Journal Description
Logistics
Logistics
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal of logistics and supply chain management published quarterly online by MDPI. The first issue has been released in December 2017.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), RePEc, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 25.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 9.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Management Information Systems)
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.8 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Electrifying the Last-Mile Logistics (LML) in Intensive B2B Operations—An European Perspective on Integrating Innovative Platforms
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020045 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: literature on last mile logistic electrification has primarily focused either on the stakeholder interactions defining urban rules and policies for urban freight or on the technical aspects of the logistic EVs. Methods: the article incorporates energy sourcing, vehicles, logistics operation,
[...] Read more.
Background: literature on last mile logistic electrification has primarily focused either on the stakeholder interactions defining urban rules and policies for urban freight or on the technical aspects of the logistic EVs. Methods: the article incorporates energy sourcing, vehicles, logistics operation, and digital cloud environment, aiming at economic and functional viability. Using a combination of engineering and business modeling combined with the unique opportunity of the actual insights from Europe’s largest tender in the automotive aftermarket electrification. Results: the Last Mile Logistics (LML) electrification is possible and profitable without jeopardizing the high-tempo deliveries. Critical asset identification for a viable transition to EVs leads to open new lines of research for future logistic dynamics rendered possible by the digital dimensions of the logistic ecosystem. Conclusions: beyond the unquestionable benefits for the environment, the electrification of the LML constitutes an opportunity to enhance revenue and diversify income.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Its Application in Sustainable Smart Logistics)
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Impact of Healthcare 4.0 Technologies on Healthcare Supply Chain Management: A Multi-Criteria Evaluation Framework
by
Ayoninuoluwa Oluwadare, Busola Dorcas Akintayo, Olubayo Moses Babatunde and Oludolapo Akanni Olanrewaju
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020044 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: Healthcare 4.0 has transformed supply chain management in the healthcare sector, but there is a lack of comprehensive frameworks to evaluate the impact of Healthcare 4.0 technologies on sector operations, particularly in developing countries. Methods: This study introduces a multi-criteria
[...] Read more.
Background: Healthcare 4.0 has transformed supply chain management in the healthcare sector, but there is a lack of comprehensive frameworks to evaluate the impact of Healthcare 4.0 technologies on sector operations, particularly in developing countries. Methods: This study introduces a multi-criteria framework that synergically combines the techno-economic implications of Healthcare 4.0 technologies to improve healthcare supply chain management. The proposed approach innovatively integrates fuzzy VIKOR and Entropy methods to handle data vagueness and uncertainty, using data collected from healthcare supply chain specialists in Lagos, Nigeria. Results: The developed framework identifies the most and least critical technical and economic parameters for Healthcare 4.0 implementation in healthcare supply chain management. It also determines the suitability of different Healthcare 4.0 technologies for supply chain management in the healthcare sector. Conclusions: The main innovation of this study lies in the development of a comprehensive and context-specific framework for evaluating Healthcare 4.0 technologies in healthcare supply chains. The framework offers a new perspective on technology evaluation and provides practical insights for decision-makers. The findings contribute to advancing knowledge and practice in this field, promoting the proper adoption of Healthcare 4.0 technologies in healthcare, particularly in developing countries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Digital Supply Chain 4.0 Transformation)
►▼
Show Figures
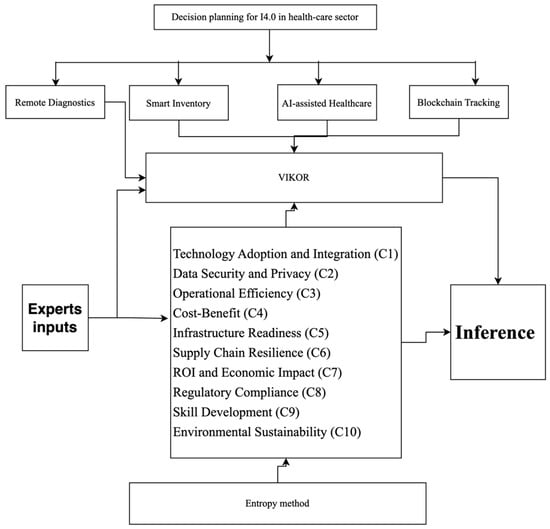
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of the Product Master Data Quality on the Logistics Process Performance
by
Diana Božić, Margareta Živičnjak, Ratko Stanković and Andrej Ignjatić
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020043 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The importance of up-to-date product master data in the digital age should not be underestimated. However, companies still struggle to ensure high-quality product data, especially in the field of logistics. Hence, the focus of our research lies in the disregard of the
[...] Read more.
Background: The importance of up-to-date product master data in the digital age should not be underestimated. However, companies still struggle to ensure high-quality product data, especially in the field of logistics. Hence, the focus of our research lies in the disregard of the importance of product data quality to the performance of logistics processes. Methods: The analysis of the influence of product data on the performance of logistics processes was carried out using data from two fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) distribution and retail companies. Data were gathered via interviews, while process activities were timed using a stopwatch, and interruptions were documented. The significance of the impact was determined using inferential statistical procedures based on the variable and the measurement scale type employed. Results: The quality of product master data has a significant impact on the performance of logistics processes; while managers are aware of the complications, they lack the motivation to detect and analyse such inaccuracies. Conclusions: The findings enhance comprehension of the obstacles generated by inadequate product data in logistics, which obstruct optimisation, and offer numerical proof of the impact of product data quality on logistics performance, thus expanding the current body of research.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ensuring Fair Compensation: Analyzing and Adjusting Freight Forwarder Liability Limits
by
Miloš Poliak and Ekaterina Salamakhina
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020042 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: Due to the absence of unified global regulations, defining the service and legal role of freight forwarders is challenging. This, as well as the lack of a standardized limit to the freight forwarder’s liability for loss or damage to the cargo,
[...] Read more.
