Journal Description
Muscles
Muscles
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on muscle biology and physiology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Effects of Coping Strategies on Health-Related Quality of Life of People with Neuromuscular Diseases
Muscles 2024, 3(2), 110-120; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3020011 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
Neuromuscular diseases (NMD) cover a broad spectrum of different rare diagnoses in which the primary lesion is in the peripheral nervous system. The impairment caused by an NMD does not only interfere with physical status but also has a clear impact on health-related
[...] Read more.
Neuromuscular diseases (NMD) cover a broad spectrum of different rare diagnoses in which the primary lesion is in the peripheral nervous system. The impairment caused by an NMD does not only interfere with physical status but also has a clear impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL). It is therefore essential to know the coping style used by these patients. This study aims to analyze the coping strategies in a sample of people with NMD and how their coping style affects their HRQoL. This cross-sectional study included 61 adult patients diagnosed with a rare NMD. WHO-DAS II, SIP, SF-36, and COPE-60 instruments were administered. The results showed that people affected by NMDs tend to use more frequent coping strategies such as active planning, personal growth, and acceptance. In contrast, the least-used strategies were restraint, mental disengagement, venting, humor, and religion, which affected HRQoL negatively. Moreover, the degree of disability was a relevant variable, with an impact on HRQoL. Social support can be considered the main coping strategy that leads to an improvement in the psychosocial HRQoL (β = 503, p < 0.001). These findings are relevant to clinical practice, given the need to understand the coping variable to improve HRQoL.
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
An Intronic Heterozygous SYNE2 Splice Site Mutation: A Rare Cause for Myalgia and hyperCKemia?
by
Theresa Paulus, Natalie Young, Emily Jessop, Carolin Berwanger, Christoph Stephan Clemen, Rolf Schröder, Rafal Ploski, Christian Hagel, Yorck Hellenbroich, Andreas Moser and Iakowos Karakesisoglou
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 100-109; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010010 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
SYNE2 mutations have been associated with skeletal and cardiac muscle diseases, including Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). Here, we present a 70-year-old male patient with muscle pain and elevated serum creatine kinase levels in whom whole-exome sequencing revealed a novel heterozygous SYNE2 splice site
[...] Read more.
SYNE2 mutations have been associated with skeletal and cardiac muscle diseases, including Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). Here, we present a 70-year-old male patient with muscle pain and elevated serum creatine kinase levels in whom whole-exome sequencing revealed a novel heterozygous SYNE2 splice site mutation (NM_182914.3:c.15306+2T>G). This mutation is likely to result in the loss of the donor splice site in intron 82. While a diagnostic muscle biopsy showed unspecific myopathological findings, immunofluorescence analyses of skeletal muscle and dermal cells derived from the patient showed nuclear shape alterations when compared to control cells. In addition, a significantly reduced nesprin-2 giant protein localisation to the nuclear envelope was observed in patient-derived dermal fibroblasts. Our findings imply that the novel heterozygous SYNE2 mutation results in a monoallelic splicing defect of nesprin-2, thereby leading to a rare cause of myalgia and hyperCKemia.
Full article
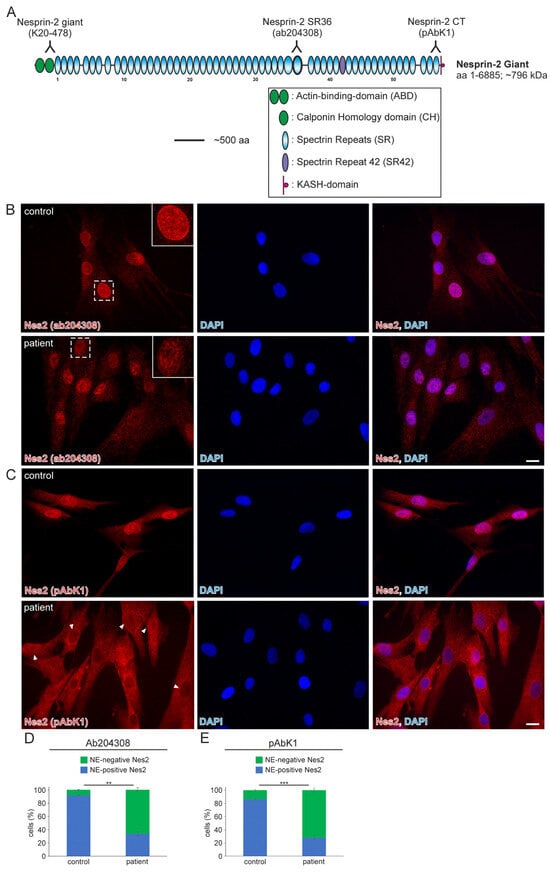
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Age-Related Differences in Physical Fitness and Performance of an “Ability Test” among Firefighters
by
Koulla Parpa and Marcos Michaelides
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 88-99; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010009 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
This study’s primary objective was to examine the differences in body composition, abdominal strength, absolute and relative power, handgrip strength, one repetition maximum for squat and bench press, and the maximum count of push-up and sit-up repetitions executed within a minute across different
[...] Read more.
