection of which patients with PDAC can benefit from pancreatoduodenectomy. A machine learning algorithm was developed for the recognition of unfavorable 1-year survival prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. This will contribute to the identification of patients who would benefit from pancreatoduodenectomy. In our cohort, the tree regression model had an AUC = 0.92 and CA = 0.85, whereas the logistic regression had an AUC = 0.74 and CA = 0.78. To further inform decision-making, a decision tree based on tree regression was developed.
Full article
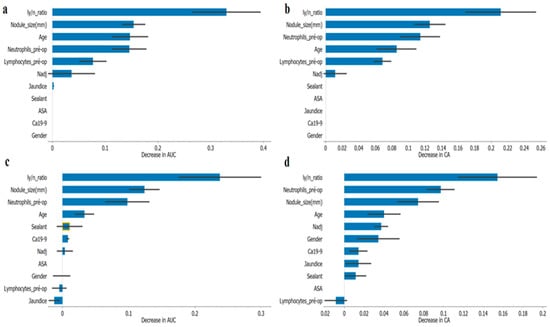
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Peripheral Blood CD8+ T-Lymphocyte Subsets Are Associated with Prognosis in Prostate Cancer Patients
by
Constantin N. Baxevanis, Savvas Stokidis, Maria Goulielmaki, Angelos D. Gritzapis and Sotirios P. Fortis
Onco 2023, 3(3), 165-174; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3030012 - 26 Jul 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Various studies have reported associations between frequencies of total peripheral blood lymphocytes and prostate cancer prognosis, but none so far has addressed the prognostic role of CD8+ T-lymphocyte subsets. Methods: A total of 43 prostate cancer patients with metastatic disease and 81
[...] Read more.
Background: Various studies have reported associations between frequencies of total peripheral blood lymphocytes and prostate cancer prognosis, but none so far has addressed the prognostic role of CD8+ T-lymphocyte subsets. Methods: A total of 43 prostate cancer patients with metastatic disease and 81 patients with non-metastatic disease were included in this study. Flow cytometry analyses were employed for determining the frequencies of peripheral CD8+ T-lymphocyte subsets. Results: Statistically significant lower levels of terminally differentiated effector (TEMRA) cells in patients with non-metastatic disease vs. patients with metastatic disease were observed. Central memory (CM) and effector memory (EM) CD8+ subsets, were found to be significantly higher in patients with non-metastatic disease vs. patients with metastatic disease. A similar profile was revealed when these CD8+ subsets were analyzed based on the patients’ Gleason scores, as well as by combined disease stage (i.e., non-metastatic vs. metastatic disease) and Gleason score. Conclusions: Peripheral blood-derived CD8+ T-lymphocyte memory subsets could function as biomarkers for the prognosis of PCa.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
NUP98 Rearrangements in AML: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
by
Sagarajit Mohanty
Onco 2023, 3(3), 147-164; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3030011 - 18 Jul 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
NUP98 fusions constitute a small subgroup of AML patients and remain a high-risk AML subtype. There are approximately 30 types of NUP98 fusions identified in AML patients. These patients show resistance to currently available therapies and poor clinical outcomes. NUP98 fusions with different
[...] Read more.
NUP98 fusions constitute a small subgroup of AML patients and remain a high-risk AML subtype. There are approximately 30 types of NUP98 fusions identified in AML patients. These patients show resistance to currently available therapies and poor clinical outcomes. NUP98 fusions with different fusion partners have oncogenic transformation potential. This review describes how the NUP98 gene acquires oncogenic properties after rearrangement with multiple partners. In the mechanistic part, the formation of nuclear bodies and dysregulation of the HoxA/Meis1 pathway are highlighted. This review also discusses mutational signatures among NUP98 fusions and their significance in leukemogenesis. It also discusses the clinical implications of NUP98 fusions and their associated mutations in AML patients. Furthermore, it highlights therapeutic vulnerabilities in these leukemias that can be exploited as therapeutic strategies. Lastly, this review discusses the gaps in our knowledge regarding NUP98 fusions in AML, as well as future research opportunities.
