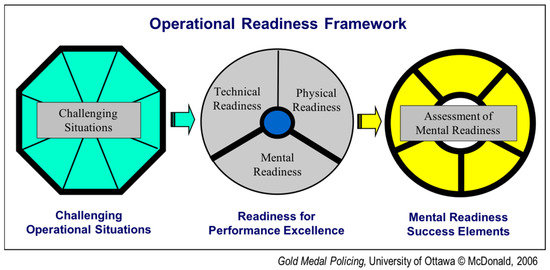
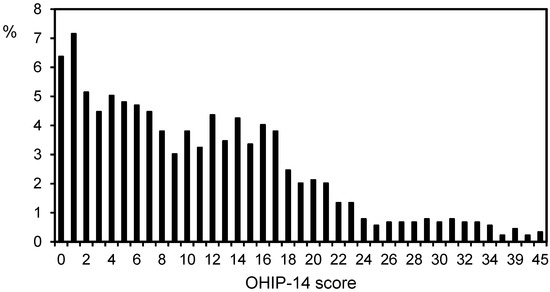
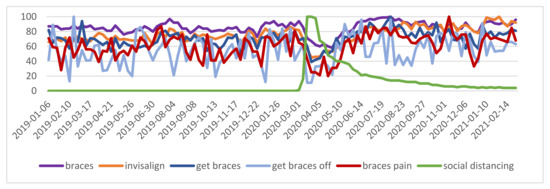
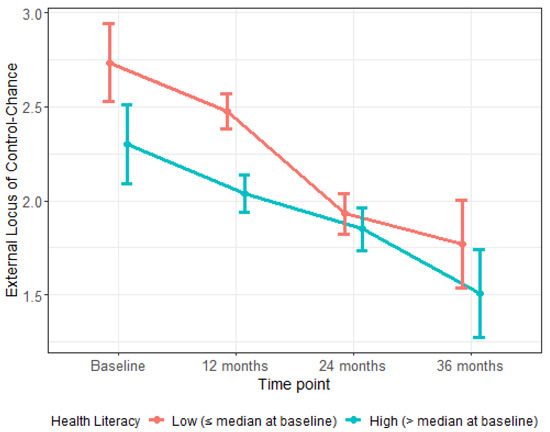
Oral and Public Health (Closed)
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601). This collection belongs to the section "Global Health".
Viewed by 91059Editor
Interests: oral medicine; dental materials; operative dentistry; oral health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The 2020 pandemic has highlighted how health plays the most important role in the life of human beings. Public health has a great impact on individuals, but also on the worldwide community, influencing social relationships and economies. The promotion of public health may be expressed as disease prevention and control as well as the limitation of related risk factors.
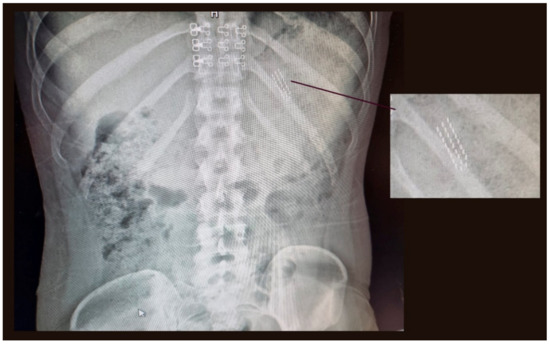
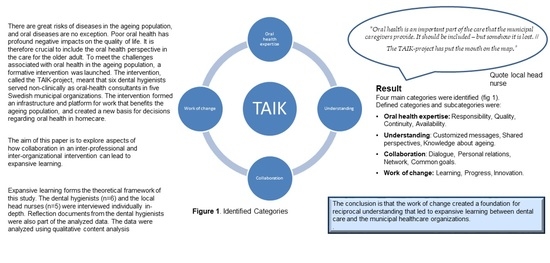
Oral diseases are the most representative noncommunicable diseases affecting a wide fraction of the global population, irrespective of gender and age. Moreover, systemic involvement caused by oral pathologies or their association with systemic conditions stress the importance of health programs aimed at drastically reducing the burden of oral diseases. Public health interventions and the reduction of risk factors should be the central core of preventive strategies, encouraging daily dental hygiene, balanced and healthy diet, and the reduction of bad habits (e.g., smoking, alcohol consumption, sedentary lifestyle), as well as regular dental visits.
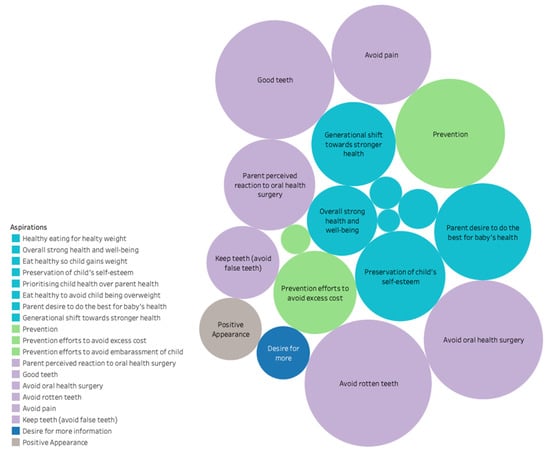
Therefore, the aim of the present Topical Collection is to provide in the near future a broad spectrum of preventive actions to promote oral as well as public health, considering the variability of the population in terms of age, gender, habits, and social and economic conditions. In addition, treatment strategies will be supplied to re-establish health and avoid local as well as systemic side-effects that in turn will affect the quality of life of people.
Prof. Dr. Gianrico Spagnuolo
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- preventive dentistry
- oral disease
- oral pathology
- systemic manifestations of oral diseases
- oral health promotion
- epidemiology