Journal Description
Information
Information
is a scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal of information science and technology, data, knowledge, and communication, and is published monthly online by MDPI. The International Society for Information Studies (IS4SI) is affiliated with Information and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Information Systems)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.1 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
A Critical Analysis of Deep Semi-Supervised Learning Approaches for Enhanced Medical Image Classification
Information 2024, 15(5), 246; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15050246 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Deep semi-supervised learning (DSSL) is a machine learning paradigm that blends supervised and unsupervised learning techniques to improve the performance of various models in computer vision tasks. Medical image classification plays a crucial role in disease diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care. However,
[...] Read more.
Deep semi-supervised learning (DSSL) is a machine learning paradigm that blends supervised and unsupervised learning techniques to improve the performance of various models in computer vision tasks. Medical image classification plays a crucial role in disease diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care. However, obtaining labeled medical image data is often expensive and time-consuming for medical practitioners, leading to limited labeled datasets. DSSL techniques aim to address this challenge, particularly in various medical image tasks, to improve model generalization and performance. DSSL models leverage both the labeled information, which provides explicit supervision, and the unlabeled data, which can provide additional information about the underlying data distribution. That offers a practical solution to resource-intensive demands of data annotation, and enhances the model’s ability to generalize across diverse and previously unseen data landscapes. The present study provides a critical review of various DSSL approaches and their effectiveness and challenges in enhancing medical image classification tasks. The study categorized DSSL techniques into six classes: consistency regularization method, deep adversarial method, pseudo-learning method, graph-based method, multi-label method, and hybrid method. Further, a comparative analysis of performance for six considered methods is conducted using existing studies. The referenced studies have employed metrics such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, AUC-ROC, and F1 score to evaluate the performance of DSSL methods on different medical image datasets. Additionally, challenges of the datasets, such as heterogeneity, limited labeled data, and model interpretability, were discussed and highlighted in the context of DSSL for medical image classification. The current review provides future directions and considerations to researchers to further address the challenges and take full advantage of these methods in clinical practices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Deep Learning for Image, Video and Signal Processing)
Open AccessArticle
Learning Circuits and Coding with Arduino Board in Higher Education Using Tangible and Graphical User Interfaces
by
Sokratis Tselegkaridis, Theodosios Sapounidis and Dimitrios Papakostas
Information 2024, 15(5), 245; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15050245 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The integration of the Arduino board into educational settings has penetrated across various educational levels. The teaching of this subject can be accomplished by (a) using real components in breadboards, (b) prefabricated modular boards that snap together, and (c) utilizing computer simulations. Yet,
[...] Read more.
The integration of the Arduino board into educational settings has penetrated across various educational levels. The teaching of this subject can be accomplished by (a) using real components in breadboards, (b) prefabricated modular boards that snap together, and (c) utilizing computer simulations. Yet, it is unknown which interface offers a more effective learning experience. Therefore, this experimental study aims to compare the effectiveness of these interfaces in a series of three laboratory exercises involving 110 university students, who were divided into three groups: (a) the first group used a tangible user interface, implementing circuits on breadboards, (b) the second group also used a tangible interface but with modular boards, and (c) the third group used a graphical user interface to simulate circuits using Tinkercad. For each laboratory exercise, students completed both pretests and posttests. Also, they provided feedback through five Likert-type attitude questions regarding their experiences. In terms of data analysis, t-tests, ANOVA, and ANCOVA, along with bootstrapping, and principal component analysis were employed. The results suggest that among the participants, those who used a graphical user interface stated that their understanding of the interconnection of components in microcontroller circuits was enhanced, while students with previous experience in microcontroller labs found the circuit creation process easier than students without experience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human–Computer Interaction in Smart Cities)
►▼
Show Figures
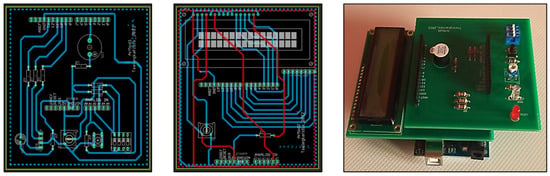
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Immersive Storytelling in Social Virtual Reality for Human-Centered Learning about Sensitive Historical Events
by
Athina Papadopoulou, Stylianos Mystakidis and Avgoustos Tsinakos
Information 2024, 15(5), 244; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15050244 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
History is a subject that students often find uninspiring in school education. This paper explores the application of social VR metaverse platforms in combination with interactive, nonlinear web platforms designed for immersive storytelling to support learning about a sensitive historical event, namely the
[...] Read more.
History is a subject that students often find uninspiring in school education. This paper explores the application of social VR metaverse platforms in combination with interactive, nonlinear web platforms designed for immersive storytelling to support learning about a sensitive historical event, namely the Asia Minor Catastrophe. The goal was to design an alternative method of learning history and investigate if it would engage students and foster their independence. A mixed-methods research design was applied. Thirty-four (n = 34) adult participants engaged in the interactive book and VR space over the course of three weeks. After an online workshop, feedback was collected from participants through a custom questionnaire. The quantitative data from the questionnaire were analyzed statistically utilizing IBM SPSS, while the qualitative responses were coded thematically. This study reveals that these two tools can enhance historical education by increasing student engagement, interaction, and understanding. Participants appreciated the immersive and participatory nature of the material. This study concludes that these technologies have the potential to enhance history education by promoting active participation and engagement.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Education, Training and Game Design with Immersive Technologies and Spatial Computing)
Open AccessArticle
Improving the Classification of Unexposed Potsherd Cavities by Means of Preprocessing
by
Randy Cahya Wihandika, Yoonji Lee, Mahendra Data, Masayoshi Aritsugi, Hiroki Obata and Israel Mendonça
Information 2024, 15(5), 243; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15050243 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The preparation of raw images for subsequent analysis, known as image preprocessing, is a crucial step that can boost the performance of an image classification model. Although deep learning has succeeded in image classification without handcrafted features, certain studies underscore the continued significance
[...] Read more.
