Journal Description
Informatics
Informatics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on information and communication technologies, human–computer interaction, and social informatics, and is published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Communication)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 30.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.1 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2022)
Latest Articles
Optimization of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Management: Novel Decision Support via Unsupervised Machine Learning
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020022 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
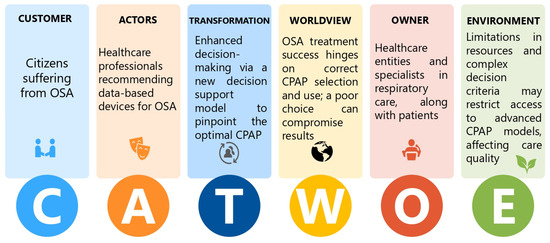
This study addresses Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), which impacts around 936 million adults globally. The research introduces a novel decision support method named Communalities on Ranking and Objective Weights Method (CROWM), which employs principal component analysis (PCA), unsupervised Machine Learning techniques, and Multicriteria
[...] Read more.
This study addresses Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), which impacts around 936 million adults globally. The research introduces a novel decision support method named Communalities on Ranking and Objective Weights Method (CROWM), which employs principal component analysis (PCA), unsupervised Machine Learning techniques, and Multicriteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) to calculate performance criteria weights of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP—key in managing OSA) and to evaluate these devices. Uniquely, the CROWM incorporates non-beneficial criteria in PCA and employs communalities to accurately represent the performance evaluation of alternatives within each resulting principal factor, allowing for a more accurate and robust analysis of alternatives and variables. This article aims to employ CROWM to evaluate CPAP for effectiveness in combating OSA, considering six performance criteria: resources, warranty, noise, weight, cost, and maintenance. Validated by established tests and sensitivity analysis against traditional methods, CROWM proves its consistency, efficiency, and superiority in decision-making support. This method is poised to influence assertive decision-making significantly, aiding healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients in selecting optimal CPAP solutions, thereby advancing patient care in an interdisciplinary research context.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Decision Science Applications and Models (DSAM))
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Digital Transformation in Omani Higher Education: Assessing Student Adoption of Video Communication during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Fatima Amer jid Almahri, Islam Elbayoumi Salem, Ahmed Mohamed Elbaz, Hassan Aideed and Zameer Gulzar
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020021 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has influenced many fields, such as communication, commerce, and education, and pushed business entities to adopt innovative technologies to continue their business operations. Students need to do the same, so it is essential to understand their acceptance of these technologies
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has influenced many fields, such as communication, commerce, and education, and pushed business entities to adopt innovative technologies to continue their business operations. Students need to do the same, so it is essential to understand their acceptance of these technologies to make them more usable for students. This paper employs the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 (UTAUT2) to identify the factors that influenced students’ acceptance and use of different online communication services as the primary tool for learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Six factors of UTAUT2 were used to measure the acceptance and use of video communication services at the Business College of the University of Technology and Applied Sciences. Two hundred students completed our online survey. The results demonstrated that social influence, facilitating conditions, hedonic motivation, and habit affect behavioral intention positively, while performance expectancy and effort expectancy have no effect on behavioral intention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human-Computer Interaction)
►▼
Show Figures
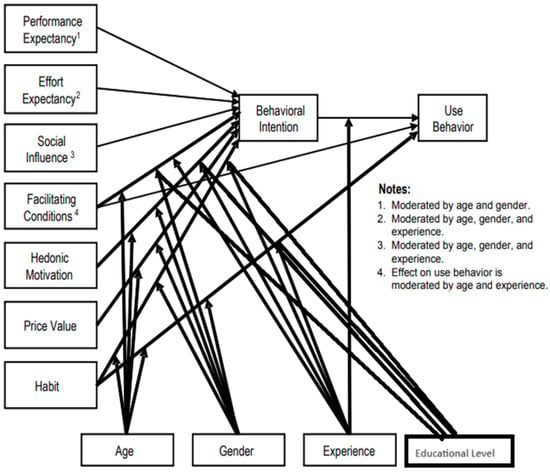
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Artificial Intelligence Chatbots in Chemical Information Seeking: Narrative Educational Insights via a SWOT Analysis
by
Johannes Pernaa, Topias Ikävalko, Aleksi Takala, Emmi Vuorio, Reija Pesonen and Outi Haatainen
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020020 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots are next-word predictors built on large language models (LLMs). There is great interest within the educational field for this new technology because AI chatbots can be used to generate information. In this theoretical article, we provide educational insights into
[...] Read more.
Artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots are next-word predictors built on large language models (LLMs). There is great interest within the educational field for this new technology because AI chatbots can be used to generate information. In this theoretical article, we provide educational insights into the possibilities and challenges of using AI chatbots. These insights were produced by designing chemical information-seeking activities for chemistry teacher education which were analyzed via the SWOT approach. The analysis revealed several internal and external possibilities and challenges. The key insight is that AI chatbots will change the way learners interact with information. For example, they enable the building of personal learning environments with ubiquitous access to information and AI tutors. Their ability to support chemistry learning is impressive. However, the processing of chemical information reveals the limitations of current AI chatbots not being able to process multimodal chemical information. There are also ethical issues to address. Despite the benefits, wider educational adoption will take time. The diffusion can be supported by integrating LLMs into curricula, relying on open-source solutions, and training teachers with modern information literacy skills. This research presents theory-grounded examples of how to support the development of modern information literacy skills in the context of chemistry teacher education.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic AI Chatbots: Threat or Opportunity?)
