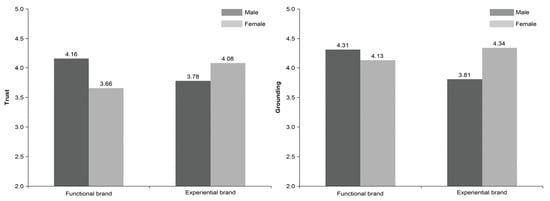
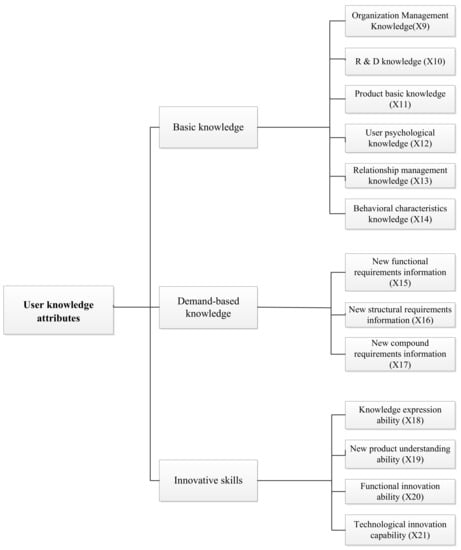
Customer Relationships in Electronic Commerce
A topical collection in Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research (ISSN 0718-1876). This collection belongs to the section "Digital Marketing and the Connected Consumer".
Viewed by 7860Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
With the rapid growth of information technology, customer relationship management has attracted an increasing amount of attention as a new strategy for companies. To acquire new customers and retain old customers, many companies tend to use information technology, such as big data, mobile devices, social media, Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, Cloud computing, to improve their services for customers. Currently, information technology is a necessary enabler of customer relationships in most organizations to store and analyze huge amounts of customer data and provide better values for customers. Moreover, the interaction interfaces between companies and customers will be changed. Through mobile devices, social media, Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, and Cloud computing, the contact points with customers will be more effective and affordable.
Since many companies likely use information technology and its applications for improving customer relationships in their businesses. It is still unclear whether the strategy can produce positive feedback from customers or better performance for companies. Moreover, before such applications can be developed and the benefits realized, companies need to address the possible challenging tasks and the obstacles possibly arise. Therefore, this Special Issue focuses on customer relationships in electronic commerce to develop a better solution for researchers and practitioners.
The related topics for the Special Issue may include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Customer value and customer relationships in electronic commerce.
- Customer data analysis and customer relationship management by using big data or data mining.
- Developing customer relationships by using social media.
- Developing customer relationships by using Internet of Things.
- Developing customer relationships by using AI technology.
- Analyzing customer data and developing service platforms by using cloud computing.
- Creating customer value by integrating the online and offline channels.
- Developing customer relationships in omni-channel commerce.
- The challenges or the obstacles of customer relationships in e-commerce.
Prof. Dr. Yung-Shen Yen
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1000 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- e-commerce
- customer value
- big data
- social media
- Internet of Things
- AI technology
- cloud computing
- online and offline channels
- omni-channel commerce