This study’s primary objective was to examine the differences in body composition, abdominal strength, absolute and relative power, handgrip strength, one repetition maximum for squat and bench press, and the maximum count of push-up and sit-up repetitions executed within a minute across different age cohorts of firefighters. Furthermore, this study aimed to evaluate the age-related differences in firefighters’ completion times of six firefighting tasks. Eighty-four male volunteer firefighters (age 33.79 ± 6.97 years) were grouped into three age categories, 20–30 years, 31–40 years, and 41–50 years, and underwent the aforementioned evaluations. One-way analysis of variance (MANOVA) revealed that age exerts a statistically significant influence (p < 0.001) on body fat percentage, waist circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio. Furthermore, age significantly affected the overall time of the ability test (p < 0.001) and the duration required to accomplish each individual task (p < 0.001). Additionally, age significantly affected abdominal strength, relative power (as measured by the step test), and the maximum count of push-up and sit-up repetitions performed within a minute. These outcomes support earlier research indicating an age-associated decrement in physical fitness parameters among firefighters. It is recommended that firefighters prioritize maintaining strength and endurance of the abdominal muscles, upper body muscular endurance, and a healthy body weight. The emphasis on specific muscular groups is essential for improving task performance within this profession.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Clinical and Therapeutic Implications of BCAAs Metabolism during Chronic Liver Disease in Humans: Crosstalk between Skeletal Muscle and Liver
by
Maria Camila Trillos-Almanza, Magnolia Martinez-Aguilar, Johanna C. Arroyave-Ospina, Frederike van Vilsteren, Hans Blokzijl and Han Moshage
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 71-87; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010008 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This comprehensive review focuses on the dynamics of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) metabolism and its clinical implications in chronic liver disease, with emphasis on the emerging concept of muscle–liver crosstalk. BCAAs, indispensable for protein synthesis and metabolic pathways, undergo unique tissue-specific processing in
[...] Read more.
This comprehensive review focuses on the dynamics of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) metabolism and its clinical implications in chronic liver disease, with emphasis on the emerging concept of muscle–liver crosstalk. BCAAs, indispensable for protein synthesis and metabolic pathways, undergo unique tissue-specific processing in skeletal muscle and liver. The liver, responsible for amino acid metabolism, plays a distinctive role in sensing BCAAs catabolism, influencing glucose regulation and contributing to the systemic metabolism of BCAAs. Within the context of chronic liver disease, compromised liver metabolism becomes evident through amino acid abnormalities, particularly in the decrease of the Fischer ratio (BCAAs/aromatic amino acids concentrations in plasma). This reduction becomes important in assessing the severity of liver dysfunction due to its associations with adverse outcomes, including increased mortality and complications related to the liver disease. BCAAs supplementation, as explored in this review, emerges as a promising avenue, displaying positive effects on skeletal muscle mass, strength, and overall nutritional status in cirrhosis management. Understanding this interplay offers insights into therapeutic strategies for chronic liver diseases, exploring the way for precision interventions in clinical practice.
Full article
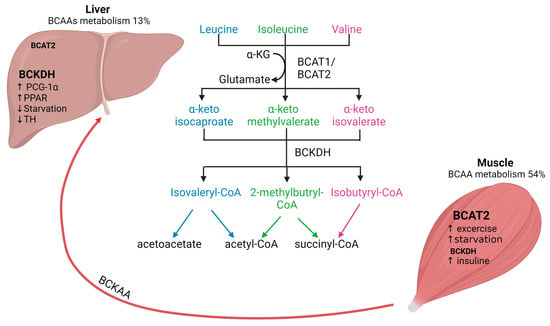
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effects of Regional Muscle Strength and Mass on Standing Long Jump Performance
by
Yuki Nakai, Yujiro Usumoto and Yasufumi Takeshita
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 60-70; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010007 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Muscle strength and mass strongly influence performance. The role of the trunk, upper limbs, and lower limbs in a specific performance is important but unclear in terms of muscle strength, muscle mass, and the degree of influence of each part. Standing long jump
[...] Read more.
Muscle strength and mass strongly influence performance. The role of the trunk, upper limbs, and lower limbs in a specific performance is important but unclear in terms of muscle strength, muscle mass, and the degree of influence of each part. Standing long jump is a performance that produces results by not only the muscles of the lower limbs working together but also the entire body, including the trunk and upper limbs. To determine the influence of muscle strength and the mass of each body part on standing long jump, 31 healthy young adults (18 males and 13 females) participated in this study. Abdominal trunk muscle strength, grip strength, and knee extension muscle strength were measured, each of which was defined as trunk, upper limb, and lower limb muscle strength. The trunk, upper limb, and lower limb muscle masses were measured using a body composition analyzer. Performance was measured using the standing long jump test (jumping power). Factors influencing standing long jump were examined. A multiple regression analysis revealed that trunk (β = 0.367, p = 0.006) and upper limb (β = 0.608, p < 0.001) muscle strength values were extracted for standing long jump (adjusted R2 = 0.574, p < 0.01). Trunk and upper limb muscle strength influence standing long jumps.
Full article
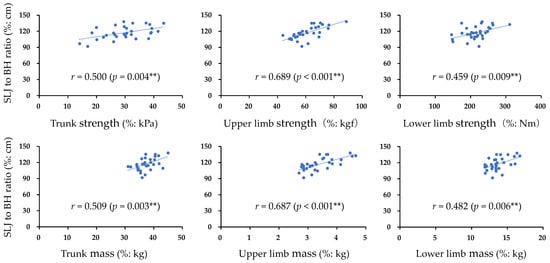
Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Sarcopenia and Pleural Mesothelioma: The Current Knowledge
by
Nikolaos D. Karakousis, Konstantinos I. Gourgoulianis, Nikolaos Papanas and Ourania S. Kotsiou
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 48-59; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010006 - 08 Feb 2024
Abstract
Pleural mesothelioma (PM) is a tumor related to adverse prognosis. The PM WHO classification has mainly identified three major subtypes of PM which are epithelioid, biphasic, and sarcomatoid. Sarcopenia is a medical issue related to a reduction in muscle mass and strength. It
[...] Read more.
