Journal Description
Journal of Risk and Financial Management
Journal of Risk and Financial Management
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on risk and financial management, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EconBiz, EconLit, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Business, Management and Accounting (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
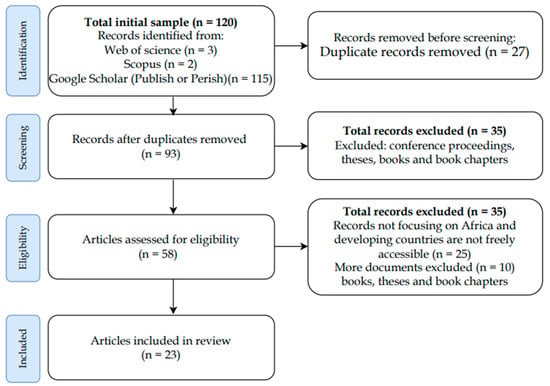
Sustaining Family Businesses through Business Incubation: An Africa-Focused Review
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(5), 178; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050178 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The influence of business incubation systems on family businesses in African economies has not been thoroughly investigated despite the potential contribution of family businesses to Africa’s economic expansion and the attainment of development goals outlined in the Africa Development Agenda 2063 and the
[...] Read more.
The influence of business incubation systems on family businesses in African economies has not been thoroughly investigated despite the potential contribution of family businesses to Africa’s economic expansion and the attainment of development goals outlined in the Africa Development Agenda 2063 and the Sustainable Development Goals. Therefore, this study investigates the potential benefits that family businesses in Africa can derive from engaging in business incubation. This study utilised an integrative literature review methodology to investigate the research question. Twenty-three peer-reviewed articles were systematically selected from the Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases using the following combination of phrases: “family business” and either “business incubation” or “business incubator”. The findings suggest ways to create a mutually beneficial relationship between family businesses and business incubators to improve long-term sustainability, promote collaboration, facilitate knowledge transfer, and foster an entrepreneurial ecosystem. It also recognises challenges, such as cultural alignment in family businesses. Business incubators in Africa can improve the sustainability of family businesses, such as during the succession, by offering support, resources, and guidance. The South African experience is a role model for the rest of the continent, in this regard. Future research should broaden the sources beyond the three databases utilised, including non-peer-reviewed sources such as grey literature, and extend the focus beyond developing economies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Family Companies)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Transformation of the Ukrainian Stock Market: A Data Properties View
by
Alex Plastun, Lesia Hariaha, Oleksandr Yatsenko, Olena Hasii and Liudmyla Sliusareva
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(5), 177; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050177 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper investigates the evolution of the Ukrainian stock market through an analysis of various data properties, including persistence, volatility, normality, and resistance to anomalies for the case of daily returns from the PFTS stock index spanning 1995–2022. Segmented into sub-periods, it aims
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates the evolution of the Ukrainian stock market through an analysis of various data properties, including persistence, volatility, normality, and resistance to anomalies for the case of daily returns from the PFTS stock index spanning 1995–2022. Segmented into sub-periods, it aims to test the hypothesis that the market’s efficiency has increased over time. To do this different statistical techniques and methods are used, including R/S analysis, ANOVA analysis, regression analysis with dummy variables, t-tests, and others. The findings present a mixed picture: while volatility and persistence demonstrate a general decreasing trend, indicating a potential shift towards a more efficient market, normality tests reveal no discernible differences between analyzed periods. Similarly, the analysis of anomalies shows no specific trends in the market’s resilience to the day-of-the-week effect. Overall, the results suggest a lack of systematic changes in data properties in the Ukrainian stock market over time, possibly due to the country’s volatile conditions, including two revolutions, economic crises, the annexation of territories, and a Russian invasion leading to the largest war in Europe since WWII. The limited impact of reforms and changes justifies the need for continued market reform and evolution post-war.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Markets, Financial Volatility and Beyond (Volume III))
►▼
Show Figures
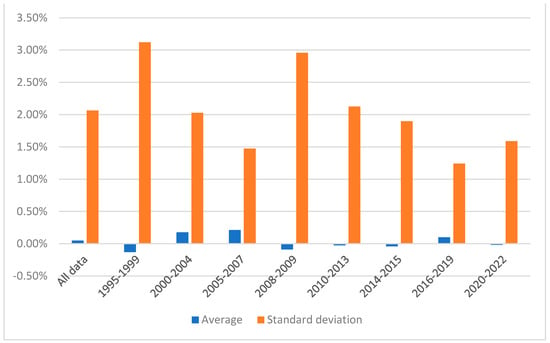
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High Risk, Constrained Return: Impact of Student Loans on Agricultural Real Estate
by
Leobardo Diosdado, Donald Lacombe and Darren Hudson
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(5), 176; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050176 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
A farming household’s decision to continue producing agricultural commodities within the United States is influenced by a multitude of factors. Thus, this study seeks to examine whether the outstanding student loan balance of any member within a farming household may explain why the
[...] Read more.
