Journal Description
Mining
Mining
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on mining science and engineering published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, GeoRef, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Mining is a companion journal of Minerals.
Latest Articles
Participatory Geomonitoring for Future Mining—Resilience Management in the Cavern Storage Epe (Germany)
Mining 2024, 4(2), 230-247; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4020014 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Integrated geo- and environmental monitoring in mining represents a high-dimensional challenge (location, altitude/depth, time and sensors). This is challenging for experts but poses great problems for a multitude of participants and stakeholders in building up a complete process understanding. The Epe research cooperation
[...] Read more.
Integrated geo- and environmental monitoring in mining represents a high-dimensional challenge (location, altitude/depth, time and sensors). This is challenging for experts but poses great problems for a multitude of participants and stakeholders in building up a complete process understanding. The Epe research cooperation aims to elucidate the ground movement at the Epe cavern storage facility with a public participation process. The research cooperation was founded by the city of Gronau, the citizens’ initiative cavern field Epe, the company EFTAS, Münster, and the Research Center of Post-Mining at the Technische Hochschule Georg Agricola, Bochum. This research cooperation is the first in Germany to involve direct collaboration between science and the public. In the cavern field, which has been in operation since the 1970s, brine is extracted, and at the same time natural gas, crude oil and helium, as well as hydrogen in the future, are stored in the subsurface. The technical focus of this work was the development of a high-resolution spatiotemporal analysis of ground movements. The area is monitored annually by the mining company’s mine surveyor. The complexity of the monitoring issue lies in the fact that the western part is a bog area and a former bog area. Furthermore, the soils in the eastern part are very humus-rich and show strong fluctuations in the groundwater and therefore complex hydraulic conditions. At the same time, there are few fixed scatterers or prominent points in the area that allow high-resolution spatiotemporal monitoring using simple radar interferometry methods. Therefore, the SBAS method (Small Baseline Subset), which is based on an aerial method, was used to analyze the radar interferometric datasets. Using an SBAS analysis, it was possible to evaluate a time series of 760 scenes over the period from 2015 to 2023. The results were integrated with the mine survey maps on the ground movement and other open geodata on the surface, the soil layers and the overburden. The results show complex forms of ground movement. The main influence is that of mining. Nevertheless, the influence of organic soils with drying out due to drought years and uplift in wet years is great. Thus, in dry years, ground subsidence accelerates, and in wet years, ground subsidence not only slows down but in some cases also causes uplift. This complexity of ground movements and the necessary understanding of the processes involved has been communicated to the interested public at several public information events as part of the research cooperation. In this way, an understanding of the mining process was built up, and transparency was created in the subsurface use, also as a part of the energy transition. In technical terms, the research cooperation also provides a workflow for developing the annual mine survey maps into an integrated geo- and environmental monitoring system with the development of a transparent participatory geomonitoring process to provide resilience management to a mining location.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Post-Mining Management)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Towards a Long-Term Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Monitoring Framework for Post-Mining Effects: Prosper-Haniel Case
by
Marcin Pawlik, Benjamin Haske, Hernan Flores, Bodo Bernsdorf and Tobias Rudolph
Mining 2024, 4(2), 211-229; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4020013 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Direct and indirect effects after mine operations cease operating must ideally be subjected to perpetual monitoring routines in order to detect possible risks or avoid adverse effects on the surrounding ecosystems at an early stage. In this contribution, mining subsidence lakes created inside
[...] Read more.
Direct and indirect effects after mine operations cease operating must ideally be subjected to perpetual monitoring routines in order to detect possible risks or avoid adverse effects on the surrounding ecosystems at an early stage. In this contribution, mining subsidence lakes created inside the nature reserve Kirchheller Heide and Hilsfeld Forest are subjected to analysis for a long-term monitoring scheme. For this purpose, we employ high-resolution unmanned aerial system (UAS)-based multispectral and thermal mapping tools to provide a fast, non-invasive and multitemporal environmental monitoring method. Specifically, we propose to monitor vegetation evolution through multispectral analysis, biotypes identification using machine learning algorithms, and water surface extent detection, together with their thermal behavior. The aim of this contribution is to present the proposed workflow and first results to establish a baseline for future analyses and subsequent surveys for long-term multi-temporal monitoring.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning Approach to Identify Important Parameters Influencing Pumping Load Shift in a Complex Dewatering System of a Deep-Level Mine
by
Fortunate Olifant, Shaun Hancock, Johan du Plessis, Jean van Laar and Corne Schutte
Mining 2024, 4(2), 189-210; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4020012 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigated the application of machine learning to optimise the pumping load shift of a complex dewatering system in a deep-level mine, aiming to reduce energy costs associated with the dewatering process, which consumes an average of 14% of the mine’s electricity.
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the application of machine learning to optimise the pumping load shift of a complex dewatering system in a deep-level mine, aiming to reduce energy costs associated with the dewatering process, which consumes an average of 14% of the mine’s electricity. Traditional practices, reliant on human control and simulations, often lead to inconsistent savings and occasional losses. The study employed multivariate linear regression (MLR) and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) on a mine dewatering system, to identify important parameters influencing the pumping load shift performance. Critical parameters significantly impacting the energy consumption of the dewatering system were identified by the best-performing model, XGBoost. Implementing a pumping schedule based on XGBoost insights resulted in consistent load shifting and enhanced energy cost savings. These findings highlight the potential of machine learning in comprehending and optimising complex systems in deep-level mines, with the case study approach proving effective in quantifying and validating real-world impacts. This approach could offer substantial energy savings through data-driven decision-making.