Pleural mesothelioma (PM) is a tumor related to adverse prognosis. The PM WHO classification has mainly identified three major subtypes of PM which are epithelioid, biphasic, and sarcomatoid. Sarcopenia is a medical issue related to a reduction in muscle mass and strength. It represents a major health issue globally because it is related to adverse effects such as hospitalization, increased length of stay, disability, increased morbidity and mortality and augmented health care expenditures. In this literature review, we attempted to examine the upcoming association between sarcopenia and PM. As recorded by the current literature, muscle loss in PM subjects was related to poorer survival and lower levels of activity. Subjects with PM had increased rates of pre-sarcopenia and malnutrition, while pre-sarcopenia was related to worse activity levels, and malnutrition was related to worse quality of life (QoL). Both tumor volume and sarcopenia were related to long-term mortality in surgically treated PM subjects, while sarcopenia was present both pre-operatively and post-operatively in these subjects. In addition, post-operative sarcopenic subjects showed a decreased 3-year overall survival (OS) in comparison with those who did not have sarcopenia, while pre-operative sarcopenia was importantly related to an increased rate of post-operative adverse outcomes. More studies are needed to validate these claims.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sarcopenia: The Impact on Health and Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceCase Report
Eculizumab as Additional Rescue Therapy in Myasthenic Crisis
by
Francesco Crescenzo, Mattia Zanoni, Laura Ferigo, Francesca Rossi, Matteo Grecò, Angelica Lupato, Alessandra Danese, Domenico Ajena and Michelangelo Turazzini
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 40-47; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010005 - 07 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
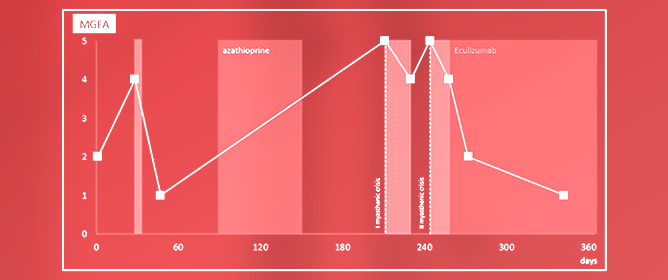
Eculizumab is a monoclonal antibody blocking the terminal complement protein C5. As demonstrated in the phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, REGAIN clinical trial, eculizumab is efficacious in acetylcholine receptor antibody (AChR-Ab)-positive refractory generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) (Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America—MGFA class II–IV). It
[...] Read more.
Eculizumab is a monoclonal antibody blocking the terminal complement protein C5. As demonstrated in the phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, REGAIN clinical trial, eculizumab is efficacious in acetylcholine receptor antibody (AChR-Ab)-positive refractory generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) (Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America—MGFA class II–IV). It has not been studied in severe myasthenic exacerbation or myasthenic crisis (MGFA V). A 73-year-old man diagnosed with myasthenia gravis AChR-Ab positivity came to our observation for symptoms of bulbar and ocular weakness and unresponsiveness or intolerability to conventional immunosuppressive therapies (prednisone and azathioprine). Due to the recurrent clinical worsening with intubation over a short-term period, the patient was treated with eculizumab. After 15 days of eculizumab treatment, we observed a significant recovery of clinical condition. We discharged the patient to an outpatient regimen, where he is continuing with maintenance doses of eculizumab and slowly tapering steroid intake. The use of eculizumab in myasthenic crises is still anecdotal. Our case aims to provide eculizumab benefit for refractory severe gMG in a practical, real-world setting beyond the criteria of the REGAIN study. Further studies are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of eculizumab in myasthenic crises.
Full article
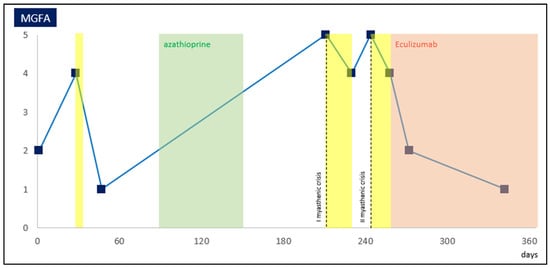
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Incobotulinumtoxin A and Yoga-like Isometric Exercise in Adolescent Idiopathic Lumbar Scoliosis—A Randomized Pilot Study
by
Loren Fishman
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 28-39; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010004 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Approximately 90% of scoliosis cases are adolescent-idiopathic (AIS). From the first appearance of scoliosis at 10–14 years of age until the age of 18, the spine is most vulnerable to deterioration; young, growing people are most susceptible to the worsening of one
[...] Read more.