A farming household’s decision to continue producing agricultural commodities within the United States is influenced by a multitude of factors. Thus, this study seeks to examine whether the outstanding student loan balance of any member within a farming household may explain why the total number of acres devoted to the production of agriculture in the United States continues to decline. Panel data from the 2007–2009 Survey of Consumer Finances are analyzed via a fixed effect model to estimate the effect of outstanding student loan balances on farmland acreage owned, controlling for other factors like farm income, debt, and land prices. The results suggest that for each additional dollar of outstanding student loan debt, there is an associated decrease of 0.0064 acres in total farmland ownership. This suggests that student loan debt may also be a factor in the decline in real estate devoted to agriculture production. The estimated effect is both economically and statistically significant. This study contributes to the literature on the risks and constraints associated with farming households that own or seek to procure additional acres of agricultural producing real estate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advancements in Real Estate Finance and Risk Management)
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Water Management Policies on Volatility Transmission in the Energy Sector
by
Elif Gormus and Katharine Harrell
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(5), 175; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050175 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
Purpose: This study evaluates the impact of the water management policies of energy companies on their volatility interactions with energy commodities. Design/methodology: We tested for volatility transmissions between 66 energy funds and fossil-fuel commodities. After identifying possible integrations, we investigated whether water management
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This study evaluates the impact of the water management policies of energy companies on their volatility interactions with energy commodities. Design/methodology: We tested for volatility transmissions between 66 energy funds and fossil-fuel commodities. After identifying possible integrations, we investigated whether water management policies, after controlling for other fund characteristics, impact the probability of integration. Results: Our findings indicate strong volatility transmission from oil prices to energy funds. However, a reverse of this information flow was not observed. From the perspective of natural gas, we found strong bi-directional integration with energy funds. When we analyzed the influence of fund characteristics on the previously established integrations, water management policies do not impact the probability of the integration of oil. However, these policies are shown to have a significant influence on integration with the natural gas market. Originality/value: While there are multiple studies that show the integration between energy companies and corresponding commodities, according to our knowledge, this is the first study that evaluates the significance of water management policies with respect to volatility integration. This study highlights the importance of water-related policies with respect to the susceptibility of energy firms to volatility contagion from the natural gas market.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Quantitative Finance in Energy)
Open AccessArticle
Driving Digital Transformation: Analyzing the Impact of Internet Banking on Profitability in the Saudi Arabian Banking Sector
by
Sonia Sayari
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(5), 174; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050174 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study examines the impact of Internet Banking on banking profitability in Saudi Arabia in a sample of conventional and Islamic banks. The study uses Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) as key metrics to measure profitability in a sample
[...] Read more.