The preparation of raw images for subsequent analysis, known as image preprocessing, is a crucial step that can boost the performance of an image classification model. Although deep learning has succeeded in image classification without handcrafted features, certain studies underscore the continued significance of image preprocessing for enhanced performance during the training process. Nonetheless, this task is often demanding and requires high-quality images to effectively train a classification model. The quality of training images, along with other factors, impacts the classification model’s performance and insufficient image quality can lead to suboptimal classification performance. On the other hand, achieving high-quality training images requires effective image preprocessing techniques. In this study, we perform exploratory experiments aimed at improving a classification model of unexposed potsherd cavities images via image preprocessing pipelines. These pipelines are evaluated on two distinct image sets: a laboratory-made, experimental image set that contains archaeological images with controlled lighting and background conditions, and a Jōmon–Yayoi image set that contains images of real-world potteries from the Jōmon period through the Yayoi period with varying conditions. The best accuracy performances obtained on the experimental images and the more challenging Jōmon–Yayoi images are 90.48% and 78.13%, respectively. The comprehensive analysis and experimentation conducted in this study demonstrate a noteworthy enhancement in performance metrics compared to the established baseline benchmark.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Deep Learning in Bioinformatics and Image Processing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sports Analytics: Data Mining to Uncover NBA Player Position, Age, and Injury Impact on Performance and Economics
by
Vangelis Sarlis and Christos Tjortjis
Information 2024, 15(4), 242; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040242 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
In the intersecting fields of data mining (DM) and sports analytics, the impact of socioeconomic, demographic, and injury-related factors on sports performance and economics has been extensively explored. A novel methodology is proposed and evaluated in this study, aiming to identify essential attributes
[...] Read more.
In the intersecting fields of data mining (DM) and sports analytics, the impact of socioeconomic, demographic, and injury-related factors on sports performance and economics has been extensively explored. A novel methodology is proposed and evaluated in this study, aiming to identify essential attributes and metrics that influence the salaries and performance of NBA players. Feature selection techniques are utilized for estimating the financial impacts of injuries, while clustering algorithms are applied to analyse the relationship between player age, position, and advanced performance metrics. Through the application of PCA-driven pattern recognition and exploratory-based categorization, a detailed examination of the effects on earnings and performance is conducted. Findings indicate that peak performance is typically achieved between the ages of 27 and 29, whereas the highest salaries are received between the ages of 29 and 34. Additionally, musculoskeletal injuries are identified as the source of half of the financial costs related to health problems in the NBA. The association between demographics and financial analytics, particularly focusing on the position and age of NBA players, is also investigated, offering new insights into the economic implications of player attributes and health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Information Communication Technologies in the Digital Era)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Automated Trace Clustering Pipeline Synthesis in Process Mining
by
Iuliana Malina Grigore, Gabriel Marques Tavares, Matheus Camilo da Silva, Paolo Ceravolo and Sylvio Barbon Junior
Information 2024, 15(4), 241; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040241 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
Business processes have undergone a significant transformation with the advent of the process-oriented view in organizations. The increasing complexity of business processes and the abundance of event data have driven the development and widespread adoption of process mining techniques. However, the size and
[...] Read more.
Business processes have undergone a significant transformation with the advent of the process-oriented view in organizations. The increasing complexity of business processes and the abundance of event data have driven the development and widespread adoption of process mining techniques. However, the size and noise of event logs pose challenges that require careful analysis. The inclusion of different sets of behaviors within the same business process further complicates data representation, highlighting the continued need for innovative solutions in the evolving field of process mining. Trace clustering is emerging as a solution to improve the interpretation of underlying business processes. Trace clustering offers benefits such as mitigating the impact of outliers, providing valuable insights, reducing data dimensionality, and serving as a preprocessing step in robust pipelines. However, designing an appropriate clustering pipeline can be challenging for non-experts due to the complexity of the process and the number of steps involved. For experts, it can be time-consuming and costly, requiring careful consideration of trade-offs. To address the challenge of pipeline creation, the paper proposes a genetic programming solution for trace clustering pipeline synthesis that optimizes a multi-objective function matching clustering and process quality metrics. The solution is applied to real event logs, and the results demonstrate improved performance in downstream tasks through the identification of sub-logs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Machine Learning and Intelligent Information Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
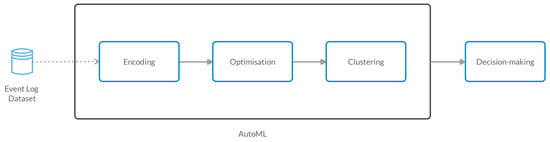
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets for Spatial and Temporal Data Intervals
by
Frederick Petry
Information 2024, 15(4), 240; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040240 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
Spatial and temporal uncertainties are found in data for many critical applications. This paper describes the use of interval-based representations of some spatial and temporal information. Uncertainties in the information can arise from multiple sources in which degrees of support and non-support occur
[...] Read more.