Full article
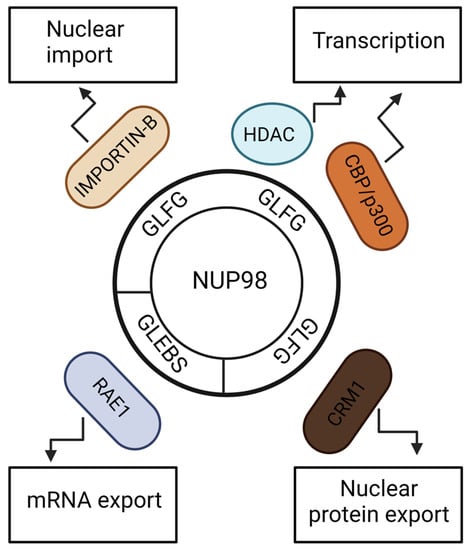
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Precision Medicine Revolutionizing Esophageal Cancer Treatment: Surmounting Hurdles and Enhancing Therapeutic Efficacy through Targeted Drug Therapies
by
Poojarani Panda, Henu Kumar Verma and Lakkakula V. K. S. Bhaskar
Onco 2023, 3(3), 127-146; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3030010 - 15 Jul 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Esophageal cancer is a formidable challenge in the realm of cancer treatment. Conventional methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy have demonstrated limited success rates in managing this disease. In response, targeted drug therapies have emerged as a promising strategy to improve outcomes
[...] Read more.
Esophageal cancer is a formidable challenge in the realm of cancer treatment. Conventional methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy have demonstrated limited success rates in managing this disease. In response, targeted drug therapies have emerged as a promising strategy to improve outcomes for patients. These therapies aim to disrupt specific pathways involved in the growth and development of esophageal cancer cells. This review explores various drugs used to target specific pathways, including cetuximab and monoclonal antibodies (gefitinib) that target the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), trastuzumab that targets human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2), drugs targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), mTOR inhibitors, and cMET inhibitors. Additionally, the article discusses the impact of drug resistance on the effectiveness of these therapies, highlighting factors such as cancer stem cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, immune-inflammatory cells, cytokines, hypoxia, and growth factors. While drug targeting approaches do not provide a complete cure for esophageal cancer due to drug resistance and associated side effects, they offer potential for improving patient survival rates.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Onco: A Promising Player Amidst Oncology Journals
by
Constantin N. Baxevanis
Onco 2023, 3(2), 125-126; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3020009 - 01 Jun 2023
Abstract
As the new Editor-in-Chief of the journal, I believe that I must continue the efforts of my predecessor even more actively and with greater enthusiasm and dedication so that the journal becomes a pole of attraction for the publication of excellent studies of
[...] Read more.
As the new Editor-in-Chief of the journal, I believe that I must continue the efforts of my predecessor even more actively and with greater enthusiasm and dedication so that the journal becomes a pole of attraction for the publication of excellent studies of basic, translational and clinical research for the treatment of cancer [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
A Comprehensive Review on the Role of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) as a Biomarker in Extra-Mammary and Extra-Gastric Cancers
by
Fnu Amisha, Paras Malik, Prachi Saluja, Nitesh Gautam, Tanvi Harishbhai Patel, Arya Mariam Roy, Sunny R. K. Singh and Sindhu Janarthanam Malapati
Onco 2023, 3(2), 96-124; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3020008 - 26 May 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The human epidermal growth factor receptors (HERs) are expressed abundantly in the human body. The tumorigenic potential of HER2/neu is linked to its overexpression, amplification or somatic mutation. The HER2 gene amplification leading to protein overexpression has been reported in 25–30% of breast
[...] Read more.