This study examines the impact of Internet Banking on banking profitability in Saudi Arabia in a sample of conventional and Islamic banks. The study uses Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) as key metrics to measure profitability in a sample of 10 Saudi conventional and Islamic banks observed over the 2013–2022 period. The used regression analysis reveals a significant effect of Internet Banking on the profitability of both conventional and Islamic banks, as indicated by the ROA and ROE metrics. These findings have implications that underscore the strategic importance of adopting Internet Banking, emphasizing its substantial contribution to the financial performance of both conventional and Islamic banks in the Saudi Arabian banking landscape. This study offers critical insights into the strategic significance of Internet Banking for Saudi Arabian banks’ profitability and future planning, in line with the 2030 Vision goals. This research also supports informed decision making in the digital era, emphasizing the pivotal role of Internet Banking in shaping the future of the Saudi Arabian banking industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Banking and Finance)
Open AccessArticle
Modeling Funding for Industrial Projects Using Machine Learning: Evidence from Morocco
by
Soukaina Laaouina and Mimoun Benali
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 173; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040173 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
Moroccan manufacturing companies investing in the metallurgical, mechanical, and electromechanical industries sector are among the contributors to the growth of the national economy. The projects they are awarded do not have the same specific features as those of operating activities within other companies.
[...] Read more.
Moroccan manufacturing companies investing in the metallurgical, mechanical, and electromechanical industries sector are among the contributors to the growth of the national economy. The projects they are awarded do not have the same specific features as those of operating activities within other companies. They share several common features, making them particularly complex to fund. In such circumstances, supervised machine learning seems to be a suitable instrument to help such enterprises in their funding decisions, especially given that linear regression methods are inadequate for predicting human decision making as human thinking is a complicated system and not linear. Based on 5198 industrial projects of 53 firms operating in the said sector, four machine learning models are used to predict the funding method for some industrial projects, including are decision tree, random forest, gradient boosting, and K-nearest neighbors (KNN). Among the four machine learning methods, the gradient boosting method appears to be most effective overall, with an accuracy of 99%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Financial Technology and Innovation)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Do ESG Factors Prove Significant Predictors of Systematic and Downside Risks in the Russian Market after Controlling for Stock Liquidity?
by
Tamara Teplova, Tatiana Sokolova and Sergei Gurov
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 172; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040172 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper reveals the impact of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) scores on systematic and downside risks in the Russian stock market. We analyze the influence of a broad set of ESG factors controlling for stock liquidity, financial indicators of companies, and macroeconomic
[...] Read more.
This paper reveals the impact of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) scores on systematic and downside risks in the Russian stock market. We analyze the influence of a broad set of ESG factors controlling for stock liquidity, financial indicators of companies, and macroeconomic indicators. The period under consideration is from 2013 to 2021. The methodology of our research is based on regression analysis with multiplicative variables to reveal the changes induced by the COVID-19 pandemic. We obtain several novel results. Social responsibility is one of the most significant non-fundamental factors influencing both systematic and downside risks. The most important environment-related component is the measure of a company’s propensity to environmental innovations. Some dimensions of stock liquidity are also significant. For some factors, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and debt burden, we find an unexpected direction of influence on liquidity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Empirical Corporate Finance and Corporate Governance in the Era of ‘New Normal’)
Open AccessArticle
Corporate Social Responsibility: Impact on Firm Performance for an Emerging Economy
by
Neeraj Singhal, Pinku Paul, Sunil Giri and Shallini Taneja
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 171; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040171 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) was usually referred to as a concept where companies initiate voluntary action towards social and environmental concerns in the context of business operations related to the stakeholders of the company prior to the CSR Act 2013 in India. Post-2013,
