-
 Neuropsychological Consequences of Massive Trauma: Implications and Clinical Interventions
Neuropsychological Consequences of Massive Trauma: Implications and Clinical Interventions -
 Impact of GLP-1 Agonists on Male Reproductive Health—A Narrative Review
Impact of GLP-1 Agonists on Male Reproductive Health—A Narrative Review -
 Acupuncture for Japanese Katakori (Chronic Neck Pain): A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind Study
Acupuncture for Japanese Katakori (Chronic Neck Pain): A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind Study -
 Giant Cell Arteritis after COVID-19 Vaccination with Long-Term Follow-Up: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Giant Cell Arteritis after COVID-19 Vaccination with Long-Term Follow-Up: A Case Report and Review of the Literature -
 Worsening Symptoms Is Associated with Larger Cerebral Blood Flow Abnormalities during Tilt-Testing in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)
Worsening Symptoms Is Associated with Larger Cerebral Blood Flow Abnormalities during Tilt-Testing in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)
Journal Description
Medicina
Medicina
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal that covers all problems related to medicine. The journal is owned by the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences (LUHS) and is published monthly online by MDPI. Partner Societies are the Lithuanian Medical Association, Vilnius University, Rīga Stradiņš University, the University of Latvia, and the University of Tartu.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
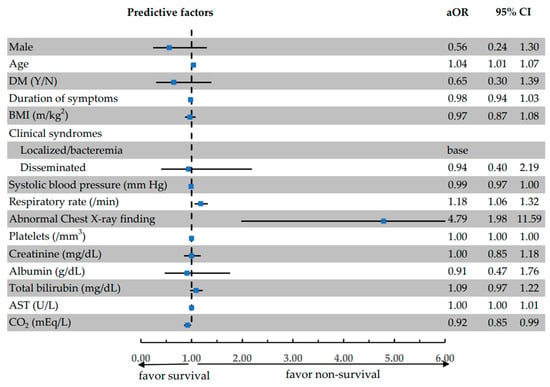
The Predictive Factors Associated with In-Hospital Mortality of Melioidosis: A Cohort Study
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 654; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040654 (registering DOI) - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, and it has a wide range of clinical symptoms. It is endemic in tropical areas, including Southeast Asia. Despite the availability of effective treatment, the mortality rate is still
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, and it has a wide range of clinical symptoms. It is endemic in tropical areas, including Southeast Asia. Despite the availability of effective treatment, the mortality rate is still high, especially in patients presenting with septic shock. The aim of this study was to determine and explore clinical characteristics, microbiology, treatment outcomes, and factors associated with in-hospital mortality which could predict prognosis and provide a guide for future treatment. Materials and Methods: The population in this retrospective cohort study included all 262 patients with a diagnosis of melioidosis who were hospitalized at Surin Hospital, Surin, Thailand, from April 2014 to March 2017. We included patients older than 15 years with a positive culture for B. pseudomallei. Data regarding the clinical characteristics, microbiology, and treatment outcomes of the patients were collected and analyzed. The patients were divided into two groups dependent on outcome, specifically non-survival and survival. Logistic regression was performed to determine the risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality. Results: Out of the 262 patients with melioidosis during the study period, 117 (44.7%) patients died. The mean age was 57.2 ± 14.4 years, and 193 (73.7%) patients were male. The most common comorbidity was diabetes (123, 46.9%), followed by chronic kidney disease (35, 13.4%) and chronic liver disease (31, 11.8%). Four risk factors were found to be associated with in-hospital mortality, including age (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.04, 95%CI: 1.01–1.07), respiration rate (aOR 1.18, 95%CI: 1.06–1.32), abnormal chest X-ray finding (aOR 4.79, 95%CI: 1.98–11.59), and bicarbonate levels (CO2) (aOR 0.92, 95%CI: 0.85–0.99). Conclusions: Our study identified age, respiration rate, abnormal chest X-ray finding, and CO2 levels are predictive factors associated with in-hospital mortality in melioidosis patients. Physicians should be aware of these factors, have access to aggressive treatment options, and closely monitor patients with these risk factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Infectious Disease)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Health Effects of Ionizing Radiation on the Human Body
by
Jasminka Talapko, Domagoj Talapko, Darko Katalinić, Ivan Kotris, Ivan Erić, Dino Belić, Mila Vasilj Mihaljević, Ana Vasilj, Suzana Erić, Josipa Flam, Sanja Bekić, Suzana Matić and Ivana Škrlec
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 653; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040653 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Radioactivity is a process in which the nuclei of unstable atoms spontaneously decay, producing other nuclei and releasing energy in the form of ionizing radiation in the form of alpha (α) and beta (β) particles as well as the emission of gamma (γ)
[...] Read more.
Radioactivity is a process in which the nuclei of unstable atoms spontaneously decay, producing other nuclei and releasing energy in the form of ionizing radiation in the form of alpha (α) and beta (β) particles as well as the emission of gamma (γ) electromagnetic waves. People may be exposed to radiation in various forms, as casualties of nuclear accidents, workers in power plants, or while working and using different radiation sources in medicine and health care. Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) occurs in subjects exposed to a very high dose of radiation in a very short period of time. Each form of radiation has a unique pathophysiological effect. Unfortunately, higher organisms—human beings—in the course of evolution have not acquired receptors for the direct “capture” of radiation energy, which is transferred at the level of DNA, cells, tissues, and organs. Radiation in biological systems depends on the amount of absorbed energy and its spatial distribution, particularly depending on the linear energy transfer (LET). Photon radiation with low LET leads to homogeneous energy deposition in the entire tissue volume. On the other hand, radiation with a high LET produces a fast Bragg peak, which generates a low input dose, whereby the penetration depth into the tissue increases with the radiation energy. The consequences are mutations, apoptosis, the development of cancer, and cell death. The most sensitive cells are those that divide intensively—bone marrow cells, digestive tract cells, reproductive cells, and skin cells. The health care system and the public should raise awareness of the consequences of ionizing radiation. Therefore, our aim is to identify the consequences of ARS taking into account radiation damage to the respiratory system, nervous system, hematopoietic system, gastrointestinal tract, and skin.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Epidemiology & Public Health)
Open AccessArticle
Effects of the Neuropeptides Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase Activating Polypeptide and Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide in Male Fertility
by
Roba Bdeir, Maha S. Al-Keilani and Khaldoun Khamaiseh
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 652; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040652 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The neuroendocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including reproduction, with evidence suggesting its significant involvement in male fertility and sperm development. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) are expressed