Open AccessArticle
A Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) Approach to Improve Marketing Success
by
Ivo Pereira, Ana Madureira, Nuno Bettencourt, Duarte Coelho, Miguel Ângelo Rebelo, Carolina Araújo and Daniel Alves de Oliveira
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020019 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
The exponential growth of data in the digital age has led to a significant demand for innovative approaches to assess data in a manner that is both effective and efficient. Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) is a category of services that offers
[...] Read more.
The exponential growth of data in the digital age has led to a significant demand for innovative approaches to assess data in a manner that is both effective and efficient. Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) is a category of services that offers considerable potential for organisations to extract valuable insights from their data while reducing the requirement for heavy technical expertise. This article explores the use of MLaaS within the realm of marketing applications. In this study, we provide a comprehensive analysis of MLaaS implementations and their benefits within the domain of marketing. Furthermore, we present a platform that possesses the capability to be customised and expanded to address marketing’s unique requirements. Three modules are introduced: Churn Prediction, One-2-One Product Recommendation, and Send Frequency Prediction. When applied to marketing, the proposed MLaaS system exhibits considerable promise for use in applications such as automated detection of client churn prior to its occurrence, individualised product recommendations, and send time optimisation. Our study revealed that AI-driven campaigns can improve both the Open Rate and Click Rate. This approach has the potential to enhance customer engagement and retention for businesses while enabling well-informed decisions by leveraging insights derived from consumer data. This work contributes to the existing body of research on MLaaS in marketing and offers practical insights for businesses seeking to utilise this approach to enhance their competitive edge in the contemporary data-oriented marketplace.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning)
►▼
Show Figures
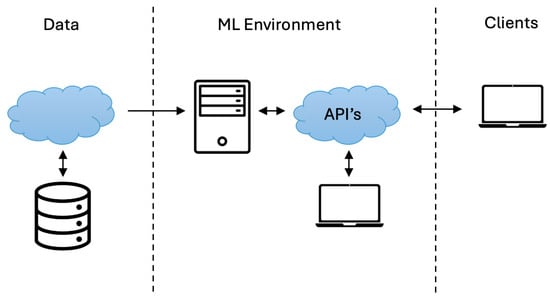
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Variations in Pattern of Social Media Engagement between Individuals with Chronic Conditions and Mental Health Conditions
by
Elizabeth Ayangunna, Gulzar Shah, Kingsley Kalu, Padmini Shankar and Bushra Shah
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020018 - 14 Apr 2024
Abstract
The use of the internet and supported apps is at historically unprecedented levels for the exchange of health information. The increasing use of the internet and social media platforms can affect patients’ health behavior. This study aims to assess the variations in patterns
[...] Read more.
The use of the internet and supported apps is at historically unprecedented levels for the exchange of health information. The increasing use of the internet and social media platforms can affect patients’ health behavior. This study aims to assess the variations in patterns of social media engagement between individuals diagnosed with either chronic diseases or mental health conditions. Data from four iterations of the Health Information National Trends Survey Cycle 4 from 2017 to 2020 were used for this study with a sample size (N) = 16,092. To analyze the association between the independent variables, reflecting the presence of chronic conditions or mental health conditions, and various levels of social media engagement, descriptive statistics and logistic regression were conducted. Respondents who had at least one chronic condition were more likely to join an internet-based support group (Adjusted Odds Ratio or AOR = 1.5; Confidence Interval, CI = 1.11–1.93) and watch a health-related video on YouTube (AOR = 1.2; CI = 1.01–1.36); respondents with a mental condition were less likely to visit and share health information on social media, join an internet-based support group, and watch a health-related video on YouTube. Race, age, and educational level also influence the choice to watch a health-related video on YouTube. Understanding the pattern of engagement with health-related content on social media and how their online behavior differs based on the patient’s medical conditions can lead to the development of more effective and tailored public health interventions that leverage social media platforms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Health Informatics)
►▼
Show Figures
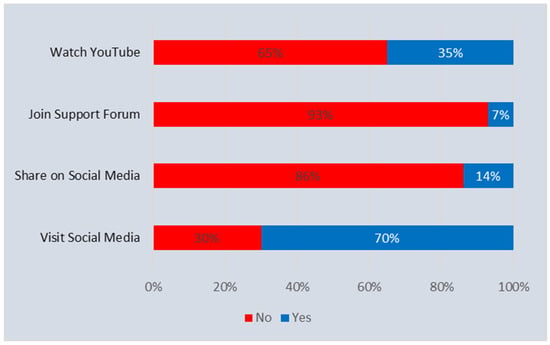
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Governors in the Digital Era: Analyzing and Predicting Social Media Engagement Using Machine Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Japan
by
Salama Shady, Vera Paola Shoda and Takashi Kamihigashi
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020017 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the social media posts of prefectural governors in Japan during the COVID-19 pandemic. It investigates the correlation between social media activity levels, governors’ characteristics, and engagement metrics. To predict citizen engagement of a specific tweet, machine
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the social media posts of prefectural governors in Japan during the COVID-19 pandemic. It investigates the correlation between social media activity levels, governors’ characteristics, and engagement metrics. To predict citizen engagement of a specific tweet, machine learning models (MLMs) are trained using three feature sets. The first set includes variables representing profile- and tweet-related features. The second set incorporates word embeddings from three popular models, while the third set combines the first set with one of the embeddings. Additionally, seven classifiers are employed. The best-performing model utilizes the first feature set with FastText embedding and the XGBoost classifier. This study aims to collect governors’ COVID-19-related tweets, analyze engagement metrics, investigate correlations with governors’ characteristics, examine tweet-related features, and train MLMs for prediction. This paper’s main contributions are twofold. Firstly, it offers an analysis of social media engagement by prefectural governors during the COVID-19 pandemic, shedding light on their communication strategies and citizen engagement outcomes. Secondly, it explores the effectiveness of MLMs and word embeddings in predicting tweet engagement, providing practical implications for policymakers in crisis communication. The findings emphasize the importance of social media engagement for effective governance and provide insights into factors influencing citizen engagement.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Social Informatics and Digital Humanities)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Key Industry 4.0 Organisational Capability Prioritisation towards Organisational Transformation
by
Stefan Smuts and Alta van der Merwe
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020016 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Industry 4.0 aids organisational transformation powered by innovative technologies and connectivity. In addition to navigating complex Industry 4.0 concepts and characteristics, organisations must also address organisational consequences related to fast-paced organisational transformation and resource efficacy. The optimal allocation of organisational resources and capabilities
[...] Read more.