Full article
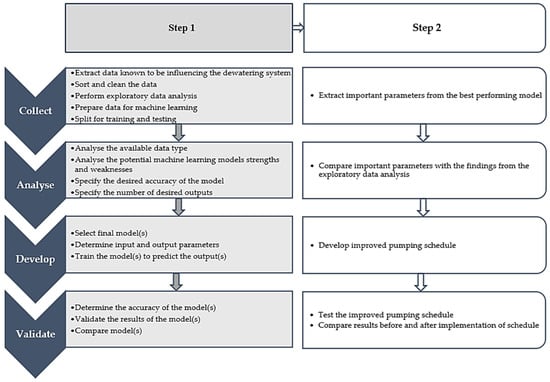
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Influence of Explosive and Rock Mass Properties on Blast Damage in a Single-Hole Blasting
by
Magreth S. Dotto and Yashar Pourrahimian
Mining 2024, 4(1), 168-188; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010011 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
In rock blasting for mining production, stress waves play a major role in rock fracturing, along with explosive gases. Better energy distribution improves fragmentation and safety, lowers production costs, increases productivity, and controls ore losses and dilution. Blast outcomes vary significantly depending on
[...] Read more.
In rock blasting for mining production, stress waves play a major role in rock fracturing, along with explosive gases. Better energy distribution improves fragmentation and safety, lowers production costs, increases productivity, and controls ore losses and dilution. Blast outcomes vary significantly depending on the choice of the explosive and the properties of the rock mass encountered. This study analyzes the effects of rock mass and explosive properties on blast outcomes via numerical simulation using data from the case study, and later validates the simulation results from the field blast fragmentation. The findings suggest that, for a given set of rock properties, the choice of explosive has a major influence on the resulting fragmentation. Strong explosives (high VOD and detonation pressure) favor large fracture extents in hard rocks, while weaker explosives offer a better distribution of explosive energy and fractures. The presence of rock structures such as rock contacts and joints influences the propagation of stress waves and fractures depending on the structures’ material properties, the intensity and orientations, and the direction and strength of the stress wave. When the stress wave encounters a contact depending on its direction, it is enhanced when traveling from soft to hard and attenuates in the opposite direction. The ability of the stress wave to cause fracturing on the opposite side of the contact depends on the intensity of the transmitted wave and the strength of the rock. Transmitted wave intensity is a function of the strength of the incident wave and the impedance difference between the interface materials. The presence of joints in the rock mass affects the propagation of the stress wave, mainly depending on the infill material properties and the angle at which the stress wave approaches the joint. Less compressible, higher stiffness joints transmit more energy. More energy is also transmitted in the areas where the stress wave hits the joint perpendicularly. Joints parallel to the free face offer additional fracturing on the opposite side of the joint. Other parameters, such as the joint width, continuity, fracture frequency, and the distance from the charge, enhance the effects. To achieve effective fragmentation, the blast design should mitigate the effect of variability in the rock mass via explosive selection and pattern design to ensure adequate energy distribution within the limits of geometric design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Women’s Special Issue Series: Mining)
►▼
Show Figures
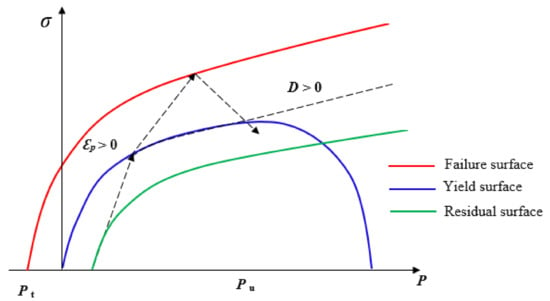
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Use and Recovery of Extractive Waste and Tailings for Sustainable Raw Materials Supply
by
Susanna Mancini, Marco Casale, Antonio Tazzini and Giovanna Antonella Dino
Mining 2024, 4(1), 149-167; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010010 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
Extractive waste (EW), including tailings, is produced in large quantities during mining activities. In recent years, the linear economic model (“take-use-and-throw” approach) has been replaced by a circular approach, emphasizing the sustainable use and recovery of EW. The development of innovative protocols, such
[...] Read more.
Extractive waste (EW), including tailings, is produced in large quantities during mining activities. In recent years, the linear economic model (“take-use-and-throw” approach) has been replaced by a circular approach, emphasizing the sustainable use and recovery of EW. The development of innovative protocols, such as Best Available Techniques (BATs), which aim at the technological and process improvement of more sustainable mining activities and at the production of renewable, highly performing green materials, has led to technological advancements, expertise in sustainability, and a reduced ecological footprint, potentially causing positive economic and social impacts and reducing environmental ones. Extractive waste and tailings, if suitably characterized, can be used to improve and make sustainable the works connected to the management of mining activities. The qualitative–quantitative characterization of EW is essential for subsequent reuse and for assessing the risk to human health and the extent of environmental impacts in the various matrices. The application areas vary according to the type of waste and mining tailings, the morphological characteristics of the deposits, and the geological, geomorphological, and logistic context of the area. Integrated protocols for sustainable EW exploitation and positive impacts on the economic, environmental, and technological/social level are analyzed. The present paper aims at providing an overview of challenges and potentialities connected to extractive waste (EW) management and potential exploitation to recover raw materials (RM), critical raw materials (CRM), and secondary raw materials (SRM).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Women’s Special Issue Series: Mining)
►▼
Show Figures
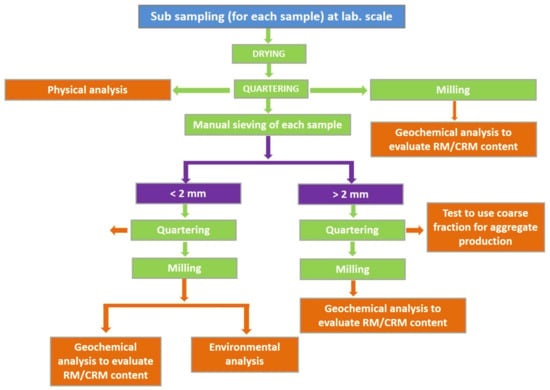
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
A Review of In Situ Leaching (ISL) for Uranium Mining
by
Guihe Li and Jia Yao
Mining 2024, 4(1), 120-148; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010009 - 02 Mar 2024
Abstract
Uranium, a cornerstone for nuclear energy, facilitates a clean and efficient energy conversion. In the era of global clean energy initiatives, uranium resources have emerged as a vital component for achieving sustainability and clean power. To fulfill the escalating demand for clean energy,
[...] Read more.
