Journal Description
Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine
Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal of otorhinolaryngology, hearing and balance medical studies, published semiannually online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 16 days; acceptance to publication in 5.8 days (median values for MDPI journals in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
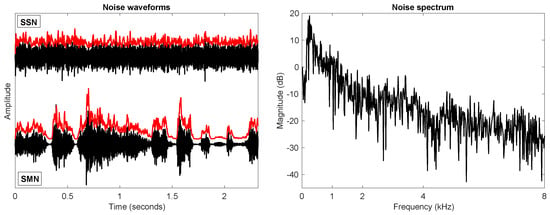
The Intelligibility Benefits of Modern Computer-Synthesized Speech for Normal-Hearing and Hearing-Impaired Listeners in Non-Ideal Listening Conditions
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010005 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Speech intelligibility is a concern for public health, especially in non-ideal listening conditions where listeners often listen to the target speech in the presence of background noise. With advances in technology, synthetic speech has been increasingly used in lieu of actual human voices
[...] Read more.
Speech intelligibility is a concern for public health, especially in non-ideal listening conditions where listeners often listen to the target speech in the presence of background noise. With advances in technology, synthetic speech has been increasingly used in lieu of actual human voices in human–machine interfaces, such as public announcement systems, answering machines, virtual personal assistants, and GPS, to interact with users. However, previous studies showed that speech generated by computer speech synthesizers was often intrinsically less natural and intelligible than natural speech produced by human speakers. In terms of noise, listening to synthetic speech is challenging for listeners with normal hearing (NH), not to mention for hearing-impaired (HI) listeners. Recent developments in speech synthesis have significantly improved the naturalness of synthetic speech. In this study, the intelligibility of speech generated by commercial synthesizers from Google, Amazon, and Microsoft was evaluated by both NH and HI listeners in different noise conditions. Compared to a natural female voice as the baseline, listeners’ listening performance suggested that some of the synthetic speech was significantly more intelligible even at rather adverse listening conditions for the NH cohort. Further acoustical analyses revealed that elongated vowel sounds and reduced spectral tilt were primarily responsible for improved intelligibility for NH, but not for HI due to their impairment at high frequencies and possible cognitive decline associated with aging.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Halmágyi–Curthoys Head Impulse (Thrust) Test with Romberg’s Test in Detection of Vestibular Hypofunctioning in Vertigo Patients
by
Santhosh Kumar Rajamani, Radha Srinivasan Iyer and Anusha Venkatraman
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010004 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aimed to compare the diagnostic efficacy of the Halmágyi–Curthoys head impulse (thrust) test and Romberg’s test in detecting vestibular hypofunctioning among two groups of 50 vertigo patients each; the two groups were randomly assigned. The assessment utilized the visual analog scale
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to compare the diagnostic efficacy of the Halmágyi–Curthoys head impulse (thrust) test and Romberg’s test in detecting vestibular hypofunctioning among two groups of 50 vertigo patients each; the two groups were randomly assigned. The assessment utilized the visual analog scale (VAS) to quantify subjective experiences of vertigo. The results revealed distinctive patterns in the detection of vestibular hypofunctioning, highlighting the strengths and limitations of each test. The Halmágyi–Curthoys head impulse test demonstrated utility in identifying vestibular hypofunctioning and its effect on vestibulo–ocular reflexes, particularly in cases with sudden head movements. Romberg’s test was useful in assessing postural instability in vestibular hypofunctioning due to defects in vestibulospinal reflexes. The integration of VAS scores provided valuable subjective insights into the patient experience. This comparative analysis contributes to a nuanced understanding of diagnostic tools for vestibular hypofunctioning in vertigo patients, offering clinicians valuable information for tailored assessments and interventions.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Body Image Concerns in People Who Underwent a Total Laryngectomy
by
Isabel Guimarães, Gabriela Torrejano, Raquel Aires, Filomena Gonçalves, Susana Vaz Freitas, Paula Correia, Cláudia Romeiro, Inês Silvestre, Rita Bom, Paulo Martins and Ana R. Santos
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010003 - 14 Feb 2024
Abstract
Background: Body image is a potential psychological burden after total laryngectomy (TL) with devastating effects on patients’ health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and communication. This study focused on TL patients to determine the prevalence of dissatisfied body image and whether they have poorer
[...] Read more.
Background: Body image is a potential psychological burden after total laryngectomy (TL) with devastating effects on patients’ health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and communication. This study focused on TL patients to determine the prevalence of dissatisfied body image and whether they have poorer HRQOL and difficulty adjusting to their new voice than TL patients with satisfied body image. It also aimed to investigate the potential predictors of body image. Methods: A multicenter cross-sectional study was conducted. For TL patients, the Body Image Scale (BIS), the European Organization for Research on Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire, Core and Neck Module (EORTC QLQ C30 and EORCT H&N35), and the Self-Experiences of Communication after Laryngeal cancer (SECEL) were used. Patients were categorized as dissatisfied with their body image if the BIS score was ≥8. Multiple regression analysis was performed using the BIS as the dependent measure and HRQOL (QLQ C30 and H& N35) and communication (SECEL) as independent variables. Results: Overall, 31.3% of TL patients had dissatisfied body image, significantly worse HRQOL, and difficulty adjusting to their new voice than patients with satisfied body image. The regression model showed that social eating and socializing (H&N35) and adjustment to their new voice (SECEL) were independent predictors of body image. The model explained 52% of the variance. Conclusions: Screening TL patients at risk for body image concerns may help develop effective interventions to optimize HRQOL and patient communication.