Spatial and temporal uncertainties are found in data for many critical applications. This paper describes the use of interval-based representations of some spatial and temporal information. Uncertainties in the information can arise from multiple sources in which degrees of support and non-support occur in evaluations. This motivates the use of intuitionistic fuzzy sets to permit the use of the positive and negative memberships to capture these uncertainties. The interval representations will include both simple and complex or nested intervals. The relationships between intervals such as overlapping, containing, etc. are then developed for both the simple and complex intervals. Such relationships are required to support the aggregation approaches of the interval information. Both averaging and merging approaches to interval aggregation are then developed. Furthermore, potential techniques for the associated aggregation of the interval intuitionistic fuzzy memberships are provided. A motivating example of maritime depth data required for safe navigation is used to illustrate the approach. Finally, some potential future developments are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trend on Fuzzy Systems and Intelligent Decision Making Theory: A Themed Issue Dedicated to Dr. Ronald R. Yager)
►▼
Show Figures
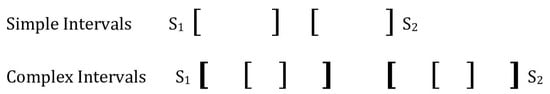
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Deep Learning-Based Road Pavement Inspection by Integrating Visual Information and IMU
by
Chen-Chiung Hsieh, Han-Wen Jia, Wei-Hsin Huang and Mei-Hua Hsih
Information 2024, 15(4), 239; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040239 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study proposes a deep learning method for pavement defect detection, focusing on identifying potholes and cracks. A dataset comprising 10,828 images is collected, with 8662 allocated for training, 1083 for validation, and 1083 for testing. Vehicle attitude data are categorized based on
[...] Read more.
This study proposes a deep learning method for pavement defect detection, focusing on identifying potholes and cracks. A dataset comprising 10,828 images is collected, with 8662 allocated for training, 1083 for validation, and 1083 for testing. Vehicle attitude data are categorized based on three-axis acceleration and attitude change, with 6656 (64%) for training, 1664 (16%) for validation, and 2080 (20%) for testing. The Nvidia Jetson Nano serves as the vehicle-embedded system, transmitting IMU-acquired vehicle data and GoPro-captured images over a 5G network to the server. The server recognizes two damage categories, low-risk and high-risk, storing results in MongoDB. Severe damage triggers immediate alerts to maintenance personnel, while less severe issues are recorded for scheduled maintenance. The method selects YOLOv7 among various object detection models for pavement defect detection, achieving a mAP of 93.3%, a recall rate of 87.8%, a precision of 93.2%, and a processing speed of 30–40 FPS. Bi-LSTM is then chosen for vehicle vibration data processing, yielding 77% mAP, 94.9% recall rate, and 89.8% precision. Integration of the visual and vibration results, along with vehicle speed and travel distance, results in a final recall rate of 90.2% and precision of 83.7% after field testing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Deep Learning for Image, Video and Signal Processing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Constructing Semantic Summaries Using Embeddings
by
Georgia Eirini Trouli, Nikos Papadakis and Haridimos Kondylakis
Information 2024, 15(4), 238; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040238 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
The increase in the size and complexity of large knowledge graphs now available online has resulted in the emergence of many approaches focusing on enabling the quick exploration of the content of those data sources. Structural non-quotient semantic summaries have been proposed in
[...] Read more.
The increase in the size and complexity of large knowledge graphs now available online has resulted in the emergence of many approaches focusing on enabling the quick exploration of the content of those data sources. Structural non-quotient semantic summaries have been proposed in this direction that involve first selecting the most important nodes and then linking them, trying to extract the most useful subgraph out of the original graph. However, the current state of the art systems use costly centrality measures for identifying the most important nodes, whereas even costlier procedures have been devised for linking the selected nodes. In this paper, we address both those deficiencies by first exploiting embeddings for node selection, and then by meticulously selecting approximate algorithms for node linking. Experiments performed over two real-world big KGs demonstrate that the summaries constructed using our method enjoy better quality. Specifically, the coverage scores obtained were 0.8, 0.81, and 0.81 for DBpedia v3.9 and 0.94 for Wikidata dump 2018, across 20%, 25%, and 30% summary sizes, respectively. Additionally, our method can compute orders of magnitude faster than the state of the art.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Information in 2024–2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Scalable and Automated Framework for Tracking the Likely Adoption of Emerging Technologies
by
Lowri Williams, Eirini Anthi and Pete Burnap
Information 2024, 15(4), 237; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040237 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
While new technologies are expected to revolutionise and become game-changers in improving the efficiency and practices of our daily lives, it is also critical to investigate and understand the barriers and opportunities faced by their adopters. Such findings can serve as an additional
[...] Read more.