Background: Approximately 90% of scoliosis cases are adolescent-idiopathic (AIS). From the first appearance of scoliosis at 10–14 years of age until the age of 18, the spine is most vulnerable to deterioration; young, growing people are most susceptible to the worsening of one or more scoliotic curves. An effective non-surgical means of remediation would be welcome. Design: This was a randomized, controlled, two-arm study assessing the safety and efficacy of combining incobotulinum injections with yoga to reverse lumbar and thoracolumbar AIS. Methods: In a private clinic setting, non-pregnant, healthy 12–18 year-olds were either taught a symmetrical “placebo” yoga pose (control sub-group 1), performed the side plank (Vasisthasana) three times daily with a placebo injection (control sub-group 2) or performed the three-times-daily side plank with a botulinum injection (intervention group 3). Injection: For the injection, 33 IU of incobotulinumtoxin type A (Xeomin) was injected into the concave-side lumbar paraspinals and quadratus lumborum at L2–3 and the psoas muscle at L3–4, or participants were injected similarly with a placebo. Randomization was achieved using random.org. Objective: The objective was to determine whether the treatment of muscular asymmetry with botulinum toxin injections and side planks is safe and effective in AIS. Results/Outcome: Eleven intervention and thirteen placebo patients (Groups 1 + 2), who were 12–18 years old, completed the three-month study. Mean daily side plank time = 165 s. The mean initial lumbar curvature was 36.9 degrees (SD 14.36), (p < 0.0001); the mean Group 3 curvature at 3 weeks was 29.5 degrees (SD 14.23) (p < 0.0001); and the mean Group 3 curvature at 3 months was 26.0 degrees (SD 12.81). Onset vs. 3-month value: p < 0.0001. Harms were limited to one patient in Group 2 and one in Group 3, who complained of transient shoulder pain and supported themselves temporarily on their forearm instead of the palm of the extended hand. Conclusion: Muscle strength asymmetry appears to be relevant to AIS treatment. Incobotulinum injections combined with side planks performed with the convex side downward may be more effective in reversing lumbar AIS than placebo exercises or side planks and placebo injections.
Full article
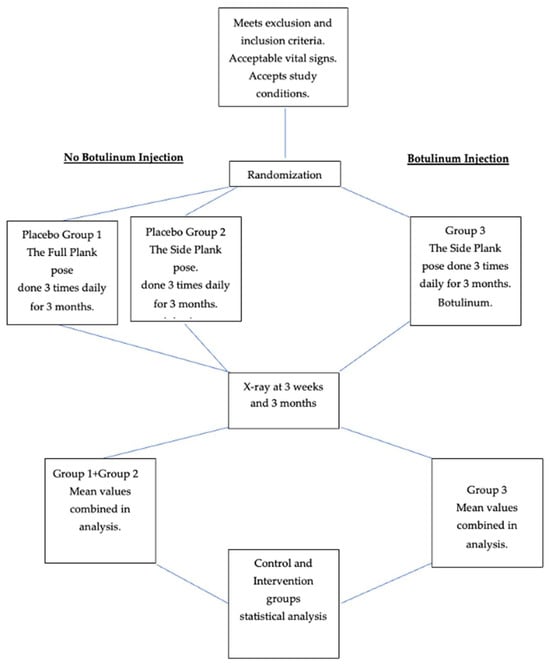
Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Neuromuscular Rehabilitation of the Brachioradialis Muscle after Distal Radius Fracture in Two Professional Soccer Players Using Electromyographic Biofeedback
by
Verónica Morales-Sánchez, Rafael E. Reigal, Verónica García-Morales, Antonio Hernández-Mendo and Coral Falcó
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 16-27; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010003 - 23 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The use of electromyographic biofeedback (EMG-BF) in the rehabilitation of injuries has been widely referenced in the psychological literature. However, despite some pioneering work in the field of sports, its use in the rehabilitation of sports injuries has hardly been explored. A case
[...] Read more.
The use of electromyographic biofeedback (EMG-BF) in the rehabilitation of injuries has been widely referenced in the psychological literature. However, despite some pioneering work in the field of sports, its use in the rehabilitation of sports injuries has hardly been explored. A case of two professional soccer players who each suffered a distal radius fracture is presented here. Parallel to the rehabilitation plan established by medical services, an intervention strategy using EMG-BF was established. An EMG-BF intervention was performed on the brachioradialis muscle with the aim of improving the voluntary control of its electromyographic activity. The study protocol was registered with the identifier NCT05376072. An ABA design was used. In each session, a pre- and postline was recorded to determine the EMG gain acquired at each point of the session. After six sessions, the intervention was terminated. One more follow-up session was performed. The results obtained indicated the efficacy of the intervention; a statistically significant increase in muscle activity in the brachioradialis muscle was observed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
PNPT1 Spectrum Disorders: An Underrecognized and Complex Group of Neurometabolic Disorders
by
Paulo Sgobbi, Igor Braga Farias, Paulo de Lima Serrano, Bruno de Mattos Lombardi Badia, Hélvia Bertoldo de Oliveira, Alana Strucker Barbosa, Camila Alves Pereira, Vanessa de Freitas Moreira, Marco Antônio Troccoli Chieia, Adriel Rêgo Barbosa, Pedro Henrique Almeida Fraiman, Vinícius Lopes Braga, Roberta Ismael Lacerda Machado, Sophia Luiz Calegaretti, Isabela Danziato Fernandes, Roberta Correa Ribeiro, Marco Antonio Orsini Neves, Wladimir Bocca Vieira de Rezende Pinto and Acary Souza Bulle Oliveira
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 4-15; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010002 - 19 Jan 2024
Abstract
An 18-year-old man presented with slowly progressive infancy-onset spasticity of the lower limbs and cerebellar ataxia, associated with painless strabismus, intellectual disability, urinary incontinence, bilateral progressive visual loss, and cognitive decline since early adolescence. A neurological examination disclosed spastic dysarthria, left eye divergent
[...] Read more.