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
Cochlear Implantation in a Patient with Implanted Trigeminus Stimulator—Clinical Considerations for Using Two Different Electrical Stimulators in the Same Patient and Our Results
by
Daniel Polterauer, Maike Neuling, Sophia Stoecklein and Joachim Mueller
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010002 - 31 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Implantation of two electrical stimulators of different cranial nerves in one patient is rare. We report the case of a forty-seven-year-old patient already implanted with a trigeminus nerve stimulator. In addition, this patient suffered from hearing problems. In one ear, the patient was
[...] Read more.
Implantation of two electrical stimulators of different cranial nerves in one patient is rare. We report the case of a forty-seven-year-old patient already implanted with a trigeminus nerve stimulator. In addition, this patient suffered from hearing problems. In one ear, the patient was deaf. On the other side, the patient wore a bone conduction hearing aid to improve hearing. In this complex situation, we decided to check the possibility of cochlear implantation on the deaf side. Finally, we managed to provide electrical stimulation of the auditory pathway of the deaf ear to improve the patient’s hearing tests. In addition, this case report shows how the trigeminus stimulator interferes with the electrical stimulation in auditory evoked potentials measurement of the auditory brainstem and cortex via EABR (evoked auditory brainstem response) resp. EALR (evoked auditory late response).
Full article
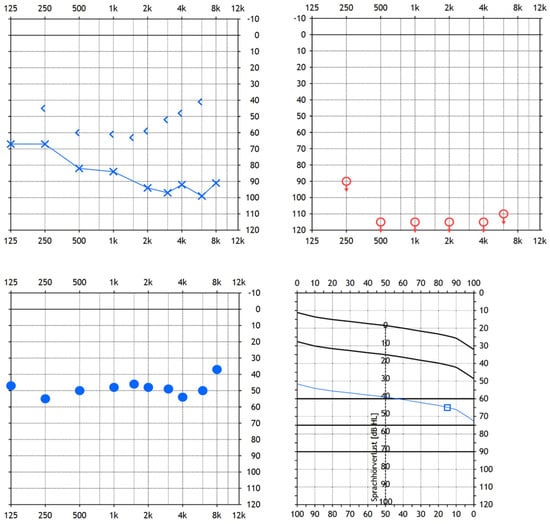
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond Ultrasound: Multimodal Cross-Sectional Imaging for Preoperative Imaging of Parotid Gland Tumors: A Primer for Radiology Trainees
by
Esmat Mahmoud, Eman Mahdi, Humera Ahsan, Joseph P. Cousins, Carlos Leiva-Salinas and Ayman Nada
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2024, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm5010001 - 23 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Even if the management of parotid gland tumors depends on the histopathological subtype, preoperative imaging of parotid gland tumors is clinically relevant. Preoperative imaging gives insight into the differentiation between benign and malignant tumors, which might potentially decrease the number of unnecessary aggressive
[...] Read more.
Even if the management of parotid gland tumors depends on the histopathological subtype, preoperative imaging of parotid gland tumors is clinically relevant. Preoperative imaging gives insight into the differentiation between benign and malignant tumors, which might potentially decrease the number of unnecessary aggressive surgeries. Characteristic imaging findings on cross-sectional imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can help narrow the differential diagnosis and guide the further management of patients presenting with parotid masses. While MRI is imperative for the determination of perineural spread, which is frequently encountered with malignant parotid tumors, CT is important for the evaluation of osseous invasion. Furthermore, multi-parametric MRI protocols provide insights into the tumor behavior and internal composition, which is helpful in the case of benign mixed tumors and others. While distant metastasis is uncommon with parotid neoplasms, PET/CT provides a valuable tool for the improved evaluation of loco-regional and distant metastatic disease. This article discusses the imaging features of common benign and malignant parotid tumors.
Full article
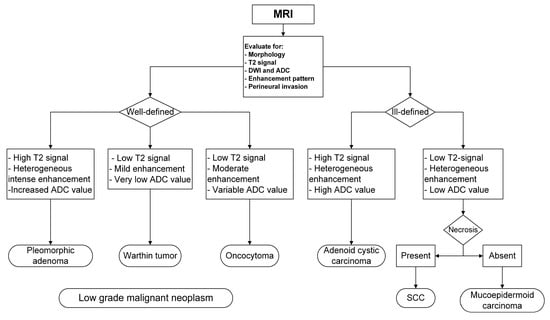
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Pharyngocutaneous Fistula after Laryngectomy: An Umbrella Systematic Review to Uncover Lacunae in Meta-Analyses
by
Karthik Nagaraja Rao, Ripudaman Arora, Ambesh Singh, Prajwal Dange and Nitin M. Nagarkar
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4020011 - 11 Oct 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective—The objective of this study was to systematically assess meta-analyses to determine the lacunae in the literature for PCF following laryngectomy. Methods—Bibliometric analysis were carried out on meta-analyses on PCF after total laryngectomy for laryngeal cancer in the PubMed database. Results—Twenty-four meta-analyses were
[...] Read more.