The human epidermal growth factor receptors (HERs) are expressed abundantly in the human body. The tumorigenic potential of HER2/neu is linked to its overexpression, amplification or somatic mutation. The HER2 gene amplification leading to protein overexpression has been reported in 25–30% of breast cancers and 10–30% of gastric/gastroesophageal cancers. While HER2 is a well-documented predictive, prognostic, and therapeutic marker in breast and gastric/gastroesophageal cancers, its relevance has also been demonstrated in multiple other malignancies. In this article, we will conduct an extensive review of current data pertaining to HER2 amplification, overexpression, or mutation in cancers other than breast and gastric cancers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Tumor Immune Microenvironment Signaling Networks Supporting Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
by
Lawrence P. McKinney, Rajesh Singh, I. King Jordan, Sooryanarayana Varambally, Eric B. Dammer and James W. Lillard, Jr.
Onco 2023, 3(2), 81-95; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3020007 - 10 Apr 2023
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common cause of cancer death in American men. Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is the most lethal form of PCa and preferentially metastasizes to the bones through incompletely understood molecular mechanisms. Herein, we processed RNA sequencing
[...] Read more.
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common cause of cancer death in American men. Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is the most lethal form of PCa and preferentially metastasizes to the bones through incompletely understood molecular mechanisms. Herein, we processed RNA sequencing data from patients with mCRPC (n = 60) and identified 14 gene clusters (modules) highly correlated with mCRPC bone metastasis. We used a novel combination of weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and upstream regulator and gene ontology analyses of clinically annotated transcriptomes to identify the genes. The cyan module (M14) had the strongest positive correlation (0.81, p = 4 × 10−15) with mCRPC bone metastasis. It was associated with two significant biological pathways through KEGG enrichment analysis (parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion, and action and protein digestion and absorption). In particular, we identified 10 hub genes (ALPL, PHEX, RUNX2, ENPP1, PHOSPHO1, PTH1R, COL11A1, COL24A1, COL22A1, and COL13A1) using cytoHubba of Cytoscape. We also found high gene expression for collagen formation, degradation, absorption, cell-signaling peptides, and bone regulation processes through Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Molecular Profiling and Identification of Molecular Signatures Associated with Tissue Development, Tumorigenesis, and Anticancer Agents’ Action)
►▼
Show Figures
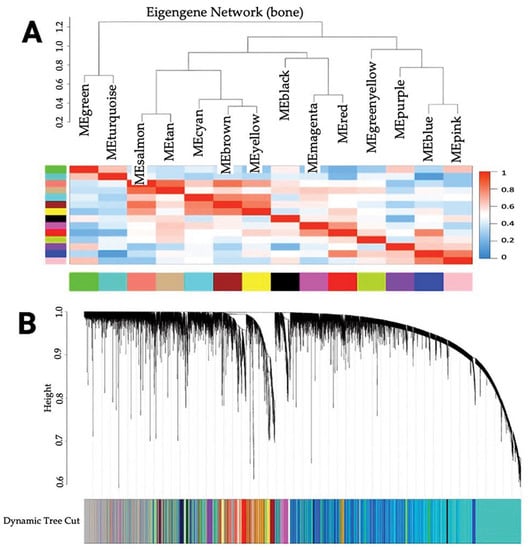
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CT Radiomics and Clinical Feature Model to Predict Lymph Node Metastases in Early-Stage Testicular Cancer
by
Catharina Silvia Lisson, Sabitha Manoj, Daniel Wolf, Jasper Schrader, Stefan Andreas Schmidt, Meinrad Beer, Michael Goetz, Friedemann Zengerling and Christoph Gerhard Sebastian Lisson
Onco 2023, 3(2), 65-80; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3020006 - 10 Apr 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
Accurate retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis (LNM) prediction in early-stage testicular germ cell tumours (TGCTs) harbours the potential to significantly reduce over- or undertreatment and treatment-related morbidity in this group of young patients as an important survivorship imperative. We investigated the role of computed
[...] Read more.