Background: Due to the absence of unified global regulations, defining the service and legal role of freight forwarders is challenging. This, as well as the lack of a standardized limit to the freight forwarder’s liability for loss or damage to the cargo, introduces misunderstandings into his relationship with the client. The purpose of this study is to analyze the most widely used limit for freight forwarder’s liability, set in Special Drawing Rights (SDR) units, and to adjust it, which will allow for maintaining the purchasing power of the compensation amount over different periods of time. Methods: In this study, two methods of adjusting the liability limit were proposed. In accordance with the first one, the limit was adjusted considering the impact of dollar inflation on the SDR unit. The second method involves changes in the limit of liability, taking into account changes in world prices for goods. Results: The result of this study showed that the second method is more functional, helping to preserve the purchasing power of the liability limit most effectively over time. Conclusions: This study revealed the fluctuating purchasing power of the forwarder’s liability limit over time and suggests utilizing a methodology tied to changes in global goods’ prices for adjustment.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Business Continuity on Supply Chain Practices and Resilience Due to COVID-19
by
Behzad Maleki Vishkaei and Pietro De Giovanni
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020041 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Business continuity entails the potential negative consequences of uncertainty on a firm’s ability to achieve strategic objectives. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted business continuity due to lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures. Consequently, firms adopted specific supply chain (SC) practices
[...] Read more.
Background: Business continuity entails the potential negative consequences of uncertainty on a firm’s ability to achieve strategic objectives. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted business continuity due to lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures. Consequently, firms adopted specific supply chain (SC) practices to effectively navigate this global crisis. Methods: This research adopted a stochastic approach based on Bayesian Networks to evaluate the implications of business continuity on firms’ decisions to embrace SC practices, focusing on omnichannel strategies, SC coordination, and technologies such as artificial intelligence systems, big data and machine learning, and mobile applications. Results: Our findings revealed that firms facing disruption in a single performance area can apply specific strategies to maintain resilience. However, multiple areas of underperformance necessitate a varied approach. Conclusions: According to our empirical analysis, omnichannel strategies are critical when disruptions simultaneously impact quality, inventory, sales, and ROI, particularly during major disruptions such as the COVID-19 pandemic. AI and big data become vital when multiple risks coalesce, enhancing areas such as customer service and supply chain visibility. Moreover, supply chain coordination and mobile app adoption are effective against individual performance risks, proving crucial in mitigating disruption impacts across various business aspects. These findings help policy-makers and business owners to have a better understanding of how business continuity based on performance resistance to disruptions pushes companies to adopt different practices including new technologies and supply chain coordination. Accordingly, they can use the outputs of this study to devise strategies for improving resilience considering their supply chain vulnerabilities.
Full article
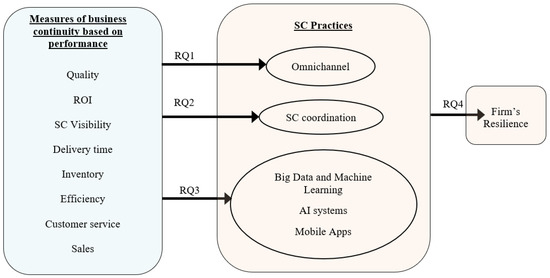
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Auction-Based Truck Appointment System for Marine Terminals
by
Ilias Alexandros Parmaksizoglou, Alessandro Bombelli and Alexei Sharpanskykh
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020040 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Increased maritime trade has led to a surge in drayage operations, causing congestion and environmental issues in port areas. Truck Appointment Systems (TASs) are commonly used to manage truck arrival rates, yet transparency and equity in slot allocation remain problematic, fostering distrust
[...] Read more.
Background: Increased maritime trade has led to a surge in drayage operations, causing congestion and environmental issues in port areas. Truck Appointment Systems (TASs) are commonly used to manage truck arrival rates, yet transparency and equity in slot allocation remain problematic, fostering distrust between Licensed Motor Carriers (LMCs) and Marine Terminal Operators (MTOs). Methods: This study proposes a polycentric approach to improve truck scheduling and ensure that those impacted by decisions are involved in the decision-making process. A single-round auction mechanism focused on optimizing the truck hauling process through a pricing policy that promotes sincere bidding is introduced. The proposed approach employs an optimization strategy to achieve equitable coordination in truck synchronization through means of adaptable capacity management. Results: Numerical experiments assessing scenarios of noncollaborative behavior against partial collaboration between MTOs and LMCs demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in enhancing user satisfaction and terminal conditions for a case study focused on a medium-sized terminal. Collaboration between trucking companies is shown to increase utility per monetary unit spent on slot acquisition. Conclusions: The polycentric strategy offers a solution to TAS limitations by ensuring stakeholder participation with respect to flexibility and transparency by ensuring that those impacted by decisions are involved in the decision-making process.