Objective—The objective of this study was to systematically assess meta-analyses to determine the lacunae in the literature for PCF following laryngectomy. Methods—Bibliometric analysis were carried out on meta-analyses on PCF after total laryngectomy for laryngeal cancer in the PubMed database. Results—Twenty-four meta-analyses were considered eligible and chosen for analysis. Six meta-analyses (25%) focused on the risk factors for PCF in TL. Four meta-analyses (16.6%) focused on the role of the onlay flap. Four meta-analyses (16.6%) focused on the timing of feed initiation. Three meta-analyses (12.5%) focused on using a stapler for pharyngeal closure. Two meta-analyses focused on types of pharyngeal reconstruction. Other meta-analyses analyzed the use of salivary bypass tubes, the method of pharyngeal closure, organ preservation protocols on PCF, primary and secondary TEP, and the effect of non-surgical treatment on PCF. Conclusion—Despite plenty of published meta-analyses, there is a lack of scrutiny on certain critical aspects of PCF.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Reconstruction of Conchal Defects after Chemically Assisted Dissection of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
by
Fabio Piazza, Annamaria Iole Palmeri, Andrea Bacciu, Giuseppe Spriano and Giuseppe Mercante
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(2), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4020010 - 15 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: En block resection of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the concha represents a reconstruction challenge, due to the complex topography and difficult access. Objective: The objective of the present paper is to describe the chemically assisted dissection (CADISS) of SCC originating in
[...] Read more.
Background: En block resection of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the concha represents a reconstruction challenge, due to the complex topography and difficult access. Objective: The objective of the present paper is to describe the chemically assisted dissection (CADISS) of SCC originating in the auricular concha and the following reconstruction of the conchal cavity with a post-auricular island flap (PIF), taking care to minimize injury to the donor site. Methods: Twenty-six patients having a diagnosis of SCC of the auricular concha were included in the study. ‘En bloc’ removal of the tumor was accomplished, leaving the adjacent conchal cartilage attached to the tumor and using the CADISS technique to preserve the deep perichondrium. A PIF was used to repair the auricular conchal defect. Results: Flaps were normal at 10 days and at 1-month follow-up. No tumor recurrence was observed. No complications were observed. According to the SCAR scale, good aesthetic outcomes were achieved in all cases, both at the auricular concha and at the donor site. Conclusion: CADISS facilitates the complete removal of the tumor with the preservation of the surrounding normal tissues. A post-auricular island flap can be easily pulled through a post-auricular tunnel to repair the defect and the donor site can be closed primarily.
Full article
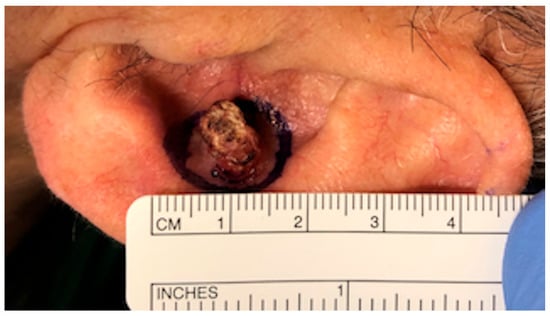
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Does the Remote Microphone Still Outperform the Pre-Processing Algorithms? A Group Study in Adult Nucleus Recipients
by
Francesco Lazzerini, Luca Baldassari, Adriana Angileri, Luca Bruschini, Stefano Berrettini and Francesca Forli
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(2), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4020009 - 12 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Despite the evolution of hearing aids and cochlear implants, noisy environments are reportedly still an important hurdle for persons with hearing loss, especially in the process of speech recognition. The development of pre-processing algorithms and the pairing with a wireless device can bring
[...] Read more.
Despite the evolution of hearing aids and cochlear implants, noisy environments are reportedly still an important hurdle for persons with hearing loss, especially in the process of speech recognition. The development of pre-processing algorithms and the pairing with a wireless device can bring relief to this situation, but it is still under scrutiny whether one or the other is more effective. The purpose of this study was to compare the benefits of speech recognition in a noisy environment by recipients of cochlear implants when using the pre-processing automatic algorithms or when using a wireless microphone. Twenty-nine participants were selected, aged 14 to 83, suffering from sensorineural hearing loss and recipients of cochlear implants for at least 6 months. The proprietary Cochlear Limited SCAN technology uses pre-processing algorithms to attenuate various noises; the wireless device MiniMic2 uses a 2.4 GHz connection to facilitate communications between the recipient and the signal source. Participants were asked to repeat 20 sentences randomly generated by the adaptive Italian Matrix Sentence Test, first while using the SCAN technology and then with the wireless MiniMic2. Both signal and noise were administered through a single loudspeaker set 1 m away from the subject. Significantly better results in speech recognition of noise were achieved with the wireless MiniMic2 when compared to the SCAN technology.