Industry 4.0 aids organisational transformation powered by innovative technologies and connectivity. In addition to navigating complex Industry 4.0 concepts and characteristics, organisations must also address organisational consequences related to fast-paced organisational transformation and resource efficacy. The optimal allocation of organisational resources and capabilities to large transformational programs, as well as the significant capital investment associated with digital transformation, compel organisations to prioritize their efforts. Hence, this study investigates how key Industry 4.0 organisational capabilities could be prioritized towards organisational digital transformation. Data were collected from 49 participants who had completed a questionnaire containing 26 statement actions aligned to sensing, seizing, transforming and supporting organisational capability domains. By analysing the data, statement actions were prioritized and operationalized into a prototyped checklist. Two organisations applied the prototyped checklist, illustrating unique profiles and transformative actions. The operationalisation of the checklist highlighted its utility in establishing where an organisation operates in terms of digital transformation, as well as what additional steps might be followed to improve its capability prioritisation based on low checklist scores. By understanding the prioritisation of Industry 4.0 capabilities, organisations could ensure that resources are allocated optimally for business value creation based on organisational capabilities prioritisation.
Full article
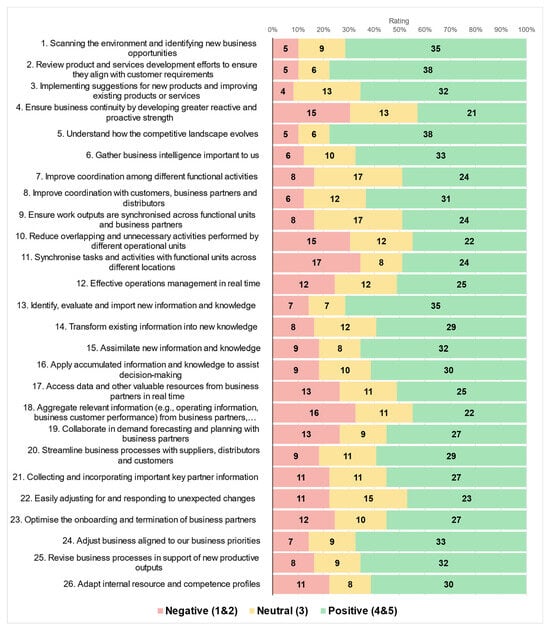
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Detecting Structured Query Language Injections in Web Microservices Using Machine Learning
by
Edwin Peralta-Garcia, Juan Quevedo-Monsalbe, Victor Tuesta-Monteza and Juan Arcila-Diaz
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020015 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
Structured Query Language (SQL) injections pose a constant threat to web services, highlighting the need for efficient detection to address this vulnerability. This study compares machine learning algorithms for detecting SQL injections in web microservices trained using a public dataset of 22,764 records.
[...] Read more.
Structured Query Language (SQL) injections pose a constant threat to web services, highlighting the need for efficient detection to address this vulnerability. This study compares machine learning algorithms for detecting SQL injections in web microservices trained using a public dataset of 22,764 records. Additionally, a software architecture based on the microservices approach was implemented, in which trained models and the web application were deployed to validate requests and detect attacks. A literature review was conducted to identify types of SQL injections and machine learning algorithms. The results of random forest, decision tree, and support vector machine were compared for detecting SQL injections. The findings show that random forest outperforms with a precision and accuracy of 99%, a recall of 97%, and an F1 score of 98%. In contrast, decision tree achieved a precision of 92%, a recall of 86%, and an F1 score of 97%. Support Vector Machine (SVM) presented an accuracy, precision, and F1 score of 98%, with a recall of 97%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning)
►▼
Show Figures
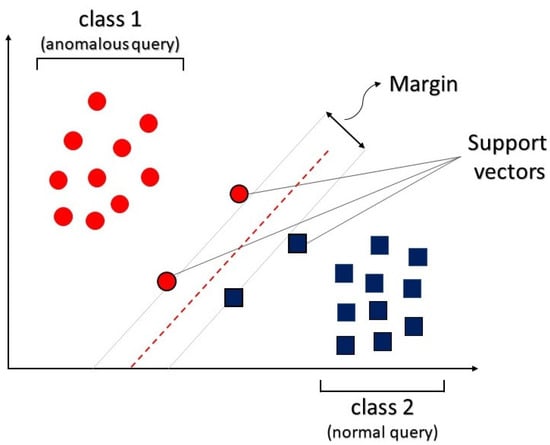
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Computational Ensemble Gene Co-Expression Networks for the Analysis of Cancer Biomarkers
by
Julia Figueroa-Martínez, Dulcenombre M. Saz-Navarro, Aurelio López-Fernández, Domingo S. Rodríguez-Baena and Francisco A. Gómez-Vela
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020014 - 28 Mar 2024
Abstract
Gene networks have become a powerful tool for the comprehensive examination of gene expression patterns. Thanks to these networks generated by means of inference algorithms, it is possible to study different biological processes and even identify new biomarkers for such diseases. These biomarkers
[...] Read more.
