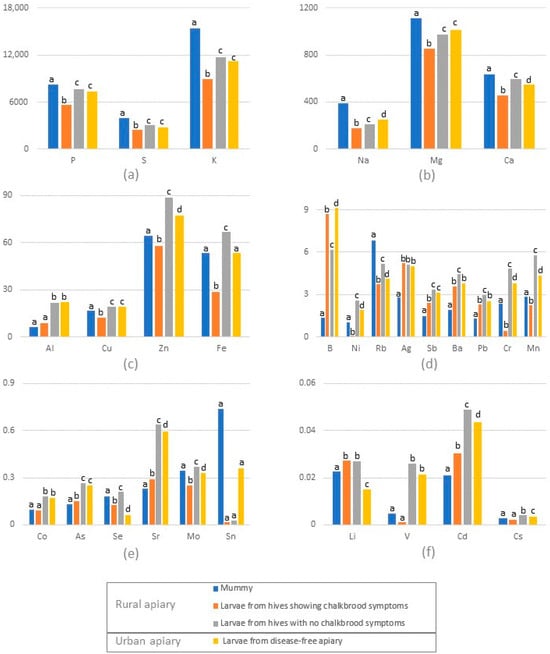
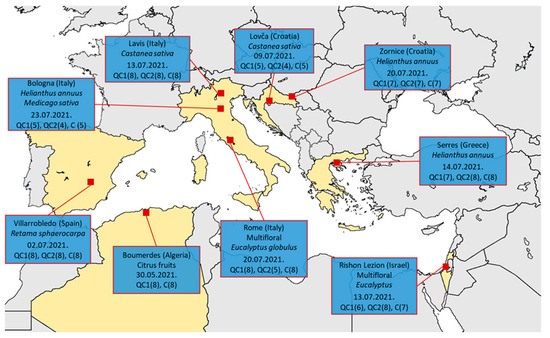
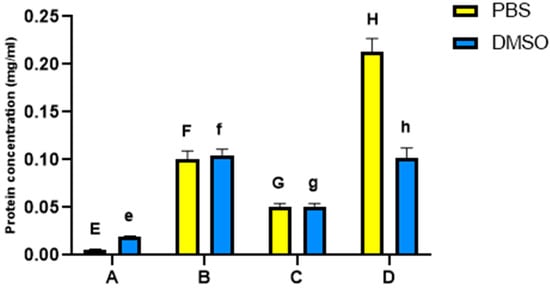
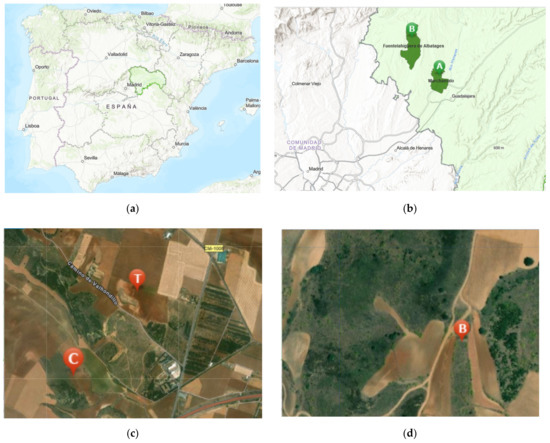
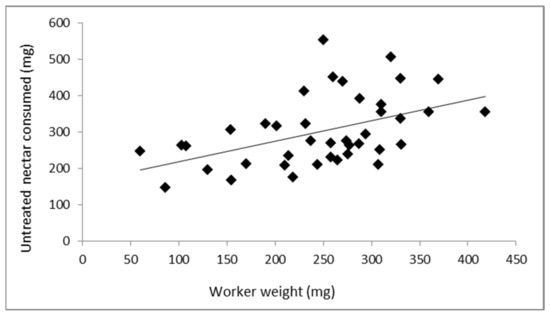
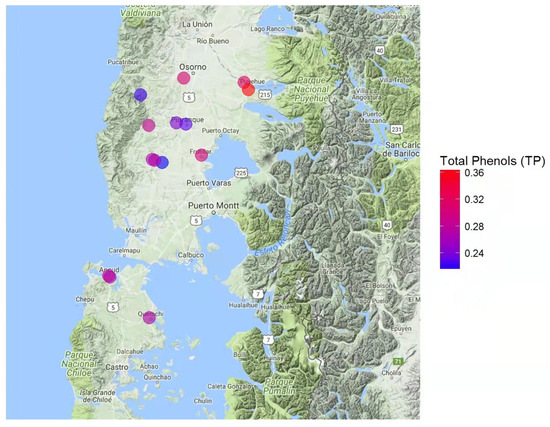
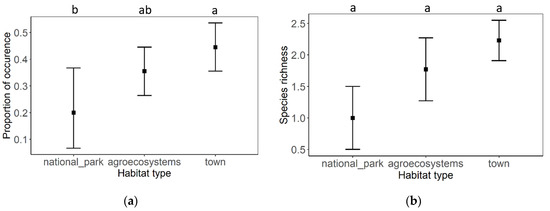
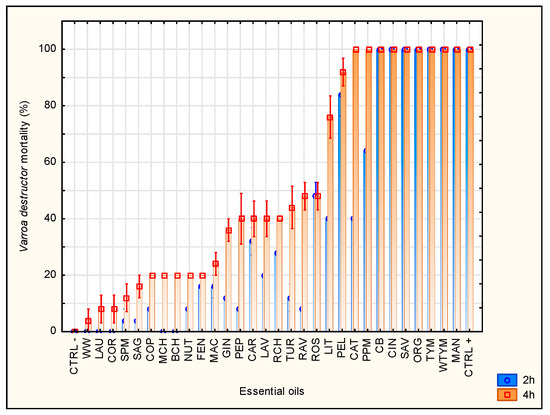
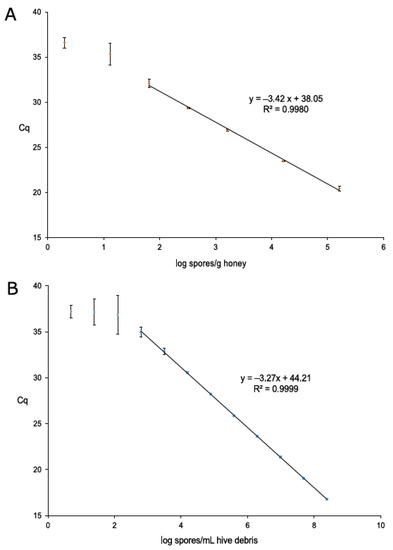
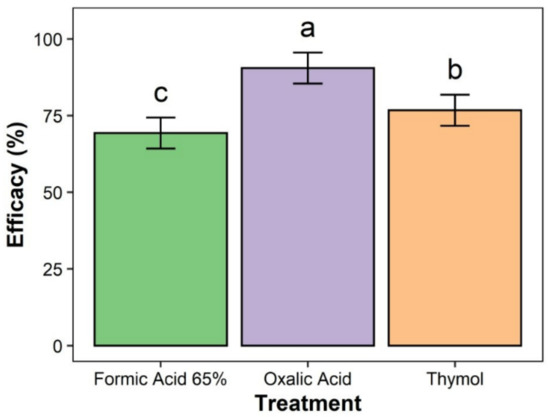
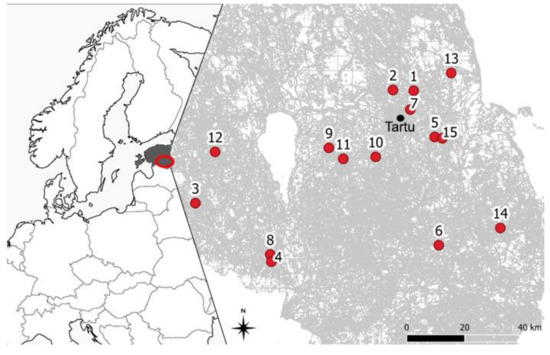
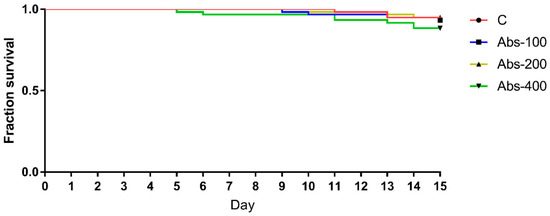
Impact of Environmental Factors and Management Practices on Bee Health
A topical collection in Insects (ISSN 2075-4450). This collection belongs to the section "Insect Societies and Sociality".
Viewed by 61182Editors
Interests: biology and pathology of honeybees; bumblebees; wild bees; disease diagnostic methods; one-health approach; Apis mellifera veterinary medicine; apian products; environment monitoring
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: animal pathology; animal experimentation and welfare; honey bee diseases; disease control; environmental monitoring; regulations
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection deals with different stressors of global importance which are reducing the number of honeybee and bumblebee colonies as well as Osmia spp. solitary bees. Many factors, such as the presence of pathogens, pests, predators, invasive species, nest destructors, negative environmental drivers, agricultural intensification, habitat loss, and managing practices, are reported as the main causes of bee depopulation and losses in rearing operations and apiaries. We would like to publish articles focusing on the impact of environmental factors and management practices on bee health. Therefore, we are searching for papers focusing on the novel epidemiology studies, diagnostic tools and technologies, monitoring programs, managing practices, biosecurity–control–eradication measures, and disinfection methods as well as development of new bee disease control strategies.
Prof. Dr. Ivana Tlak Gajger
Dr. Franco Mutinelli
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Insects is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- honeybees
- bumblebees
- Osmia spp. solitary bees
- diseases
- pathogens
- pests
- predators
- nest destructors
- environmental factors
- managing practices
- biosecurity–control–eradication measures
- disinfection methods