Accurate retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis (LNM) prediction in early-stage testicular germ cell tumours (TGCTs) harbours the potential to significantly reduce over- or undertreatment and treatment-related morbidity in this group of young patients as an important survivorship imperative. We investigated the role of computed tomography (CT) radiomics models integrating clinical predictors for the individualised prediction of LNM in early-stage TGCT. Ninety-one patients with surgically proven testicular germ cell tumours and contrast-enhanced CT were included in this retrospective study. Dedicated radiomics software was used to segment 273 retroperitoneal lymph nodes and extract features. After feature selection, radiomics-based machine learning models were developed to predict LN metastasis. The robustness of the procedure was controlled by 10-fold cross-validation. Using multivariable logistic regression modelling, we developed three prediction models: a radiomics-only model, a clinical-only model, and a combined radiomics–clinical model. The models’ performances were evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Finally, decision curve analysis was performed to estimate the clinical usefulness of the predictive model. The radiomics-only model for predicting lymph node metastasis reached a greater discrimination power than the clinical-only model, with an AUC of 0.87 (±0.04; 95% CI) vs. 0.75 (±0.08; 95% CI) in our study cohort. The combined model integrating clinical risk factors and selected radiomics features outperformed the clinical-only and the radiomics-only prediction models, and showed good discrimination with an area under the curve of 0.89 (±0.03; 95% CI). The decision curve analysis demonstrated the clinical usefulness of our proposed combined model. The presented combined CT-based radiomics–clinical model represents an exciting non-invasive tool for individualised LN metastasis prediction in testicular germ cell tumours. Multi-centre validation is required to generate high-quality evidence for its clinical application.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Artificial Intelligence in Cancer, Biology and Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
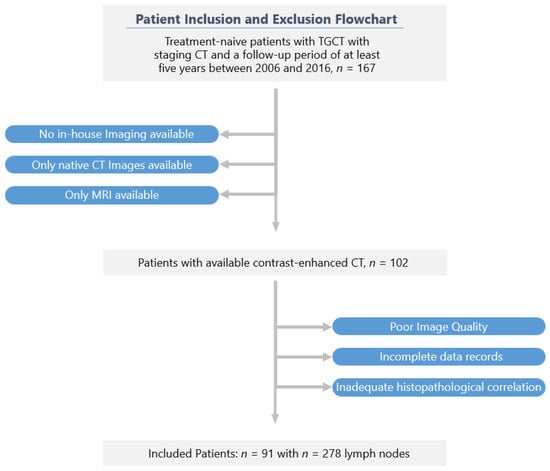
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Chart Diagnostic System Improves the Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
by
Ayako Nomura, Takayuki Ishida, Hiroshi Hijioka, Takuya Yoshimura, Hajime Suzuki, Eturo Nozoe and Norifumi Nakamura
Onco 2023, 3(1), 53-64; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3010005 - 07 Feb 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Purpose: To establish a diagnosis method based on imaging findings and histopathological factors associated with cervical lymph node metastasis. Methods: A total of 1587 cervical lymph nodes that were detected using imaging tools in 73 OSCC patients who underwent surgical treatment were enrolled
[...] Read more.