[...] Read more.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) was usually referred to as a concept where companies initiate voluntary action towards social and environmental concerns in the context of business operations related to the stakeholders of the company prior to the CSR Act 2013 in India. Post-2013, the voluntary initiative was replaced by regulatory guidelines to address social and environmental concerns. The CSR applicability–investment gap was used as a base concept in this study with instrumental theory; the study offers a strategic perspective of CSR and how organizations emphasized maximizing stakeholders’ value. In order to further investigate the effect of CSR on corporate financial performance (CFP) through the measure of shareholders’ value, i.e., the return on equity (ROE), the study used the sample from the National Stock Exchange (NSE)-Nifty-100 indexed companies of Emerging Economy—India for a span of fourteen years (2009–2023). The vast majority of research in this domain is conducted in developed countries; the research gap is filled by this study by considering India and drawing samples from multiple industries. The empirical model was developed by using panel data regression, where the dependent variable was ROE, and the independent variables were earning per share (EPS), log total income (LTI), CSR applicability/profit after tax (CRSAPPPAT), and CSR investment/profit after tax (CSRIPAT). The findings also highlighted the CSR applicability and investment of the firms during pre- and post-Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) periods. The same was also analyzed for the firms committed to CSR and not committed to CSR. The results indicated that there is no significant impact of the CSR/ESG initiatives (applicability and investment) on the ROE of the firms. The performance could be better if the companies minimize the CSR/ESG promise–performance gap through effective communication with stakeholders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Corporate Sustainability and Firm Performance: Models, Practices and Policy Perspective)
►▼
Show Figures
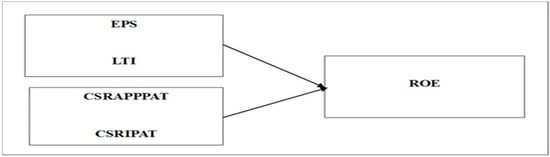
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Estimating Asset Parameters Using Levy’s Moment Matching Method
by
Masatoshi Miyake
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 170; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040170 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
Conventionally, the unknown parameters in Merton’s model are set using a calibration method that estimates the current asset value and volatility from observable stock prices. This paper describes a completely different approach for estimating these asset parameters. The proposed approach uses Levy’s moment
[...] Read more.
Conventionally, the unknown parameters in Merton’s model are set using a calibration method that estimates the current asset value and volatility from observable stock prices. This paper describes a completely different approach for estimating these asset parameters. The proposed approach uses Levy’s moment matching method to derive an equation for the asset value based on the sum of equity and debt on the balance sheet, with the current debt value treated as an unknown and estimated from stock prices. Empirical analysis reveals that this method results in simpler calculations than the calibration method and can estimate the asset parameters and default probability to the same degree of accuracy. An additional advantage of the proposed method is that it estimates the asset correlation if the current debt value is known, allowing Merton’s model to be extended to multiple companies. The asset correlation obtained by the proposed method is estimated from multiple parameters related to equity, debt, and the evaluation period, which is useful when the influence of equity volatility, leverage, and time must be considered in estimating asset correlations based on equity correlations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematics and Finance)
►▼
Show Figures
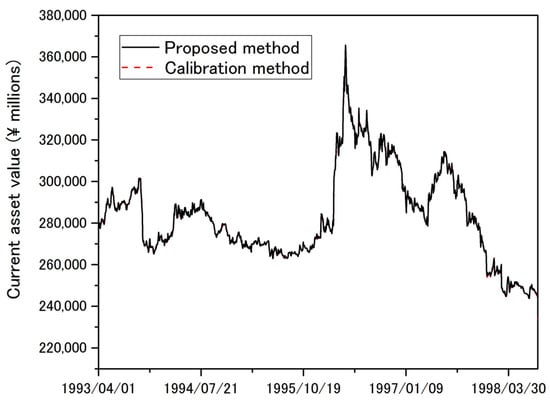
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Information Content of Stock Splits: In the Context of Stock Splits Concurrently Announced with Earnings
by
Joohyung Ha
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 169; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040169 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper examines the market responses to concurrent earnings and stock split announcements for evidence on the information content of stock splits. The majority of stock split research excludes splits announced with other information events due to confounding issues. However, it is difficult
[...] Read more.
This paper examines the market responses to concurrent earnings and stock split announcements for evidence on the information content of stock splits. The majority of stock split research excludes splits announced with other information events due to confounding issues. However, it is difficult to extract the information content of splits by merely focusing on the standalone split announcement because stock splits are devoid of any information regarding firms’ future cash flows. This study explicitly considers how a stock split is evaluated in conjunction with current earnings. This study shows that the market reacts more positively to earnings news concurrently announced with stock splits, consistent with the idea that splits are favorable news. Furthermore, this study finds that stock returns of concurrent split–earnings announcers exhibit a greater association with future cash flows, suggesting that investors should value stock splits favorably for more persistent earnings ahead.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Financial Markets)
Open AccessArticle
Testing and Ranking of Asset Pricing Models Using the GRS Statistic
by
Mark J. Kamstra and Ruoyao Shi
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 168; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040168 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
We clear up an ambiguity in the statement of the GRS statistic by providing the correct formula of the GRS statistic and the first proof of its F-distribution in the general multiple-factor case. Casual generalization of the Sharpe-ratio-based interpretation of the single-factor GRS
[...] Read more.
