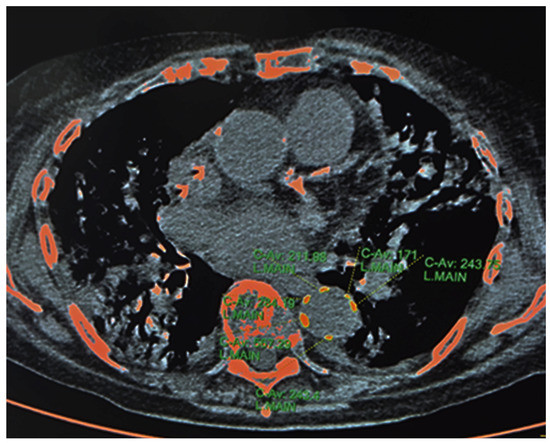
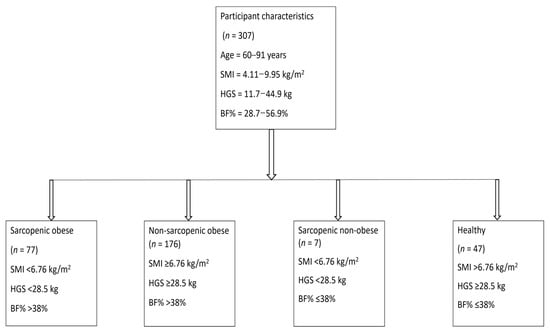
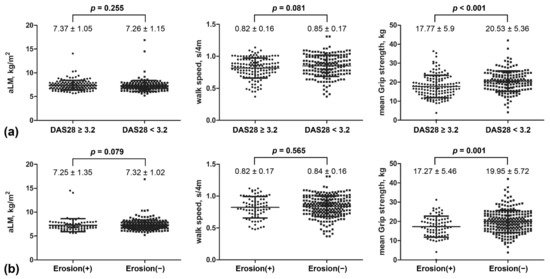
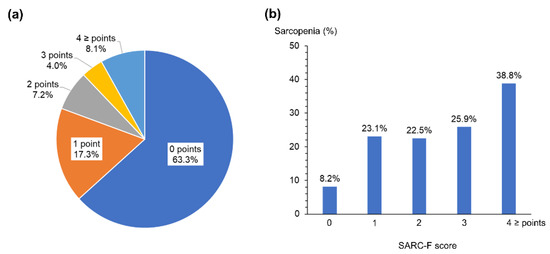
Sarcopenia: Skeletal Muscle Health and Ageing (Closed)
A topical collection in Journal of Clinical Medicine (ISSN 2077-0383). This collection belongs to the section "Epidemiology & Public Health".
Viewed by 74456Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Sarcopenia is a skeletal muscle disease identified by low muscle mass and characterised by weakness and impaired physical function. Muscle decline is progressive over the adult life course and may be accelerated in older age or aggravated by periods of disuse due to illness, injury, hospitalisation, sedentary living, malnutrition, and the presence of co-morbidities, eventually leading to sarcopenia. The socio-economic costs of sarcopenia will increase considerably as the global population of older adults rises at a greater rate than the other age groups. This highlights the pressing need to raise awareness of sarcopenia and the possible therapeutic strategies, and to understand the underlying disease processes. For this Topical Collection of “Sarcopenia: Skeletal Muscle Health and Ageing”, we are inviting relevant original research, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses covering the following:
- The incidence of sarcopenia in the general population and amongst specialist populations where disuse or deconditioning are major concerns
- The use of exercise, lifestyle, or pharmaceutical therapies to combat sarcopenia
- Application of new technologies to diagnose and manage sarcopenia
- The risk of adverse outcomes when sarcopenic individuals experience illness, serious injury, or surgery
- The distinction between sarcopenia, wasting, and cachexia
- Interventions that can be applied as pre-habilitation or at the bedside to prevent accelerated muscle wasting and improve recovery outcomes.
Prof. Jamie McPhee
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Clinical Medicine is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- skeletal muscle
- sarcopenia
- wasting
- frailty
- exercise