Journal Description
Infectious Disease Reports
Infectious Disease Reports
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed open access journal on infectious diseases published bimonthly online by MDPI (from Volume 12 Issue 3 - 2020).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Benefits of Publishing: We aim to be a leading journal on infectious diseases and to be in the top 20 journals listed in the Journal Citation Report (JCR) in this specific category in the near future.
Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Narrative Review Explaining the Role of HLA-A, -B, and -C Molecules in COVID-19 Disease in and around Africa
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 380-406; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020029 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has left a devasting effect on various regions globally. Africa has exceptionally high rates of other infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis (TB), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and malaria, and was not impacted by COVID-19 to the extent of
[...] Read more.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has left a devasting effect on various regions globally. Africa has exceptionally high rates of other infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis (TB), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and malaria, and was not impacted by COVID-19 to the extent of other continents Globally, COVID-19 has caused approximately 7 million deaths and 700 million infections thus far. COVID-19 disease severity and susceptibility vary among individuals and populations, which could be attributed to various factors, including the viral strain, host genetics, environment, lifespan, and co-existing conditions. Host genetics play a substantial part in COVID-19 disease severity among individuals. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) was previously been shown to be very important across host immune responses against viruses. HLA has been a widely studied gene region for various disease associations that have been identified. HLA proteins present peptides to the cytotoxic lymphocytes, which causes an immune response to kill infected cells. The HLA molecule serves as the central region for infectious disease association; therefore, we expect HLA disease association with COVID-19. Therefore, in this narrative review, we look at the HLA gene region, particularly, HLA class I, to understand its role in COVID-19 disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Post COVID-19: Latest Advances, Challenges and Methodologies)
Open AccessArticle
Global Measles Surveillance: Trends, Challenges, and Implications for Public Health Interventions
by
Francesco Branda, Marta Giovanetti, Chiara Romano, Domenico Benvenuto, Alessandra Ciccozzi, Daria Sanna, Massimo Ciccozzi and Fabio Scarpa
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 367-379; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020028 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Measles, a highly contagious disease primarily affecting children, carries serious health risks, including complications and mortality. Vaccination remains the most effective preventive measure against measles transmission. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated challenges in surveillance and immunization efforts, leaving millions of people exposed to
[...] Read more.
Measles, a highly contagious disease primarily affecting children, carries serious health risks, including complications and mortality. Vaccination remains the most effective preventive measure against measles transmission. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated challenges in surveillance and immunization efforts, leaving millions of people exposed to preventable diseases such as measles. Globally accelerated immunization campaigns are critical for achieving regional elimination goals and mitigating the risk of outbreaks. Our team has developed an open-access database for global measles monitoring, facilitating standardized data collection and analysis. The analysis of measles cases from 2011 to 2023 reveals fluctuating trends, with notable increases in Africa in 2019 and 2023, indicating potential gaps in control strategies. Using an automated signal detection tool developed by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) team, we identified significant variations between World Health Organization (WHO) regions, underscoring the importance of continuous monitoring to detect epidemiological changes early. These results underscore the need for robust surveillance systems and accelerated vaccination efforts to safeguard public health.
Full article
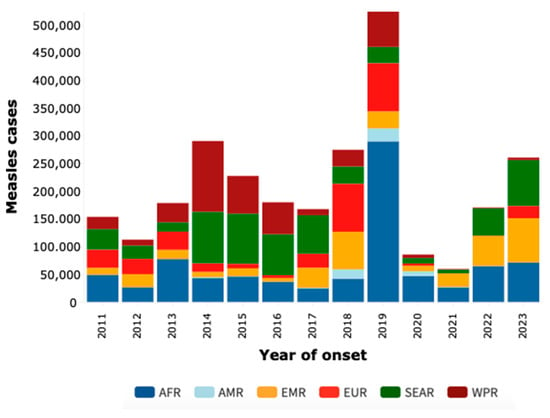
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multicenter Study of the Effectiveness of Antifungal Stewardship Team Intervention for Candidemia in Japan in 2008–2021
by
Mieko Tokano, Norihito Tarumoto, Jun Sakai, Kazuo Imai, Sakaru Koizumi, Haruka Karaushi, Tamotsu Hatanaka, Etsuko Kishi, Masafumi Seki, Koutaro Mitsutake and Shigefumi Maesaki
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 356-366; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020027 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
Candidemia, linked to high mortality rates, requires prompt antifungal therapy for better outcomes. Treatment is structured as an action bundle, which is beneficial when followed closely. However, the Japanese action bundle lacks detailed guidance on severe complications like endocarditis or ocular issues. To
[...] Read more.