Full article
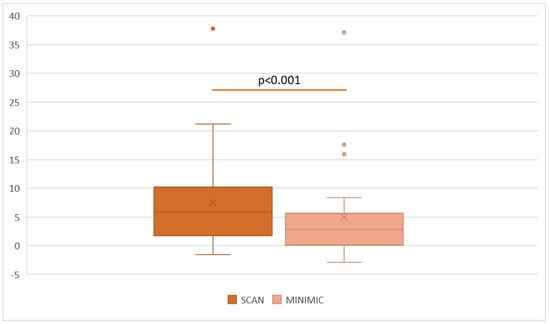
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bilateral Vocal Nodules Multidimensional Assessment: Pre- and Post- Speech Language Pathology Intervention
by
Rita Alegria, Susana Vaz-Freitas, Fátima Maia and Maria Conceição Manso
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(2), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4020008 - 05 Sep 2023
Abstract
(1) Background: Vocal fold nodules are bilateral lesions that can have an important negative impact on a person’s job performance, social interaction, and quality of life. This study aims to analyze multidimensional voice evaluation outcomes in a group of patients with bilateral vocal
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Vocal fold nodules are bilateral lesions that can have an important negative impact on a person’s job performance, social interaction, and quality of life. This study aims to analyze multidimensional voice evaluation outcomes in a group of patients with bilateral vocal fold nodules who underwent voice therapy. (2) Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed in 42 patients on the following voice evaluations, before and after voice therapy: visual-perceptual (video-laryngostroboscopic evaluation), auditory-perceptual voice analysis based on the GRBAS scale, and aerodynamic voice analysis. Data were collected from January 2001 to December 2019. Data analyses were performed with non-parametric tests (Wilcoxon test) using α = 0.05. (3) Results: The patient average age was 33.6.1 ± 10 years (range 19–60), and 95.2% were female. Voice therapy was delivered by an experienced speech-language pathologist once a week, with an average of 9.8 ± 3 appointments (range 8–17). Vocal fold lesions disappeared in 40.4% of the patients after voice therapy, especially in participants receiving early voice therapy (p = 0.035). When comparing pre- and post-therapy audio-perceptual results, all parameters were improved with statistical significance (p < 0.05) except for the asthenic voice scale. Aerodynamic parameters were all improved but without statistical significance (p > 0.05); (4) Conclusions: Early timing to initiate voice therapy after the onset of symptoms or diagnosis seems to be an important factor for the success of voice therapy (absence of vocal fold nodules).
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Effective Vowel Stimuli for Measuring Occlusion Effect in the Pediatric Population
by
Hemanth Narayan Shetty, Srirangam Vijayakumar Narasimhan and Sharath Mahanthesh
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(2), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4020007 - 17 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Past studies have reported that there are higher sound-pressure levels for each vowel in a child’s ear canal than those in adults due to reduced volume and a shorter ear canal. Furthermore, longer vocal tracts are associated with lower formant frequencies, and vice
[...] Read more.
Past studies have reported that there are higher sound-pressure levels for each vowel in a child’s ear canal than those in adults due to reduced volume and a shorter ear canal. Furthermore, longer vocal tracts are associated with lower formant frequencies, and vice versa. The structural differences in this regard may reflect the difference in the occlusion effect. Thus, the present study compares the sound pressure levels (SPLs) and first formant frequencies of children and adults with normal hearing and determines the best vowel stimulus to assess the occlusion effect. A repeated measures research design was utilized to investigate the best stimulus with which to measure the occlusion effect among children and adults. Group 1 included ten children, and Group 2 comprised ten adults with normal hearing. The SPLs at frequencies between 200 Hz and 1000 Hz for three uttered vowels, with steps of 100 Hz, were measured using a hearing aid analyzer. The recorded vowels were saved in a ‘.wav’ format for formant frequency analysis. Furthermore, a paired comparison method was used to identify the vowel stimulus that most effectively induced the occlusion effect. A significantly higher SPL was observed for children compared to adults for each vowel. The formant frequency F1 value was higher for children than adults for each vowel, constituting a significant finding. In the paired comparison, the occlusion effect was reported to be significantly greater with respect to the vowel /u/ among adults, while it was reported to be greater in relation to the vowel /i/ among children. The vowel /u/ was the best stimulus with which to assess the occlusion effect among adults. The vowel /i/ was the best stimulus with which to assess the occlusion effect among children.
Full article
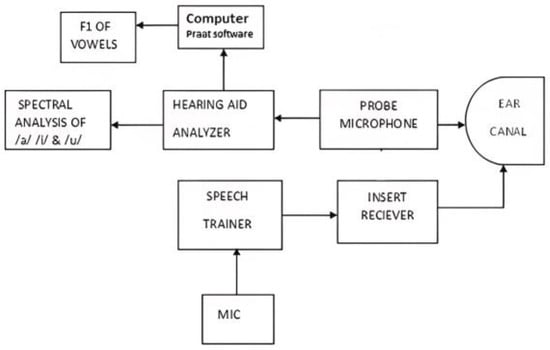
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Next-Generation Auditory Steady-State Responses in Normal-Hearing Adults: A Pilot Test–Retest Reliability Study
by
Hanan Hamad, Nilesh J. Washnik and Chandan H. Suresh
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(2), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4020006 - 10 Jul 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Auditory Steady-State Response (ASSR) provides objective and ear-specific information essential for early and appropriate intervention. Test–retest reliability is essential for audiological monitoring. The test–retest reliability of the ASSR has received limited attention. Only a handful of studies found in the literature investigated
[...] Read more.
The Auditory Steady-State Response (ASSR) provides objective and ear-specific information essential for early and appropriate intervention. Test–retest reliability is essential for audiological monitoring. The test–retest reliability of the ASSR has received limited attention. Only a handful of studies found in the literature investigated the test–retest reliability of old-generation ASSR using amplitude or mixed modulated stimuli. However, to our knowledge, no published reports have specifically examined the test–retest reliability of the next-generation ASSR using Chirp family stimuli as implemented in the Interacoustics Eclipse system. This pilot study investigated (a) the test–retest reliability of air conduction (AC) ASSR thresholds across two test sessions and (b) the relationship between differences in ASSR thresholds across two sessions to the residual noise levels in normal-hearing adults. Methods: Fifteen normal-hearing adults (12 females) (30 ears) with an average age of 28 years were recruited for the study. The ASSRs were recorded using a two-channel recording montage. The automatic default stimuli and recording protocol using 90 Hz ASSR, and the accuracy method (p < 0.01) as implemented in the Eclipse system is used to measure ASSR. Results: The study demonstrated strong test–retest reliability for ASSR across frequencies (500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz, and 4000 Hz). Notably, the highest reliability was observed at 500 Hz. The mean test–retest reliability of ASSR was found to be comparable to pure-tone thresholds, but the intra-subject variability is higher for ASSR compared to pure-tone thresholds. Additionally, no significant correlation was found between the difference in ASSR residual noise levels at the threshold and the difference in ASSR thresholds at all tested frequencies. Conclusion: The next-generation system demonstrated strong test–retest reliability across the frequencies examined in this pilot study. Particularly, an improvement in reliability was observed at 500 Hz compared to the old-generation ASSR. This enhancement can be attributed to the utilization of narrow-band CE-chirp stimuli, which generate large amplitude responses, and the implementation of an improved detection paradigm involving multiple harmonics spectral and phase analysis. This pilot study only enrolled adults with normal hearing, and future investigations should include a larger sample size comprising both normal-hearing and hearing-impaired individuals, as well as the pediatric population.