Purpose: To establish a diagnosis method based on imaging findings and histopathological factors associated with cervical lymph node metastasis. Methods: A total of 1587 cervical lymph nodes that were detected using imaging tools in 73 OSCC patients who underwent surgical treatment were enrolled to evaluate the association between imaging findings (long diameter, short diameter, long–short ratio, US findings (hilum and internal echo), contrast effect with enhanced CT, standardized uptake value (SUV) max and SUV average with 18F FDG-Positron Emission Tomography (PET)) and metastatic cervical lymph nodes. In 57 OSCC patients, biopsy specimens were evaluated for histopathologic factors (budding score, lymphatic invasion, vascular invasion, nerve invasion, and YK classification) and the presence of cervical lymph node metastases. Cervical lymph node metastasis was determined based on histopathological examination of the lymph nodes of patients with no metastasis observed 3 years after primary surgery. Results: In total, 22 of the 73 patients had cervical lymph node metastasis pathologically. In the comparison of the presence of metastatic lymph nodes, univariate analysis showed significant differences in cervical lymph node long and short diameter, long/short ratio, internal echo, rim enhancement, SUV max, SUV average, budding score, and vascular invasion. Multivariable analysis showed significant differences in internal echo, rim enhancement, SUV max, and budding score. Conclusions: We propose a chart diagnostic system that combines imaging and histopathological findings to improve the diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis.
Full article
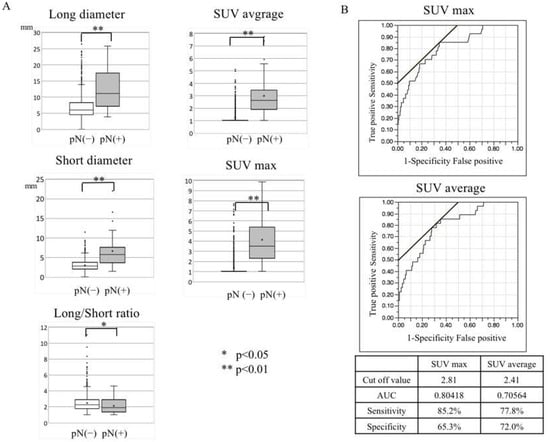
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fractionated Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (FVMAT) for Oligometastatic Brain Tumor
by
Chi-Yuan Yeh, Peng-An Lai, Fang-Hui Liu and Chin-Chiao He
Onco 2023, 3(1), 43-52; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3010004 - 02 Feb 2023
Abstract
Intracranial metastasis is very common in adult cancer patients with an overall incidence of approximately 10–40%. The most common primary tumors responsible for this in adults are lung and breast cancer. Brain metastasis signifies a grave prognosis, with a median survival of 6
[...] Read more.
Intracranial metastasis is very common in adult cancer patients with an overall incidence of approximately 10–40%. The most common primary tumors responsible for this in adults are lung and breast cancer. Brain metastasis signifies a grave prognosis, with a median survival of 6 to 12 months. They are traditionally managed with palliative care and whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT). WBRT was an effective method to control brain metastases, decreasing corticosteroid use to control tumor-associated edema, and potentially improving overall survival; however, WBRT was found to be associated with a serious neurocognitive degeneration, this adverse effect (AE) follows a biphasic pattern beginning with a transient decline in mental functioning at around 4 months post-treatment, slowly leading to an irreversible neurologic impairment from months to years later. Evidence supports that WBRT can cause radiation injury to the hippocampus, which in turn will lead to a decline in neurocognitive function (NCF). Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is a relatively new type of image-guided radiotherapy that treats multiple brain metastasis simultaneously and efficiently with less neurocognitive sequelae. Eighteen cancer patients with limited (≤5 brain tumors) or oligometastatic brain tumor were treated with a spatially fractionated VMAT technique for a total dose of 30 Gy in 10 fractions, the patients tolerated the VMAT treatment with no radiation-induced neurologic toxicities after a mean follow-up of 1 year. Local control rate was 84%, and the median survival for these 19 patients was 11.3 months (range: 9.1–22.4 months). In conclusion, the VMAT is a suitable technique that is a safe and effective treatment for brain oligometastases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Cancer Biology and Radiation Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures
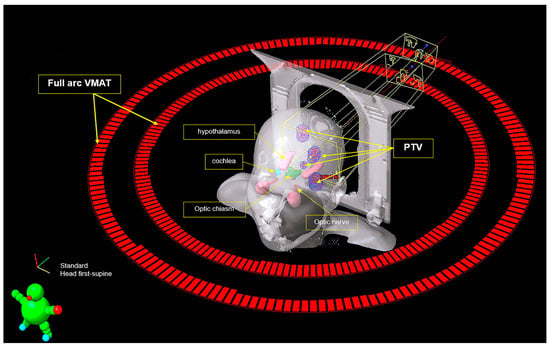
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Risk Factors and Prevention of Gastric Cancer Development—What Do We Know and What Can We Do?