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The neuroendocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including reproduction, with evidence suggesting its significant involvement in male fertility and sperm development. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) are expressed in both male and female reproductive tissues, influencing penile erection and regulating steroidogenesis in males. Therefore, our study aimed to compare the protein levels of VIP and PACAP in seminal plasma between healthy controls and sub-fertile patients. Additionally, we sought to correlate the levels of these biomarkers with clinical, functional, and laboratory findings in the participants. Materials and Methods: The study included a total of 163 male participants for analysis. The participants were further stratified into subgroups of fertile and sub-fertile men of four subgroups according to the 2021 WHO guidelines. Seminal plasma concentrations of the neuropeptides VIP and PACAP were measured using human enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique. Results: The findings showed statistically significant differences in total sperm count, sperm concentration, total motility, and vitality (p < 0.001) between the fertile group and the sub-fertile group. Specifically, significant differences found between healthy males and oligoasthenospermic patients (p = 0.002), and between asthenospermic and oligoasthenospermic patients (p = 0.039). An ROC analysis showed associated sensitivity and specificity values of 62.2% and 55.6%, respectively, to PACAP seminal levels differentiated between sub-fertile patients from fertile males (p = 0.028). No significant difference in seminal levels of VIP was found between the sub-fertile and fertile groups. Conclusions: Previous research leads to the point of PACAP active involvement in spermatogenesis. In accordance to our study, in human semen samples, we have seen a significance change in PACAP levels amongst patients with low sperm count or with both low sperm count and low motility, hinting at its contribution and acting as a possible factor in this complex process. Thus, alterations in the levels or actions of these neuropeptides have been associated with certain reproductive disorders in males.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in the Management of Male Infertility: Innovative Strategies and Emerging Technologies for Improved Diagnosis and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
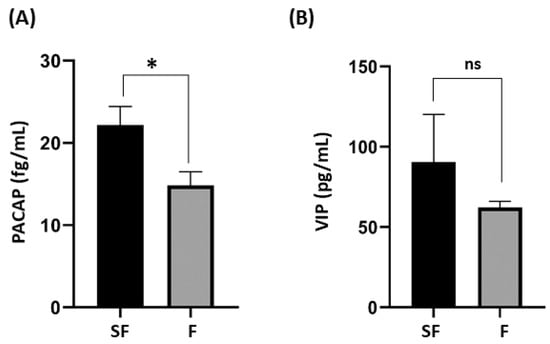
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Uterine Cesarean Scar Tissue—An Immunohistochemical Study
by
Maciej Ziętek, Małgorzata Świątkowska-Feund, Sylwester Ciećwież, Tomasz Machałowski and Małgorzata Szczuko
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 651; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040651 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Wound healing encompasses a multitude of factors and entails the establishment of interactions among components of the basement membrane. The quantification of particle concentrations can serve as valuable biomarkers for assessing biomechanical muscle properties. The objective of this study
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Wound healing encompasses a multitude of factors and entails the establishment of interactions among components of the basement membrane. The quantification of particle concentrations can serve as valuable biomarkers for assessing biomechanical muscle properties. The objective of this study was to examine the immunoexpression and immunoconcentration of myometrial collagen type VI, elastin, alpha-smooth muscle actin, and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, as well as the expression of platelets and clusters of differentiation 31 in the uterine scar following a cesarean section (CS). Materials and Methods: A total of 177 biopsies were procured from a cohort of pregnant women who were healthy, specifically during the surgical procedure of CS. The participants were categorized into seven distinct groups. Group 1 consisted of primiparas, with a total of 52 individuals. The subsequent groups were organized based on the duration of time that had elapsed since their previous CS. The analysis focused on the immunoexpression and immunoconcentration of the particles listed. Results: No significant variations were observed in the myometrial immunoconcentration of collagen type VI, elastin, smooth muscle myosin, and endothelial cell cluster of differentiation 31 among the analyzed groups. The concentration of alpha-smooth muscle actin in the myometrium was found to be significantly higher in patients who underwent CS within a period of less than 2 years since their previous CS, compared to those with a longer interval between procedures. Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the immunoconcentration of uterine myometrial scar collagen type VI, elastin, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, alpha-smooth muscle actin, and endothelial cell marker cluster of differentiation 31 remains consistent regardless of the duration elapsed since the previous CS. The findings indicate that there are no significant alterations in the biomechanical properties of the uterine muscle beyond a period of 13 months following a CS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Obstetrics and Gynecology)
Open AccessArticle
Addressing Thalassaemia Management from Patients’ Perspectives: An International Collaborative Assessment
by
Eleftheria C. Economidou, Michael Angastiniotis, Demetris Avraam, Elpidoforos S. Soteriades and Androulla Eleftheriou
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 650; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040650 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The effective management of chronic diseases, particularly hereditary and rare diseases and thalassaemia, is an important indicator of the quality of healthcare systems. We aimed to assess healthcare services in different countries for thalassaemia patients by using publicly available
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The effective management of chronic diseases, particularly hereditary and rare diseases and thalassaemia, is an important indicator of the quality of healthcare systems. We aimed to assess healthcare services in different countries for thalassaemia patients by using publicly available health indicators and by surveying thalassaemia patients and their caregivers. Materials and Methods: We reviewed official worldwide databases from the WHO, World Bank, and scientific resources, and we used a structured patient-tailored self-completed questionnaire to survey thalassaemia patients and their caregivers in 2023. Results: A total of 2082 participants were surveyed (mean age, 27 years; males, 42%). About 1 in 4 respondents did not complete high-school education, while 24% had a bachelor’s degree. About a third of respondents were married and were in either full- or part-time employment. The vast majority (~80%) had initiated transfusion therapy between 1 and 4 years of age. Only 42% reported no delays in receiving blood transfusion, while 47% reported occasional delays and 8% serious delays. About half of patients reported being very satisfied (11%) or satisfied (38%) with the quality of services provided, while 1 in 3 patients reported being unsatisfied or very unsatisfied, and that their access to treatment was difficult or very difficult due to traveling expenses and the high cost of treatment. Conclusions: Important improvements in the care of thalassaemia patients have been documented during the past few decades. Nevertheless, additional focus is required through national healthcare systems to effectively address the many unmet needs revealed by our recent survey, as well as to achieve satisfactory patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Epidemiology & Public Health)
►▼