We clear up an ambiguity in the statement of the GRS statistic by providing the correct formula of the GRS statistic and the first proof of its F-distribution in the general multiple-factor case. Casual generalization of the Sharpe-ratio-based interpretation of the single-factor GRS statistic to the multiple-portfolio case makes experts in asset pricing studies susceptible to an incorrect formula. We illustrate the consequences of using the incorrect formulas that the ambiguity in GRS leads to—over-rejecting and misranking asset pricing models. In addition, we suggest a new approach to ranking models using the GRS statistic p-value.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Journal of Risk and Financial Management)
Open AccessArticle
What Drives Asset Returns Comovements? Some Empirical Evidence from US Dollar and Global Stock Returns (2000–2023)
by
Marco Tronzano
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 167; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040167 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper focuses on returns comovements in global stock portfolios including the US Dollar as a defensive asset. The main contribution is the selection of a large set of macroeconomic and financial variables as potential drivers of these comovements and the emphasis on
[...] Read more.
This paper focuses on returns comovements in global stock portfolios including the US Dollar as a defensive asset. The main contribution is the selection of a large set of macroeconomic and financial variables as potential drivers of these comovements and the emphasis on the predictive accuracy of proposed econometric models. One-year US Expected Inflation stands out as the most important predictor, while models including a larger number of variables yield significant predictive gains. Larger forecast errors, due to parameters instabilities, are documented during major financial crises and the COVID-19 pandemic period. Some research directions to improve the forecasting power of econometric models are discussed in the concluding section.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue International Financial Markets and Risk Finance)
►▼
Show Figures
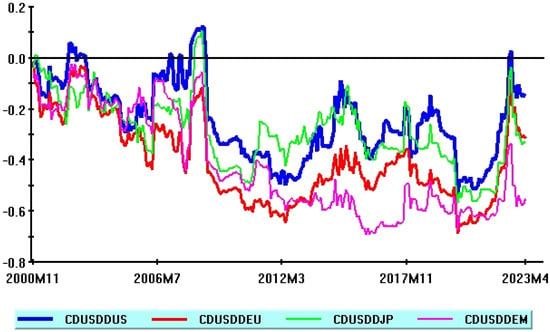
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investor Perception of ESG Performance: Examining Investment Intentions in the Chinese Stock Market with Social Self-Efficacy Moderation
by
Xiaojia Zhang, Li Ma and Miao Zhang
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 166; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040166 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
The increasing importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors has sparked scholarly interest in how company reputation influences stock market investment decisions. Most ESG research has focused on secondary data from public firms, ignoring the potential of surveys as a research tool.
[...] Read more.
The increasing importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors has sparked scholarly interest in how company reputation influences stock market investment decisions. Most ESG research has focused on secondary data from public firms, ignoring the potential of surveys as a research tool. Addressing this gap, our study investigates the relationship between retail investors’ perceptions of corporate ESG performance and their investment attitude, as well as the impact on intention, with social self-efficacy serving as a moderator. The theoretical framework of this research was adopted from the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and previous studies that used TPB to measure intention reveal a range of explanations for the connection between the factors influencing intention through attitude. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis was used in this study, and the new findings show that Chinese investors’ perceptions of corporate ESG performance positively influence their investment attitudes and intentions. Furthermore, social self-efficacy moderates the relationship between the corporate environment and governance performance, attitudes, and intentions. Accordingly, this study identifies the contribution of explaining how investment intentions are related to corporate ESG performance, which has been based on past ESG studies, to lay a platform for sustainable corporate practices in the Chinese stock market.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Financial Markets)
►▼
Show Figures
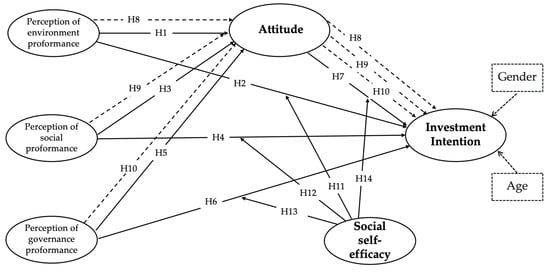
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating the Application of Digital Tools for Information Management in Financial Control: Evidence from Bulgaria
by
Zhelyo Zhelev and Silviya Kostova
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 165; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040165 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper discusses the application of digital information management tools in the context of financial control. In Bulgaria, such research is innovative as it is the first time that digital transformation in crucial financial control institutions, which influence the formation of the revenue
[...] Read more.