Uranium, a cornerstone for nuclear energy, facilitates a clean and efficient energy conversion. In the era of global clean energy initiatives, uranium resources have emerged as a vital component for achieving sustainability and clean power. To fulfill the escalating demand for clean energy, continual advancements in uranium mining technologies are imperative. Currently, established uranium mining methods encompass open-pit mining, underground mining, and in situ leaching (ISL). Notably, in situ leaching stands out due to its environmental friendliness, efficient extraction, and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, it unlocks the potential of extracting uranium from previously challenging low-grade sandstone-hosted deposits, presenting novel opportunities for uranium mining. This comprehensive review systematically classifies and analyzes various in situ leaching techniques, exploring their core principles, suitability, technological advancements, and practical implementations. Building on this foundation, it identifies the challenges faced by in situ leaching and proposes future improvement strategies. This study offers valuable insights into the sustainable advancement of in situ leaching technologies in uranium mining, propelling scientific research and practical applications in the field.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Sustainable Mining Engineering 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
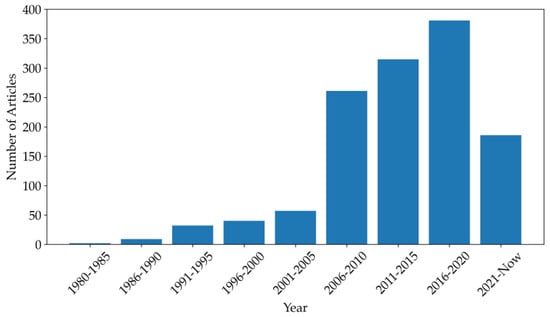
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Development of a New Smart Evacuation Modeling Technique for Underground Mines Using Mathematical Programming
by
Richard Meij, Masoud Soleymani Shishvan and Javad Sattarvand
Mining 2024, 4(1), 106-119; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010008 - 23 Feb 2024
Abstract
Navigating miners during an evacuation using smart evacuation technology can significantly decrease the evacuation time of an underground mine in case of emergency hazards. This paper presents a mathematical programming model to calculate the most efficient escape path for miners as a critical
[...] Read more.
Navigating miners during an evacuation using smart evacuation technology can significantly decrease the evacuation time of an underground mine in case of emergency hazards. This paper presents a mathematical programming model to calculate the most efficient escape path for miners as a critical component of smart evacuation technology. In this model, the total evacuation distance of the crew is minimized and scenarios with blocked pathways and stamina categories for the miners are simulated. The findings revealed that all the tested scenarios were technically feasible. Using the feature that filters out blocked pathways has no downsides as safer routes are calculated and there is no penalty in the computation time. This paper also discusses the social and technical issues that must be resolved before the algorithm can be implemented as an actual escape solution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Mining Innovation)
►▼
Show Figures
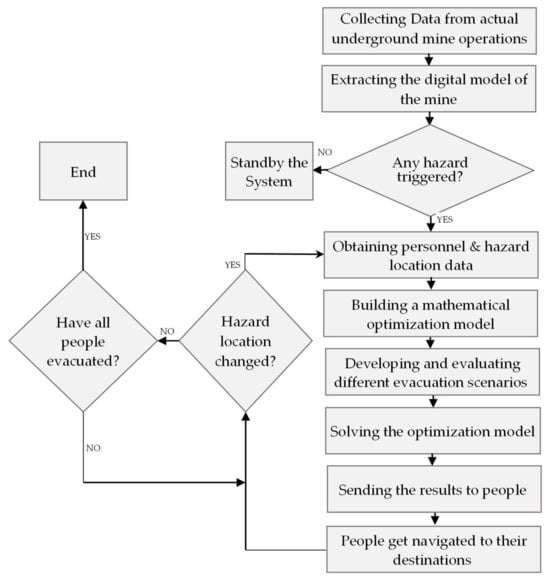
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sub-Surface Soil Characterization Using Image Analysis: Material Recognition Using the Grey Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Applied to a Video-CPT-Cone
by
Oksana Khomiak, Jörg Benndorf and Gerald Verbeek
Mining 2024, 4(1), 91-105; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010007 - 20 Feb 2024
Abstract
The geotechnical characterization of the subsurface is a key requirement for most soil investigations, incl. those for reclaiming landfills and waste dumps associated with mining operations. New sensor technology, combined with intelligent analysis algorithms, allow for a faster and less expensive acquisition of
[...] Read more.