Show Figures
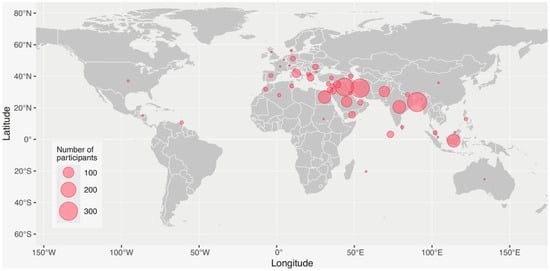
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Pringle Maneuver Applied during Living Donor Hepatectomy on the Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Observed in the Donors and Recipients
by
Yasin Dalda, Sami Akbulut, Tevfik Tolga Sahin, Adem Tuncer, Zeki Ogut, Basri Satilmis, Ozlem Dalda, Mehmet Gul and Sezai Yilmaz
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 649; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040649 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical and laboratory changes of ischemia and reperfusion injury in the remnant livers of donors with and without Pringle maneuver. Furthermore, we evaluated the recipients who have been transplanted with
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical and laboratory changes of ischemia and reperfusion injury in the remnant livers of donors with and without Pringle maneuver. Furthermore, we evaluated the recipients who have been transplanted with liver grafts from these donors. Methods and Materials: A total of 108 patients (54 living liver donors and 54 liver recipients) who underwent donor hepatectomy and recipients who living donor liver transplantation, were included in this randomized double-blind study between February 2021 and June 2021. The donors were divided into two groups: Pringle maneuver applied (n = 27) and Pringle maneuver not applied (n = 27). Similarly, recipients with implanted liver obtained from these donors were divided into two groups as the Pringle maneuver was performed (n = 27) and not performed (n = 27). Blood samples from donors and recipients were obtained on pre-operative, post-operative 0 h day (day of surgery), post-operative 1st day, post-operative 2nd day, post-operative 3rd day, post-operative 4th day, post-operative 5th day, and liver tissue was taken from the graft during the back table procedures. Liver function tests and complete blood count, coagulation tests, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, and β-galactosidase measurements, and histopathological findings were examined. Results: There was no statistically significant difference in the parameters of biochemical analyses for ischemia-reperfusion injury at all periods in the donors with and without the Pringle maneuver. Similarly, there was no statistically significant difference between in the recipients in who received liver grafts harvested with and without the Pringle maneuver. There was no statistically significant difference between the two recipient groups in terms of perioperative bleeding and early bile duct complications (p = 0.685). In the histopathological examinations, hepatocyte damage was significantly higher in the Pringle maneuver group (p = 0.001). Conclusions: Although the histological scoring of hepatocyte damage was found to be higher in the Pringle maneuver group, the Pringle maneuver did not augment ischemia-reperfusion injury in donors and recipients that was evaluated by clinical and laboratory analyses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
►▼
Show Figures
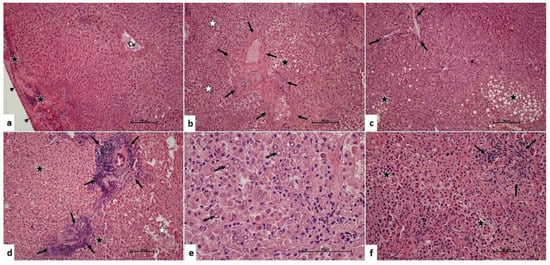
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Cracking the Code: Investigating the Correlation between Aerobic Vaginitis and Preterm Labor
by
Panagiota Zarmakoupi, Alexandros Psarris, Christina Karasmani, Panagiotis Antsaklis, Marianna Theodora, Michael Syndos, Andreas Pampanos, Kalliopi I. Pappa, Ekaterini Domali, Nikolaos Thomakos, Karolina Akinosoglou, Aristotelis Tsiakalos and George Daskalakis
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 648; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040648 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Aerobic vaginitis (AV) is a distinct clinical entity characterized by inflammation and abnormal vaginal microflora. Often mistaken for bacterial vaginosis, AV remains relatively unknown and underdiagnosed. AV’s understanding is evolving, with some experts suggesting it may primarily be an immunological disorder, the prevalence
[...] Read more.
Aerobic vaginitis (AV) is a distinct clinical entity characterized by inflammation and abnormal vaginal microflora. Often mistaken for bacterial vaginosis, AV remains relatively unknown and underdiagnosed. AV’s understanding is evolving, with some experts suggesting it may primarily be an immunological disorder, the prevalence of which has a range of 7–13% in non-pregnant women and 4.1–8.3% during pregnancy. Pregnancy can affect susceptibility to vaginal infections, leading to adverse outcomes for the woman and the newborn. This review summarizes the correlation between AV and adverse pregnancy outcomes, particularly preterm birth, the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among neonates. An improved understanding of AV’s impact on pregnancy outcomes can lead to early recognition, proper management, and effective interventions. While some studies support an association between AV and preterm labor, the existing knowledge of this relationship remains limited. The evidence suggests that AV may contribute to adverse pregnancy outcomes, mainly preterm birth, but further research is needed to establish a definitive link. Further studies are needed to investigate the underlying mechanisms and clarify AV’s role in premature labor. A comprehensive understanding of AV’s impact on pregnancy outcomes is crucial for early recognition, appropriate management, and effective interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Diseases during Pregnancy: Part II)
►▼
Show Figures
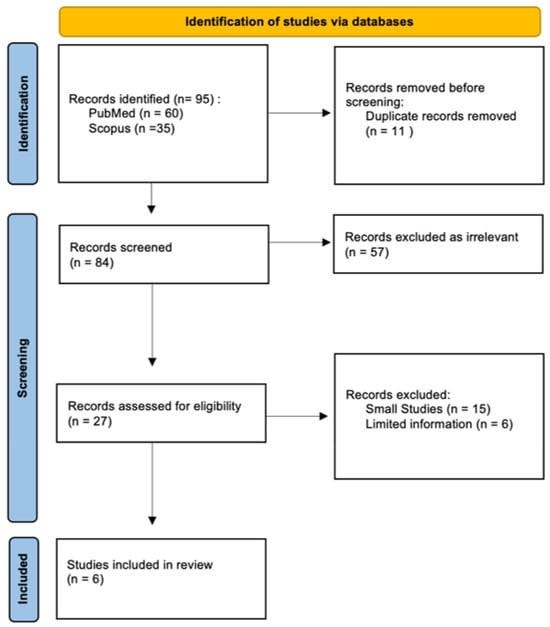
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Use of Reverse Shock Index Multiplied by Simplified Motor Score in a Five-Level Triage System: Identifying Trauma in Adult Patients at a High Risk of Mortality
by
Po-Chen Lin, Meng-Yu Wu, Da-Sen Chien, Jui-Yuan Chung, Chi-Yuan Liu, I-Shiang Tzeng, Yueh-Tseng Hou, Yu-Long Chen and Giou-Teng Yiang
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 647; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040647 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The Taiwan Triage and Acuity Scale (TTAS) is reliable for triaging patients in emergency departments in Taiwan; however, most triage decisions are still based on chief complaints. The reverse-shock index (SI) multiplied by the simplified motor score (rSI-sMS) is
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The Taiwan Triage and Acuity Scale (TTAS) is reliable for triaging patients in emergency departments in Taiwan; however, most triage decisions are still based on chief complaints. The reverse-shock index (SI) multiplied by the simplified motor score (rSI-sMS) is a more comprehensive approach to triage that combines the SI and a modified consciousness assessment. We investigated the combination of the TTAS and rSI-sMS for triage compared with either parameter alone as well as the SI and modified SI. Materials and Methods: We analyzed 13,144 patients with trauma from the Taipei Tzu Chi Trauma Database. We investigated the prioritization performance of the TTAS, rSI-sMS, and their combination. A subgroup analysis was performed to evaluate the trends in all clinical outcomes for different rSI-sMS values. The sensitivity and specificity of rSI-sMS were investigated at a cutoff value of 4 (based on previous study and the highest score of the Youden Index) in predicting injury severity clinical outcomes under the TTAS system were also investigated. Results: Compared with patients in triage level III, those in triage levels I and II had higher odds ratios for major injury (as indicated by revised trauma score < 7 and injury severity score [ISS] ≥ 16), intensive care unit (ICU) admission, prolonged ICU stay (≥14 days), prolonged hospital stay (≥30 days), and mortality. In all three triage levels, the rSI-sMS < 4 group had severe injury and worse outcomes than the rSI-sMS ≥ 4 group. The TTAS and rSI-sMS had higher area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) for mortality, ICU admission, prolonged ICU stay, and prolonged hospital stay than the SI and modified SI. The combination of the TTAS and rSI-sMS had the highest AUROC for all clinical outcomes. The prediction performance of rSI-sMS < 4 for major injury (ISS ≥ 16) exhibited 81.49% specificity in triage levels I and II and 87.6% specificity in triage level III. The specificity for mortality was 79.2% in triage levels I and II and 87.4% in triage level III. Conclusions: The combination of rSI-sMS and the TTAS yielded superior prioritization performance to TTAS alone. The integration of rSI-sMS and TTAS effectively enhances the efficiency and accuracy of identifying trauma patients at a high risk of mortality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Status and Future Directions of Bone Trauma Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