This paper discusses the application of digital information management tools in the context of financial control. In Bulgaria, such research is innovative as it is the first time that digital transformation in crucial financial control institutions, which influence the formation of the revenue part of the state budget and the spending of public funds, has been studied. The study aims to answer the research question of to what extent the application of digital tools in financial control improves its effectiveness. It analyses how modern technologies improve the efficiency and accuracy of information used in financial control institutions. The authors examine the impact of digital tools, such as database management systems, business analytics platforms, and electronic document management tools, on collecting, analyzing, and managing financial and non-financial information. The study uses descriptive statistics and a correlation analysis, which significantly contributes to establishing the relationship between implemented digital tools and improvements in financial control procedures. The results show that despite the conditions created for digitalization in financial control institutions, digital tools are used to a limited extent in the information management process. The study emphasizes the need for continuous investment in digital technologies and training to maximize the benefits of their application in financial control.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Financial Technology and Innovation)
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) in Supporting Strategic Management Decisions
by
Maria do Rosário Texeira Fernandes Justino, Joaquín Texeira-Quirós, António José Gonçalves, Marina Godinho Antunes and Pedro Ribeiro Mucharreira
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 164; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040164 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Nowadays, the dynamism caused by constant changes to strategic decisions in markets poses an additional difficulty in an organization’s management. The strategic decisions made by managers can easily become obsolete. One of the major difficulties in managing a commercial organization is predicting, with
[...] Read more.
Nowadays, the dynamism caused by constant changes to strategic decisions in markets poses an additional difficulty in an organization’s management. The strategic decisions made by managers can easily become obsolete. One of the major difficulties in managing a commercial organization is predicting, with some precision, the impact some strategic decisions have on the financial results. Business intelligence (BI) is widely used to help managers make strategic decisions. However, the methods used to achieve the conclusions are kept secret by BI company-based services. Modeling the environment may help predict the impact of an action in a real environment. A good model should provide the most accurate result of an applied action in a given environment. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are proven to be excellent in modeling environments with very high data noise. The same strategic action can have different results when applied to different organizations. A tool that allows the evaluation of an applied strategic action in an environment will be of great importance in the field of management. Modeling the environment will save time and money for the organization, allowing the performance of the strategic plan to be improved. If one evaluates the state of the environment after a certain strategic action is applied, it can be possible to mitigate its risk of failure. As we will verify, it is possible to use ANNs to model strategic environments, allowing precision in the prediction of sales and operating results using particular strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematics and Finance)
►▼
Show Figures
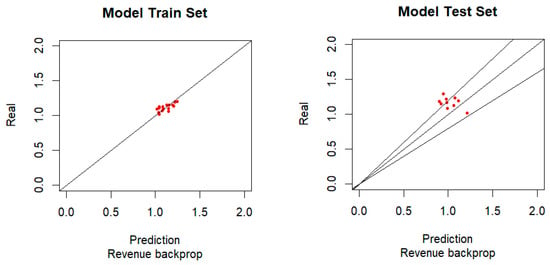
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of the Transition to the Expected Loss Model on the Portuguese Banking Sector
by
Miguel Resende, Carla Carvalho and Cecília Carmo
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 163; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040163 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study addresses the implementation of the International Financial Reporting Standard 9 (IFRS 9) in the European Union as of 1 January 2018, replacing the International Accounting Standard 39 (IAS 39) to introduce a new model for recognizing Loan Loss Provisions (LLP), based