by
Paulina Helisz, Weronika Gwioździk, Karolina Krupa-Kotara, Mateusz Grajek, Joanna Głogowska-Ligus and Jerzy Słowiński
Onco 2023, 3(1), 26-42; https://doi.org/10.3390/onco3010003 - 30 Jan 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common causes of cancer-related deaths. Gastric tumors show a high aggressiveness, which, in turn, contributes to a low survival rate of fewer than 12 months. Considering the above, it was decided to review the current
[...] Read more.
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common causes of cancer-related deaths. Gastric tumors show a high aggressiveness, which, in turn, contributes to a low survival rate of fewer than 12 months. Considering the above, it was decided to review the current scientific studies that indicate the potential prevention of gastric cancer and clarify the relationship between gastric cancer and the composition of the microorganisms inhabiting the human body. Accordingly, a review paper was prepared based on 97 scientific sources from 2011 to 2022. Particular attention was paid to the most recent scientific studies from the last five years, which account for more than 80% of the cited sources. Taking care of one’s overall health, including undertaking treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection, and following a diet high in anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory ingredients are the most important factors in reducing the risk of developing gastric cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Non Herbal Nutraceutical, Probiotic, Vitamins and Fatty Acids in Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
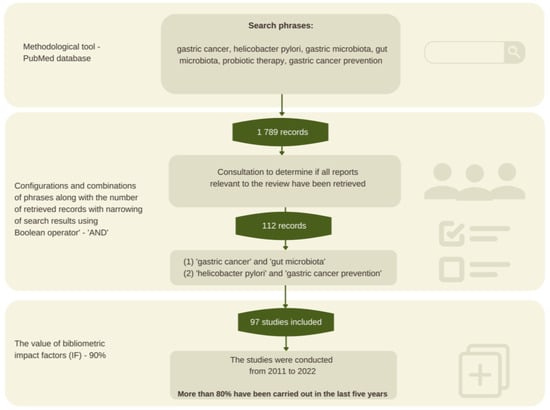
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cancers, Current Oncology, JCM, Onco
Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Topic Editors: Shenglin Huang, Linlin Guo, Jialei WangDeadline: 20 July 2024
Topic in
Biology, Cancers, Current Oncology, Diseases, Onco
miRNAs in Pathophysiology of Disease
Topic Editors: Francesca Orso, Roberto Coppo, Federico VirgaDeadline: 12 November 2024
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, JCM, JPM, Onco
Targeting Tumor Microvasculature of Malignant Metastatic Tumor
Topic Editors: Prabhu Thirusangu, Vigneshwaran Vellingiri, Prabhakar ThippegowdaDeadline: 25 November 2024
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Cells, IJMS, Onco
Advances in Colorectal Cancer Therapy
Topic Editors: Niki Christou, Mireille Verdier, Fabrice LallouéDeadline: 20 December 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Onco
Current Challenge and Future Advances for Lung Cancer: Genetics, Instrumental Diagnosis and Treatment 2.0
Guest Editor: Giovanni VicidominiDeadline: 15 August 2024
Special Issue in
Onco
Targeting of Tumor Dormancy Pathway
Guest Editors: Athanassios Kotsinas, Constantin N. BaxevanisDeadline: 31 October 2024
Special Issue in
Onco
The Evolving Landscape of Contemporary Cancer Therapies
Guest Editor: Constantin N. BaxevanisDeadline: 15 November 2024