Candidemia, linked to high mortality rates, requires prompt antifungal therapy for better outcomes. Treatment is structured as an action bundle, which is beneficial when followed closely. However, the Japanese action bundle lacks detailed guidance on severe complications like endocarditis or ocular issues. To address this, we adjusted the action bundle and assessed outcomes with and without AFT intervention. We strengthened protocols for blood cultures and organ assessments, and the AFT contacted the primary physician when yeast-like fungi were detected in the patient’s blood culture bottles. Analyzing 204 candidemia cases from 2008–2021, we observed increased adherence and reduced mortality post-AFT intervention. Ophthalmology consultations rose significantly, but many patients had only one visit, suggesting inadequate follow-up. If endophthalmitis is diagnosed, a change in the treatment approach may be necessary. There is a possibility that abnormal ocular findings will be detected during subsequent visits, which highlights the need for improvement in ophthalmology follow-up rates as a future challenge for our AFT activities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antimicrobial Stewardship)
►▼
Show Figures
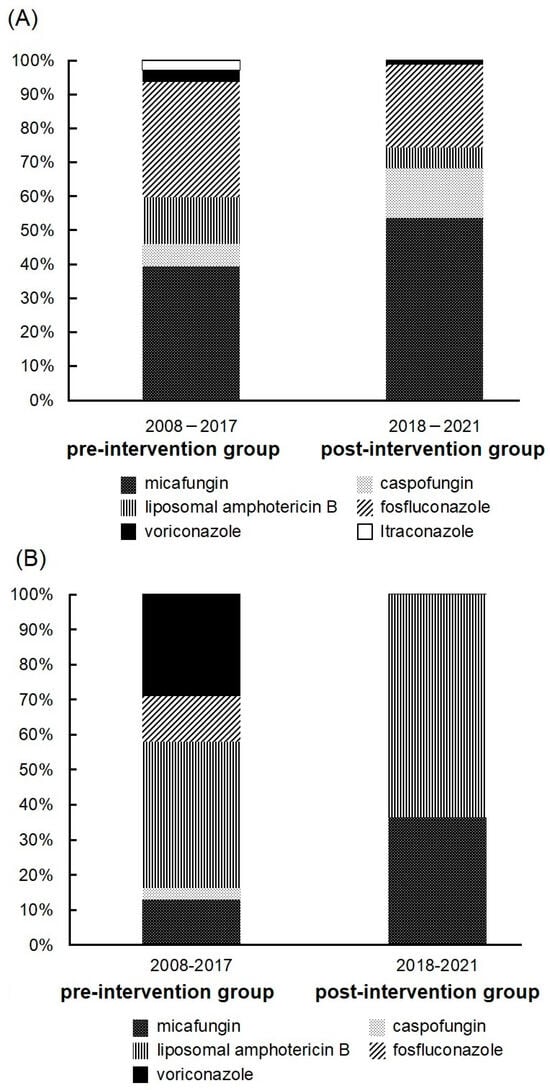
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections in Recipients of Bone Marrow Transplants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Matteo Riccò, Salvatore Parisi, Silvia Corrado, Federico Marchesi, Marco Bottazzoli and Davide Gori
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 317-355; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020026 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common cause of respiratory tract infections. Usually associated with infants and children, an increasing amount of evidence suggests that RSV can cause substantial morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised individuals, including recipients of bone marrow transplantation (BMT).
[...] Read more.
Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common cause of respiratory tract infections. Usually associated with infants and children, an increasing amount of evidence suggests that RSV can cause substantial morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised individuals, including recipients of bone marrow transplantation (BMT). The present systematic review was therefore designed in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines to collect available evidence about RSV infections in BMT recipients. Three medical databases (PubMed, Embase, and MedRxiv) were therefore searched for eligible observational studies published up to 30 September 2023 and collected cases were pooled in a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics. Reporting bias was assessed by means of funnel plots and regression analysis. Overall, 30 studies were retrieved, including 20,067 BMT cases and 821 RSV infection episodes. Of them, 351 were lower respiratory tract infections, and a total of 78 RSV-related deaths were collected. A pooled attack rate of 5.40% (95% confidence interval [95%CI] 3.81 to 7.60) was identified, with a corresponding incidence rate of 14.77 cases per 1000 person-years (95%CI 9.43 to 20.11), and a case fatality ratio (CFR) of 7.28% (95%CI 4.94 to 10.60). Attack rates were higher in adults (8.49%, 95%CI 5.16 to 13.67) than in children (4.79%, 95%CI 3.05 to 7.45), with similar CFR (5.99%, 95%CI 2.31 to 14.63 vs. 5.85%, 95%CI 3.35 to 10.02). By assuming RSV attack rates as a reference group, influenza (RR 0.518; 95%CI 0.446 to 0.601), adenovirus (RR 0.679, 95%CI 0.553 to 0.830), and human metapneumovirus (RR 0.536, 95%CI 0.438 to 0.655) were associated with a substantially reduced risk for developing corresponding respiratory infection. Despite the heterogeneous settings and the uneven proportion of adult and pediatric cases, our study has identified high attack rates and a substantial CFR of RSV in recipients of BMT, stressing the importance of specifically tailored preventive strategies and the need for effective treatment options.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Infections in the Immuncompromised Host)
►▼
Show Figures
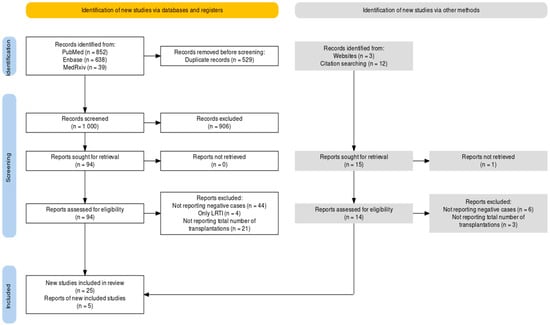
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current Progress and Future Perspectives in Contact and Releasing-Type Antimicrobial Coatings of Orthopaedic Implants: A Systematic Review Analysis Emanated from In Vitro and In Vivo Models
by
Angelos Kaspiris, Elias Vasiliadis, Evangelia Pantazaka, Ioanna Lianou, Dimitra Melissaridou, Matthaios Savvidis, Fotios Panagopoulos, Georgios Tsalimas, Michail Vavourakis, Ioannis Kolovos, Olga D. Savvidou and Spiros G. Pneumaticos
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 298-316; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020025 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Despite the expanding use of orthopedic devices and the application of strict pre- and postoperative protocols, the elimination of postoperative implant-related infections remains a challenge. Objectives: To identify and assess the in vitro and in vivo properties of antimicrobial-, silver- and iodine-based
[...] Read more.
Background: Despite the expanding use of orthopedic devices and the application of strict pre- and postoperative protocols, the elimination of postoperative implant-related infections remains a challenge. Objectives: To identify and assess the in vitro and in vivo properties of antimicrobial-, silver- and iodine-based implants, as well as to present novel approaches to surface modifications of orthopedic implants. Methods: A systematic computer-based review on the development of these implants, on PubMed and Web of Science databases, was carried out according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. Results: Overall, 31 in vitro and 40 in vivo entries were evaluated. Regarding the in vitro studies, antimicrobial-based coatings were assessed in 12 entries, silver-based coatings in 10, iodine-based in 1, and novel-applied coating technologies in 8 entries. Regarding the in vivo studies, antimicrobial coatings were evaluated in 23 entries, silver-coated implants in 12, and iodine-coated in 1 entry, respectively. The application of novel coatings was studied in the rest of the cases (4). Antimicrobial efficacy was examined using different bacterial strains, and osseointegration ability and biocompatibility were examined in eukaryotic cells and different animal models, including rats, rabbits, and sheep. Conclusions: Assessment of both in vivo and in vitro studies revealed a wide antimicrobial spectrum of the coated implants, related to reduced bacterial growth, inhibition of biofilm formation, and unaffected or enhanced osseointegration, emphasizing the importance of the application of surface modification techniques as an alternative for the treatment of orthopedic implant infections in the clinical settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Infection Prevention and Control)
►▼
Show Figures
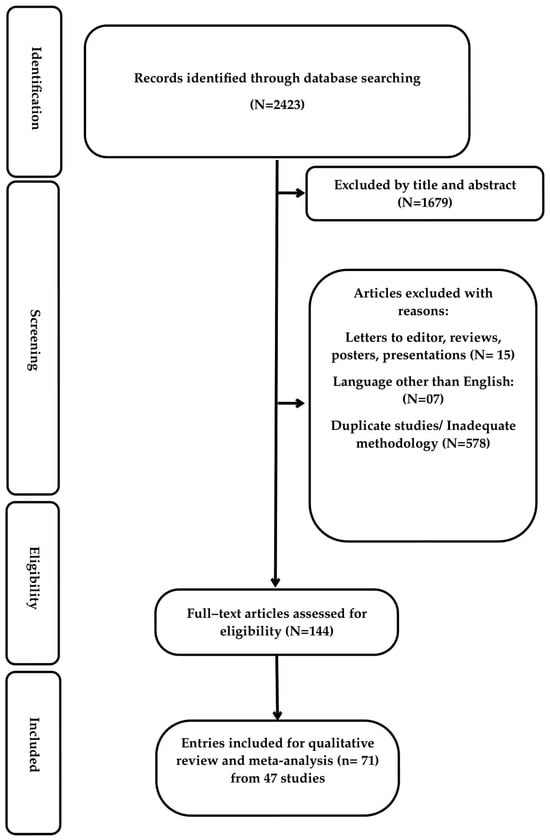
Figure 1
Open AccessCommentary
On the SARS-CoV-2 Variants
by
Fabio Scarpa, Francesco Branda, Nicola Petrosillo and Massimo Ciccozzi
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 289-297; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020024 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
The evolutionary dynamics of viruses, particularly exemplified by SARS-CoV-2 during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, underscore the intricate interplay between genetics, host adaptation, and viral spread. This paper delves into the genetic evolution of SARS-CoV-2, emphasizing the implications of viral variants on global health.