The geotechnical characterization of the subsurface is a key requirement for most soil investigations, incl. those for reclaiming landfills and waste dumps associated with mining operations. New sensor technology, combined with intelligent analysis algorithms, allow for a faster and less expensive acquisition of the necessary information without loss of data quality. The use of advanced technologies to support and back up common site investigation techniques, such as cone penetration testing (CPT), can enhance the underground characterization process. This study aims to investigate the possibilities of image analysis for material recognition to advance the geotechnical characterization process. The grey level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) image processing technique is used in a wide range of study fields to estimate textures, patterns and structure anomalies. This method was adjusted and applied to process the video recorded during a CPT sounding, in order to distinguish soil types by its changing surface characteristics. From the results of the video processing, it is evident that the GLCM technique can identify transitions in soil types that were captured in the video recording. This enables the prospect of image analysis not just for soil investigations, but also for monitoring of the conveyor belt in the mining field, to allow for efficient preliminary decision making, material documentation and quality control by providing information in a cost effective and efficient manner.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Post-Mining Management)
►▼
Show Figures
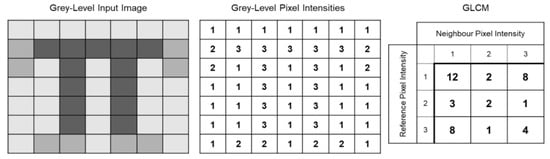
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sulphuric Acid Digestion of Anatase Concentrate
by
Carolina Nogueira da Silva, Liliani Pacheco Tavares Nazareth, Mônica Elizetti de Freitas and Ana Claudia Queiroz Ladeira
Mining 2024, 4(1), 79-90; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010006 - 06 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The processing of anatase ores by sulphuric acid digestion is well known for its low titanium dissolution yields, which makes the process economically and technically unfeasible. Anatase is considered much less reactive than other forms of titanium such as ilmenite and rutile. Generally,
[...] Read more.
The processing of anatase ores by sulphuric acid digestion is well known for its low titanium dissolution yields, which makes the process economically and technically unfeasible. Anatase is considered much less reactive than other forms of titanium such as ilmenite and rutile. Generally, to enhance its dissolution, thermal processes along with acid and/or alkaline leaching processes are necessary. Studies of direct sulphuric acid digestion are few and the reported yields of titanium dissolution are <48%. This study investigated the main parameters of sulphuric digestion of anatase such as temperature, anatase:acid ratio, and time of reaction. Dissolution of titanium of around 86% were obtained at relatively mild conditions such as, temperature at 220 °C, grain size of 62 µm, an anatase:sulphuric acid ratio of 1:2, and 4 h of reaction. A comprehensive characterization of the resulting material indicated a content of 56.5% of TiO2 and 15% iron oxide—the main impurity. It also contained silica, aluminum, phosphorus, calcium, and rare earth elements (REE) in concentrations that varied from 1.61% to 6.01%.
Full article
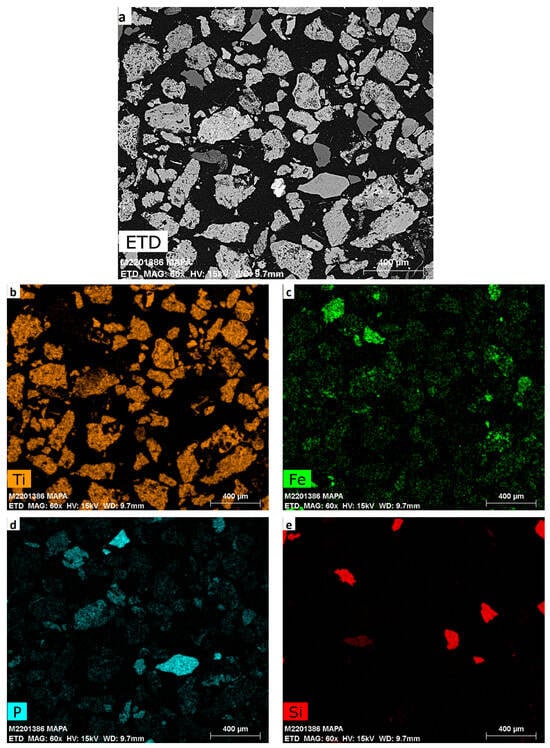
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Mine Closure Risk Rating System for South Africa
by
Megan J. Cole
Mining 2024, 4(1), 58-78; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010005 - 30 Jan 2024
Abstract
Mine closure is a growing concern in mining countries around the world due to the associated environmental and social impacts. This is particularly true in developing countries like South Africa where poverty, social deprivation and unemployment are widespread and environmental governance is not
[...] Read more.