Full article
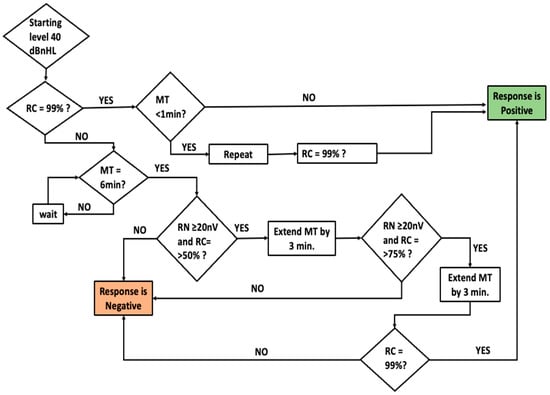
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Risk Factors for Voice Disorders among Fado Singers: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Pedro Pestana, Susana Vaz-Freitas and Maria Conceição Manso
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4010005 - 19 Jun 2023
Abstract
Fado is an urban Portuguese musical style rooted in popular culture. Previously found data suggests that Fado singers may have an increased risk of developing voice disorders. (1) Aim: To determine the risk factors for the development of voice disorders among Fado singers.
[...] Read more.
Fado is an urban Portuguese musical style rooted in popular culture. Previously found data suggests that Fado singers may have an increased risk of developing voice disorders. (1) Aim: To determine the risk factors for the development of voice disorders among Fado singers. (2) Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted through the administration of a questionnaire containing questions related to voice disorders in singers. The relationship between personal and social data, musical background, performance demands and habits, vocal health and wellbeing, and strategies to overcome voice problems are reported. Beyond a comprehensive characterization, odds ratios (ORs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the association with voice disorders were calculated through univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. (3) Results: The significant risk factors for voice disorders were as follows in decreasing order: nose-related disorders; decongestants or antihistamines; oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy; previous smoking habits; and vocal fatigue after performances. (4) Conclusion: These activities significantly increased the risk of developing voice disorders. The evidence from this study and the relative low prevalence of self-reported voice disorders suggest that these singers may develop a kind of protective combination of factors beyond the scope of this research.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Acoustic Quality of the External Environment: Indications on Questionnaire Structure for Investigating Subjective Perception
by
Anna Magrini, Gelsomina Di Feo and Andrea Cerniglia
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4010004 - 19 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The subjective judgment on the annoyance produced by noise is always an important tool to complete an investigation, and to find the best way for its reduction. Therefore, acoustic analyses for environmental improvement frequently combine objective measures with subjective surveys to gain a
[...] Read more.
The subjective judgment on the annoyance produced by noise is always an important tool to complete an investigation, and to find the best way for its reduction. Therefore, acoustic analyses for environmental improvement frequently combine objective measures with subjective surveys to gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem. The technical specification, concerning the “Assessment of noise annoyance by means of social and socio-acoustic surveys”, ISO/TS 15666 (revised in 2021), has represented a basis for these activities since 2003, when it aimed to obtain information about noise annoyance “at home”. The more recent ISO/TS 12913-2 (2018), aimed at soundscape studies, investigations and applications, provides guidelines for conducting social and socio-acoustic surveys to assess noise annoyance and, in particular, it gives detailed indications on data collection and reporting. The indications provided by the technical specifications represent a common guideline for addressing the implementation of a subjective survey in the acoustic field, and to make investigations as comparable as possible. However, they do not cover all the fields of acoustic subjective investigations. Therefore, to make the collection of information from questionnaires more effective, it is useful to have a broader review of the issues that need to be addressed. To support this type of activity, this paper collects and presents relevant observations for the design of subjective survey questionnaires focused on outdoor acoustic quality. Drawing on previous research studies and experiences, it provides a series of observations on the main aspects to be considered in order to structure multipurpose acoustic evaluation questionnaires, including discussion of the general considerations for questionnaire structure, administration methods, population sample characterization, question formulation, and classification. It also deals with specific indications related to acoustic evaluations, such as the characteristics of annoying noise, boundary conditions, subjective feelings, and source features.
Full article
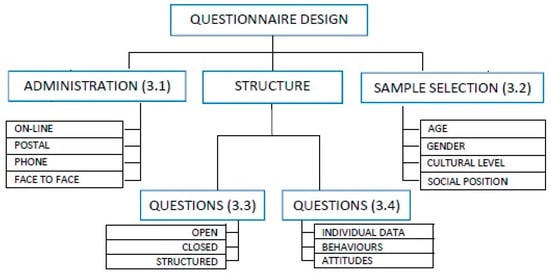
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Influence of Cochlear Volume on Temporal Changes of Impedance among Cochlear Implant Patients
by
Henrique F. Pauna, Maria Stella A. Do Amaral, Daniela S. Fonseca, Rodrigo Pessini, Denny M. Garcia, Jéssica Echeverria, Alexandre C. Guimarães, Vagner A. R. Da Silva and Miguel A. Hyppolito
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4010003 - 31 May 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: There is evidence that the cochlear volume may influence audiometric thresholds and CI electrodes’ impedance. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the impedance changes over time and correlate them to the residual volume of the cochlea. Methods: An MRI
[...] Read more.