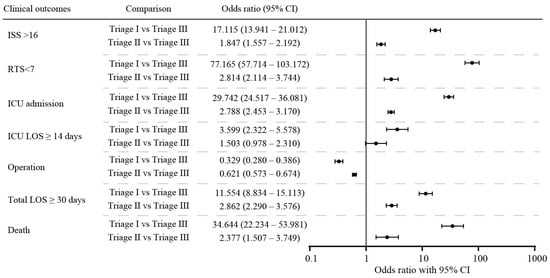
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Intraoperative Patient Positioning on the Success of Intertrochanteric Fracture Surgery in Older Patients
by
Onur Kaya, Buğra Kundakçı, Cem Önder, Vahap Kurt, Emre Atmaca and Fatih Tunç
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 646; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040646 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The incidence of hip fractures in people of advanced ages is increasing due to our aging society. Patient positioning for the intertrochanteric fractures of the femur can be performed in various ways. The aim of this study is to clinically
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The incidence of hip fractures in people of advanced ages is increasing due to our aging society. Patient positioning for the intertrochanteric fractures of the femur can be performed in various ways. The aim of this study is to clinically and radiologically compare the use of the supine hemilithotomy position, the lateral decubitus position, and the traction table when performing proximal femoral nail (PFN) surgery for femoral intertrochanteric fractures in the geriatric age group. Materials and Methods: A total of 170 elderly patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures were included in this cross-sectional study. The patients were divided into three groups (the supine hemilithotomy group, the lateral decubitus group, and the fracture table group). For the postoperative period, complications, length of stay in the intensive care unit, and length of stay in hospital were examined, while in postoperative radiographs, tip–apex distances (TADs), collodiaphyseal angles (CDAs), and Cleveland–Bosworth quadrants were examined to evaluate the placement of the lag screw in the femoral head. The quality of fracture reduction was evaluated according to the modified Baumgaertner criteria. Results: The mean age of the patients was 77.8 ± 8.8; 57.6% of patients were female. According to the modified Baumgaertner criteria, it was determined that patients with ‘poor’ reduction quality had an approximately ten times higher risk of cut-out than those with ‘good’ reduction quality (OR = 10.111, p = 0.002, 95% confidence interval; 2.313–44.207). The operative time for patients in the fracture table group was longer than that of the other groups Additionally, the CDA in the supine hemilithotomy position group was longer. Conclusions: Although PFN surgery using the traction table is longer in terms of surgical time compared to surgery performed in the lateral decubitus position and the supine hemilitotomy position, it is advantageous in terms of better TAD and CDA values and lower complication rates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Updates and Future Perspectives on Orthopedic Trauma, Fracture Management and Rehabilitation)
►▼
Show Figures
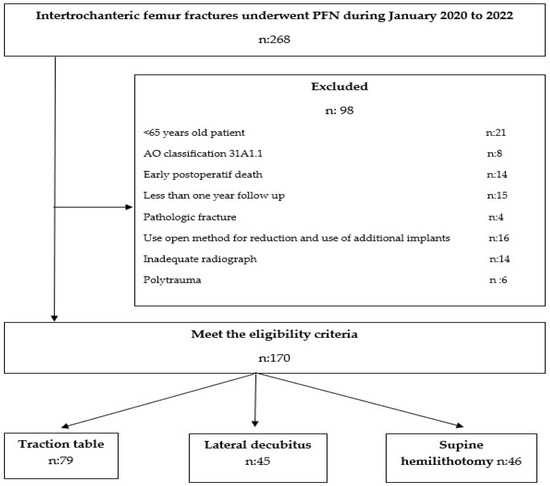
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Integrating Clinical Neuropsychology and Psychotic Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Analysis of Cognitive Dynamics, Interventions, and Underlying Mechanisms
by
Evgenia Gkintoni, Maria Skokou and Philippos Gourzis
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 645; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040645 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The study aims to provide a comprehensive neuropsychological analysis of psychotic spectrum disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression. It focuses on the critical aspects of cognitive impairments, diagnostic tools, intervention efficacy, and the roles of genetic and environmental
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The study aims to provide a comprehensive neuropsychological analysis of psychotic spectrum disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression. It focuses on the critical aspects of cognitive impairments, diagnostic tools, intervention efficacy, and the roles of genetic and environmental factors in these disorders. The paper emphasizes the diagnostic significance of neuropsychological tests in identifying cognitive deficiencies and their predictive value in the early management of psychosis. Materials and Methods: The study involved a systematic literature review following the PRISMA guidelines. The search was conducted in significant databases like Scopus, PsycINFO, PubMed, and Web of Science using keywords relevant to clinical neuropsychology and psychotic spectrum disorders. The inclusion criteria required articles to be in English, published between 2018 and 2023, and pertinent to clinical neuropsychology’s application in these disorders. A total of 153 articles were identified, with 44 ultimately included for detailed analysis based on relevance and publication status after screening. Results: The review highlights several key findings, including the diagnostic and prognostic significance of mismatch negativity, neuroprogressive trajectories, cortical thinning in familial high-risk individuals, and distinct illness trajectories within psychosis subgroups. The studies evaluated underline the role of neuropsychological tests in diagnosing psychiatric disorders and emphasize early detection and the effectiveness of intervention strategies based on cognitive and neurobiological markers. Conclusions: The systematic review underscores the importance of investigating the neuropsychological components of psychotic spectrum disorders. It identifies significant cognitive impairments in attention, memory, and executive function, correlating with structural and functional brain abnormalities. The paper stresses the need for precise diagnoses and personalized treatment modalities, highlighting the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, and psychosocial factors. It calls for a deeper understanding of these neuropsychological processes to enhance diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Psychiatry)
►▼
Show Figures
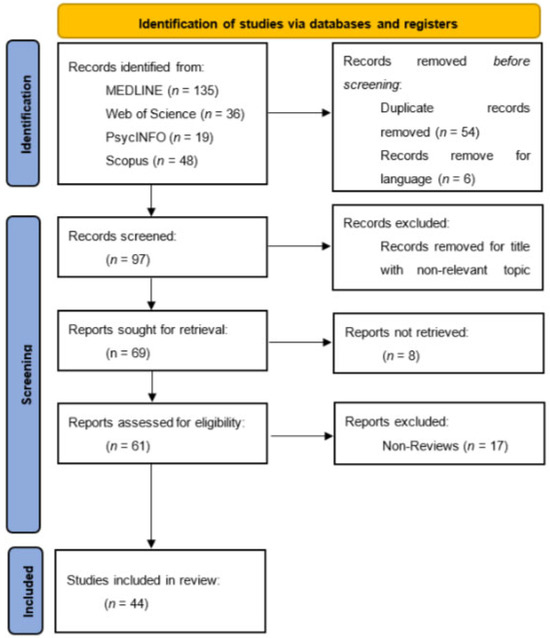
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Acute Infectious Purpura Fulminans Complicated by Bacterial Translocation after Rectal Cancer Surgery: A Case Report
by
Ryo Nakanishi, Heita Ozawa, Naoyuki Toyota, Minori Mise, Ritsuto Akutsu and Shin Fujita
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 644; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040644 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
The patient was a man in his 80s who had undergone laparoscopic anterior resection for rectal cancer. Bowel obstruction occurred on the third postoperative day but improved with a decompression tube by the fifth postoperative day. A high fever (in the 38 °C
[...] Read more.