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the implementation of the International Financial Reporting Standard 9 (IFRS 9) in the European Union as of 1 January 2018, replacing the International Accounting Standard 39 (IAS 39) to introduce a new model for recognizing Loan Loss Provisions (LLP), based on Expected Credit Loss (ECL). This model responds to criticisms of the former Incurred Credit Loss (ICL) system for its inability to reflect credit losses in a timely manner, potentially exacerbating the effects of financial crises. This study focuses on the effects of adopting the ECL model on the level of Loan Loss Allowances (LLA) in loans, own equity, and the Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio across 13 Portuguese commercial banks. A mean comparison test is used to evaluate scenarios before and after the application of the ECL model, highlighting the importance of regulator actions and the adequacy of loss recognition policies, including the effects of European Union. The results obtained demonstrate significant negative impacts on the net values of loans, own equity, and the CET1 ratio upon adopting the IFRS 9 ECL model due to the widespread increase in LLAs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Accounting, Reporting and Disclosure)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Alignment of Financial Signaling and Stock Return Synchronicity
by
Tarek Eldomiaty, Islam Azzam, Karim Tarek Hamed Afifi and Mohamed Hashim Rashwan
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 162; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040162 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
Financial signaling and stock return synchronicity may not be at crossroads. This paper optimizes the signaling effect of firms’ financial indicators on stock return synchronicity. The ultimate objective is to align firms’ financial signaling and stock return synchronicity, which implies a benefit of
[...] Read more.
Financial signaling and stock return synchronicity may not be at crossroads. This paper optimizes the signaling effect of firms’ financial indicators on stock return synchronicity. The ultimate objective is to align firms’ financial signaling and stock return synchronicity, which implies a benefit of hedging against fluctuations in the stock market index. The data cover quarterly periods from June 1992 to March 2022 for the non-financial firms listed in the DJIA30 and NASDAQ100. This paper examines the observed return synchronicity as the dependent variable. The independent variables are classified into six groups namely, Solvency (or Liquidity) ratios, Assets Efficiency ratios, Expense Control ratios, Debt (or Leverage) ratios, Profitability ratios, and Dividend ratios. The analysis is conducted on two different groups. The first group examines the observed firms’ financials that affect observed stock return synchronicity. The second group examines optimal firms’ financials that help optimize stock return synchronicity. The final results show that (a) current stock return synchronicity is affected positively by cash ratio, and negatively by receivables and historical growth of earnings; (b) optimal stock return synchronicity can be elevated using significant financial indicators namely, Inventory/Current Assets, Net Working Capital/Total Assets, Net worth/Fixed Assets, and Sales Annual Growth; (c) agency conflicts between managers and shareholders can be mitigated by the aforementioned financial indicators, which do not include debt financing being the common source of agency conflicts; and (d) dividends are still insignificant to stock return synchronization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Accounting)
Open AccessArticle
Stock Overvaluation, Management Myopia, and Long-Term Firm Performance
by
Jialin Song, Luyu Wang, Sihong Wu and Yiyi Su
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 161; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040161 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
How does stock overvaluation in secondary financial markets affect long-term firm performance when significant corporate “insiders” seek to realize self-benefit? Using a sample of Chinese listed companies from 2007 to 2018, we find that overvaluation of stock price has a negative impact on
[...] Read more.
How does stock overvaluation in secondary financial markets affect long-term firm performance when significant corporate “insiders” seek to realize self-benefit? Using a sample of Chinese listed companies from 2007 to 2018, we find that overvaluation of stock price has a negative impact on long-term firm performance. Moreover, our results show that management myopia mediates the relationship between stock overevaluation and long-term performance. Our study enriches the discussion of stock overvaluation and extends the management myopia literature by considering unique aspects of the irrational behavior of firm decision makers, providing implications for governments to improve their capital market reform and development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Markets, Financial Volatility and Beyond (Volume III))
►▼
Show Figures
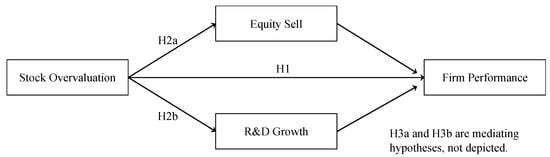
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Diversification Benefits of Foreign Real Estate: Evidence from 40 Years of Data
by
C. Mitchell Conover, Joseph D. Farizo, H. Swint Friday and David S. North
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 160; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040160 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
We investigate the potential of global real estate to improve the long-term performance of a US equity portfolio, utilizing a recent dataset of 40 years’ worth of US stocks, US real estate, 13 foreign stock markets, and 13 foreign real estate markets across
[...] Read more.