Background: There is evidence that the cochlear volume may influence audiometric thresholds and CI electrodes’ impedance. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the impedance changes over time and correlate them to the residual volume of the cochlea. Methods: An MRI scan was performed via 3-D reconstruction before every surgery to obtain a residual volume for each ear. We performed repeated assessments of electrode impedance, both intra-operatively and post-implant, at the following intervals: 3 months, 6 months, and one year. The same type of perimodiolar array was implanted for each. Results: Thirty-four patients (10 (29.41%) male patients and 24 (70.59%) female patients) were evaluated. Patients received the implants between 2008 and 2017. The mean age of implantation was 13 ± 17.17 years, and the average of hearing thresholds improved after one year of the surgery. The mean cochlear volumes of the implanted ears were 68.16 ± 10.74 mm3 (right ear) and 56.54 ± 13.75 mm3 (left ear). We observed an increase in the basal electrodes’ impedance at the 3rd month. Yet, for the apical electrodes’ impedance, there was a decrease in averaged values. Conclusions: Post-operative impedance measurements were increased when compared to the intraoperatively measured basal values. Newly formed connective tissue is thought to be the cause of the higher impedance values.
Full article
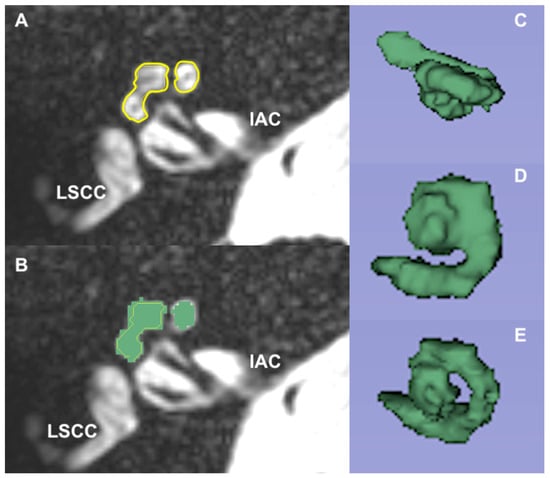
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Tinnitus, Aural Fullness, and Hearing Loss in a Patient with Acoustic Neuroma and Pituitary Macroadenoma
by
Mirko Aldè, Lorenzo Pignataro and Diego Zanetti
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4010002 - 27 Mar 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We report the case of a 51-year-old woman with multiple otologic and vestibular symptoms. She presented with two different types of tinnitus in her right ear, vertigo, and fluctuating aural symptoms in the left ear. She also complained of disequilibrium; chronic headache; hyperhidrosis;
[...] Read more.
We report the case of a 51-year-old woman with multiple otologic and vestibular symptoms. She presented with two different types of tinnitus in her right ear, vertigo, and fluctuating aural symptoms in the left ear. She also complained of disequilibrium; chronic headache; hyperhidrosis; amenorrhea; insomnia; broadened hands and feet; and widened, thickened, and stubby fingers. The patient underwent careful collection of medical history, otomiscroscopy, pure tone audiometry, tympanometry, reflex threshold measurements, vestibular assessments, blood tests, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and cone beam computed tomography (CBTC) of the head. The audiogram showed: (1) a mild low-to-mid frequency conductive hearing loss, and a sharply sloping sensorineural hearing loss above 4000 Hz in the right ear; (2) a mild low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss in the left ear. MRI with 3D FLAIR sequences detected an acoustic neuroma (7.4 mm × 5.2 mm) in the middle-third of the right internal auditory canal, a pituitary macroadenoma (13 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm) and left saccular hydrops. The CBCT scan documented an outbreak of otosclerosis (3 mm) around the fissula ante fenestram in the right ear. Therefore, acoustic neuroma (right ear), growth hormone-secreting macroadenoma of the pituitary gland, Menière’s disease (left ear), and otosclerosis (right ear) were diagnosed/strongly suspected. A watch-and-wait strategy was adopted for acoustic neuroma and otosclerosis, while transsphenoidal surgery was successfully performed to remove the pituitary macroadenoma. This case report confirms that multiple otologic disorders can occur simultaneously in the same patient, requiring prompt audiological and imaging evaluations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Occurrence of Human Defensins and S100 Proteins in Head and Neck Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) Entities: hBD3 and S100A4 as Potential Biomarkers to Evaluate Successful Surgical Therapy
by
Eva Dröge, Rainer Probstmeier, Matthias Wenghoefer and Jochen Winter
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2023, 4(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm4010001 - 22 Feb 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The goal of this study is the identification of potential marker molecules for characterizing different basal cell carcinoma entities, to help improve clinical decisions for surgical resection therapy. Methods: Three different entities, sclerodermiform, solid and superficial basal cell carcinomas, were subjected to
[...] Read more.