An 18-year-old man presented with slowly progressive infancy-onset spasticity of the lower limbs and cerebellar ataxia, associated with painless strabismus, intellectual disability, urinary incontinence, bilateral progressive visual loss, and cognitive decline since early adolescence. A neurological examination disclosed spastic dysarthria, left eye divergent strabismus, bilateral ophthalmoparesis, impaired smooth pursuit, severe spastic paraparesis of the lower limbs with global brisk tendon reflexes, bilateral extensor plantar responses, and bilateral ankle clonus reflex. Bilateral dysdiadochokinesia of the upper limbs, Stewart-Holmes rebound phenomenon, bilateral dysmetria, and a bilateral abnormal finger-to-nose test were observed. Markedly reduced bilateral visual acuity (right side 20/150, left side 20/400) and moderate to severe optic atrophy were detected. Neuroimaging studies showed cerebellar atrophy and bilateral optic nerves and optic tract atrophy as the main findings. As a complicated Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia, autosomal dominant Spinocerebellar Ataxia, or inherited neurometabolic disorders were suspected, a large next-generation sequencing-based gene panel testing disclosed the heterozygous pathogenic variant c.162-1G>A in intron 1 of the PNPT1 gene. A diagnosis of PNPT1-related spastic ataxia was established. Clinicians must be aware of the possibility of PNPT1 pathogenic variants in cases of spastic ataxia and spastic paraplegias that are associated with optic atrophy and marked cognitive decline, regardless of the established family history of neurological compromise.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Clinical Advances in Neuromuscular Diseases: Neurometabolic Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Muscles: An Overview of 2023 and Future Perspective
by
Corrado Angelini
Muscles 2024, 3(1), 1-3; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010001 - 02 Jan 2024
Abstract
Ending the year is an opportunity to reflect on the past twelve months [...]
Full article
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Sex-Related Differences of Weight Bearing and Non-Weight Bearing Muscle Properties
by
Omid Nabavizadeh and Ashley A. Herda
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 400-412; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040031 - 15 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study evaluated muscle composition, quality, and strength of non-weight bearing and weight bearing muscles between males and females. Twenty-eight, healthy males (n = 14; mean ± SD; age = 25.1 ± 4.2 years; height = 181.9 ± 10.6 cm; weight =
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated muscle composition, quality, and strength of non-weight bearing and weight bearing muscles between males and females. Twenty-eight, healthy males (n = 14; mean ± SD; age = 25.1 ± 4.2 years; height = 181.9 ± 10.6 cm; weight = 91.6 ± 17.2 kg) and females (n = 14; age = 25.0 ± 3.4 years; height = 165.9 ± 6.9 cm; weight = 66.0 ± 10.2 kg) underwent body composition assessment to estimate body fat (%BF) and total-body, arm, and leg fat-free mass (TFFM, ArmFFM, and LegFFM, respectively) and muscle composition via B-mode ultrasound to measure muscle cross-sectional area (mCSA), echo intensity (EI), and thickness (mT) of four muscles [rectus femoris (RF), vastus lateralis (VL), flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS), and flexor carpi radialis (FCR)]. Additionally, upper- [handgrip strength (HG)] and lower-body [leg extension (LE)] maximal strength were measured, recorded, and expressed relative to FFM to determine muscle quality (MQ) for the dominant arm and leg, respectively. Males had greater TFFM, ArmFFM, and LegFFM (p < 0.001), mCSA for RF, VL, FCR, and FDS (p < 0.001), and mT for RF, VL (p < 0.001–0.006). Females had greater EI for RF, VL, and FDS (p = 0.003–0.01). Negative correlations were identified between EI and MQ for all muscles in males and females, however, no significance was determined. Despite the sex differences in absolute strength and size, muscle quality (relative strength) was not different for the upper nor lower body.
Full article
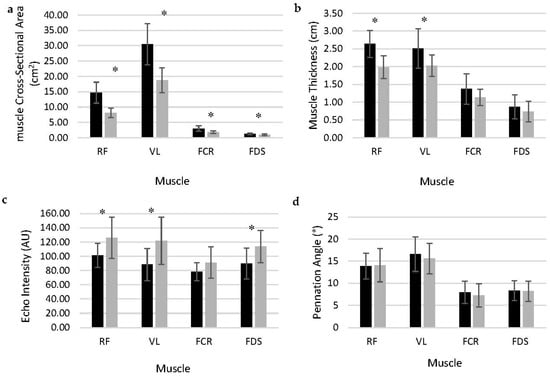
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence of Ten Gene Variants Involved in Muscular Phenotypes in a Mexican Mestizo Population
by
Luz Berenice López-Hernández, Guillermina Avila-Ramírez, Ariadna Del Villar-Morales, Mónica Alejandra Anaya-Segura, Luis Angel Montes-Almanza, Froylan Arturo García-Martínez, Antonio Miranda-Duarte, Carlos Antonio Sosa-Flores, Martha Eunice Rodríguez-Arellano, Ileana Chavez-Maisterra, Alexandra Berenice Luna-Angulo, Miriam Pavelth Casillas-Ávila and Benjamín Gómez-Díaz
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 389-399; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040030 - 08 Dec 2023
Abstract
Several reports have provided evidence that there are genetic variants of genes such as MSTN, BDRKB2, ACTN3 and ADRB2 that are involved in a better response to adaptation during resistance or strength training, while other genes such as GRB14, AGT
[...] Read more.