Mine closure is a growing concern in mining countries around the world due to the associated environmental and social impacts. This is particularly true in developing countries like South Africa where poverty, social deprivation and unemployment are widespread and environmental governance is not strong. South Africa has 230 operating mines located in diverse natural and social settings. Over 6 million people live in urban and rural mining host communities who will be significantly affected by mine closure. The national, provincial and local governments need guidance in identifying high-risk areas and relevant policy and programmatic interventions. This paper describes the development of a quantitative mine closure risk rating system that assesses the likelihood of mine closure, the risk of social impact and the risk of environmental impact of mine closure for every operating mine in the country. The paper visualises the high likelihood of closure and environmental impacts for numerous coal and gold mines, and the significant social risks in the deprived rural platinum and chrome mining areas. The rating system was tested with 10 mines and 19 experts, and the resulting maps are communicated in an online South African Mine Closure Risk and Opportunity Atlas. The risk ratings could be used in mine closure planning and management by mining companies, consultancies, governments and affected communities. While this risk rating system has been designed for South Africa, the methodology and framework could be applied to any mining country in the world.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Innovative Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Mining)
►▼
Show Figures
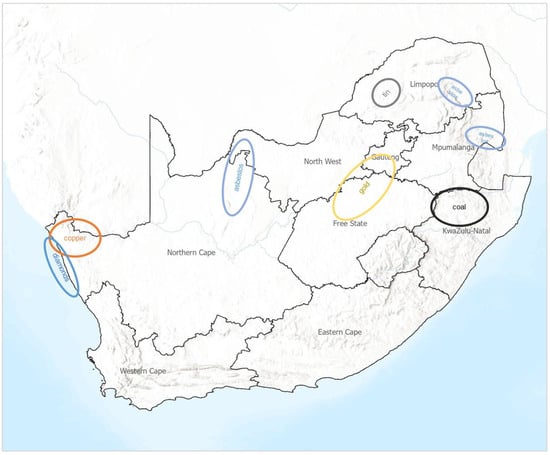
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Removal of Fe3+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption on Natural Eco-Friendly Brazilian Palygorskites
by
Antonieta Middea, Luciana dos Santos Spinelli, Fernando Gomes de Souza Junior, Thais de Lima Alves Pinheiro Fernandes, Luiz Carlos de Lima, Vitoria Maria Tupinamba Souza Barthem, Otávio da Fonseca Martins Gomes and Reiner Neumann
Mining 2024, 4(1), 37-57; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010004 - 19 Jan 2024
Abstract
This work focuses on the characterization of five palygorskite clays from the Brazilian state of Piaui and their feasibility as eco-friendly adsorbents for the removal of Fe3+ ions from aqueous solutions. For characterization, we applied the techniques of X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray
[...] Read more.
This work focuses on the characterization of five palygorskite clays from the Brazilian state of Piaui and their feasibility as eco-friendly adsorbents for the removal of Fe3+ ions from aqueous solutions. For characterization, we applied the techniques of X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS), size distribution measurements, density measurement by He pycnometry, superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometry, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA/DTA), zeta potential measurement, hydrophobicity determination by contact angle, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area analysis (BET technique) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Batch experiments were performed in function of process parameters such as contact time and initial concentration of Fe3+. The natural palygorskites (Palys) had excellent performance for the removal of Fe3+ from aqueous solutions by adsorption (around 60 mg/g), and the Langmuir is supposedly the best model fitted the experimental data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Sustainable Recycling and Reuse of Industrial By-Products or Waste from Geo-Resource Exploitation)
►▼
Show Figures
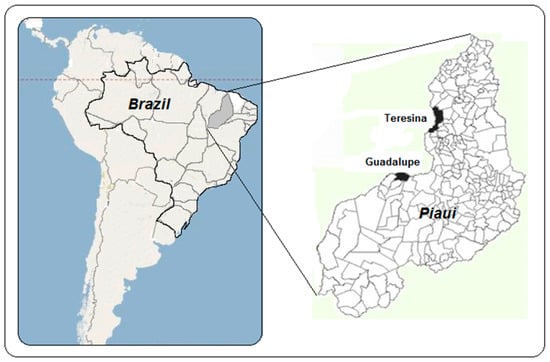
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Flow Liquefaction Susceptibility in Non-Plastic Silty Soils Using the Seismic Cone
by
Helena Paula Nierwinski, Fernando Schnaid and Edgar Odebrecht
Mining 2024, 4(1), 21-36; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010003 - 05 Jan 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The state parameter allows the evaluation of the in situ state of soils, which can be particularly useful in tailings impoundments where flow liquefaction is the most common failure model. Positive state parameter values characterize a contractive response during shearing and, for non-plastic
[...] Read more.
The state parameter allows the evaluation of the in situ state of soils, which can be particularly useful in tailings impoundments where flow liquefaction is the most common failure model. Positive state parameter values characterize a contractive response during shearing and, for non-plastic soils, can indicate flow liquefaction susceptibility. This paper presents a methodology to classify and estimate the state parameter (Ψ) for non-plastic silty soils based on seismic cone penetration measurements. The method expands on a previous methodology developed for sands that use the ratio of the small strain shear modulus and the cone tip resistance G0/qt for classification and Ψ assessment. For non-plastic silty soils, drainage conditions during cone penetration must be accounted for and are used to allow soil classification and correct the cone tip resistance. An empirical formulation is proposed to correct qt for partial drainage measurements and predict Ψ for non-plastic silty soils. Mining tailings results of in situ and laboratory tests were used to validate the proposed methodology producing promising responses. The Ψ value estimated through the proposed methodology are in the range of those obtained from laboratory tests, indicating an adequate prediction of behavior for non-plastic silty soils.
Full article
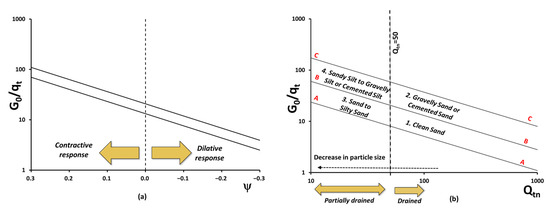
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Maximizing Mining Operations: Unlocking the Crucial Role of Intelligent Fleet Management Systems in Surface Mining’s Value Chain
by
Arman Hazrathosseini and Ali Moradi Afrapoli
Mining 2024, 4(1), 7-20; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010002 - 22 Dec 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
On the one side, the operational expenses of mining enterprises are showing an upward trend; and on the other side, conventional mining fleet management systems (FMSs) are falling short in addressing the high-dimensionality, stochasticity, and autonomy needed in increasingly complex operations. These major
[...] Read more.