While new technologies are expected to revolutionise and become game-changers in improving the efficiency and practices of our daily lives, it is also critical to investigate and understand the barriers and opportunities faced by their adopters. Such findings can serve as an additional feature in the decisionmaking process when analysing the risks, costs, and benefits of adopting an emerging technology in a particular setting. Although several studies have attempted to perform such investigations, these approaches adopt a qualitative data collection methodology, which is limited in terms of the size of the targeted participant group and is associated with a significant manual overhead when transcribing and inferring results. This paper presents a scalable and automated framework for tracking the likely adoption and/or rejection of new technologies from a large landscape of adopters. In particular, a large corpus of social media texts containing references to emerging technologies was compiled. Text mining techniques were applied to extract the sentiments expressed towards technology aspects. In the context of the problem definition herein, we hypothesise that the expression of positive sentiment implies an increase in the likelihood of impacting a technology user’s acceptance to adopt, integrate, and/or use the technology, and negative sentiment implies an increase in the likelihood of impacting the rejection of emerging technologies by adopters. To quantitatively test our hypothesis, a ground truth analysis was performed to validate that the sentiments captured by the text mining approach were comparable to the results provided by human annotators when asked to label whether such texts positively or negatively impact their outlook towards adopting an emerging technology. The collected annotations demonstrated comparable results to those of the text mining approach, illustrating that the automatically extracted sentiments expressed towards technologies are useful features in understanding the landscape faced by technology adopters, as well as serving as an important decisionmaking component when, for example, recognising shifts in user behaviours, new demands, and emerging uncertainties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Information Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
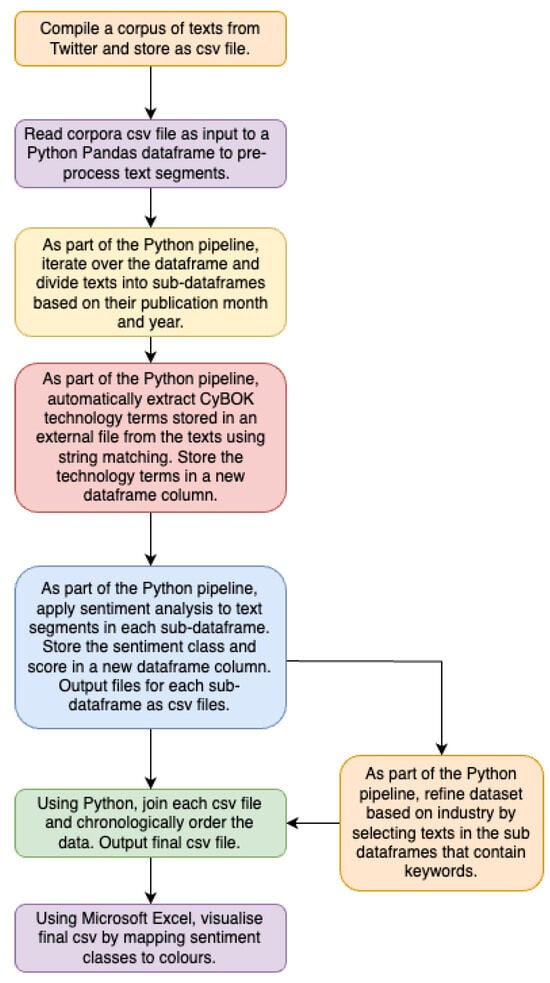
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation Approach to Assess Usefulness of Tourism Reviews by Considering Bias Identified in Sentiments and Articulacy
by
Dimitrios K. Kardaras, Christos Troussas, Stavroula G. Barbounaki, Panagiota Tselenti and Konstantinos Armyras
Information 2024, 15(4), 236; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040236 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Assessing the usefulness of reviews has been the aim of several research studies. However, results regarding the significance of usefulness determinants are often contradictory, thus decreasing the accuracy of reviews’ helpfulness estimation. Also, bias in user reviews attributed to differences, e.g., in gender,
[...] Read more.
Assessing the usefulness of reviews has been the aim of several research studies. However, results regarding the significance of usefulness determinants are often contradictory, thus decreasing the accuracy of reviews’ helpfulness estimation. Also, bias in user reviews attributed to differences, e.g., in gender, nationality, etc., may result in misleading judgments, thus diminishing reviews’ usefulness. Research is needed for sentiment analysis algorithms that incorporate bias embedded in reviews, thus improving their usefulness, readability, credibility, etc. This study utilizes fuzzy relations and fuzzy synthetic evaluation (FSE) in order to calculate reviews’ usefulness by incorporating users’ biases as expressed in terms of reviews’ articulacy and sentiment polarity. It selected and analyzed 95,678 hotel user reviews from Tripadvisor, written by users from five specific nationalities. The findings indicate that there are differences among nationalities in terms of the articulacy and sentiment of their reviews. The British are most consistent in their judgments expressed in titles and the main body of reviews. For the British and the Greeks, review titles suffice to convey any negative sentiments. The Dutch use fewer words in their reviews than the other nationalities. This study suggests that fuzzy logic captures subjectivity which is often found in reviews, and it can be used to quantify users’ behavioral differences, calculate reviews’ usefulness, and provide the means for developing more accurate voting systems.
Full article
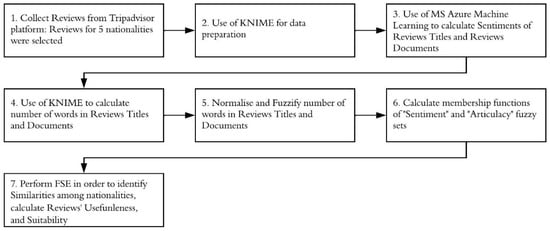
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Overview on the Advancements of Support Vector Machine Models in Healthcare Applications: A Review
by
Rosita Guido, Stefania Ferrisi, Danilo Lofaro and Domenico Conforti
Information 2024, 15(4), 235; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040235 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Support vector machines (SVMs) are well-known machine learning algorithms for classification and regression applications. In the healthcare domain, they have been used for a variety of tasks including diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of disease outcomes. This review is an extensive survey on the
[...] Read more.