Full article
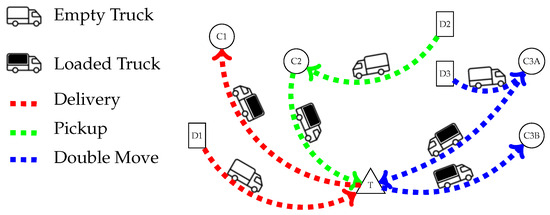
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of Brazilian Green Coffee Production and Its Logistical Corridors on the International Coffee Market
by
Paula Ferreira da Cruz Correia, João Gilberto Mendes dos Reis, Pedro Sanches Amorim, Jaqueline Severino da Costa and Márcia Terra da Silva
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020039 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: The coffee industry is one of the most important world supply chains, with an estimated consumption of two billion cups daily, making it the most consumed beverage worldwide. Coffee beans are primarily grown in tropical countries, with Brazil accounting for almost 50%
[...] Read more.
Background: The coffee industry is one of the most important world supply chains, with an estimated consumption of two billion cups daily, making it the most consumed beverage worldwide. Coffee beans are primarily grown in tropical countries, with Brazil accounting for almost 50% of the production. The objective of this study is to examine the Brazilian trade between 2018 and 2022, focusing on state producers, logistical corridors, and importer countries. Methods: The methodology approach revolves around a quantitative method using Social Network Analysis measures. Results: The results reveal a massive concentration in local production (99.5%—Minas Gerais), port movements (99.9%—Santos, Itaguai, and Rio de Janeiro), and country buyers (80.9%—the United States, United Kingdon, and Japan). Conclusions: The study concludes that the Brazilian green coffee supply chain relies on a fragile and overloaded logistical network. Due to that, this study indicates that the stakeholders and decision-makers involved must consider this high concentration of production in some areas and companies. They must also address the bottlenecks in logistical corridors and the fierce competition involved in acquiring and processing Brazilian coffee production because these factors can drastically affect the revenue of the companies operating in this sector.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Building Resilient Reverse Supply Chains: Strategies, Technologies, and Sustainable Practices)
►▼
Show Figures
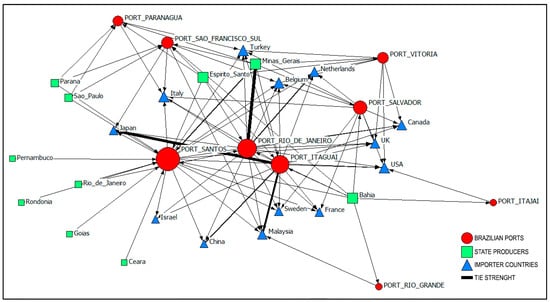
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analyzing Barriers to Internet of Things (IoT) Adoption in Humanitarian Logistics: An ISM–DEMATEL Approach
by
Abderahman Rejeb, Karim Rejeb and Imen Zrelli
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020038 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Effective humanitarian logistics (HL) is essential in disaster response. The “Internet of Things” (IoT) holds potential to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of HL, yet adoption is slowed by numerous barriers. Methods: This study employs interpretive structural modeling (ISM) and
[...] Read more.
Background: Effective humanitarian logistics (HL) is essential in disaster response. The “Internet of Things” (IoT) holds potential to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of HL, yet adoption is slowed by numerous barriers. Methods: This study employs interpretive structural modeling (ISM) and decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) to explore and classify barriers to IoT integration in HL. Results: A total of 12 barriers were identified, classified, and ranked according to their driving power and dependence. Key barriers include lack of standardization, organizational resistance, data quality issues, and legal challenges. Conclusions: Overcoming these barriers could significantly improve relief operations, reduce errors, and enhance decision-making processes in HL. This investigation is the first of its kind into IoT barriers in HL, laying the groundwork for further research and providing valuable insights for HL managers.
Full article
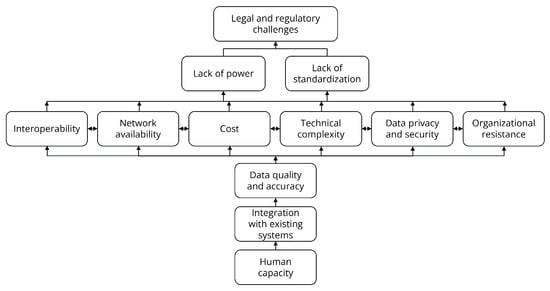
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Logistics Hub and Route Optimization in the Physical Internet Paradigm
by
Hisatoshi Naganawa, Enna Hirata, Nailah Firdausiyah and Russell G. Thompson
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020037 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The global logistics industry is facing looming challenges related to labor shortages and low-efficiency problems due to the lack of logistics facilities and resources, resulting in increased logistics delays. The Physical Internet is seen as a way to take logistics into the
[...] Read more.
