-
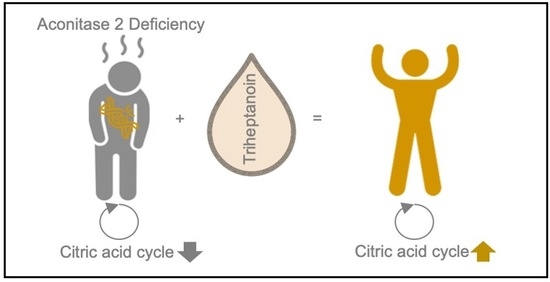
 Bayesian 13C-Metabolic Flux Analysis of Parallel Tracer Experiments in Granulocytes: A Directional Shift within the Nonoxidative Pentose Phosphate Pathway Supports Phagocytosis
Bayesian 13C-Metabolic Flux Analysis of Parallel Tracer Experiments in Granulocytes: A Directional Shift within the Nonoxidative Pentose Phosphate Pathway Supports Phagocytosis -
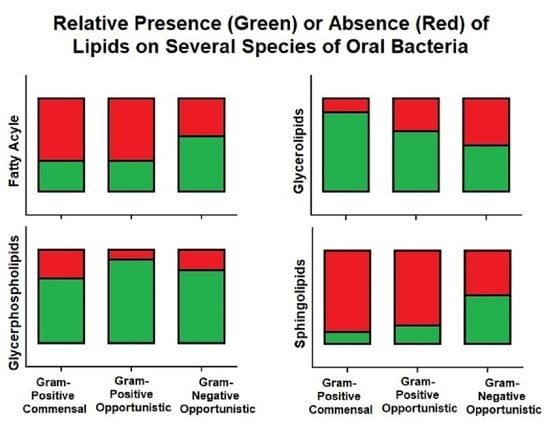
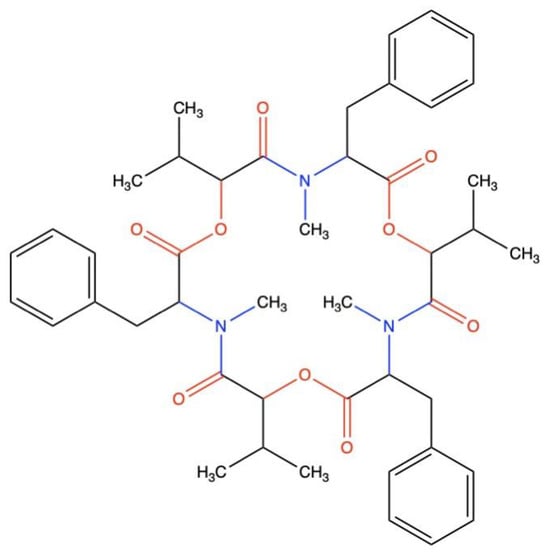
 Phytocompounds and Regulation of Flavonoids in In Vitro-Grown Safflower Plant Tissue by Abiotic Elicitor CdCl2
Phytocompounds and Regulation of Flavonoids in In Vitro-Grown Safflower Plant Tissue by Abiotic Elicitor CdCl2 -
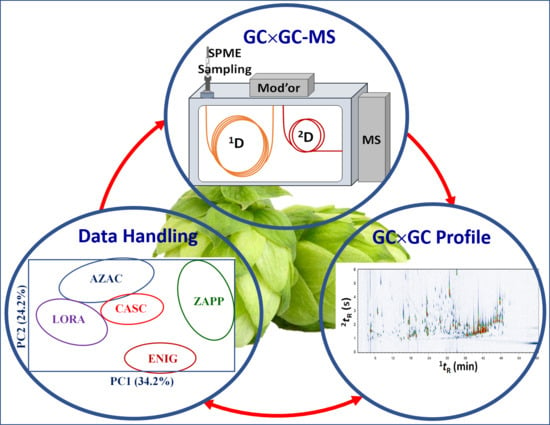
 Metabolic Changes and Their Associations with Selected Nutrients Intake in the Group of Women Environmentally Exposed to Arsenic
Metabolic Changes and Their Associations with Selected Nutrients Intake in the Group of Women Environmentally Exposed to Arsenic -
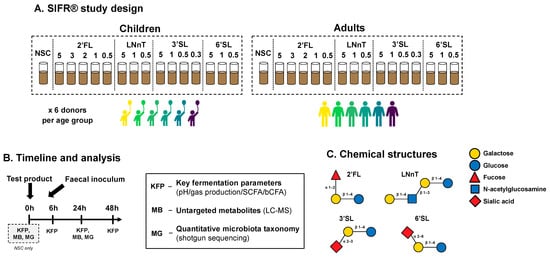
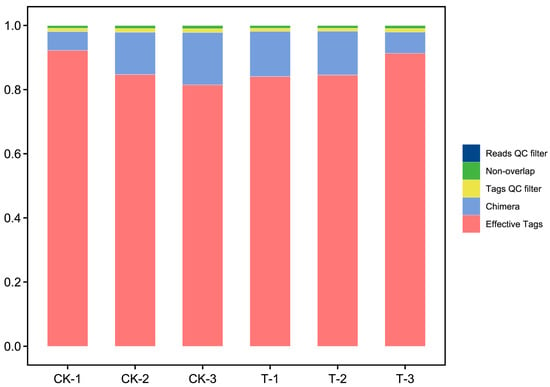
 metabCombiner 2.0: Disparate Multi-Dataset Feature Alignment for LC-MS Metabolomics
metabCombiner 2.0: Disparate Multi-Dataset Feature Alignment for LC-MS Metabolomics -
 Genome-Wide Association (GWAS) Applied to Carcass and Meat Traits of Nellore Cattle
Genome-Wide Association (GWAS) Applied to Carcass and Meat Traits of Nellore Cattle
Journal Description
Metabolites
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q2 (Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 31 May 2024
Deadline: 30 June 2024
Deadline: 31 July 2024
Deadline: 31 August 2024
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 25 April 2024
Deadline: 30 April 2024
Deadline: 25 May 2024
Deadline: 1 June 2024