The patient was a man in his 80s who had undergone laparoscopic anterior resection for rectal cancer. Bowel obstruction occurred on the third postoperative day but improved with a decompression tube by the fifth postoperative day. A high fever (in the 38 °C range) was also observed. Blood culture tests detected two sets of the gram-negative bacilli Klebsiella aerogenes within 24 h of collection. On the seventh postoperative day, the patient subsequently went into septic shock with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). On the eighth postoperative day, the fingertips and toes became black, and the palms and dorsal surfaces of both feet were dark purple due to peripheral circulatory failure. This suggested acute infectious purpura associated with sepsis (acute infectious purpura fulminans (AIPF)). Intensive care was provided; however, the necrosis of both middle fingers worsened, both middle fingers were gangrenous, and the patient died on the thirtieth postoperative day. AIPF is rarely reported, especially in early-onset cases after elective surgery. We encountered a rare complication of bacterial translocation from postoperative bowel obstruction, leading to AIPF.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
►▼
Show Figures
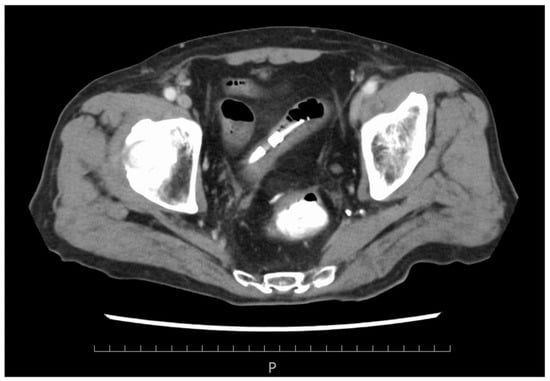
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Relationship between Depressive Symptoms, Caregiver Strain, and Social Support with Dementia Grief in Family Caregivers
by
Miriam Sánchez-Alcón, Almudena Garrido-Fernández, José María Cano-Rojas, José Luis Sánchez-Ramos and Juan Diego Ramos-Pichardo
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 643; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040643 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Dementia grief in family caregivers of people with dementia refers to grieving prior to the death of the care recipient. It is related to psychosocial risk factors that may have a negative impact on the health of these family
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Dementia grief in family caregivers of people with dementia refers to grieving prior to the death of the care recipient. It is related to psychosocial risk factors that may have a negative impact on the health of these family caregivers. This study aimed to describe the relationship between depressive symptoms, caregiver strain, and social support with dementia grief in family caregivers of people with dementia. Materials and Methods: A descriptive correlational cross-sectional study was conducted. A total of 250 family caregivers of people with dementia participated. Dementia grief was the main variable, and depressive symptoms, caregiver strain, and social support were assessed. Additionally, socio-demographic data were collected. Descriptive statistics were calculated, and a bivariate correlation analysis and a multiple linear regression analysis were performed for dementia grief. Results: Higher scores for dementia grief were found in women, in family caregivers of patients at advanced stages of dementia, and in family caregivers with a low level of education. High levels of depressive symptoms and caregiver strain and low levels of social support indicated greater intensity of dementia grief. Depressive symptomatology was the variable with the greatest influence on dementia grief. Caregiver strain and social support also related to dementia grief, but to a lesser extent. Conclusions: In family caregivers, depressive symptoms, caregiver strain, and social support are related to the intensity of dementia grief, with a greater influence of depressive symptoms. Moreover, being female, having a low level of education, and caring for a care recipient at an advanced stage of dementia are factors associated with increased dementia grief. Concerning study limitations, the sample was restricted, belonging to a specific region of Spain and to a Provincial Federation of associations. It is necessary to exercise caution in generalizing results due to the sociodemographic and geographical characteristics of the sample.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Commemorative Issue Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Alzheimer’s Foundation of America: Understanding and Treating Alzheimer’s Disease)
Open AccessArticle
Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Saudi Arabia and Its Association with Socioeconomic Status and Depression
by
Majed Alnabulsi, Ahmad Abdullah Imam, Atheer Ahmed Alawlaqi, Fatimah Hussain Alhawaj, Ghazal Fareed Jamjoom, Lina Dakhil Alsaeidi, Fatma El-Sayed Hassan and Shakeel Ahmed Ansari
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 642; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040642 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Several RCTs have reported significant reductions in depression symptoms with the Mediterranean diet (MedDiet), but observational studies have reported inconsistent findings. Moreover, studies have rarely investigated the mediating role of socioeconomic status (SES), including objective material status, in adherence to
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Several RCTs have reported significant reductions in depression symptoms with the Mediterranean diet (MedDiet), but observational studies have reported inconsistent findings. Moreover, studies have rarely investigated the mediating role of socioeconomic status (SES), including objective material status, in adherence to the MedDiet and its impact on depressive symptoms in the same population. Therefore, this cross-sectional study investigated the relationship between adherence to the MedDiet, socioeconomic factors, and depression severity. Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional online survey was conducted between June and December 2022 across Saudia Arabia. The snowball sampling technique was used to recruit participants aged ≥18 years. Mediterranean diet adherence screener (MEDAS) and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) were used to assess adherence to the MedDiet and depression severity. An SES index, validated in the Saudi Arabian context, was used to assess SES. The data were analyzed using the Chi-square and Pearson’s correlation tests. Results: Only 21% of our study population (n = 467) was MedDiet adherent. Adherence was significantly associated with education (p = 0.014) but not employment status among traditional SES indicators. Similarly, only television ownership (p = 0.009) was associated with MedDiet adherence among the 20 objective material possessions investigated. Nonetheless, the MedDiet-adherent group had a significantly lower PHQ-9 score than the non-adherent group (6.16 ± 0.68 vs. 8.35 ± 0.31, p = 0.002). A moderate but significantly negative correlation between MEDAS and PHQ-9 scores (r = −0.16, p = 0.001) was noted. Conclusions: MedDiet adherence was associated with lower depression severity scores. In addition to education and television ownership, adherence was not associated with any objective indicators of SES.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Importance and Consequences of Nutrition and Diet Plans for the Management of Gastrointestinal Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