Background: The global logistics industry is facing looming challenges related to labor shortages and low-efficiency problems due to the lack of logistics facilities and resources, resulting in increased logistics delays. The Physical Internet is seen as a way to take logistics into the next generation of transformation. This research proposes a Physical Internet-enabled system that allows multiple companies to efficiently share warehouses and trucks to achieve operational efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions. Methods: We propose a novel demography-weighted combinatorial optimization model utilizing a genetic algorithm and the Lin–Kernighan heuristic. The model is tested with real data simulations to evaluate its performance. Results: The results show that compared to the existing model presented in a previous study, our proposed model improves location optimality and distributive routing efficiency and reduces CO2 emissions by 54%. Conclusions: By providing a well-founded novel model, this research makes an important contribution to the implementation of the Physical Internet by computing optimal logistics hubs and routes as well as providing a solution to cut CO2 emissions by half.
Full article
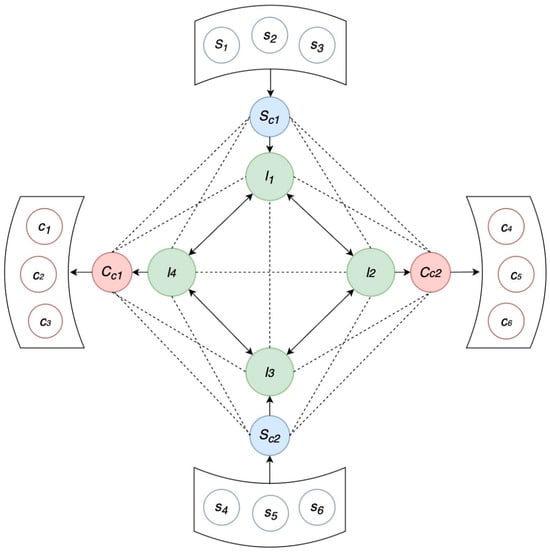
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Criteria Approach for Quantifying the Impact of Global Megatrends on the Pulp and Paper Industry: Insights into Digitalization, Social Behavior Change, and Sustainability
by
Keren A. Vivas, Ramon E. Vera, Sudipta Dasmohapatra, Ronald Marquez, Sophie Van Schoubroeck, Naycari Forfora, Antonio José Azuaje, Richard B. Phillips, Hasan Jameel, Jason A. Delborne, Daniel Saloni, Richard A. Venditti and Ronalds Gonzalez
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020036 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: The pulp and paper industry (P&PI) is undergoing significant disruption driven by global megatrends that necessitate advanced tools for predicting future behavior and adapting strategies accordingly. Methods: This work utilizes a multi-criteria framework to quantify the effects of digitalization, changes
[...] Read more.
Background: The pulp and paper industry (P&PI) is undergoing significant disruption driven by global megatrends that necessitate advanced tools for predicting future behavior and adapting strategies accordingly. Methods: This work utilizes a multi-criteria framework to quantify the effects of digitalization, changes in social behavior, and sustainability as three major megatrends transforming the P&PI industry, with a specific focus on hygiene tissue products. Thus, the research combines a comprehensive literature review, insights from a Delphi study, and topic modeling to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the present and future impacts of these global megatrends. Results: The findings suggest an urgent need to identify alternative raw materials to prevent potential supply chain disruptions. Moreover, due to shifts in social behavior, it becomes critical for businesses to substantiate their sustainability claims with hard data to avoid the risk of a “greenwashing” perception among consumers. Conclusions: This study provides decision support for strategic planning by highlighting actionable insights, quantitative predictions, and trend analysis, alongside the examination of consumer and market trends. It aims to incorporate diverse stakeholder perspectives and criteria into decision-making processes, thereby enriching the strategic planning and sustainability efforts within the P&PI industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Its Application in Sustainable Smart Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures
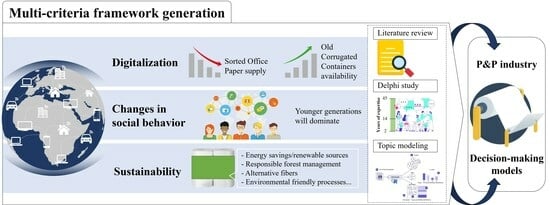
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Third-Party Reverse Logistics Selection: A Literature Review
by
Samin Yaser Anon, Saman Hassanzadeh Amin and Fazle Baki
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020035 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: This literature review delves into the concept of ‘Third-party Reverse Logistics selection’, focusing on its process and functionality using deterministic and uncertain decision-making models. In an increasingly globalized world, Reverse Logistics (RL) plays a vital role in optimizing supply chain management,
[...] Read more.
Background: This literature review delves into the concept of ‘Third-party Reverse Logistics selection’, focusing on its process and functionality using deterministic and uncertain decision-making models. In an increasingly globalized world, Reverse Logistics (RL) plays a vital role in optimizing supply chain management, reducing waste, and achieving sustainability objectives. Deterministic decision-making models employ predefined criteria and variables, utilizing mathematical algorithms to assess factors such as cost, reliability, and capacity across various geographical regions. Uncertain decision-making models, on the other hand, incorporate the unpredictability of real-world scenarios by considering the uncertainties and consequences of decision making and choices based on incomplete information, ambiguity, unreliability, and the option for multiple probable outcomes. Methods: Through an examination of 41 peer-reviewed journal publications between the years 2020 and 2023, this review paper explores these concepts and problem domains within three categories: Literature Reviews (LR), Deterministic Decision-Making (DDM) models, and Uncertain Decision-Making (UDM) models. Results: In this paper, observations and future research directions are discussed. Conclusions: This paper provides a comprehensive review of third-party reverse logistics selection papers.
