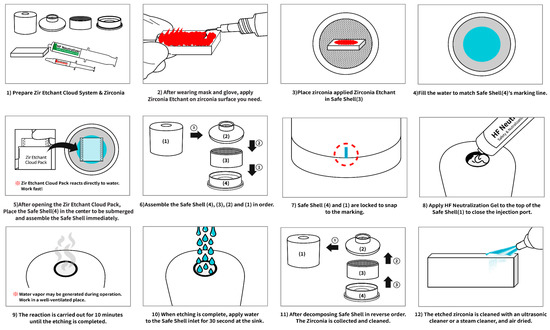
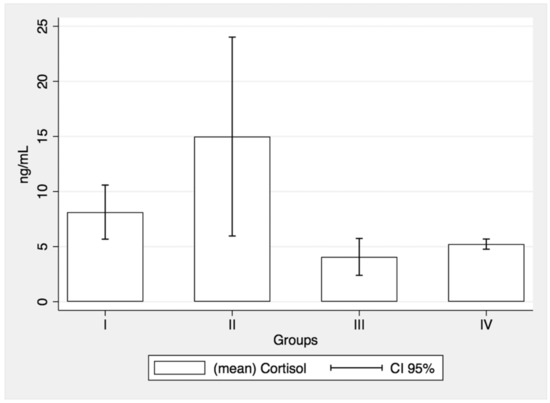
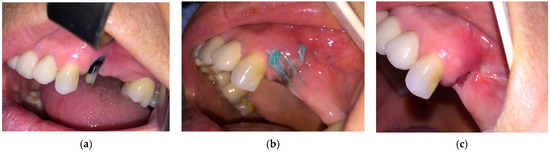
New Concepts for Dental Treatments and Evaluations
A topical collection in Medicina (ISSN 1648-9144). This collection belongs to the section "Dentistry".
Viewed by 60656Editors
Interests: optical coherence tomography; micro-computer tomography; nanotechnologies; ceramics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. Doctoral School, Polytechnic University of Timisoara, 300006 Timisoara, Romania
Interests: optomechatronics; laser systems; biomedical imaging; optical coherence tomography (OCT); measuring systems; optical metrology; materials study; biomaterials characterization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Dental medicine has benefited from significant advances in terms of both diagnosis and treatment. Thus, well-established techniques such as radiography, microscopy, and the gold standard of histopathology for clinical assessments as well as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and micro-CT for research purposes are being complemented by rapidly evolving techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT). The latter targets both hard and soft tissue of the oral cavity, including the use of Doppler OCT.
Modern dental treatments, such as laser-based procedures, complement the classical approaches.
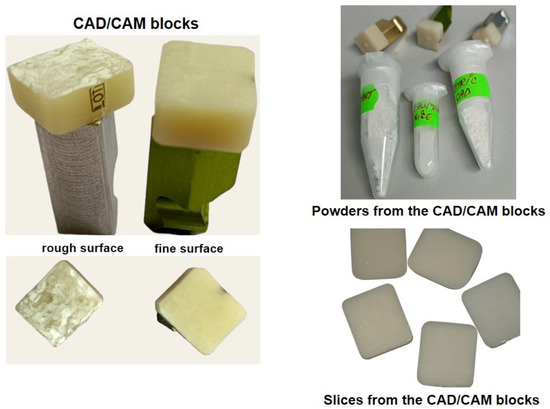
Biomaterials have been developed, including for dental crowns, scaffolds (for example, for bone augmentation in implantology), or dental adhesives.
The aim of this Special Issue is to provide a forum for contributions regarding all the above topics as well as other relevant and timely aspects concerning techniques for both diagnosis and treatment in addition to their assessment.
While this forum is open to all researchers in the fields above, it also provides a topical selection of papers presented at the 1st International Conference ‘Advances in 3OM: Opto-Mechatronics, Opto-Mechanics, and Optical Metrology’ (Timisoara, Romania), organized in celebration of 100 years of the Polytechnic University of Timisoara but also in the frame of UNESCO’s International Day of Light (IDL).
All types of contributions, e.g., research papers, reviews, and communications are welcome.
Prof. Cosmin Sinescu
Prof. Virgil-Florin Duma
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Medicina is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1800 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- dental medicine
- dental treatments
- prosthodontics
- lasers in dentistry
- dental evaluations
- biomedical imaging
- optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- confocal microscopy
- micro-CT
- non-destructive testing (NDT)
- biomaterials
- dental adhesives
- scaffolds