We investigate the potential of global real estate to improve the long-term performance of a US equity portfolio, utilizing a recent dataset of 40 years’ worth of US stocks, US real estate, 13 foreign stock markets, and 13 foreign real estate markets across diverse regions. Despite a modest performance in terms of risk and return, foreign real estate has consistently lower correlations with US stocks compared to foreign equities. Rolling correlation analysis indicates that foreign real estate markets remain relatively segmented compared to foreign equity, despite increasing financial market correlations over time. Efficient frontier analysis demonstrates that portfolios including foreign real estate consistently outperform those limited to US stocks and US real estate or those including foreign stocks, indicating the importance of foreign real estate in optimizing portfolio performance. Subperiod analysis reveals that foreign real estate retains its diversification benefits even in the latter, more integrated period. Our results are robust when using Conditional Value-at-Risk as a measure of risk. Overall, our findings highlight the persistent diversification benefits and superior risk-adjusted returns from incorporating foreign real estate into US equity portfolios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advancements in Real Estate Finance and Risk Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pathways to Success: The Interplay of Industry and Venture Capital Clusters in Entrepreneurial Company Exits
by
Saurabh Ahluwalia and Sul Kassicieh
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17(4), 159; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17040159 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study investigates the dynamics within entrepreneurial ecosystems, focusing on the influence of venture capital (VC) financing clusters and industry clusters on startup success. VC financing clusters, geographic hubs with intense VC funding activities, and industry clusters, regions with concentrated sector-specific firms, are
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the dynamics within entrepreneurial ecosystems, focusing on the influence of venture capital (VC) financing clusters and industry clusters on startup success. VC financing clusters, geographic hubs with intense VC funding activities, and industry clusters, regions with concentrated sector-specific firms, are integral components. Expanding existing research that links proximity to these clusters with successful exits through mergers and acquisitions (M&A), our study includes initial public offerings (IPOs) as a vital exit strategy. Results show that affiliations with venture capitalists in prominent VC financing clusters enhance M&A and IPO success for startups. Intriguingly, startups in industry strongholds exhibit a greater likelihood of M&A success, but, this effect is not seen for IPO exits. Additionally, the absence of startup co-location with venture capitalists in VC financing hubs does not impact IPO exits but hinders M&A success. These nuanced insights highlight the complex relationships within entrepreneurial ecosystems and underscore the need for tailored perspectives considering diverse exit pathways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Business and Entrepreneurship)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Administrative Sciences, Businesses, Economies, IJERPH, JRFM, Risks, Systems
Risk Management in Public Sector
Topic Editors: Matthias Beck, Andrew WattersonDeadline: 20 October 2024
Topic in
Commodities, Economies, Energies, JRFM, FinTech
Energy Market and Energy Finance
Topic Editors: Junhua Zhao, Julien ChevallierDeadline: 31 December 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JRFM
Low Frequency Algorithmic Trading
Guest Editor: Pankaj TopiwalaDeadline: 1 May 2024
Special Issue in
JRFM
Blockchain Technologies and Cryptocurrencies
Guest Editors: Ahmet Faruk Aysan, Oguzhan Cepni, Erdinc AkyildirimDeadline: 1 June 2024
Special Issue in
JRFM
Innovative Approaches to Evaluating Credit Risk: Data, Models and Strategies
Guest Editors: Caterina Liberati, Lisa Crosato, David VeganzonesDeadline: 15 June 2024
Special Issue in
JRFM
Banking during the COVID-19 PandemiaGuest Editor: Pierluigi MurroDeadline: 30 June 2024