Full article
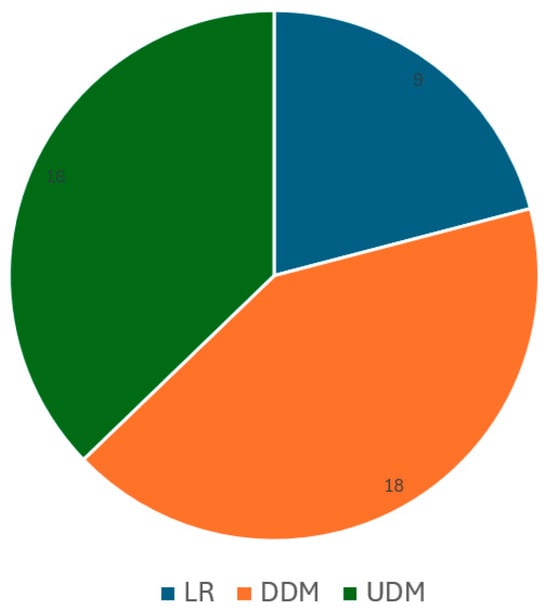
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stock Levels and Repair Sourcing in a Periodic Review Exchangeable Item Repair System
by
Yahel Giat
Logistics 2024, 8(2), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020034 - 22 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Exchangeable item repair systems are inventory systems. A nonfunctional item is exchanged for a functional item and returns to the system after being repaired. In our periodic review setting, repair is performed either in-house or outsourced. When repair is in-house, a repaired
[...] Read more.
Background: Exchangeable item repair systems are inventory systems. A nonfunctional item is exchanged for a functional item and returns to the system after being repaired. In our periodic review setting, repair is performed either in-house or outsourced. When repair is in-house, a repaired item is returned to stock regardless of the repair status of the other items in its order. In contrast, with outsourced repair, the entire order must be repaired for it to return to stock. Methods: We develop formulas for the window fill rate (probability for a customer to be served within a given time window) to measure the system’s performance and compute it for each repair model. The cost of outsourcing is the difference between the number of spares needed to maintain a target performance level when repair is internal and when it is outsourced. Results and Conclusions: In our numerical example, we show that the window fill rate in both models is S-shaped in the number of spares and show how the graph shifts to the right when customer tolerance decreases and order cycle time increases. Further, we show that the cost of outsourcing is increasing with customer tolerance and with the target performance level.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence, Logistics Analytics, and Automation)
►▼
Show Figures
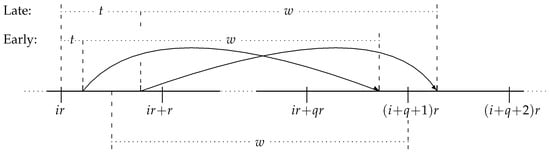
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Designing an Intelligent Scoring System for Crediting Manufacturers and Importers of Goods in Industry 4.0
by
Mohsin Ali, Abdul Razaque, Joon Yoo, Uskenbayeva Raissa Kabievna, Aiman Moldagulova, Satybaldiyeva Ryskhan, Kalpeyeva Zhuldyz and Aizhan Kassymova
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010033 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The modern credit card system is critical, but it has not been fully examined to meet the unique financial needs of a constantly changing number of manufacturers and importers. Methods: An intelligent credit card system integrates the features of artificial
[...] Read more.
Background: The modern credit card system is critical, but it has not been fully examined to meet the unique financial needs of a constantly changing number of manufacturers and importers. Methods: An intelligent credit card system integrates the features of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. The decentralized and unchangeable ledger of the Blockchain technology significantly reduces the risk of fraud while maintaining real-time transaction recording. On the other hand, the capabilities of AI-driven credit assessment algorithms enable more precise, effective, and customized credit choices that are specifically tailored to meet the unique financial profiles of manufacturers and importers. Results: Several metrics, including predictive credit risk, fraud detection, credit assessment accuracy, default rate comparison, loan approval rate comparison, and other important metrics affecting the credit card system, have been investigated to determine the effectiveness of modern credit card systems when using Blockchain technology and AI. Conclusion: The study of developing an intelligent scoring system for crediting manufacturers and importers of goods in Industry 4.0 can be enhanced by incorporating user adoption. The changing legislation and increasing security threats necessitate ongoing monitoring. Scalability difficulties can be handled by detailed planning that focuses on integration, data migration, and change management. The research may potentially increase operational efficiency in the manufacturing and importing industries.