Gene networks have become a powerful tool for the comprehensive examination of gene expression patterns. Thanks to these networks generated by means of inference algorithms, it is possible to study different biological processes and even identify new biomarkers for such diseases. These biomarkers are essential for the discovery of new treatments for genetic diseases such as cancer. In this work, we introduce an algorithm for genetic network inference based on an ensemble method that improves the robustness of the results by combining two main steps: first, the evaluation of the relationship between pairs of genes using three different co-expression measures, and, subsequently, a voting strategy. The utility of this approach was demonstrated by applying it to a human dataset encompassing breast and prostate cancer-associated stromal cells. Two gene networks were computed using microarray data, one for breast cancer and one for prostate cancer. The results obtained revealed, on the one hand, distinct stromal cell behaviors in breast and prostate cancer and, on the other hand, a list of potential biomarkers for both diseases. In the case of breast tumor, ST6GAL2, RIPOR3, COL5A1, and DEPDC7 were found, and in the case of prostate tumor, the genes were GATA6-AS1, ARFGEF3, PRR15L, and APBA2. These results demonstrate the usefulness of the ensemble method in the field of biomarker discovery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Informatics Algorithms and Applications to Biomedicine and Healthcare)
►▼
Show Figures
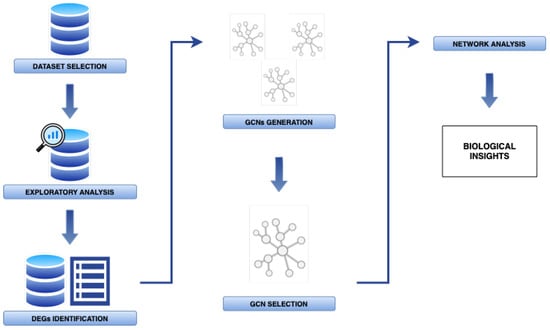
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Research Interest in ChatGPT and Other Natural Language Processing Tools from a Public Health Perspective: A Bibliometric Analysis
by
Giuliana Favara, Martina Barchitta, Andrea Maugeri, Roberta Magnano San Lio and Antonella Agodi
Informatics 2024, 11(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11020013 - 22 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Natural language processing, such as ChatGPT, demonstrates growing potential across numerous research scenarios, also raising interest in its applications in public health and epidemiology. Here, we applied a bibliometric analysis for a systematic assessment of the current literature related to the applications
[...] Read more.
Background: Natural language processing, such as ChatGPT, demonstrates growing potential across numerous research scenarios, also raising interest in its applications in public health and epidemiology. Here, we applied a bibliometric analysis for a systematic assessment of the current literature related to the applications of ChatGPT in epidemiology and public health. Methods: A bibliometric analysis was conducted on the Biblioshiny web-app, by collecting original articles indexed in the Scopus database between 2010 and 2023. Results: On a total of 3431 original medical articles, “Article” and “Conference paper”, mostly constituting the total of retrieved documents, highlighting that the term “ChatGPT” becomes an interesting topic from 2023. The annual publications escalated from 39 in 2010 to 719 in 2023, with an average annual growth rate of 25.1%. In terms of country production over time, the USA led with the highest overall production from 2010 to 2023. Concerning citations, the most frequently cited countries were the USA, UK, and China. Interestingly, Harvard Medical School emerges as the leading contributor, accounting for 18% of all articles among the top ten affiliations. Conclusions: Our study provides an overall examination of the existing research interest in ChatGPT’s applications for public health by outlining pivotal themes and uncovering emerging trends.
Full article
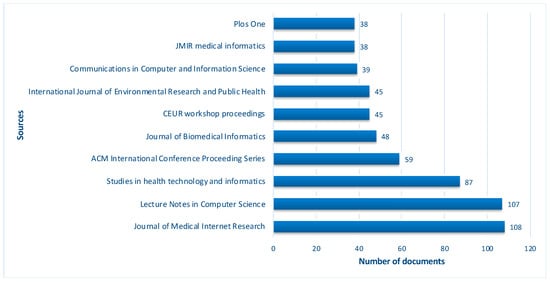
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Causes and Mitigation Practices of Requirement Volatility in Agile Software Development
by
Abdulghafour Mohammad and Job Mathew Kollamana
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010012 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
One of the main obstacles in software development projects is requirement volatility (RV), which is defined as uncertainty or changes in software requirements during the development process. Therefore, this research tries to understand the underlying factors behind the RV and the best practices
[...] Read more.
One of the main obstacles in software development projects is requirement volatility (RV), which is defined as uncertainty or changes in software requirements during the development process. Therefore, this research tries to understand the underlying factors behind the RV and the best practices to reduce it. The methodology used for this research is based upon qualitative research using interviews with 12 participants with experience in agile software development projects. The participants hailed from Austria, Nigeria, the USA, the Philippines, Armenia, Sri Lanka, Germany, Egypt, Canada, and Turkey and held roles such as project managers, software developers, Scrum Masters, testers, business analysts, and product owners. Our findings based on our empirical data revealed six primary factors that cause RV and three main agile practices that help to mitigate it. Theoretically, this study contributes to the body of knowledge relating to RV management. Practically, this research is expected to aid software development teams in comprehending the reasons behind RV and the best practices to effectively minimize it.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Multidimensional Embeddings for Decision Support Using Advanced Visualization Techniques
by
Olga Kurasova, Arnoldas Budžys and Viktor Medvedev
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010011 - 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
As artificial intelligence has evolved, deep learning models have become important in extracting and interpreting complex patterns from raw multidimensional data. These models produce multidimensional embeddings that, while containing a lot of information, are often not directly understandable. Dimensionality reduction techniques play an
[...] Read more.