On the one side, the operational expenses of mining enterprises are showing an upward trend; and on the other side, conventional mining fleet management systems (FMSs) are falling short in addressing the high-dimensionality, stochasticity, and autonomy needed in increasingly complex operations. These major drivers for change have convinced researchers to search for alternatives including artificial-intelligence-enabled algorithms recommended by Mining 4.0. The present study endeavors to scrutinize this transition from a business management point of view. In other words, a literature review is carried out to gain insight into the evolutionary trajectory of mining FMSs and the need for intelligent algorithms. Afterward, a holistic supply chain layout and then a detailed value chain diagram are depicted to meticulously inspect the effect of technological advancements on FMSs and subsequently the profit margin. The proposed value-chain diagram is advantageous in explaining the economic justification of such intelligent systems, illustratively, for shareholders in the industry. Moreover, it will show new research directions for mining scholars.
Full article
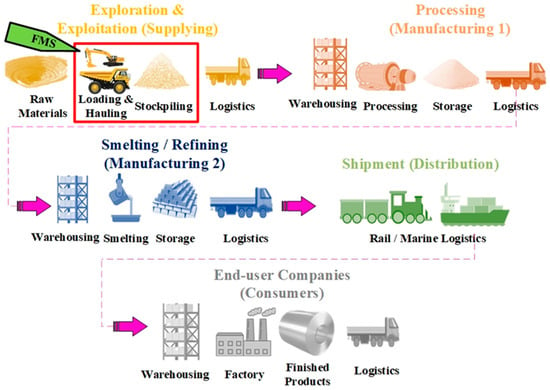
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Editorial for Special Issue “Envisioning the Future of Mining”
by
Juan M. Menéndez-Aguado, Oscar Jaime Restrepo Baena and Jessica M. Smith
Mining 2024, 4(1), 1-6; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining4010001 - 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
According to the International Energy Agency, clean energy transitions significantly increase strategic minerals demand [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Envisioning the Future of Mining)
Open AccessReview
Advancements in Mine Closure and Ecological Reclamation: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Overview (1980–2023)
by
Hamza Zine, Abdelhak El Mansour, Rachid Hakkou, Eleni G. Papazoglou and Mostafa Benzaazoua
Mining 2023, 3(4), 798-813; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3040044 - 16 Dec 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Faced with the ongoing energy transition and the escalating fragility of our natural ecosystems, ecological reclamation emerges as an imperative necessity. Investigation within this field has been in progress since the early 20th century. To gauge the advancements in this realm, elucidate the
[...] Read more.
Faced with the ongoing energy transition and the escalating fragility of our natural ecosystems, ecological reclamation emerges as an imperative necessity. Investigation within this field has been in progress since the early 20th century. To gauge the advancements in this realm, elucidate the evolving research trends, and emphasize pertinent metrics, it is essential to perform a comprehensive overview of the subject. Undertaking this bibliometric study is necessary to clarify research’s current state of play, grasp research hotspots, showcase outstanding researchers, and predict future research trends. In this work, 40,386 articles were retrieved from the Scopus and Web of Science databases, and bibliometric analysis was carried out using the Biblioshiny R package (Version 4.0.0, K-Synth Srl, Naples, Italy), and Python (PyCharm Community Edition 2023.2.1)o understand the progress in this research field from 1980 to 2023. The findings reveal a consistent upward trend in the publication rate within the field of mine closure and ecological reclamation over this timeframe, culminating in 6705 articles by 2022. Notably, authors and institutions from China have taken the lead, followed closely by those from the USA and Canada in terms of article publications. This prominence can be attributed to these countries’ rapid economic growth and energetic transition, which has frequently come at the expense of environmental quality, and a rise in reclamation challenges. In this sense, the circular economy has risen in force recently, which highlights the withdrawal of the old linear economy. In coming research on mine closure and ecological reclamation, multi-scale ecological reclamation research should be reinforced, and social and economic concerns should be integrated. This study pinpointed current research hotspots and forecasted potential future research areas, providing a scientific baseline for future studies in mine closure and ecological reclamation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Sustainable Mining Engineering 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
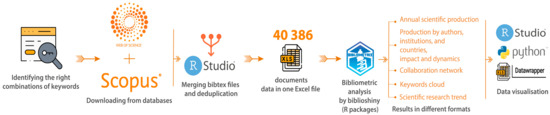
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mine Productivity Upper Bounds and Truck Dispatch Rules
by
Adriano Chaves Lisboa, Felipe Luz Barbosa Castro and Pedro Vinícius Almeida Borges de Venâncio
Mining 2023, 3(4), 786-797; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3040043 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper proposes an upper bound for mine productivity (useful for long-term planning) and also a simple truck dispatch rule (useful for short-term operations) that demonstrates how tight the upper bound can be using a simulation. It also proposes a greedy search to