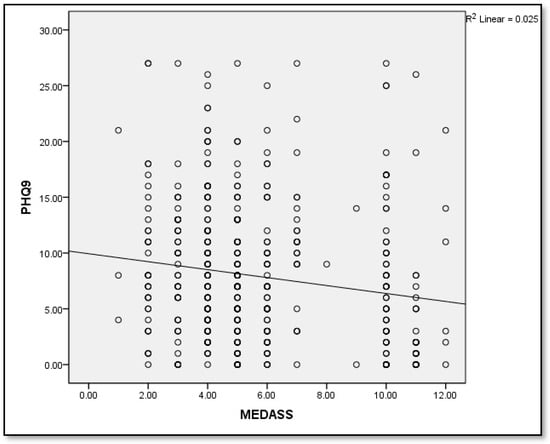
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
O2 Saturation Predicted the ICU Stay of COVID-19 Patients in a Hospital at Altitude: A Low-Cost Tool for Post-Pandemic
by
Jaime Vásquez-Gómez, Lucero Gutierrez-Gutierrez, Pablo Miranda-Cuevas, Luis Ríos-Florez, Luz Casas-Condori, Marcia Gumiel and Marcelo Castillo-Retamal
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 641; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040641 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Patients at high altitudes with COVID-19 may experience a decrease in their partial oxygen saturation (PO2S) levels. The objective was to assess the association between PO2S and intensive care unit (ICU) stay in patients at
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Patients at high altitudes with COVID-19 may experience a decrease in their partial oxygen saturation (PO2S) levels. The objective was to assess the association between PO2S and intensive care unit (ICU) stay in patients at high altitudes with COVID-19. Materials and Methods: Clinical records of 69 COVID-19 patients (36% women) admitted to the ICU were analyzed. Median values were considered for intra-group categories (“≤11 days” and “>11 days” in the ICU) and for PO2S height categories (“<90%” and “≥90%”). Logistic regression and linear regression models adjusted for confounding variables were used. Results: Patients with >11 days in the ICU had 84% lower odds of having a PO2S ≥ 90% (OR: 0.16 [CI: 0.02, 0.69], p = 0.005) compared to those with ≤11 days in the ICU. An increase in PO2S by 1% reduced ICU stay by 0.22 days (β: −0.22 [CI: −0.33, −0.11], p < 0.001), potentially leading to a reduction of up to 1.44 days. Conclusions: PO2S is a crucial factor in estimating ICU stays for COVID-19 patients at high altitudes and serves as an accessible and cost-effective measure. It should be used in infected patients to complement the prognosis of post-pandemic ICU stay.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Impact on Human Health, Lifestyle and Quality of Care after COVID-19)
Open AccessArticle
Socioeconomic and Other Risk Factors for Retear after Arthroscopic Surgery for Nontraumatic Rotator Cuff Tear
by
Jung Sub Lee, Kuen Tak Suh, Won Chul Shin, Jung Yun Bae, Tae Sik Goh, Sung Won Jung, Min-Hyeok Choi and Suk-Woong Kang
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 640; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040640 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Few studies have investigated the socioeconomic factors associated with retear after rotator cuff repair. This study aimed to identify the risk factors, including socioeconomic factors, for rotator cuff retear in patients who underwent arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Materials and Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Few studies have investigated the socioeconomic factors associated with retear after rotator cuff repair. This study aimed to identify the risk factors, including socioeconomic factors, for rotator cuff retear in patients who underwent arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included 723 patients diagnosed with full-thickness rotator cuff tears who underwent arthroscopic rotator cuff repair from March 2010 to March 2021. The outcome variable was rotator cuff retear observed on postoperative magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasonography. Sex, age, obesity, diabetes, symptom duration, and tear size were the independent variables. Socioeconomic variables included occupation, educational level, type of medical insurance, and area of residence. We compared patients with and without retear and estimated the effects of the independent factors on retear risk. Results: The mean age of the patients, symptom duration, and tear size were 62.4 ± 8.0 years, 1.8 ± 1.7 years, and 21.8 ± 12.5 mm, respectively. The age, type of medical insurance, diabetes, tear size, and symptom duration differed significantly between patients with and without retearing (p < 0.05). Age, occupation, type of medical insurance, diabetes, initial tear size, and symptom duration significantly affected the risk of retear. Patients who performed manual labor had a significantly higher retear rate (p = 0.005; OR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.23–3.11). The highest retear risk was seen in patients with Medicaid insurance (p < 0.001; OR, 4.34; 95% CI, 2.09–9.02). Conclusions: Age, initial tear size, and symptom duration significantly affect retear risk after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Occupation and type of medical insurance were also risk factors for retear. Socioeconomically vulnerable patients may be at a greater risk of retear. Proactive efforts are required to expand early access to medical care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Orthopedics and Sports Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
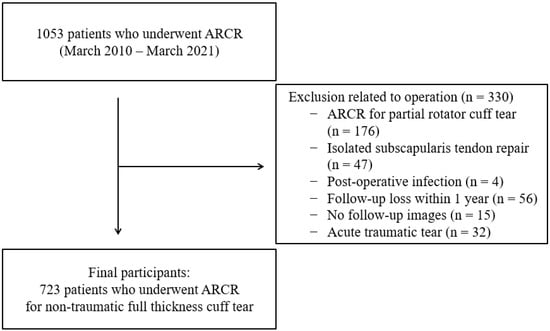
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Olmutinib Reverses Thioacetamide-Induced Cell Cycle Gene Alterations in Mice Liver and Kidney Tissues, While Wheat Germ Treatment Exhibits Limited Efficacy at Gene Level
by
Seema Zargar, Tanveer A. Wani, Salman Alamery and Fatimah Yaseen
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 639; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040639 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: TAA is potent hepatic/renal toxicant. Conversely, WGO is a potent dietary supplement with impressive antioxidant properties. Olmutinib is an apoptotic chemotherapy drug that does not harm the liver or kidney. This study investigated the impact of olmutinib and wheat
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: TAA is potent hepatic/renal toxicant. Conversely, WGO is a potent dietary supplement with impressive antioxidant properties. Olmutinib is an apoptotic chemotherapy drug that does not harm the liver or kidney. This study investigated the impact of olmutinib and wheat germ oil (WGO) on Thioacetamide (TAA)-induced gene alterations in mice liver and kidney tissues. Materials and Methods: Adult male C57BL/6 mice were exposed to 0.3% TAA in drinking water for 14 days, followed by the oral administration of olmutinib (30 mg/kg) and WGO (1400 mg/kg) for 5 consecutive days. Treatment groups included the following: groups I (control), II (TAA-exposed), III (TAA + olmutinib), IV (TAA + WGO), and V (TAA + olmutinib + WGO). Results: The findings revealed that TAA exposure increased MKi67 and CDKN3 gene expression in liver and kidney tissues. Olmutinib treatment effectively reversed these TAA-induced effects, significantly restoring MKi67 and CDKN3 gene expression. WGO also reversed MKi67 effects in the liver but exhibited limited efficacy in reversing CDKN3 gene alterations induced by TAA exposures in both the liver and kidney. TAA exposure showed the tissue-specific expression of TP53, with decreased expression in the liver and increased expression in the kidney. Olmutinib effectively reversed these