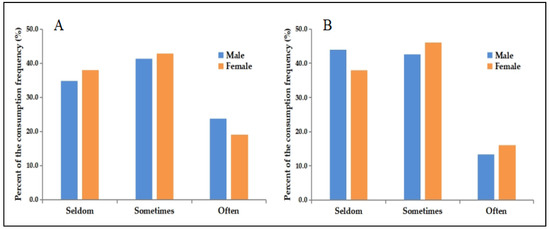
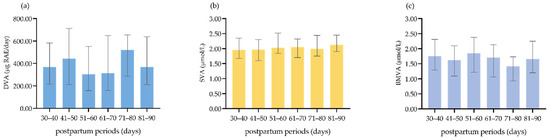
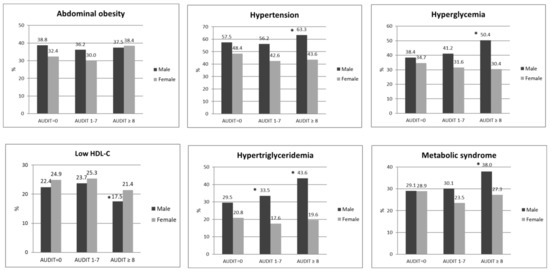
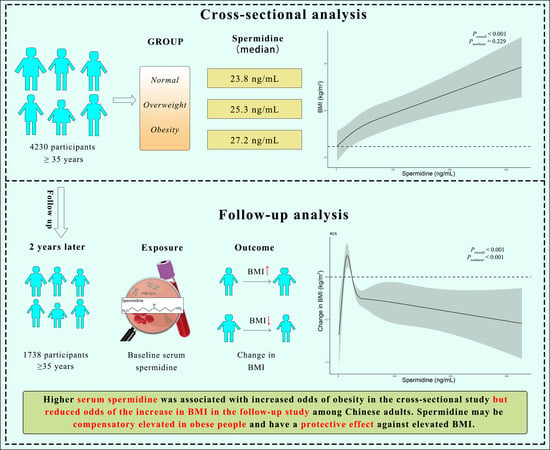
Nutritional Epidemiology among Chinese Populations
A topical collection in Nutrients (ISSN 2072-6643). This collection belongs to the section "Nutritional Epidemiology".
Viewed by 115789Editors
Interests: obesity; nutrition epidemiology; health education and promotion
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: balance dietary; metabolic syndrome; nutrition evaluation; nutrition education
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
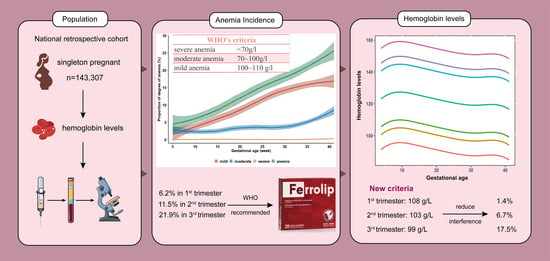
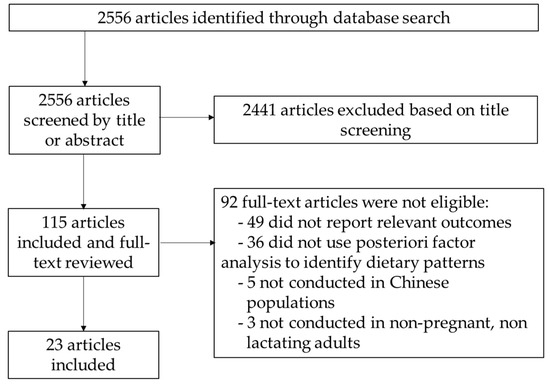
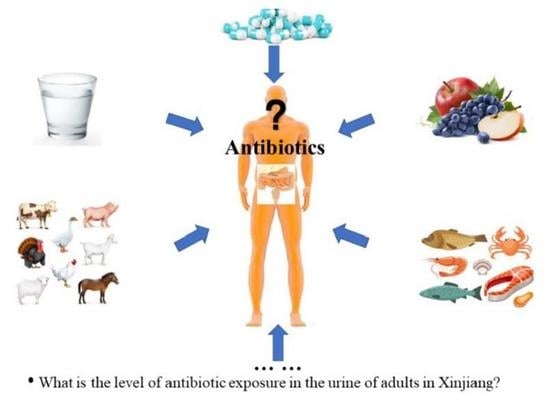
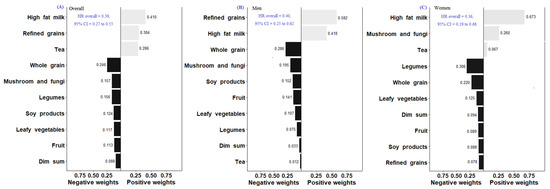
In this Topical Collection of Nutrients, we invite papers related to nutritional epidemiology among Chinese populations. The dietary patterns of people in China have undergone substantial changes in recent years related to the rapid economic development in the country. In the meantime, traditional dietary patterns of Chinese populations in other countries and regions are also evolving during acculturation and fusion with other dietary patterns. With the rise in chronic disease prevalence in China and among people of Chinese descent in other countries and regions, there is an urgent need to understand the relationship between Chinese dietary patterns and components and chronic disease development in order to improve diet-related health outcomes linked to these populations. Delineating the specific diet and disease relationship requires the development of robust dietary assessment and epidemiological research methods. Of particular interest is the use of big data in nutritional epidemiology and nutrigenetic and nutrigenomic approaches for precision nutrition in population studies.
This Topical Collection is dedicated to improving the knowledge of nutritional epidemiology among Chinese populations and publishing selected papers that address important issues including, but not limited to, the following topics:
Epidemiological research methods for diet and disease relationship;
Relationship between dietary patterns and chronic diseases;
Associations between nutrient intake and health/disease status;
The link between malnutrition and the risk of obesity and infectious diseases;
Impact of nutritional interventions on health;l Issues related to nutritional epidemiology and dietary evaluation;
Big data prediction of nutrition and health;
Nutrigenetic and nutrigenomic approaches for precision nutrition;
Issues related to biomarkers, digital technology and dietary assessment;
Acculturation, dietary changes, and health outcomes among Chinese immigrants.
We invite submissions of original research articles, systemic reviews, or meta-analysis related to one of the above topics.
Prof. Dr. Liang Wang
Prof. Dr. Gangqiang Ding
Prof. Dr. Xinyin Jiang
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Nutrients is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- chronic disease
- nutritional epidemiology
- dietary pattern
- Chinese population
- precision nutrition