Early-Career Researchers in Chemistry (Closed)
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049).
Viewed by 13870Editors
Interests: organic electrochemistry and electrosynthesis; sensors and biosensors fabrication; built heritage
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: gas chromatography; mass spectrometry; physical and chemical properties of food and relationship with human sensory perception; sensory analysis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
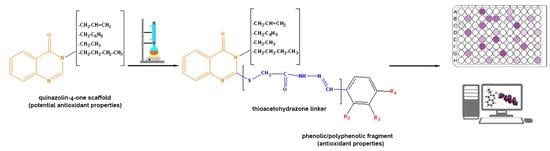
Interests: synthetic organic chemistry; carbohydrate-based glycomimetics; glycosidase inhibitors; iminosugar synthesis; lysosomal storage diseases; Gaucher disease; Parkinson disease
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
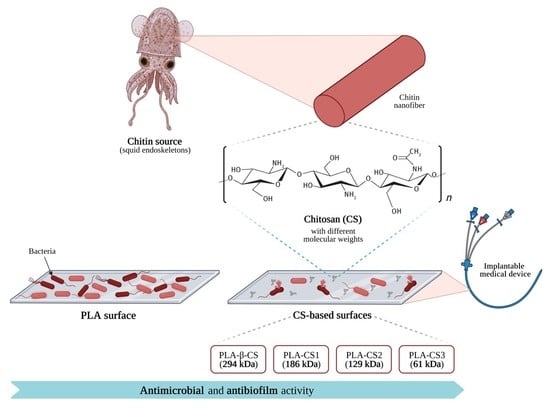
Interests: bee keeping products (propolis, honeys, royal jelly, pollen); pyrrolizidine alkaloids; regulatory issues on herbal medicines (EMA, NCAs); phenolics; herbals for veterinary use
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: computational chemistry; quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics; molecular dynamics; docking; catalysis; enzymology; thermochemistry; reaction mechanisms; sulfur biochemistry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: drug discovery; enzyme inhibitors; cannabinoids; psychoactive molecules; multiple sclerosis; inflammatory disorders; mental health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: activation and functionalization of elemental phosphorus; activation of small inorganic and organic molecules; transition-metal hydrides and molecular hydrogen chemistry; materials for H-storage; carbon dioxide capture and valorization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
As the guest editors of a timely, topical and high-quality collection titled “Early-Career Researchers in Chemistry” in Molecules, we are delighted to announce this exciting initiative, and we are particularly encouraging “Early-Career Researchers” in all areas of chemistry around the world to take part. This collection will bring together the latest high-quality contributions from early-career researchers in chemistry actively working in all fields of chemistry at the early stages of their careers (i.e. within the first 5 years of their independent career).
We invite submissions of original research and review articles from early-career researchers that explore contemporary issues in all fields of Chemistry for inclusion in this topical collection of Molecules. A preliminary review of the submissions by the editors will be conducted to assess suitability, after which the peer review process will begin.
This initiative is designed to increase the visibility and reputation of early-career researchers in the chemical research community with a focus on quality, innovation and breakthrough research.
Prof. Dr. Antonella Curulli
Prof. Dr. Eugenio Aprea
Dr. Francesca Cardona
Prof. Dr. Ioanna Chinou
Prof. Dr. James Gauld
Prof. Dr. Lakshmi Kotra
Prof. Dr. Maurizio Peruzzini
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.