Support vector machines (SVMs) are well-known machine learning algorithms for classification and regression applications. In the healthcare domain, they have been used for a variety of tasks including diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of disease outcomes. This review is an extensive survey on the current state-of-the-art of SVMs developed and applied in the medical field over the years. Many variants of SVM-based approaches have been developed to enhance their generalisation capabilities. We illustrate the most interesting SVM-based models that have been developed and applied in healthcare to improve performance metrics on benchmark datasets, including hybrid classification methods that combine, for instance, optimization algorithms with SVMs. We even report interesting results found in medical applications related to real-world data. Several issues around SVMs, such as selection of hyperparameters and learning from data of questionable quality, are discussed as well. The several variants developed and introduced over the years could be useful in designing new methods to improve performance in critical fields such as healthcare, where accuracy, specificity, and other metrics are crucial. Finally, current research trends and future directions are underlined.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning in Italy)
►▼
Show Figures
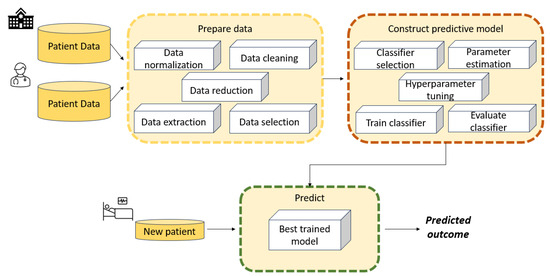
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploiting Properties of Student Networks to Enhance Learning in Distance Education
by
Rozita Tsoni, Evgenia Paxinou, Aris Gkoulalas-Divanis, Dimitrios Karapiperis, Dimitrios Kalles and Vassilios S. Verykios
Information 2024, 15(4), 234; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040234 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Distance Learning has become the “new normal”, especially during the pandemic and due to the technological advances that are incorporated into the teaching procedure. At the same time, the augmented use of the internet has blurred the borders between distance and conventional learning.
[...] Read more.
Distance Learning has become the “new normal”, especially during the pandemic and due to the technological advances that are incorporated into the teaching procedure. At the same time, the augmented use of the internet has blurred the borders between distance and conventional learning. Students interact mainly through LMSs, leaving their digital traces that can be leveraged to improve the educational process. New knowledge derived from the analysis of digital data could assist educational stakeholders in instructional design and decision making regarding the level and type of intervention that would benefit learners. This work aims to propose an analysis model that can capture the students’ behaviors in a distance learning course delivered fully online, based on the clickstream data associated with the discussion forum, and additionally to suggest interpretable patterns that will support education administrators and tutors in the decision-making process. To achieve our goal, we use Social Network Analysis as networks represent complex interactions in a meaningful and easily interpretable way. Moreover, simple or complex network metrics are becoming available to provide valuable insights into the students’ social interaction. This study concludes that by leveraging the imprint of these actions in an LMS and using metrics of Social Network Analysis, differences can be spotted in the communicational patterns that go beyond simple participation recording. Although HITS and PageRank algorithms were created with completely different targeting, it is shown that they can also reveal methodological features in students’ communicational approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Real-World Applications of Machine Learning Techniques)
►▼
Show Figures
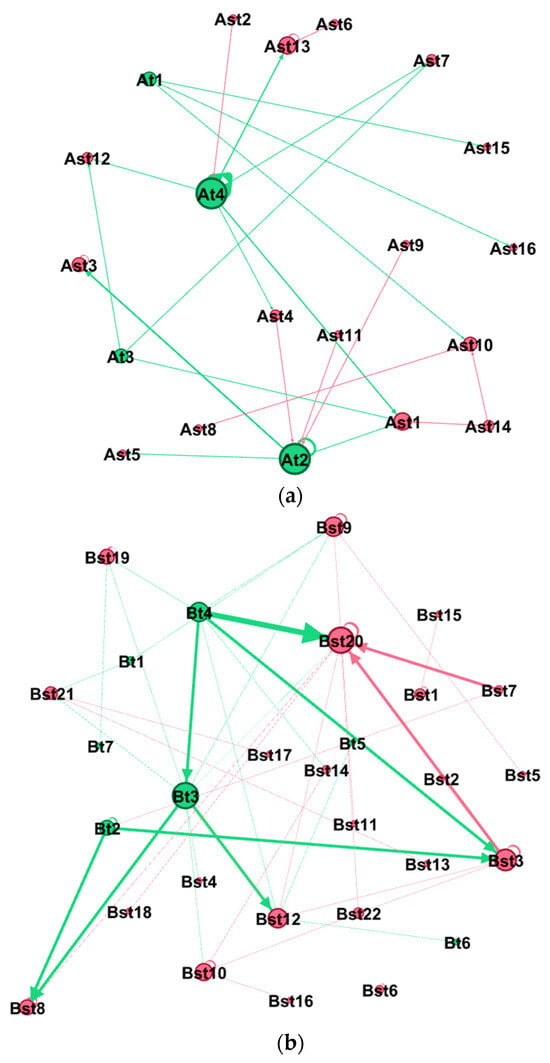
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Child Safety in Online Gaming: The Development and Application of Protectbot, an AI-Powered Chatbot Framework
by
Anum Faraz, Fardin Ahsan, Jinane Mounsef, Ioannis Karamitsos and Andreas Kanavos
Information 2024, 15(4), 233; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040233 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study introduces Protectbot, an innovative chatbot framework designed to improve safety in children’s online gaming environments. At its core, Protectbot incorporates DialoGPT, a conversational Artificial Intelligence (AI) model rooted in Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2 (GPT-2) technology, engineered to simulate human-like interactions within
[...] Read more.