Several reports have provided evidence that there are genetic variants of genes such as MSTN, BDRKB2, ACTN3 and ADRB2 that are involved in a better response to adaptation during resistance or strength training, while other genes such as GRB14, AGT and END1 are reported to be associated with the risk of suffering from some diseases such as diabetes, hypertension or obesity. A cross-sectional study from a Mexican Mestizo population was performed to estimate the frequency of 10 gene variants in 8 genes involved in athletic performance or chronic degenerative diseases, MSTN (rs1805085, rs1805086), BDKRB2 (rs1799722), FST (rs1423560), ACTN3 (rs1815739), ADRB2 (rs1042713, rs1042714), GRB14 (rs8192673), AGT (rs699) and EDN1 (rs5370), and to compare frequencies from 26 populations reported in the Database of 1000 Genomes project. Genotype frequencies fitted the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, except for MST rs1805086 and FST rs1423560, and our study revealed significant differences in the distribution of frequencies of some of these gene variants among populations reported in the 1000 Genomes Project. Our findings provide insights regarding the genetic background of our population, and future case–control studies can be carried out with more accurate sample sizes for genetic association studies. Our results may be also useful in recognizing the roles and mechanisms contributing to athletic performance and/or chronic degenerative diseases in Mexicans.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Endurance and Ultra-Endurance: Implications of Training, Recovery, Nutrition, and Technology on Performance and Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceSystematic Review
A Straightforward Approach to Analyze Skeletal Muscle MRI in Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy for Differential Diagnosis: A Systematic Review
by
Ryo Morishima and Benedikt Schoser
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 374-388; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040029 - 08 Nov 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
Skeletal muscle MRI studies in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) have increased over the past decades, improving the utility of MRI as a differential diagnostic tool. Nevertheless, the relative rarity of individual genotypes limits the scope of what each study can address, making it
[...] Read more.
Skeletal muscle MRI studies in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) have increased over the past decades, improving the utility of MRI as a differential diagnostic tool. Nevertheless, the relative rarity of individual genotypes limits the scope of what each study can address, making it challenging to obtain a comprehensive overview of the MRI image of this splintered group. Furthermore, MRI studies have varied in their methods for assessing fat infiltration, which is essential in skeletal muscle MRI evaluation. It stayed problematic and impeded attempts to integrate multiple studies to cover the core MRI features of a distinct LGMD. In this study, we conducted a systematic review of LGMD in adults published until April 2023; 935 references were screened in PubMed and EMBASE, searches of the gray literature, and additional records were added during the screening process. Finally, 39 studies were included in our final analysis. We attempted to quantitatively synthesize the MRI data sets from the 39 individual studies. Finally, we illustrated ideal and simple MRI muscle involvement patterns of six representative LGMD genotypes. Our summary synthesis reveals a distinct distribution pattern of affected muscles by LGMD genotypes, which may be helpful for a quick first-tier differential diagnosis guiding genetic diagnostics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Clinical Advances in Neuromuscular Diseases: Neurometabolic Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Efficacy of Electromyographic Biofeedback in the Recovery of the Vastus Lateralis after Knee Injury: A Single-Group Case Study
by
Verónica Morales-Sánchez, Rafael E. Reigal, Raul Antunes, Rui Matos, Antonio Hernández-Mendo and Diogo Monteiro
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 361-373; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040028 - 07 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Electromyographic biofeedback (EMG-BF) is a technique that can contribute to the improvement of muscle tone and control in the rehabilitation process after injury. The aim of this research was to determine the effectiveness of EMG-BF in increasing the electromyographic activity of the vastus
[...] Read more.
Electromyographic biofeedback (EMG-BF) is a technique that can contribute to the improvement of muscle tone and control in the rehabilitation process after injury. The aim of this research was to determine the effectiveness of EMG-BF in increasing the electromyographic activity of the vastus lateralis after knee injury. The sample consisted of four individuals who had undergone surgery or rehabilitation to resolve either a partial meniscal tear or a patellar tendon strain. The intervention consisted of a program of ten sessions of EMG-BF work. Twelve trials were performed in each session, in which participants were instructed to target the muscle tension produced by the vastus lateralis of the uninjured hemilateral limb. Of the twelve trials in each session, the first three and the last three were performed without feedback, and the intermediate six with feedback. The recording of muscle activity was performed using CY-351/2 Mioback equipment, which allowed the amplitude of the electromyographic signal to be evaluated. The results indicated that the sample analyzed reached greater amplitude during the biofeedback trials, both for the maximum (Z = −13.43, p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.64, 95% CI (0.27, 1.01)) and mean (Z = −7.26, p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.24, 95% CI (−0.12, 0.60)) values. The amplitude also increased throughout the ten sessions, both for the maximum (Z = −3.06, p < 0.01, Cohen’s d = 1.37, 95% CI (0.29, 2.45)) and mean (Z = −3.06, p < 0.01, Cohen’s d = 1.20, 95% CI (0.34, 2.08)) values. Thus, the results highlight the efficacy of this technique in improving muscle activity, suggesting that it is a useful therapeutic procedure in injury recovery.