Background: The goal of this study is the identification of potential marker molecules for characterizing different basal cell carcinoma entities, to help improve clinical decisions for surgical resection therapy. Methods: Three different entities, sclerodermiform, solid and superficial basal cell carcinomas, were subjected to immunohistochemical microscopy and histomorphometric analyses for human α- (DEFA1/3; DEFA4) and β-defensins (hBD1/2/3) and special S100 proteins (S100A4/7/8/9). Thirty specimens of the three entities were evaluated. Analyses were performed by comparing tissue and cellular localization and staining intensities of tumorous with non-tumorous areas. Staining intensities were semiquantitatively examined by using an RGB-based model. Results: Human defensins are present in all three entities of basal cell carcinomas. They all show cytoplasmic immunostaining in cells of the epithelium, stroma and tumor. Notably, human β-defensin3 is accumulated in the cell nuclei of sclerodermiform and superficial basal cell carcinomas. S100A4 and A7 are undetectable in tumor regions. However, S100A4 occurs in cancer-associated stroma cells with nuclear staining in superficial basal cell carcinomas. Conclusion: Two candidates, namely hBD3 and S100A4, might be used as potential clinical tools for evaluating successful surgical resection therapy to avoid aesthetic and functional facial deformation.
Full article
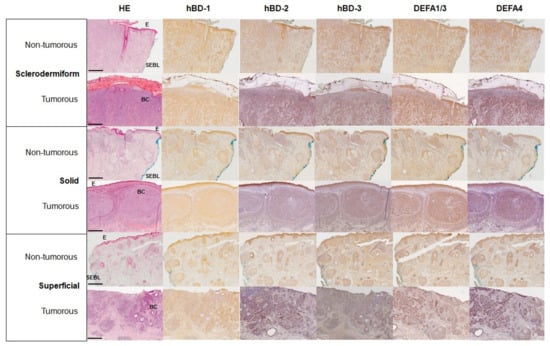
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Early Identification of Hearing Loss and Language Development at 32 Months of Age
by
Anne B. Harris, Elizabeth Seeliger, Christi Hess, Allison L. Sedey, Kayla Kristensen, Yen Lee and Winnie Chung
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2022, 3(4), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3040008 - 24 Oct 2022
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examines the relationship between the early identification of hearing loss and language outcomes for deaf/hard of hearing (D/HH) children, with bilateral or unilateral hearing loss and with or without additional disabilities. It was hypothesized that hearing loss identified by 3 months
[...] Read more.
This study examines the relationship between the early identification of hearing loss and language outcomes for deaf/hard of hearing (D/HH) children, with bilateral or unilateral hearing loss and with or without additional disabilities. It was hypothesized that hearing loss identified by 3 months of age would be associated with better language outcomes. Using a prospective, longitudinal design, 86 families completed developmental instruments at two time points: at an average age of 14.8 months and an average age of 32.1 months. Multiple regression examined how hearing loss identified by 3 months of age contributed to later language outcomes while controlling for developmental level at the first time point. Hearing loss identified by 3 months of age was positively associated with better language outcomes for D/HH children at 32 months of age; however, D/HH children still exhibited language delays, compared to normative scores for same-aged hearing peers for reported measures. Language outcomes of children with unilateral hearing loss were not better than those of children with mild-to-moderate bilateral hearing loss. Children with additional disabilities and more severe bilateral hearing loss had lower language scores than those without.
Full article
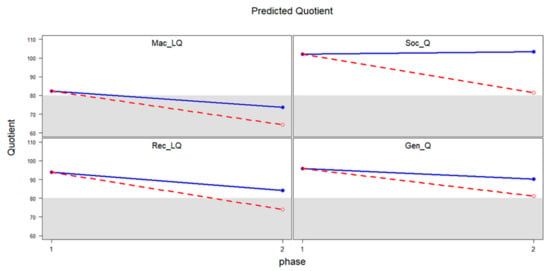
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Machine Learning in the Management of Lateral Skull Base Tumors: A Systematic Review
by
Kotaro Tsutsumi, Sina Soltanzadeh-Zarandi, Pooya Khosravi, Khodayar Goshtasbi, Hamid R. Djalilian and Mehdi Abouzari
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2022, 3(4), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3040007 - 28 Sep 2022
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The application of machine learning (ML) techniques to otolaryngology remains a topic of interest and prevalence in the literature, though no previous articles have summarized the current state of ML application to management and the diagnosis of lateral skull base (LSB) tumors. Subsequently,
[...] Read more.
The application of machine learning (ML) techniques to otolaryngology remains a topic of interest and prevalence in the literature, though no previous articles have summarized the current state of ML application to management and the diagnosis of lateral skull base (LSB) tumors. Subsequently, we present a systematic overview of previous applications of ML techniques to the management of LSB tumors. Independent searches were conducted on PubMed and Web of Science between August 2020 and February 2021 to identify the literature pertaining to the use of ML techniques in LSB tumor surgery written in the English language. All articles were assessed in regard to their application task, ML methodology, and their outcomes. A total of 32 articles were examined. The number of articles involving applications of ML techniques to LSB tumor surgeries has significantly increased since the first article relevant to this field was published in 1994. The most commonly employed ML category was tree-based algorithms. Most articles were included in the category of surgical management (13; 40.6%), followed by those in disease classification (8; 25%). Overall, the application of ML techniques to the management of LSB tumor has evolved rapidly over the past two decades, and the anticipated growth in the future could significantly augment the surgical outcomes and management of LSB tumors.