This study introduces Protectbot, an innovative chatbot framework designed to improve safety in children’s online gaming environments. At its core, Protectbot incorporates DialoGPT, a conversational Artificial Intelligence (AI) model rooted in Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2 (GPT-2) technology, engineered to simulate human-like interactions within gaming chat rooms. The framework is distinguished by a robust text classification strategy, rigorously trained on the Publicly Available Natural 2012 (PAN12) dataset, aimed at identifying and mitigating potential sexual predatory behaviors through chat conversation analysis. By utilizing fastText for word embeddings to vectorize sentences, we have refined a support vector machine (SVM) classifier, achieving remarkable performance metrics, with recall, accuracy, and F-scores approaching 0.99. These metrics not only demonstrate the classifier’s effectiveness, but also signify a significant advancement beyond existing methodologies in this field. The efficacy of our framework is additionally validated on a custom dataset, composed of 71 predatory chat logs from the Perverted Justice website, further establishing the reliability and robustness of our classifier. Protectbot represents a crucial innovation in enhancing child safety within online gaming communities, providing a proactive, AI-enhanced solution to detect and address predatory threats promptly. Our findings highlight the immense potential of AI-driven interventions to create safer digital spaces for young users.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Do (AI) Chatbots Pose any Special Challenges for Trust and Privacy?)
►▼
Show Figures
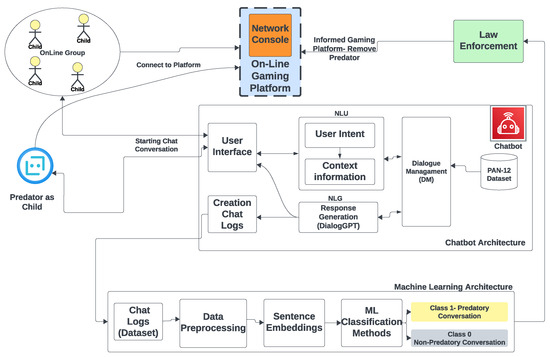
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cloud Broker: Customizing Services for Cloud Market Requirements
by
Evangelia Filiopoulou, Georgios Chatzithanasis, Christos Michalakelis and Mara Nikolaidou
Information 2024, 15(4), 232; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040232 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Cloud providers offer various purchasing options to enable users to tailor their costs according to their specific requirements, including on-demand, reserved instances, and spot instances. On-demand and spot instances satisfy short-term workloads, whereas reserved instances fulfill long-term instances. However, there are workloads that
[...] Read more.
Cloud providers offer various purchasing options to enable users to tailor their costs according to their specific requirements, including on-demand, reserved instances, and spot instances. On-demand and spot instances satisfy short-term workloads, whereas reserved instances fulfill long-term instances. However, there are workloads that fall outside of either long-term or short-term categories. Consequently, there is a notable absence of services specifically tailored for medium-term workloads. On-demand services, while offering flexibility, often come with high costs. Spot instances, though cost-effective, carry the risk of termination. Reserved instances, while stable and less expensive, may have a remaining period that extends beyond the duration of users’ tasks. This gap underscores the need for solutions that address the unique requirements and challenges associated with medium-term workloads in the cloud computing landscape. This paper introduces a new cloud broker that introduces IaaS services for medium-term workloads. On one hand, this broker strategically reserves resources from providers, and on the other hand, it interacts with users. Its interaction with users is twofold. It collects users’ preferences regarding commitment term for medium-term workloads and then transforms the leased resources based on commitment term, aligning with the requirements of most users. To ensure profitability, the broker sells these services utilizing an auction algorithm. Hence, in this paper, an auction algorithm is introduced and developed, which treats cloud services as virtual assets and integrates the depreciation over time. The findings affirm the lack of services that fulfill medium workloads while ensuring the financial viabilty and profitability of the broker, given that the estimated return on investment (ROI) is acceptable.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Technoeconomics of the Internet of Things)
►▼
Show Figures
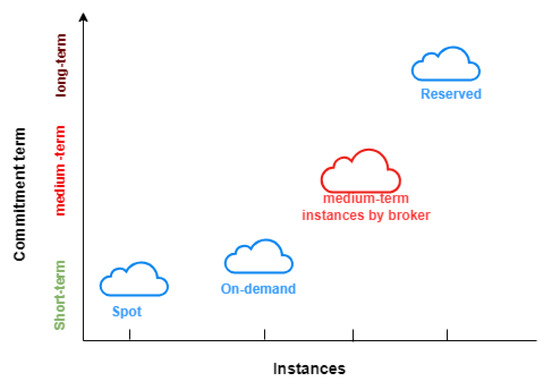
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Two-Stage Convolutional Neural Network for Classification of Movement Patterns in Tremor Patients
by
Patricia Weede, Piotr Dariusz Smietana, Gregor Kuhlenbäumer, Günther Deuschl and Gerhard Schmidt
Information 2024, 15(4), 231; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040231 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Accurate tremor classification is crucial for effective patient management and treatment. However, clinical diagnoses are often hindered by misdiagnoses, necessitating the development of robust technical methods. Here, we present a two-stage convolutional neural network (CNN)-based system for classifying physiological tremor, essential tremor (ET),
[...] Read more.