As artificial intelligence has evolved, deep learning models have become important in extracting and interpreting complex patterns from raw multidimensional data. These models produce multidimensional embeddings that, while containing a lot of information, are often not directly understandable. Dimensionality reduction techniques play an important role in transforming multidimensional data into interpretable formats for decision support systems. To address this problem, the paper presents an analysis of dimensionality reduction and visualization techniques that embrace complex data representations and are useful inferences for decision systems. A novel framework is proposed, utilizing a Siamese neural network with a triplet loss function to analyze multidimensional data encoded into images, thus transforming these data into multidimensional embeddings. This approach uses dimensionality reduction techniques to transform these embeddings into a lower-dimensional space. This transformation not only improves interpretability but also maintains the integrity of the complex data structures. The efficacy of this approach is demonstrated using a keystroke dynamics dataset. The results support the integration of these visualization techniques into decision support systems. The visualization process not only simplifies the complexity of the data, but also reveals deep patterns and relationships hidden in the embeddings. Thus, a comprehensive framework for visualizing and interpreting complex keystroke dynamics is described, making a significant contribution to the field of user authentication.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning)
►▼
Show Figures
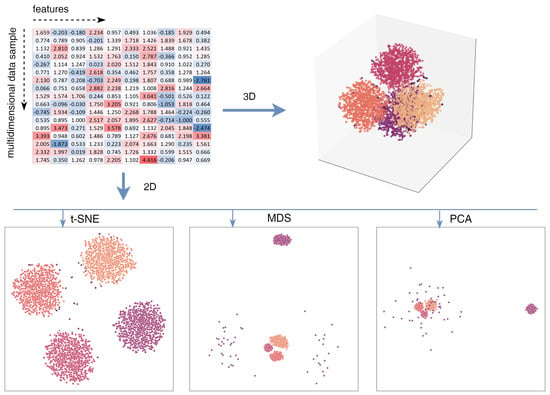
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unveiling Insights: A Bibliometric Analysis of Artificial Intelligence in Teaching
by
Malinka Ivanova, Gabriela Grosseck and Carmen Holotescu
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010010 - 25 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The penetration of intelligent applications in education is rapidly increasing, posing a number of questions of a different nature to the educational community. This paper is coming to analyze and outline the influence of artificial intelligence (AI) on teaching practice which is an
[...] Read more.
The penetration of intelligent applications in education is rapidly increasing, posing a number of questions of a different nature to the educational community. This paper is coming to analyze and outline the influence of artificial intelligence (AI) on teaching practice which is an essential problem considering its growing utilization and pervasion on a global scale. A bibliometric approach is applied to outdraw the “big picture” considering gathered bibliographic data from scientific databases Scopus and Web of Science. Data on relevant publications matching the query “artificial intelligence and teaching” over the past 5 years have been researched and processed through Biblioshiny in R environment in order to establish a descriptive structure of the scientific production, to determine the impact of scientific publications, to trace collaboration patterns and to identify key research areas and emerging trends. The results point out the growth in scientific production lately that is an indicator of increased interest in the investigated topic by researchers who mainly work in collaborative teams as some of them are from different countries and institutions. The identified key research areas include techniques used in educational applications, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. Additionally, there is a focus on applicable technologies like ChatGPT, learning analytics, and virtual reality. The research also explores the context of application for these techniques and technologies in various educational settings, including teaching, higher education, active learning, e-learning, and online learning. Based on our findings, the trending research topics can be encapsulated by terms such as ChatGPT, chatbots, AI, generative AI, machine learning, emotion recognition, large language models, convolutional neural networks, and decision theory. These findings offer valuable insights into the current landscape of research interests in the field.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genealogical Data-Driven Visits of Historical Cemeteries
by
Angelica Lo Duca, Matteo Abrate, Andrea Marchetti and Manuela Moretti
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010009 - 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
This paper describes the Integration of Archives and Cultural Places (IaCuP) project, which aims to integrate information about a historical cemetery, including its map and grave inventory, with genealogical and documentary knowledge extracted from relevant historical archives. The integrated data are accessible to
[...] Read more.