tissue-specific alterations in TP53 expression. While WGO treatment alone could not reverse the gene alterations induced by TAA exposure, the co-administration of olmutinib and WGO exhibited a remarkable potentiation of therapeutic effects in both the liver and kidney. The gene interaction analysis revealed 77.4% of physical interactions and co-localization between MKi67, CDKN3, and TP53 expressions. Protein–protein interaction networks also demonstrated physical interactions between MKi67, TP53, and CDKN3, forming complexes or signaling cascades. Conclusions: It was predicted that the increased expression of the MKi67 gene by TAA leads to the increase in TP53, which negatively regulates the cell cycle via increased CDKN3 expression in kidneys and the restoration of TP53 levels in the liver. These findings contribute to our understanding of the effects of olmutinib and WGO on TAA-induced gene expression changes and highlight their contrasting effects based on cell cycle alterations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Medical Genetics, Genomics and Precision Medicine: From a Molecular Perspective to Clinical Practice)
►▼
Show Figures
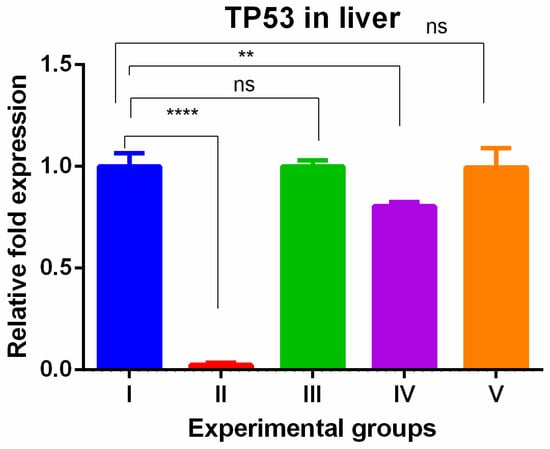
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Management of Malignant Gastric Outlet Obstruction: A Comprehensive Review on the Old, the Classic and the Innovative Approaches
by
Alessandro Fugazza, Marta Andreozzi, Hamid Asadzadeh Aghdaei, Agustin Insausti, Marco Spadaccini, Matteo Colombo, Silvia Carrara, Maria Terrin, Alessandro De Marco, Gianluca Franchellucci, Kareem Khalaf, Pardis Ketabi Moghadam, Chiara Ferrari, Andrea Anderloni, Giovanni Capretti, Gennaro Nappo, Alessandro Zerbi and Alessandro Repici
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 638; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040638 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Gastrojejunostomy is the principal method of palliation for unresectable malignant gastric outlet obstructions (GOO). Gastrojejunostomy was traditionally performed as a surgical procedure with an open approach butrecently, notable progress in the development of minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopic gastrojejunostomies have emerged. Additionally,
[...] Read more.
Gastrojejunostomy is the principal method of palliation for unresectable malignant gastric outlet obstructions (GOO). Gastrojejunostomy was traditionally performed as a surgical procedure with an open approach butrecently, notable progress in the development of minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopic gastrojejunostomies have emerged. Additionally, advancements in endoscopic techniques, including endoscopic stenting (ES) and endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastroenterostomy (EUS-GE), are becoming more prominent. ES involves the placement of self-expandable metal stents (SEMS) to restore luminal patency. ES is commonly the first choice for patients deemed unfit for surgery or at high surgical risk. However, although ES leads to rapid improvement of symptoms, it carries limitations like higher stent dysfunction rates and the need for frequent re-interventions. Recently, EUS-GE has emerged as a potential alternative, combining the minimally invasive nature of the endoscopic approach with the long-lasting effects of a gastrojejunostomy. Having reviewed the advantages and disadvantages of these different techniques, this article aims to provide a comprehensive review regarding the management of unresectable malignant GOO.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Latest Advances in Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy)
►▼
Show Figures
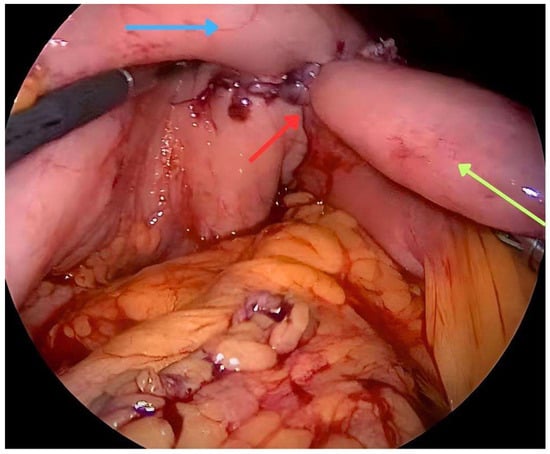
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association between Genetic Polymorphism of SCN1A, GABRA1 and ABCB1 and Drug Responsiveness in Vietnamese Epileptic Children
by
Hai Xuan Tang, Muoi Dang Ho, Nhung Phuong Vu, Hung Vu Cao, Vinh Anh Ngo, Van Thi Nguyen, Thuan Duc Nguyen and Ton Dang Nguyen
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 637; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040637 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Drug resistant epilepsy (DRE) is a major hurdle in epilepsy, which hinders clinical care, patients’ management and treatment outcomes. DRE may partially result from genetic variants that alter proteins responsible for drug targets and drug transporters in the brain. We
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Drug resistant epilepsy (DRE) is a major hurdle in epilepsy, which hinders clinical care, patients’ management and treatment outcomes. DRE may partially result from genetic variants that alter proteins responsible for drug targets and drug transporters in the brain. We aimed to examine the relationship between SCN1A, GABRA1 and ABCB1 polymorphism and drug response in epilepsy children in Vietnam. Materials and Methods: In total, 213 children diagnosed with epilepsy were recruited in this study (101 were drug responsive and 112 were drug resistant). Sanger sequencing had been performed in order to detect six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) belonging to SCN1A (rs2298771, rs3812718, rs10188577), GABRA1 (rs2279020) and ABCB1 (rs1128503, rs1045642) in study group. The link between SNPs and drug response status was examined by the Chi-squared test or the Fisher’s exact test. Results: Among six investigated SNPs, two SNPs showed significant difference between the responsive and the resistant group. Among those, heterozygous genotype of SCN1A rs2298771 (AG) were at higher frequency in the resistant patients compared with responsive patients, playing as risk factor of refractory epilepsy. Conversely, the heterozygous genotype of SCN1A rs3812718 (CT) was significantly lower in the resistant compared with the responsive group. No significant association was found between the remaining four SNPs and drug response. Conclusions: Our study demonstrated a significant association between the SCN1A genetic polymorphism which increased risk of drug-resistant epilepsy in Vietnamese epileptic children. This important finding further supports the underlying molecular mechanisms of SCN1A genetic variants in the pathogenesis of drug-resistant epilepsy in children.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurology)
Open AccessArticle
Time Course of Asymptomatic Stenosis in Multiple Lumbar Spinal Stenosis—Five-Year Results of Selective Decompression of Symptomatic Levels
by
Kazuyuki Watanabe, Koji Otani, Takuya Nikaido, Kinshi Kato, Hiroshi Kobayashi, Shoji Yabuki, Shin-ichi Konno and Yoshihiro Matsumoto
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 636; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040636 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: In the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS), finding stenosis with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) does not always correlate with symptoms such as sciatica or intermittent claudication. We perform decompression surgery only for cases where the levels diagnosed from neurological findings
[...] Read more.