Accurate tremor classification is crucial for effective patient management and treatment. However, clinical diagnoses are often hindered by misdiagnoses, necessitating the development of robust technical methods. Here, we present a two-stage convolutional neural network (CNN)-based system for classifying physiological tremor, essential tremor (ET), and Parkinson’s disease (PD) tremor. Employing acceleration signals from the hands of 408 patients, our system utilizes both medically motivated signal features and (nearly) raw data (by means of spectrograms) as system inputs. Our model employs a hybrid approach of data-based and feature-based methods to leverage the strengths of both while mitigating their weaknesses. By incorporating various data augmentation techniques for model training, we achieved an overall accuracy of 88.12%. This promising approach demonstrates improved accuracy in discriminating between the three tremor types, paving the way for more precise tremor diagnosis and enhanced patient care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Signal Processing and Machine Learning II)
►▼
Show Figures
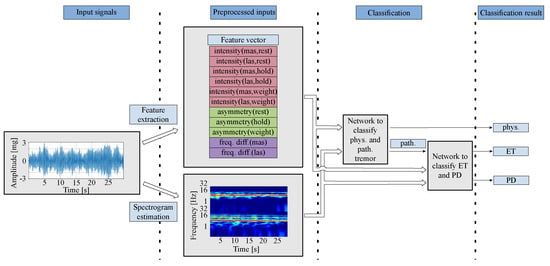
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Dynamic Contextual Feature Fusion Model for Small Object Detection in Satellite Remote-Sensing Images
by
Hongbo Yang and Shi Qiu
Information 2024, 15(4), 230; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040230 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Ground objects in satellite images pose unique challenges due to their low resolution, small pixel size, lack of texture features, and dense distribution. Detecting small objects in satellite remote-sensing images is a difficult task. We propose a new detector focusing on contextual information
[...] Read more.
Ground objects in satellite images pose unique challenges due to their low resolution, small pixel size, lack of texture features, and dense distribution. Detecting small objects in satellite remote-sensing images is a difficult task. We propose a new detector focusing on contextual information and multi-scale feature fusion. Inspired by the notion that surrounding context information can aid in identifying small objects, we propose a lightweight context convolution block based on dilated convolutions and integrate it into the convolutional neural network (CNN). We integrate dynamic convolution blocks during the feature fusion step to enhance the high-level feature upsampling. An attention mechanism is employed to focus on the salient features of objects. We have conducted a series of experiments to validate the effectiveness of our proposed model. Notably, the proposed model achieved a 3.5% mean average precision (mAP) improvement on the satellite object detection dataset. Another feature of our approach is lightweight design. We employ group convolution to reduce the computational cost in the proposed contextual convolution module. Compared to the baseline model, our method reduces the number of parameters by 30%, computational cost by 34%, and an FPS rate close to the baseline model. We also validate the detection results through a series of visualizations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Research in Target Detection and Recognition in Remote Sensing Images)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A User Study on Modeling IoT-Aware Processes with BPMN 2.0
by
Yusuf Kirikkayis, Michael Winter and Manfred Reichert
Information 2024, 15(4), 229; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040229 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) into business process management (BPM) aims to increase the automation level, efficiency, transparency, and comprehensibility of the business processes taking place in the physical world. The IoT enables the seamless networking of physical devices, allowing for the
[...] Read more.
Integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) into business process management (BPM) aims to increase the automation level, efficiency, transparency, and comprehensibility of the business processes taking place in the physical world. The IoT enables the seamless networking of physical devices, allowing for the enrichment of processes with real-time data about the physical world and, thus, for optimized process automation and monitoring. To realize these benefits, the modeling of IoT-aware processes needs to be appropriately supported. Despite the great attention paid to this topic, more clarity is needed about the current state of the art of corresponding modeling solutions. Capturing IoT characteristics in business process models visually or based on labels is essential to ensure effective design and communication of IoT-aware business processes. A clear discernibility of IoT characteristics can enable the precise modeling and analysis of IoT-aware processes and facilitate collaboration among different stakeholders. With an increasing number of process model elements, it becomes crucial that process model readers can understand the IoT aspects of business processes in order to make informed decisions and to optimize the processes with respect to IoT integration. This paper presents the results of a large user study (N = 249) that explored the perception of IoT aspects in BPMN 2.0 process models to gain insights into the IoT’s involvement in business processes that drive the successful implementation and communication of IoT-aware processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in IoT and Cyber/Physical System)
►▼
Show Figures
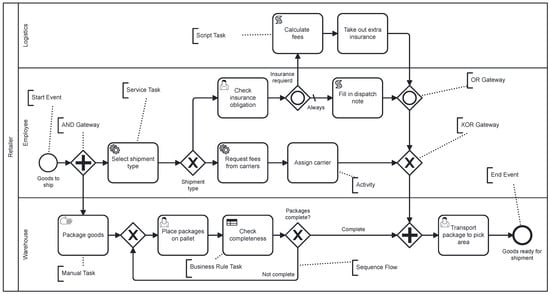
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ensemble Modeling with a Bayesian Maximal Information Coefficient-Based Model of Bayesian Predictions on Uncertainty Data
by
Tisinee Surapunt and Shuliang Wang
Information 2024, 15(4), 228; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040228 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Uncertainty presents unfamiliar circumstances or incomplete information that may be difficult to handle with a single model of a traditional machine learning algorithm. They are possibly limited by inadequate data, an ambiguous model, and learning performance to make a prediction. Therefore, ensemble modeling
[...] Read more.