This paper describes the Integration of Archives and Cultural Places (IaCuP) project, which aims to integrate information about a historical cemetery, including its map and grave inventory, with genealogical and documentary knowledge extracted from relevant historical archives. The integrated data are accessible to cemetery visitors through an interactive mobile application, enabling them to navigate a graphical representation of the cemetery while exploring comprehensive visualizations of genealogical data. The basic idea stems from the desire to provide people with access to the rich context of cultural sites, which have often lost their original references over the centuries, making it challenging for individuals today to interpret the meanings embedded within them. The proposed approach leverages large language models (LLMs) to extract information from relevant documents and Web technologies to represent such information as interactive visualizations. As a practical case study, this paper focuses on the Jewish Cemetery in Pisa and the Historical Archives of the Jewish Community in Pisa, working on the genealogical tree of one of the most representative families resting in the cemetery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Social Informatics and Digital Humanities)
►▼
Show Figures
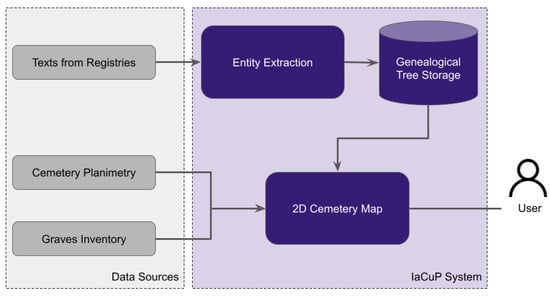
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Topic Extraction: BERTopic’s Insight into the 117th Congress’s Twitterverse
by
Margarida Mendonça and Álvaro Figueira
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010008 - 17 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As social media (SM) becomes increasingly prevalent, its impact on society is expected to grow accordingly. While SM has brought positive transformations, it has also amplified pre-existing issues such as misinformation, echo chambers, manipulation, and propaganda. A thorough comprehension of this impact, aided
[...] Read more.
As social media (SM) becomes increasingly prevalent, its impact on society is expected to grow accordingly. While SM has brought positive transformations, it has also amplified pre-existing issues such as misinformation, echo chambers, manipulation, and propaganda. A thorough comprehension of this impact, aided by state-of-the-art analytical tools and by an awareness of societal biases and complexities, enables us to anticipate and mitigate the potential negative effects. One such tool is BERTopic, a novel deep-learning algorithm developed for Topic Mining, which has been shown to offer significant advantages over traditional methods like Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), particularly in terms of its high modularity, which allows for extensive personalization at each stage of the topic modeling process. In this study, we hypothesize that BERTopic, when optimized for Twitter data, can provide a more coherent and stable topic modeling. We began by conducting a review of the literature on topic-mining approaches for short-text data. Using this knowledge, we explored the potential for optimizing BERTopic and analyzed its effectiveness. Our focus was on Twitter data spanning the two years of the 117th US Congress. We evaluated BERTopic’s performance using coherence, perplexity, diversity, and stability scores, finding significant improvements over traditional methods and the default parameters for this tool. We discovered that improvements are possible in BERTopic’s coherence and stability. We also identified the major topics of this Congress, which include abortion, student debt, and Judge Ketanji Brown Jackson. Additionally, we describe a simple application we developed for a better visualization of Congress topics.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Uncovering the Limitations and Insights of Packet Status Prediction Models in IEEE 802.15.4-Based Wireless Networks and Insights from Data Science
by
Mariana Ávalos-Arce, Heráclito Pérez-Díaz, Carolina Del-Valle-Soto and Ramon A. Briseño
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010007 - 26 Jan 2024
Abstract
Wireless networks play a pivotal role in various domains, including industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and mobile sensor networks. This research investigates the critical issue of packet loss in modern wireless networks and aims to identify the conditions within a network’s environment that
[...] Read more.
Wireless networks play a pivotal role in various domains, including industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and mobile sensor networks. This research investigates the critical issue of packet loss in modern wireless networks and aims to identify the conditions within a network’s environment that lead to such losses. We propose a packet status prediction model for data packets that travel through a wireless network based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and are exposed to five different types of interference in a controlled experimentation environment. The proposed model focuses on the packetization process and its impact on network robustness. This study explores the challenges posed by packet loss, particularly in the context of interference, and puts forth the hypothesis that specific environmental conditions are linked to packet loss occurrences. The contribution of this work lies in advancing our understanding of the conditions leading to packet loss in wireless networks. Data are retrieved with a single CC2531 USB Dongle Packet Sniffer, whose pieces of information on packets become the features of each packet from which the classifier model will gather the training data with the aim of predicting whether a packet will unsuccessfully arrive at its destination. We found that interference causes more packet loss than that caused by various devices using a WiFi communication protocol simultaneously. In addition, we found that the most important predictors are network strength and packet size; low network strength tends to lead to more packet loss, especially for larger packets. This study contributes to the ongoing efforts to predict and mitigate packet loss, emphasizing the need for adaptive models in dynamic wireless environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digital Society: Interdisciplinary Insights and Applications of Wireless Connectivity)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Relationship between Career Satisfaction and University Learning Using Data Science Models
by
Sofía Ramos-Pulido, Neil Hernández-Gress and Gabriela Torres-Delgado
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010006 - 24 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Current research on the career satisfaction of graduates limits educational institutions in devising methods to attain high career satisfaction. Thus, this study aims to use data science models to understand and predict career satisfaction based on information collected from surveys of university alumni.
[...] Read more.
Current research on the career satisfaction of graduates limits educational institutions in devising methods to attain high career satisfaction. Thus, this study aims to use data science models to understand and predict career satisfaction based on information collected from surveys of university alumni. Five machine learning (ML) algorithms were used for data analysis, including the decision tree, random forest, gradient boosting, support vector machine, and neural network models. To achieve optimal prediction performance, we utilized the Bayesian optimization method to fine-tune the parameters of the five ML algorithms. The five ML models were compared with logistic and ordinal regression. Then, to extract the most important features of the best predictive model, we employed the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), a novel methodology for extracting the significant features in ML. The results indicated that gradient boosting is a marginally superior predictive model, with 2–3% higher accuracy and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) compared to logistic and ordinal regression. Interestingly, concerning low career satisfaction, those with the worst scores for the phrase “how frequently applied knowledge, skills, or technological tools from the academic training” were less satisfied with their careers. To summarize, career satisfaction is related to academic training, alumni satisfaction, employment status, published articles or books, and other factors.