Background: In the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS), finding stenosis with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) does not always correlate with symptoms such as sciatica or intermittent claudication. We perform decompression surgery only for cases where the levels diagnosed from neurological findings are symptomatic, even if multiple stenoses are observed on MRI. The objective of this study was to examine the time course of asymptomatic stenosis in patients with LSS after they underwent decompression surgery for symptomatic stenosis. Materials and Methods: The participants in this study comprised 137 LSS patients who underwent single-level L4–5 decompression surgery from 2003 to 2013. The dural sac cross-sectional area at the L3–4 disc level was calculated based on preoperative MRI. A cross-sectional area less than 50 mm2 was defined as stenosis. The patients were grouped, according to additional spinal stenosis at the L3–4 level, into a double group (16 cases) with L3–4 stenosis, and a single group (121 cases) without L3–4 stenosis. Incidences of new-onset symptoms originating from L3–4 and additional L3–4-level surgery were examined. Results: Five years after surgery, 98 cases (72%) completed follow-up. During follow-up, 2 of 12 patients in the double group (16.7%) and 9 of 86 patients in the single group (10.5%) presented with new-onset symptoms originating from L3–4, showing no significant difference between groups. Additional L3–4 surgery was performed for one patient (8.3%) in the double group and three patients (3.5%) in the single group; again, no significant difference was shown. Conclusion: Patients with asymptomatic L3–4 stenosis on preoperative MRI were not prone to develop new symptoms or need additional L3–4-level surgery within 5 years after surgery when compared to patients without preoperative L3–4 stenosis. These results indicate that prophylactic decompression for asymptomatic levels is unnecessary.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Orthopedics)
►▼
Show Figures
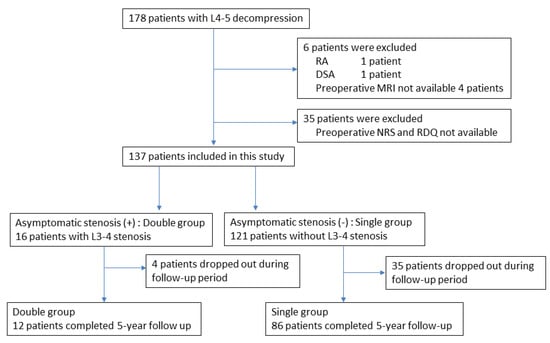
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Review of Pregnancy Management following Bariatric Procedures
by
Iulia Huluță, Livia-Mihaela Apostol, Radu Botezatu, Anca Maria Panaitescu, Corina Gică, Romina-Marina Sima, Nicolae Gică and Florina Mihaela Nedelea
Medicina 2024, 60(4), 635; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040635 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
The increasing prevalence of bariatric surgery among women of childbearing age raises critical questions about the correct management of pregnancy following these procedures. This literature review delves into the multifaceted considerations surrounding pregnancy after bariatric surgery, with a particular focus on the importance
[...] Read more.
The increasing prevalence of bariatric surgery among women of childbearing age raises critical questions about the correct management of pregnancy following these procedures. This literature review delves into the multifaceted considerations surrounding pregnancy after bariatric surgery, with a particular focus on the importance of preconception counselling, appropriate nutrition assessment, and the necessity of correct folic acid supplementation. Key areas of investigation include nutrient absorption challenges, weight gain during pregnancy, and potential micronutrient deficiencies. Examining the relationship between bariatric surgery and birth defects, particularly heart and musculoskeletal issues, uncovers a twofold increase in risk for women who underwent surgery before pregnancy, with the risk emphasized before folic acid fortification. In contrast, a nationwide study suggests that infants born to mothers with bariatric surgery exhibit a reduced risk of major birth defects, potentially associated with improved glucose metabolism. In addition, this review outlines strategies for managing gestational diabetes and other pregnancy-related complications in individuals with a history of bariatric surgery. By synthesizing existing literature, this paper aims to provide healthcare providers with a comprehensive framework for the correct management of pregnancy in this unique patient population, promoting the health and well-being of both mother and child.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue High-Risk Pregnancy - Series II)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Medicina Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Anatomia, Biology, Medicina, Pathophysiology, Tomography
Human Anatomy and Pathophysiology, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Francesco Cappello, Mugurel Constantin RusuDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Dentistry Journal, JCM, JFB, Medicina
Diagnosis and Treatment of Dental Diseases and Tempromandibular Joints
Topic Editors: Rafał Obuchowicz, Małgorzata Pihut, Karolina Nurzynska, Andrzej UrbanikDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topic in
JCDD, JCM, Medicina, Membranes, ARM
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
Topic Editors: Patrick Honore, Isabelle MichauxDeadline: 30 November 2024
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, JCM, Medicina, Neurology International
Advances in Exercise-Induced Neurogenesis, Neuronal and Functional Adaptations in Neurorehabilitation
Topic Editors: Carlos Bernal-Utrera, Cleofas Rodriguez-Blanco, Maria Livia Carrascal MorenoDeadline: 22 December 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Medicina
Advances in Cardiac Interventions and Surgery in the COVID-19 Era
Guest Editor: Attila RokaDeadline: 20 April 2024
Special Issue in
Medicina
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: From Diagnose to Treatment
Guest Editor: Athanasia PatakaDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Medicina
Diagnosis and Treatment of Diseases of the Facial Skeleton, Oral Cavity, and Paranasal Sinuses
Guest Editors: Kamil Nelke, Maciej Dobrzyński, Marceli ŁukaszewskiDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Medicina
Updates on Post-mastectomy Breast Reconstruction
Guest Editors: Glenda Giorgia Caputo, Rossella Sgarzani, Pier Camillo ParodiDeadline: 30 May 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interventional Oncology
Collection Editors: François Cornelis, Matthias Barral, Adrian Kastler, Dimitrios Filippiadis
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Frontiers in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Jimmy T. Efird, Tithi Biswas
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interdisciplinary Medicine – The Key For Personalized Medicine
Collection Editor: Camelia Diaconu
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Advances in Cornea, Cataract, and Refractive Surgery
Collection Editor: Ivo Guber