Full article
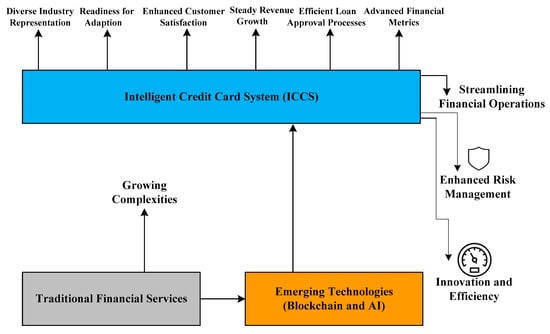
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modelling a Logistics and Financial Supply Chain Network during the COVID-19 Era
by
Sina Abbasi, Ilias Vlachos, Ali Samadzadeh, Shayan Etemadifar, Mohamad Afshar and Mohsen Amra
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010032 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Supply chain networks (SCNs) have been interrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic, leaving them open to financial losses. SCs have been impacted by the pandemic, necessitating the adoption of sustainable practices and dynamic capacities to ensure resilience and performance. Several studies have
[...] Read more.
Background: Supply chain networks (SCNs) have been interrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic, leaving them open to financial losses. SCs have been impacted by the pandemic, necessitating the adoption of sustainable practices and dynamic capacities to ensure resilience and performance. Several studies have focused on this subject, offering insights into the importance of sustainable supply-chain management, corporate governance, big data management activities, and digital technology in minimising the consequences of the pandemic and fostering sustainability. Methods: This study suggests an analytical framework for assessing environmentally friendly procedures and dynamic capacities to assure performance in a disruptive environment. Results: The following are some of the important details and contributions in this article: (1) developed a conceptual framework for assessing dynamic capacities and sustainable behaviours considering COVID-19, (2) concentrates on financial ratios during COVID-19, and (3) established drivers for sustainable practices and competencies during disruption and unpredictable business settings. Conclusions: The suggested model can assist practitioners in creating and implementing sustainable supply chain (SC) activities and tracking and assessing their effects on the sustainability of businesses. So, the proposed model can assist managers in creating and implementing sustainable supply-chain activities and tracking and analysing their effects on the sustainability of businesses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Its Application in Sustainable Smart Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating the Crash Protection Performance of a Medical Carrier Bag for Drone Transport
by
Fraser McLeod, Tom Cherrett, Andy Oakey, Katherine Theobald, Tim Waters, Matt Grote, John Armstrong, Jack Denny and Alex Murray
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010031 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Drone transport regulations in Europe require a crash-protected container (CPC) to be used for the carriage of dangerous goods. With increasing interest in the use of drones for medical logistics, the motivation behind this research was to investigate whether the existing approved
[...] Read more.
Background: Drone transport regulations in Europe require a crash-protected container (CPC) to be used for the carriage of dangerous goods. With increasing interest in the use of drones for medical logistics, the motivation behind this research was to investigate whether the existing approved medical carriers could also pass as CPCs. To date, there has been little practical experimentation on or theoretical research into the crash protection performance of medical containers. Methods: Addressing this gap, this paper reports findings from a series of drop test experiments to investigate the crashworthiness of a standard medical carrier bag used by the National Health Service (NHS) in the UK. Th drop tests were performed from heights of up to 122 m using standard medical carriers containing bags of dyed saline to examine the robustness of the carrier and whether it could contain any leakages, a key requirement for transporting dangerous goods. Results: The tests found that the medical carrier failed on some drops, with the zipped lid being identified as the main weakness. Conclusions: A new understanding of the carrier’s terminal velocity, impact acceleration, and failure mechanisms were gained and subsequent strengthening and waterproofing remedial measures recommended. New insights and practical recommendations are provided relating to performing formal drop tests and how to conduct these using a drone.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic New Technological Solutions, Research Methods, Simulation and Analytical Models That Support the Development of Modern Transport Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
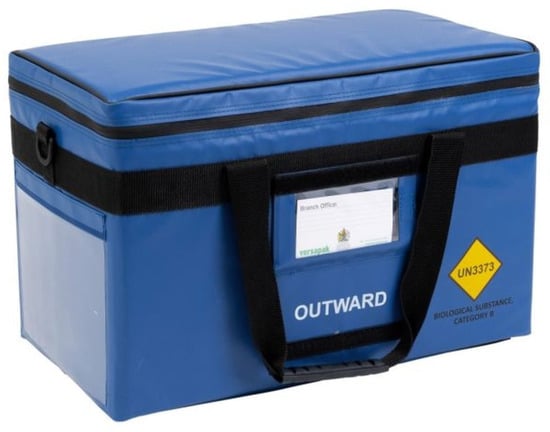

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Implementation Challenges of the Electronic Freight Transport Information (eFTI) Regulation: An Empirical Perspective from Greece
by
Thomas K. Dasaklis, Evangelia Kopanaki, Panos T. Chountalas, Nikolaos P. Rachaniotis, Theodore G. Voutsinas, Kyriakos Giannakis and Gregory Chondrokoukis
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010030 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: The electronic Freight Transport Information (eFTI) regulation is critical in modernizing freight transport (FT) within the European Union by establishing a framework for the electronic exchange of information. Despite its importance, there is a notable gap in the literature regarding the
[...] Read more.