Full article
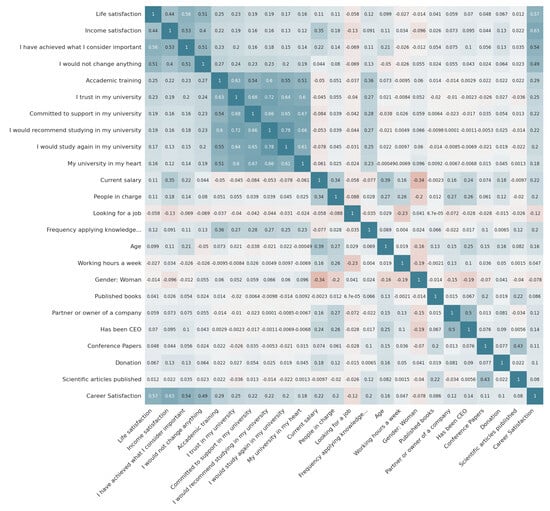
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Augmented Reality Technology for Chest ECG Electrode Placement Practice
by
Charlee Kaewrat, Dollaporn Anopas, Si Thu Aung and Yunyong Punsawad
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010005 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This study presents an augmented reality application for training chest electrocardiography electrode placement. AR applications featuring augmented object displays and interactions have been developed to facilitate learning and training of electrocardiography (ECG) chest lead placement via smartphones. The AR marker-based technique was used
[...] Read more.
This study presents an augmented reality application for training chest electrocardiography electrode placement. AR applications featuring augmented object displays and interactions have been developed to facilitate learning and training of electrocardiography (ECG) chest lead placement via smartphones. The AR marker-based technique was used to track the objects. The proposed AR application can project virtual ECG electrode positions onto the mannequin’s chest and provide feedback to trainees. We designed experimental tasks using the pre- and post-tests and practice sessions to verify the efficiency of the proposed AR application. The control group was assigned to learn chest ECG electrode placement using traditional methods, whereas the intervention group was introduced to the proposed AR application for ECG electrode placement. The results indicate that the proposed AR application can encourage learning outcomes, such as chest lead ECG knowledge and skills. Moreover, using AR technology can enhance students’ learning experiences. In the future, we plan to apply the proposed AR technology to improve related courses in medical science education.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human-Computer Interaction)
►▼
Show Figures
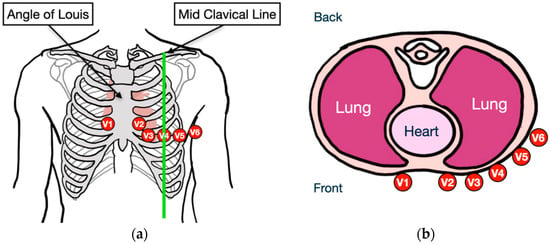
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Relation between Contextual Social Determinants of Health and COVID-19 Occurrence and Hospitalization
by
Aokun Chen, Yunpeng Zhao, Yi Zheng, Hui Hu, Xia Hu, Jennifer N. Fishe, William R. Hogan, Elizabeth A. Shenkman, Yi Guo and Jiang Bian
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010004 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
It is prudent to take a unified approach to exploring how contextual social determinants of health (SDoH) relate to COVID-19 occurrence and outcomes. Poor geographically represented data and a small number of contextual SDoH examined in most previous research studies have left a
[...] Read more.
It is prudent to take a unified approach to exploring how contextual social determinants of health (SDoH) relate to COVID-19 occurrence and outcomes. Poor geographically represented data and a small number of contextual SDoH examined in most previous research studies have left a knowledge gap in the relationships between contextual SDoH and COVID-19 outcomes. In this study, we linked 199 contextual SDoH factors covering 11 domains of social and built environments with electronic health records (EHRs) from a large clinical research network (CRN) in the National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) to explore the relation between contextual SDoH and COVID-19 occurrence and hospitalization. We identified 15,890 COVID-19 patients and 63,560 matched non-COVID-19 patients in Florida between January 2020 and May 2021. We adopted a two-phase multiple linear regression approach modified from that in the exposome-wide association (ExWAS) study. After removing the highly correlated SDoH variables, 86 contextual SDoH variables were included in the data analysis. Adjusting for race, ethnicity, and comorbidities, we found six contextual SDoH variables (i.e., hospital available beds and utilization, percent of vacant property, number of golf courses, and percent of minority) related to the occurrence of COVID-19, and three variables (i.e., farmers market, low access, and religion) related to the hospitalization of COVID-19. To our best knowledge, this is the first study to explore the relationship between contextual SDoH and COVID-19 occurrence and hospitalization using EHRs in a major PCORnet CRN. As an exploratory study, the causal effect of SDoH on COVID-19 outcomes will be evaluated in future studies.