Full article
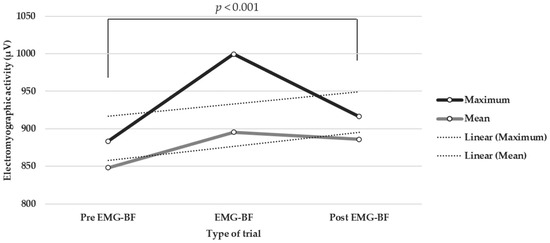
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
The Correlation between Core Muscular Endurance, Body Composition, and Back Pain in Firefighters: An Observational Study
by
Shelby Sanregret, Austin Alan Kohler, Andrew Ray Moore and Angelia Maleah Holland-Winkler
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 353-360; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040027 - 24 Oct 2023
Abstract
Firefighters are at a higher risk for experiencing back pain due to the nature of their job, but physical fitness may help to reduce this risk. Therefore, the primary purpose of this study was to determine if a correlation between subjective back pain
[...] Read more.
Firefighters are at a higher risk for experiencing back pain due to the nature of their job, but physical fitness may help to reduce this risk. Therefore, the primary purpose of this study was to determine if a correlation between subjective back pain severity and core muscular endurance exists in firefighters. A secondary purpose was to determine if age or body composition were correlated with back pain severity. This cross-sectional study was performed at a fire department during their Physical Fitness Assessment Program and included 72 male firefighters. Measures included weight, body fat percentage, maximal plank hold times for core muscular endurance, and the Oswestry Low Back Pain Disability Questionnaire. A Pearson product correlation analysis was performed between back pain score and each of the following variables: body fat percentage, BMI, age, and plank hold times. A second set of correlation coefficient analyses was performed between the same variables exclusively in subjects who reported back pain. This study found that, within this population of firefighters, there was no significant correlation between back pain and plank times or body composition variables, although there was a trend toward significant correlations between BMI and body fat percentage when only subjects with back pain were considered.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Muscles)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Advances and Prospects in Understanding Vertebrate Cardiac Conduction System, Pacemaker Cell, and Cardiac Muscle Development: Toward Novel Biological Therapies
by
Ridwan Opeyemi Bello, Shannon Frew, Yusra Siddiqui and Rashid Minhas
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 338-352; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040026 - 12 Oct 2023
Abstract
The heart is composed of muscle cells called cardiomyocytes, including a specialized population named pacemaker cells that form the cardiac conduction system (CCS), which is responsible for generating the action potential dictating heart contractions. Failure of the CCS system leads to cardiac arrhythmias,
[...] Read more.
The heart is composed of muscle cells called cardiomyocytes, including a specialized population named pacemaker cells that form the cardiac conduction system (CCS), which is responsible for generating the action potential dictating heart contractions. Failure of the CCS system leads to cardiac arrhythmias, which require complicated therapies and often the surgical implantation of electrical pacemakers. However, recent research has focused on the development of novel therapies using biological pacemakers that aim to substitute electrical devices. While most signaling pathways and transcription factors involved in the development of the pacemaker cells are known, the upstream regulatory networks need to be predicted through computer-based databases, mathematical modeling, as well as the functional testing of the regulatory elements in vivo, indicating the need for further research. Here, we summarize the current knowledge about the vertebrate myocardial CCS system and the development of the pacemaker cells, as well as emphasize the areas of future research to clarify the regulation of muscle pacemaker cells and the ease of development of biological therapies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mechanisms of Muscle Homeostasis in Health and Disease: From Specification of Muscle Progenitors to Muscle Fibre Maintenance)
►▼
Show Figures
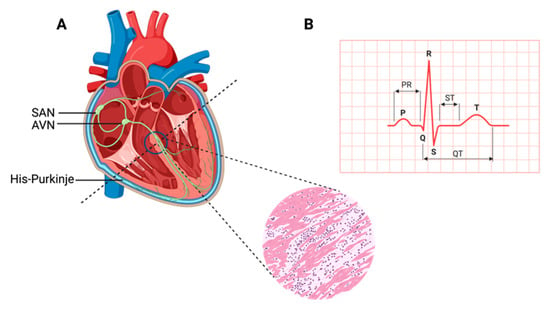
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Discrepancy of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate Measurements between a Blood Meter and GC-MS Methods in Healthy Humans
by
Angelia Maleah Holland-Winkler, Andrew R. Moore, Jenna K. Ansley, Noah A. Fritz and Ilya Bederman
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 327-337; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040025 - 27 Sep 2023
Abstract
Ketone salt (KS) supplementation induces temporary nutritional ketosis to achieve potential exercise performance and health benefits. Racemic KS includes both D/L isomers of β-hydroxybutyrate, yet commercially available measurement devices (i.e., blood meters) only measure the D variant. The aim of this study was
[...] Read more.