Uncertainty presents unfamiliar circumstances or incomplete information that may be difficult to handle with a single model of a traditional machine learning algorithm. They are possibly limited by inadequate data, an ambiguous model, and learning performance to make a prediction. Therefore, ensemble modeling is proposed as a powerful model for enhancing predictive capabilities and robustness. This study aims to apply Bayesian prediction to ensemble modeling because it can encode conditional dependencies between variables and present the reasoning model using the BMIC model. The BMIC has clarified knowledge in the model which is ready for learning. Then, it was selected as the base model to be integrated with well-known algorithms such as logistic regression, K-nearest neighbors, decision trees, random forests, support vector machines (SVMs), neural networks, naive Bayes, and XGBoost classifiers. Also, the Bayesian neural network (BNN) and the probabilistic Bayesian neural network (PBN) were considered to compare their performance as a single model. The findings of this study indicate that the ensemble model of the BMIC with some traditional algorithms, which are SVM, random forest, neural networks, and XGBoost classifiers, returns 96.3% model accuracy in prediction. It provides a more reliable model and a versatile approach to support decision-making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trend on Fuzzy Systems and Intelligent Decision Making Theory: A Themed Issue Dedicated to Dr. Ronald R. Yager)
►▼
Show Figures
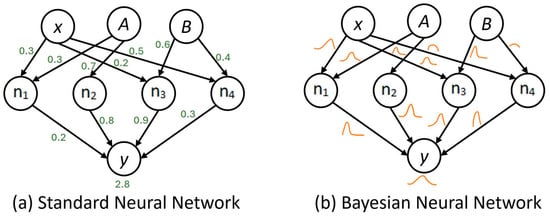
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Optimized Deep Learning Approach for Detecting Fraudulent Transactions
by
Said El Kafhali, Mohammed Tayebi and Hamza Sulimani
Information 2024, 15(4), 227; https://doi.org/10.3390/info15040227 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The proliferation of new technologies and advancements in existing ones are altering our perspective of the world. So, continuous improvements are needed. A connected world filled with a vast amount of data was created as a result of the integration of these advanced
[...] Read more.
The proliferation of new technologies and advancements in existing ones are altering our perspective of the world. So, continuous improvements are needed. A connected world filled with a vast amount of data was created as a result of the integration of these advanced technologies in the financial sector. The advantages of this connection came at the cost of more sophisticated and advanced attacks, such as fraudulent transactions. To address these illegal transactions, researchers and engineers have created and implemented various systems and models to detect fraudulent transactions; many of them produce better results than others. On the other hand, criminals change their strategies and technologies to imitate legitimate transactions. In this article, the objective is to propose an intelligent system for detecting fraudulent transactions using various deep learning architectures, including artificial neural networks (ANNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and long short-term memory (LSTM). Furthermore, the Bayesian optimization algorithm is used for hyperparameter optimization. For the evaluation, a credit card fraudulent transaction dataset was used. Based on the many experiments conducted, the RNN architecture demonstrated better efficiency and yielded better results in a shorter computational time than the ANN LSTM architectures.
Full article
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Information Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
AI, Algorithms, BDCC, Future Internet, Informatics, Information, Languages, Publications
AI Chatbots: Threat or Opportunity?
Topic Editors: Antony Bryant, Roberto Montemanni, Min Chen, Paolo Bellavista, Kenji Suzuki, Jeanine Treffers-DallerDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Drones, Information, Sensors
Recent Advances and Technologies in Emergency Response, Security and Disaster Management Applications
Topic Editors: Evangelos Maltezos, Eleftherios Ouzounoglou, Panagiotis Michalis, Angelos Amditis, Stefanos Vrochidis, Norman Kerle, Christos NtanosDeadline: 20 May 2024
Topic in
Algorithms, Diagnostics, Entropy, Information, J. Imaging
Application of Machine Learning in Molecular Imaging
Topic Editors: Allegra Conti, Nicola Toschi, Marianna Inglese, Andrea Duggento, Matthew Grech-Sollars, Serena Monti, Giancarlo Sportelli, Pietro CarraDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Drones, Electronics, Future Internet, Information, Mathematics
Future Internet Architecture: Difficulties and Opportunities
Topic Editors: Peiying Zhang, Haotong Cao, Keping YuDeadline: 30 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Information
New Trend on Fuzzy Systems and Intelligent Decision Making Theory: A Themed Issue Dedicated to Dr. Ronald R. Yager
Guest Editors: Luis Martínez López, Lesheng Jin, Zhen-Song Chen, Humberto BustinceDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Information
AI Applications in Construction and Infrastructure
Guest Editor: Sudipta ChowdhuryDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Information
Health Data Information Retrieval
Guest Editors: Mario Ciampi, Mario SicuranzaDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Information
Text Mining: Challenges, Algorithms, Tools and Applications
Guest Editor: Fei LiuDeadline: 15 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Information
Natural Language Processing and Applications: Challenges and Perspectives
Collection Editor: Diego Reforgiato Recupero
Topical Collection in
Information
Knowledge Graphs for Search and Recommendation
Collection Editors: Pierpaolo Basile, Annalina Caputo
Topical Collection in
Information
Augmented Reality Technologies, Systems and Applications
Collection Editors: Ramon Fabregat, Jorge Bacca-Acosta, N.D. Duque-Mendez