Full article
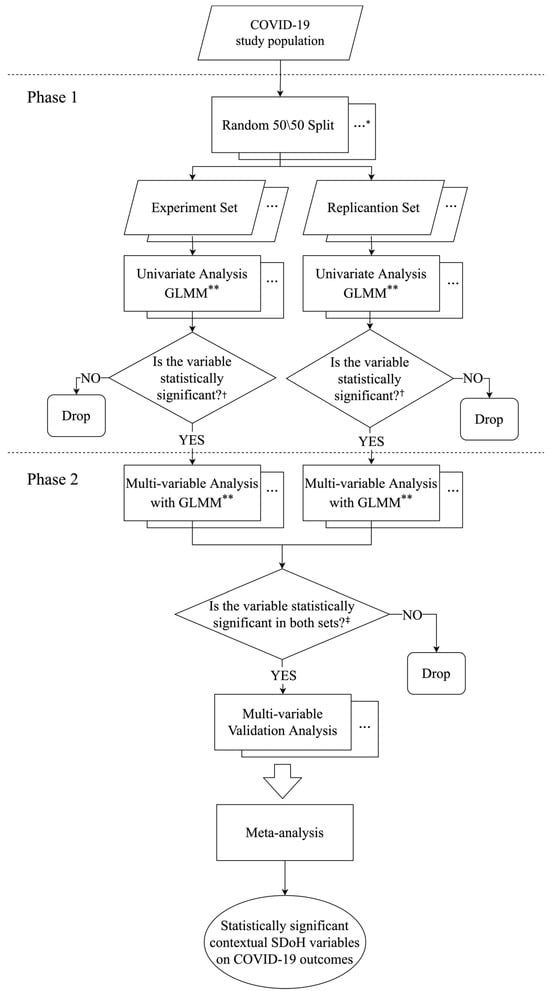
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrating IOTA’s Tangle with the Internet of Things for Sustainable Agriculture: A Proof-of-Concept Study on Rice Cultivation
by
Sandro Pullo, Remo Pareschi, Valentina Piantadosi, Francesco Salzano and Roberto Carlini
Informatics 2024, 11(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics11010003 - 28 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Addressing the critical challenges of resource inefficiency and environmental impact in the agrifood sector, this study explores the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies with IOTA’s Tangle, a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). This integration aims to enhance sustainable agricultural practices, using rice
[...] Read more.
Addressing the critical challenges of resource inefficiency and environmental impact in the agrifood sector, this study explores the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies with IOTA’s Tangle, a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). This integration aims to enhance sustainable agricultural practices, using rice cultivation as a case study of high relevance and reapplicability given its importance in the food chain and the high irrigation requirement of its cultivation. The approach employs sensor-based intelligent irrigation systems to optimize water efficiency. These systems enable real-time monitoring of agricultural parameters through IoT sensors. Data management is facilitated by IOTA’s Tangle, providing secure and efficient data handling, and integrated with MongoDB, a Database Management System (DBMS), for effective data storage and retrieval. The collaboration between IoT and IOTA led to significant reductions in resource consumption. Implementing sustainable agricultural practices resulted in a 50% reduction in water usage, 25% decrease in nitrogen consumption, and a 50% to 70% reduction in methane emissions. Additionally, the system contributed to lower electricity consumption for irrigation pumps and generated comprehensive historical water depth records, aiding future resource management decisions. This study concludes that the integration of IoT with IOTA’s Tangle presents a highly promising solution for advancing sustainable agriculture. This approach significantly contributes to environmental conservation and food security. Furthermore, it establishes that DLTs like IOTA are not only viable but also effective for real-time monitoring and implementation of sustainable agricultural practices.
Full article
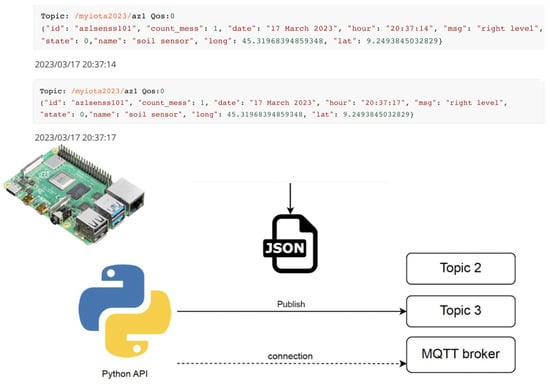
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Informatics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
AI, Algorithms, BDCC, Future Internet, Informatics, Information, Languages, Publications
AI Chatbots: Threat or Opportunity?
Topic Editors: Antony Bryant, Roberto Montemanni, Min Chen, Paolo Bellavista, Kenji Suzuki, Jeanine Treffers-DallerDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Healthcare, Informatics, IJERPH
Applications of Virtual Reality Technology in Rehabilitation
Topic Editors: Jorge Oliveira, Pedro GamitoDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Informatics, Information, Software
Software Engineering and Applications
Topic Editors: Sanjay Misra, Robertas Damaševičius, Bharti SuriDeadline: 31 October 2024
Topic in
Computers, Informatics, Information, Logistics, Mathematics, Algorithms
Decision Science Applications and Models (DSAM)
Topic Editors: Daniel Riera Terrén, Angel A. Juan, Majsa Ammuriova, Laura CalvetDeadline: 31 December 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Informatics
Health Informatics: Feature Review Papers
Guest Editors: Jiang Bian, Yi GuoDeadline: 31 July 2024
Special Issue in
Informatics
New Advances in Semantic Recognition and Analysis
Guest Editors: Daniele Toti, Andrea Pozzi, Enrico BarbieratoDeadline: 31 August 2024
Special Issue in
Informatics
Digital Society: Interdisciplinary Insights and Applications of Wireless Connectivity
Guest Editors: Carolina Del Valle Soto, Ramiro VelázquezDeadline: 30 September 2024
Special Issue in
Informatics
The Smart Cities Continuum via Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Guest Editors: Augusto Neto, Roger ImmichDeadline: 31 December 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Informatics
Promotion of Computational Thinking and Informatics Education in Pre-University Studies
Collection Editor: Francisco José García-Peñalvo
Topical Collection in
Informatics
Uncertainty in Digital Humanities
Collection Editors: Roberto Theron, Eveline Wandl-Vogt, Jennifer Cizik Edmond, Cezary Mazurek