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes an upper bound for mine productivity (useful for long-term planning) and also a simple truck dispatch rule (useful for short-term operations) that demonstrates how tight the upper bound can be using a simulation. It also proposes a greedy search to approximate the productivity upper bound, which is faster and often exact. Uncertainty is added to the simulation in order to verify how the productivity responds to it. Typically, the productivity’s upper bound is less tight close to its saturation point as a function of the number of trucks, where adding more trucks only increases queues. Furthermore, more uncertainty in the model typically leads to a less tight upper bound. The results conducted using real data from an open pit mine in Brazil show that the gap between the productivity upper bound and the productivity realization using the proposed dispatch rule for a homogeneous fleet can be less than
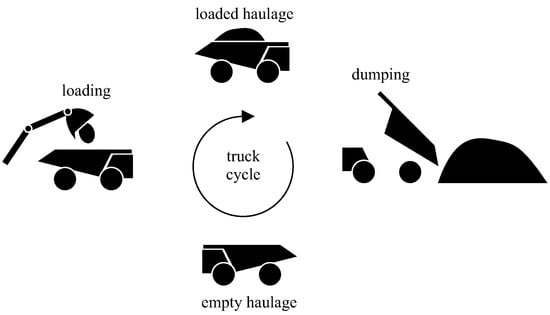
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Monte Carlo Analytic Hierarchy Process (MAHP) in Underground Mining Access Selection
by
Fernando A. C. Cardozo, Higor J. S. Campos, Carlos O. Petter and Weslei M. Ambrós
Mining 2023, 3(4), 773-785; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3040042 - 01 Dec 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
This paper presents the application of risk analysis associated with the multicriteria decision method, through the MAHP (Monte Carlo analytic hierarchy process) technique for mining. As an example of application, the problem of choosing an access and transportation route for an underground mine
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the application of risk analysis associated with the multicriteria decision method, through the MAHP (Monte Carlo analytic hierarchy process) technique for mining. As an example of application, the problem of choosing an access and transportation route for an underground mine is addressed. A decision can be made based on a technical, economic, and social-environmental approach. As a topic of interest for the modeling of mining projects, this work presents how the technique can qualify the decision-making process, reducing its subjectivity. It is verified that in comparison with the traditional AHP (analytic hierarchy process) method, the risk analysis allows considering the variability of weights and preferences assigned to criteria and options. In the example case, the following options are evaluated: shaft, ramp by diesel or electric truck, and conveyor belt.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Underground Mine Planning, Scheduling, and Optimization: Theory and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
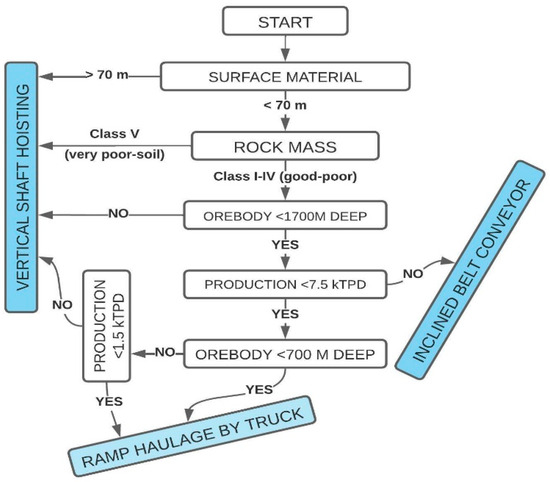
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Numerical Modeling Study for Parameter Optimization and Slope Stability Analysis in the Baganuur Lignite Coal Mine
by
Bilguun Enkhbold, Hajime Ikeda, Hisatoshi Toriya and Tsuyoshi Adachi
Mining 2023, 3(4), 755-772; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3040041 - 22 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The “Baganuur” lignite coal mine is one of the biggest open cast mines in Mongolia. However, there is a huge challenge in managing the stability of its internal dump, which prevents the proper operation of the mine and has an impact on the
[...] Read more.
The “Baganuur” lignite coal mine is one of the biggest open cast mines in Mongolia. However, there is a huge challenge in managing the stability of its internal dump, which prevents the proper operation of the mine and has an impact on the economy. To solve the internal dump slope stability problem, this study focused on incorporating the inherent mechanical properties of the rock material to build numerical models of the internal dump. By applying two software programs from Rocscience (Phase2 and Slide) and four different methods, the finite element method, the Bishop method, the Janbu simplified method, and the Spencer simplified method, the current and improved internal dump parameters were numerically simulated and analyzed. Based on the properties of the rock, the LEM and FEM were used to determine the parameters that could have an impact on the stability of the internal waste dump. The impacts of the internal dump height, dip angle, and safety berm on these parameters were studied. This study covers several analytical methods for calculating safety factors. Based on the results of the numerical simulation, it is determined that it is possible to increase the internal dump capacity by approximately 56% at a 50 m height and 28° dip angle and using a 15 m safety berm. Under similar conditions, this study presents an optimum SRF at 40 m height, 28° dip angle, and 5 m safety berm. Based on the numerical models, it is found that changes in the dip angle have a greater impact than changes in the dump height on the slope stability of an internal dump.
Full article
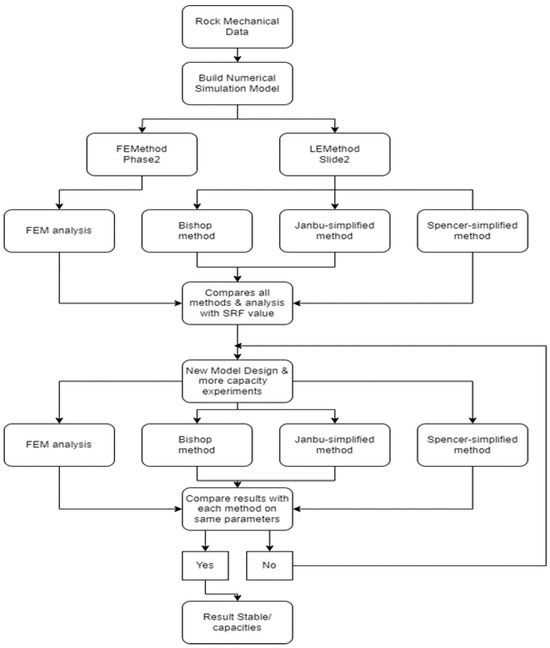
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Modelling Application in the Management of Deep Mining Excavation Stresses: An Illustrative Study
by
Tawanda Zvarivadza
Mining 2023, 3(4), 731-754; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3040040 - 21 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Numerical modelling is an important instrument for rock engineering; it can assist in the design and prediction of failure in rock masses. Dependable results can be obtained from the models if, and only if, the underlying assumptions, strengths, and weaknesses of the model
[...] Read more.