Background: The electronic Freight Transport Information (eFTI) regulation is critical in modernizing freight transport (FT) within the European Union by establishing a framework for the electronic exchange of information. Despite its importance, there is a notable gap in the literature regarding the practical implementation challenges, especially from an empirical perspective. Methods: To address this gap, our study utilized a grounded theory approach, conducting interviews with a diverse group of logistics experts from Greece. The selection of experts was strategic to ensure a comprehensive range of knowledge and expertise, including insights at the policy level as well as practical experiences. Results: Our findings highlight several significant challenges in the implementation of eFTI, including the digital skill gap among the workforce, issues with system interoperability, and diverse capacities and resources of companies of different sizes. Economic factors, regulatory frameworks and the necessity for targeted training and leadership support were also identified as crucial for the digital transition. Conclusions: The study shows that uniform eFTI implementation may not work for all organizations, highlighting the necessity for customized strategies that address specific challenges in the FT chain. Our research deepens the understanding of these issues, providing actionable insights for successful eFTI adoption.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart, Agile, Sustainable & Integrated: The Logistics of the Future)
►▼
Show Figures
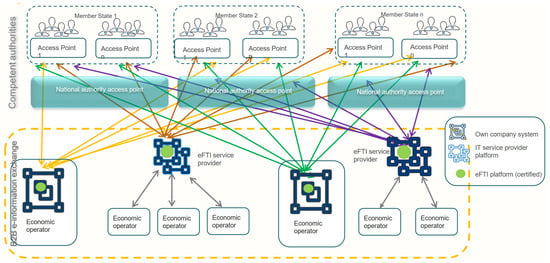
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Objective Model for Designing a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Logistics Network
by
Mojtaba Arab Momeni, Vipul Jain and Mehdi Bagheri
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010029 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The growing concern for environmental and social issues has led to a focus on designing sustainable supply chains and increasing industrial responsibility towards society. In this paper, a multi-objective mixed-integer programming model is presented for designing a sustainable closed-loop supply chain.
[...] Read more.
Background: The growing concern for environmental and social issues has led to a focus on designing sustainable supply chains and increasing industrial responsibility towards society. In this paper, a multi-objective mixed-integer programming model is presented for designing a sustainable closed-loop supply chain. The model is aimed at the minimization of the total cost with the total used facilities, the negative environmental impacts, and the maximization of the positive social impacts. Methods: The epsilon-constraint method is utilized for solving the model and further extracting the Pareto solutions. Results: The result of the research clearly shows an optimal trade-off between the conflicting objectives, where, by paying more attention to the social and environmental aspects of sustainability, the total costs are increased or by optimizing the number of facilities, a better balance between the dynamics associated with the short-term and long-term goals is reached. The results of the sensitivity analysis also show that increasing the demand of the supply chain has the greatest impact on the supply chain costs compared to other objectives. Conclusions: Consequently, investigating such comprehensive sustainable objectives provides better insights into the impact of design variables on the expectations of stakeholders.
Full article
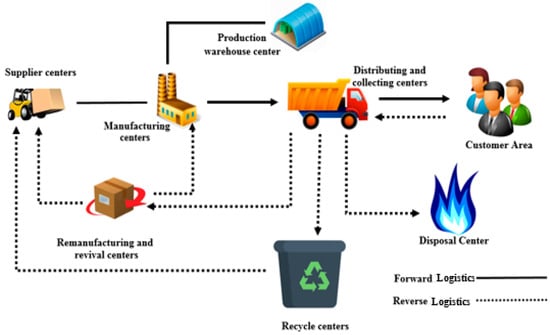
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Smart Ports in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review
by
Antonios Paraskevas, Michael Madas, Vasileios Zeimpekis and Konstantinos Fouskas
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010028 - 11 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Information and communication technologies (ICT) have introduced “smart” concepts across industries, including ports. Smart ports, leveraging IoT, cybersecurity, and cloud computing, are trending in maritime operations. They optimize data for informed decision-making, cutting costs, enhancing efficiency, mitigating risks, and fostering growth.
[...] Read more.
Background: Information and communication technologies (ICT) have introduced “smart” concepts across industries, including ports. Smart ports, leveraging IoT, cybersecurity, and cloud computing, are trending in maritime operations. They optimize data for informed decision-making, cutting costs, enhancing efficiency, mitigating risks, and fostering growth. Methods: To consolidate knowledge in this area, we are conducting a systematic literature review and meta-analysis using the PRISMA framework. Our goal is to synthesize existing insights, minimize biases, increase reliability, and effectively communicate our findings. To address the research needs mentioned, the current study focuses on implementing a systematic literature review (SLR). Results: The goals of this review are: (i) to present and describe the main categories and themes within the research topic, and (ii) to identify research gaps that will aid future research. Key findings include the identification and classification of current literature trends in the smart port performance evaluation framework and the examination of fundamental themes discussed within this area of research. Conclusions: In our review, we emphasize the smart port concept, clarifying its common interpretations amid the industry 4.0 revolution. We discuss recent advancements in emerging technologies and identify key challenges driving researchers’ exploration of the evolving smart port landscape.
Full article
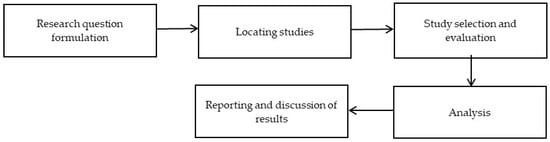
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Challenges of Industry 4.0 Adoption in the FMCG Sector: Implications for Resilient Supply Chain in Emerging Economy
by
Md Shihab Shakur, Maishat Lubaba, Binoy Debnath, A. B. M. Mainul Bari and M. Azizur Rahman
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010027 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) supply chains are experiencing various challenges due to the interactions between consumers and decision-makers during physical distribution, manufacturing, wholesale and retail. One possible strategy to address these challenges for smoothing the supply chain (SC) and logistics operations is
[...] Read more.