Full article
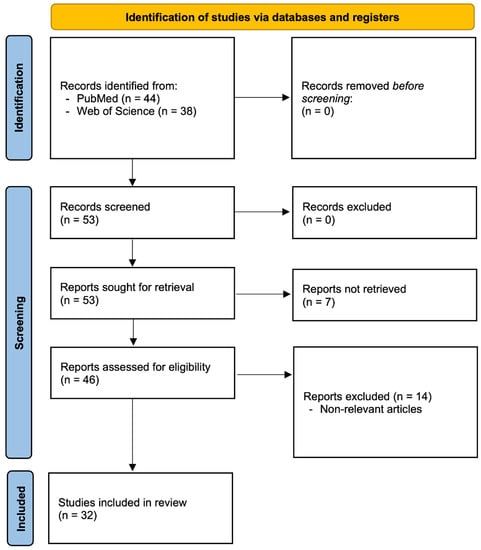
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Narrative Review of Auditory Categorisation and Its Potential Role in Tinnitus Perception
by
Dunja Vajsakovic, Michael R. D. Maslin and Grant D. Searchfield
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2022, 3(3), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3030006 - 29 Jul 2022
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Auditory categorisation is a phenomenon reflecting the non-linear nature of human perceptual spaces which govern sound perception. Categorisation training paradigms may reduce sensitivity toward training stimuli, decreasing the representation of these stimuli in auditory perceptual maps. Reduced cortical representation may have clinical implications
[...] Read more.
Auditory categorisation is a phenomenon reflecting the non-linear nature of human perceptual spaces which govern sound perception. Categorisation training paradigms may reduce sensitivity toward training stimuli, decreasing the representation of these stimuli in auditory perceptual maps. Reduced cortical representation may have clinical implications for conditions that arise from disturbances in cortical activation, such as tinnitus. This review explores the categorisation of sound, with a particular focus on tinnitus. The potential of categorisation training as a sound-based tinnitus therapy is discussed. A narrative review methodological framework was followed. Four databases (PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and ScienceDirect) were extensively searched for the following key words: categorisation, categorical perception, perceptual magnet effect, generalisation, and categorisation OR categorical perception OR perceptual magnet effect OR generalisation AND sound. Given the exploratory nature of the review and the fact that early works on categorisation are crucial to the understanding and development of auditory categorisation, all study types were selected for the period 1950–2022. Reference lists of articles were reviewed to identify any further relevant studies. The results of the review were catalogued and organised into themes. In total, 112 articles were reviewed in full, from which 59 were found to contain relevant information and were included in the review. Key themes identified included categorical perception of speech stimuli, warping of the auditory perceptual space, categorisation versus discrimination, the presence of categorisation across several modalities, and categorisation as an innate versus learned feature. Although a substantial amount of work focused on evaluating the effects of categorisation training on sound perception, only two studies investigated the effects of categorisation training on tinnitus. Implementation of a categorisation-based perceptual training paradigm could serve as a promising means of tinnitus management by reversing the changes in cortical plasticity that are seen in tinnitus, in turn altering the representation of sound within the auditory cortex itself. In the instance that the categorisation training is successful, this would likely mean a decrease in the level of activity within the auditory cortex (and other associated cortical areas found to be hyperactive in tinnitus) as well as a reduction in tinnitus salience.
Full article
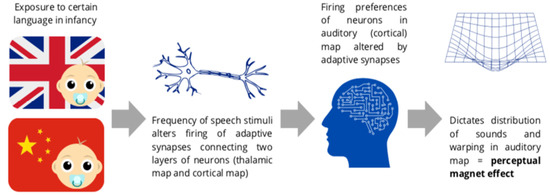
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The New Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) and Hearing Function in Adults
by
Maria Y. Boboshko, Ekaterina S. Garbaruk, Sof’ya M. Vikhnina, Larisa E. Golovanova, Elena A. Ogorodnikova, Anna V. Rabchevskaya and Ekaterina V. Zhilinskaia
J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2022, 3(2), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3020005 - 16 Jun 2022
Cited by 4
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, we assessed the impact of COVID-19 on the hearing function in adults. A total of 161 subjects were examined, and the results of a previous audiological examination of 24 patients were reviewed. Pure tone audiometry, impedancemetry, speech audiometry in quiet
[...] Read more.
In this study, we assessed the impact of COVID-19 on the hearing function in adults. A total of 161 subjects were examined, and the results of a previous audiological examination of 24 patients were reviewed. Pure tone audiometry, impedancemetry, speech audiometry in quiet and noise, the Binaural Fusion Test, the dichotic digits test, and a cognitive status examination were performed. A total of 81% of patients complained about hearing disorders, and 43% noted memory impairment. According to pure tone audiometry, 24% of the subjects had normal hearing, while 76% had some degree of hearing loss. No significant changes in hearing thresholds were found in comparison with audiological examinations performed before COVID-19. Disorder of monosyllabic words’ intelligibility in quiet was found in 33% of patients, and in 42% in noise, along with low indicators in the dichotic digits test in 54% of patients. Moreover, 71% of patients had low scores on the MoCA scale that indicated cognitive impairment. Conclusions: The deterioration of speech test scores in patients after COVID-19 can occur due to central auditory processing disorders (CAPD), memory impairment, or changes in cognitive status in general.
Full article
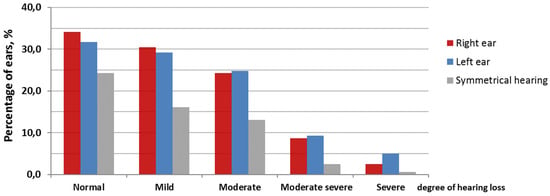
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JOHBM
Selected Papers from Annual Meeting of Japanese Society for Poster and Gait Research—JSPGR 2024
Guest Editor: Toshihisa MurofushiDeadline: 30 September 2024