Numerical modelling is an important instrument for rock engineering; it can assist in the design and prediction of failure in rock masses. Dependable results can be obtained from the models if, and only if, the underlying assumptions, strengths, and weaknesses of the model are known. A set of guidelines to implement a numerical modelling program can also be used to obtain high-quality and reliable results. The importance of a well-structured numerical modelling program to attain practically reasonable results cannot be overstated. This paper presents an analysis of the results of modelling a rock engineering problem involving deep mining excavations prone to high-stress challenges. The study used Lamodel and Examine 2D. The results obtained show that the two software programs can be used together to complement each other in attaining a deeper understanding of the influence of high stresses on mining excavations at depth. Lamodel and Examine 2D are both boundary element code-based software and are quick and easy to use. More advanced numerical modelling tools could be used, but these two were found to be suitable for the problem at hand. Many diagrams and results can be obtained from the numerical modelling of any rock engineering challenge; in this paper, only those diagrams and results deemed to be most relevant and appropriate to demonstrate the capabilities, limitations, and validity of the numerical modelling of the problem have been presented.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mechanical and Microstructural Response of Iron Ore Tailings under Low and High Pressures Considering a Wide Range of Molding Characteristics
by
Giovani Jordi Bruschi, Carolina Pereira Dos Santos, Hugo Carlos Scheuermann Filho, Camila da Silva Martinatto, Luana Rutz Schulz, João Paulo de Sousa Silva and Nilo Cesar Consoli
Mining 2023, 3(4), 712-730; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3040039 - 18 Nov 2023
Abstract
The dry stacking of filtered tailings is an option to deal with safety-related issues involving traditional slurry disposition in impoundments. Filtered tailings can be compacted to pre-define design specifications, which minimizes structural instability problems, such as those related to liquefaction. Yet, comprehending the
[...] Read more.
The dry stacking of filtered tailings is an option to deal with safety-related issues involving traditional slurry disposition in impoundments. Filtered tailings can be compacted to pre-define design specifications, which minimizes structural instability problems, such as those related to liquefaction. Yet, comprehending the tailing’s response under various stress states is essential to designing any dry stacking facility properly. Thus, the present research evaluated the mechanical response of cemented and uncemented compacted filtered iron ore tailings, considering different molding characteristics related to compaction degree and molding moisture content. Therefore, a series of one-dimensional compression tests and consolidated isotropically drained triaxial tests (CID), using 300 kPa and 3000 kPa effective confining pressures, were carried out for different specimens compacted at various molding characteristics. In addition, changes in gradation owing to both compression and shearing were evaluated using sedimentation with scanning electron microscope tests. The overall results have indicated that the 3% Portland cement addition enhanced the strength and stiffness of the compacted iron ore tailings, considering the lower confining pressure. Nevertheless, the same was not evidenced for the higher confining stress. Moreover, the dry-side molded specimens were initially stiffer, and significant particle breakage did not occur owing to one-dimensional compression but only due to shearing (triaxial condition).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Mining Innovation)
►▼
Show Figures
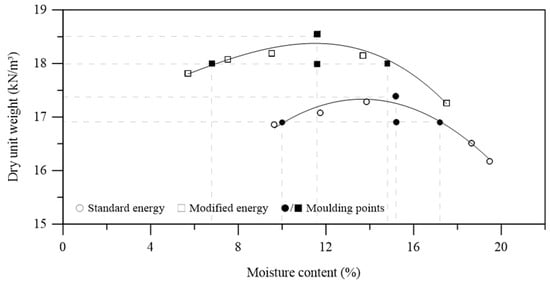
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Minerals, Mining, Sustainability
Mining Innovation
Topic Editors: Krzysztof Skrzypkowski, René Gómez, Fhatuwani Sengani, Derek B. Apel, Faham Tahmasebinia, Jianhang ChenDeadline: 1 June 2024
Topic in
Energies, IJERPH, Minerals, Mining, Safety
Exploring the Mine Environment, Safety Risk and Occupational Health
Topic Editors: Chengyu Xie, Jian Zhou, Danial Jahed Armaghani, Qingfa Chen, Wei PanDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Materials, Mining, Recycling, Resources, Sustainability
Sustainable Recycling and Reuse of Industrial By-Products or Waste from Geo-Resource Exploitation
Topic Editors: Sossio Fabio Graziano, Rossana Bellopede, Giovanna Antonella Dino, Nicola CaredduDeadline: 1 November 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Crystals, Materials, Minerals, Mining, Toxics
Innovative Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Mining
Topic Editors: Chongchong Qi, Qiusong Chen, Danial Jahed ArmaghaniDeadline: 31 March 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Mining
Post-Mining Management
Guest Editors: Jörg Benndorf, Tobias Rudolph, Jan BlachowskiDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Mining
Women’s Special Issue Series: Mining
Guest Editors: Marilena Cardu, Giovanna DinoDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Mining
Envisioning the Future of Mining, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Juan M Menéndez-Aguado, Oscar Jaime Restrepo Baena, Juan C. LucenaDeadline: 15 December 2024
Special Issue in
Mining
Feature Papers in Sustainable Mining Engineering 2024
Guest Editors: Mostafa Benzaazoua, Yassine Ait-KhouiaDeadline: 31 December 2024