Background: Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) supply chains are experiencing various challenges due to the interactions between consumers and decision-makers during physical distribution, manufacturing, wholesale and retail. One possible strategy to address these challenges for smoothing the supply chain (SC) and logistics operations is to adopt Industry 4.0 (I4.0) based technologies in the FMCG business processes. In this regard, digitalization and automation of the FMCG supply chain can be strengthened by the alluring properties of I4.0 technologies. Methods: This study identified nine significant challenges through a literature review and expert validation. Later, the challenges were evaluated using a novel multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) framework, the Bayesian best worst method (BWM). Results: The findings indicated that “requirement for substantial investment and resources”, “incompatible technological infrastructure” and “poorly structured value chain” are the most significant challenges to implementing I4.0 in the FMCG industry. Conclusions: The study is expected to significantly contribute to improving the FMCG supply chain’s resilience, sustainability, visibility, traceability and responsiveness. Additionally, the research can provide industrial practitioners valuable insights into implementing I4.0 in FMCG and similar sectors and thus promote SC sustainability and resilience in those industries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Its Application in Sustainable Smart Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Closed Queueing Networks Approach for an Optimal Heterogeneous Fleet Size of an Inter-Facility Bulk Material Transfer System
by
Mohamed Amjath, Laoucine Kerbache and James MacGregor Smith
Logistics 2024, 8(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010026 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: This study addresses optimising fleet size in a system with a heterogeneous truck fleet, aiming to minimise transportation costs in interfacility material transfer operations. Methods: The material transfer process is modelled using a closed queueing network (CQN) that considers heterogeneous nodes and
[...] Read more.
Background: This study addresses optimising fleet size in a system with a heterogeneous truck fleet, aiming to minimise transportation costs in interfacility material transfer operations. Methods: The material transfer process is modelled using a closed queueing network (CQN) that considers heterogeneous nodes and customised service times tailored to the unique characteristics of various truck types and their transported materials. The optimisation problem is formulated as a mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP), falling into the NP-Hard, making exact solution computation challenging. A numerical approximation method, a modified sequential quadratic programming (SQP) method coupled with a mean value analysis (MVA) algorithm, is employed to overcome this challenge. Validation is conducted using a discrete event simulation (DES) model. Results: The proposed analytical model tested within a steel manufacturing plant’s material transfer process. The results showed that the analytical model achieved comparable optimisation of the heterogeneous truck fleet size with significantly reduced response times compared to the simulation method. Furthermore, evaluating performance metrics, encompassing response time, utilisation rate, and cycle time, revealed minimal discrepancies between the analytical and the simulation results, approximately ±8%, ±8%, and ±7%, respectively. Conclusions: These findings affirm the presented analytical approach’s robustness in optimising interfacility material transfer operations with heterogeneous truck fleets, demonstrating real-world applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimizations and Operations Management of Modern Logistic Systems and Supply Chains)
►▼
Show Figures
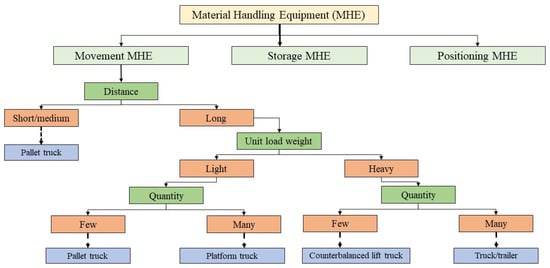
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Drones, Energies, Infrastructures, Logistics, Modelling
New Technological Solutions, Research Methods, Simulation and Analytical Models That Support the Development of Modern Transport Systems
Topic Editors: Tomasz Nowakowski, Artur Kierzkowski, Agnieszka A. Tubis, Franciszek Restel, Tomasz Kisiel, Anna Jodejko-Pietruczuk, Mateusz Zaja̧cDeadline: 30 August 2024
Topic in
Computers, Informatics, Information, Logistics, Mathematics, Algorithms
Decision Science Applications and Models (DSAM)
Topic Editors: Daniel Riera Terrén, Angel A. Juan, Majsa Ammuriova, Laura CalvetDeadline: 31 December 2024
Topic in
AI, Digital, JMSE, Logistics, Systems
Global Maritime Logistics in the Era of Industry 4.0
Topic Editors: Nam Kyu Park, Hokey MinDeadline: 28 February 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Logistics
Risk Management in Supply Chain Management - Collaboration and Behavior
Guest Editor: Scott DellanaDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Logistics
Sustainable E-commerce, Supply Chains and LogisticsGuest Editor: Shiu-Li HuangDeadline: 1 July 2024
Special Issue in
Logistics
Smart, Agile, Sustainable & Integrated: The Logistics of the Future
Guest Editors: Vasilis Zeimpekis, Michael A. MadasDeadline: 1 August 2024
Special Issue in
Logistics
Sustainable Logistics in the New Era
Guest Editor: Hao YuDeadline: 31 October 2024