Ketone salt (KS) supplementation induces temporary nutritional ketosis to achieve potential exercise performance and health benefits. Racemic KS includes both D/L isomers of β-hydroxybutyrate, yet commercially available measurement devices (i.e., blood meters) only measure the D variant. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of a blood meter to measure serum β-hydroxybutyrate in comparison with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) before and 30 min after consuming a placebo or racemic KS. In this triple-blinded cross-over study, 16 healthy adults were administered either a placebo or KS drink, and the circulating β-hydroxybutyrate concentration was measured at baseline (PRE) and 30 min following consumption (POST) using a blood ketone meter and by GC-MS. Compared to the placebo, both GC-MS and the blood meter obtained significantly greater β-hydroxybutyrate levels from PRE to POST time-points after consuming KS. Additionally, GC-MS results showed significantly higher levels of β-hydroxybutyrate with both the placebo and KS at PRE and POST time-points, as compared to the blood meter. These results indicate that (1) even in the absence of KS, the blood meter yields significantly lower β-hydroxybutyrate values than GC-MS, and (2) the inability of the blood meter to measure L-β-hydroxybutyrate values POST KS warrants the further development of publicly available ketone measurement apparatuses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Muscles)
►▼
Show Figures
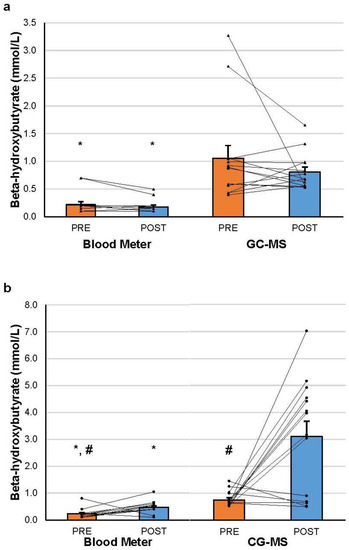
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Loop Diuretics and Sarcopenia: A Potential Association
by
Nikolaos D. Karakousis and Petros N. Georgakopoulos
Muscles 2023, 2(4), 317-326; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2040024 - 22 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Loop diuretics (LDs) are used to treat various health conditions including heart failure (HF), liver cirrhosis, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Sarcopenia is a skeletal muscle health issue related to the depletion and decrease of muscle mass and strength, leading to adverse
[...] Read more.
Background: Loop diuretics (LDs) are used to treat various health conditions including heart failure (HF), liver cirrhosis, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Sarcopenia is a skeletal muscle health issue related to the depletion and decrease of muscle mass and strength, leading to adverse outcomes including frailty syndrome, functional decline, falls, hospitalizations, augmented length of hospital stay, and increased morbidity and mortality. Methods: This study investigated the probable association between LD use and sarcopenia via conducting a non-systematic review of the existing literature. Results: In subjects with non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD), an augmented risk of sarcopenia is significantly associated with LD use. Interestingly, in patients with HF treated with LDs, thigh and arm circumferences were significantly small, which is indicative of skeletal muscle wasting. Additionally, in anorexic subjects who are more likely to be on diuretic medication, suffering also from cachexia, a higher prevalence of sarcopenia was demonstrated. In cirrhotic subjects, the treatment dosage of LDs was inversely correlated with the skeletal muscle area per year (ΔSMA). Nevertheless, in subjects with liver cirrhosis treated with LDs, who were divided into those with and those without muscle cramps, the presence of sarcopenia was similar. Conclusions: Further investigation is imperative to validate potential interplay between LDs and sarcopenia.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Degradative Signaling in ATG7-Deficient Skeletal Muscle Following Cardiotoxin Injury
by
Fasih Ahmad Rahman, Troy Campbell, Darin Bloemberg, Sarah Chapman and Joe Quadrilatero
Muscles 2023, 2(3), 299-316; https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles2030023 - 15 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Skeletal muscle is a complex tissue comprising multinucleated and post-mitotic cells (i.e., myofibers). Given this, skeletal muscle must maintain a fine balance between growth and degradative signals. A major system regulating the remodeling of skeletal muscle is autophagy, where cellular quality control is
[...] Read more.
Skeletal muscle is a complex tissue comprising multinucleated and post-mitotic cells (i.e., myofibers). Given this, skeletal muscle must maintain a fine balance between growth and degradative signals. A major system regulating the remodeling of skeletal muscle is autophagy, where cellular quality control is mediated by the degradation of damaged cellular components. The accumulation of damaged cellular material can result in elevated apoptotic signaling, which is particularly relevant in skeletal muscle given its post-mitotic nature. Luckily, skeletal muscle possesses the unique ability to regenerate in response to injury. It is unknown whether a relationship between autophagy and apoptotic signaling exists in injured skeletal muscle and how autophagy deficiency influences myofiber apoptosis and regeneration. In the present study, we demonstrate that an initial inducible muscle-specific autophagy deficiency does not alter apoptotic signaling following cardiotoxin injury. This finding is presumably due to the re-establishment of ATG7 levels following injury, which may be attributed to the contribution of a functional Atg7 gene from satellite cells. Furthermore, the re-expression of ATG7 resulted in virtually identical regenerative potential. Overall, our data demonstrate that catastrophic injury may “reset” muscle gene expression via the incorporation of nuclei from satellite cells.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cells, IJMS, JMP, Muscles
Molecular Mechanisms of Exercise and Healthspan
Topic Editors: Robert Wessells, Zhen YanDeadline: 2 November 2024
Topic in
Biomechanics, Healthcare, IJERPH, Nutrients, Sports, Sensors, Muscles, Foods
Endurance and Ultra-Endurance: Implications of Training, Recovery, Nutrition, and Technology on Performance and Health
Topic Editors: Nicolas Berger, Russ BestDeadline: 31 December 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Muscles
Sarcopenia: The Impact on Health and Disease
Guest Editors: Nikolaos Papanas, Nikolaos D. KarakousisDeadline: 31 October 2024
Special Issue in
Muscles
Women’s Special Issue Series: Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Function in Health and Disease
Guest Editors: Louise Deldicque, Tatiana Kostrominova, Jamie I. BaumDeadline: 31 March 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Muscles
Clinical Advances in Neuromuscular Diseases: Neurometabolic Disorders
Collection Editors: Corrado Angelini, Daniela Tavian