[...] Read more.
The evolutionary dynamics of viruses, particularly exemplified by SARS-CoV-2 during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, underscore the intricate interplay between genetics, host adaptation, and viral spread. This paper delves into the genetic evolution of SARS-CoV-2, emphasizing the implications of viral variants on global health. Initially emerging from the Wuhan-Hu-1 lineage, SARS-CoV-2 rapidly diversified into numerous variants, each characterized by distinct mutations in the spike protein and other genomic regions. Notable variants such as B.1.1.7 (α), B.1.351 (β), P.1 (γ), B.1.617.2 (δ), and the Omicron variant have garnered significant attention due to their heightened transmissibility and immune evasion capabilities. In particular, the Omicron variant has presented a myriad of subvariants, raising concerns about its potential impact on public health. Despite the emergence of numerous variants, the vast majority have exhibited limited expansion capabilities and have not posed significant threats akin to early pandemic strains. Continued genomic surveillance is imperative to identify emerging variants of concern promptly. While genetic adaptation is intrinsic to viral evolution, effective public health responses must be grounded in empirical evidence to navigate the evolving landscape of the pandemic with resilience and precision.
Full article
Open AccessCommentary
A One Health Platform for Future Epidemic Preparedness
by
Francesco Branda, Fabio Scarpa, Nicola Petrosillo and Massimo Ciccozzi
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 281-288; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020023 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Here, we introduce the EpiConnect Intelligence Platform (ECIP), a platform facilitating rapid, transparent data sharing and analysis to support researchers and public health officials in Europe, with a focus on Italy. ECIP provides reliable, concise, machine-readable data to aid in epidemiological understanding, standardize
[...] Read more.
Here, we introduce the EpiConnect Intelligence Platform (ECIP), a platform facilitating rapid, transparent data sharing and analysis to support researchers and public health officials in Europe, with a focus on Italy. ECIP provides reliable, concise, machine-readable data to aid in epidemiological understanding, standardize case characteristics, and estimate key parameters. The platform adheres to FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, reusable) principles, offering easily accessible and downloadable datasets for researchers’ endeavors. Future enhancements include involving national public health authorities, expanding data streams, and fostering collaboration between experts and users for improved epidemic risk monitoring. Shared standards among diverse surveillance systems are advocated to achieve common strategic goals, emphasizing the need for forward-looking policies to empower professionals to analyze disease dynamics in the context of evolving health crises. The recent emergencies underscore the importance of collective efforts towards shared strategic goals, highlighting the necessity for coordinated action to address mutual concerns affecting everyone’s lives.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Whipple Disease Presenting as Isolated Transverse Myelitis with Permanent Neurological Damage in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case Report of a Difficult Diagnosis with a Literature Review
by
Carolina Saffioti, Marta Nebiolo, Roberta Caorsi, Alessio Mesini, Mariasavina Severino, Giacomo Brisca, Elio Castagnola and Marco Gattorno
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 269-280; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020022 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We describe an atypical case of Whipple disease exclusively involving the spinal cord in an adolescent receiving immunosuppressive therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis was particularly difficult since lupus and Whipple disease can present similar clinical features and the patient’s prolonged contact
[...] Read more.
We describe an atypical case of Whipple disease exclusively involving the spinal cord in an adolescent receiving immunosuppressive therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis was particularly difficult since lupus and Whipple disease can present similar clinical features and the patient’s prolonged contact with sewage was initially not mentioned. A literature review of the clinical, imaging, diagnostic, and therapeutic challenges of Whipple disease is also performed.
Full article
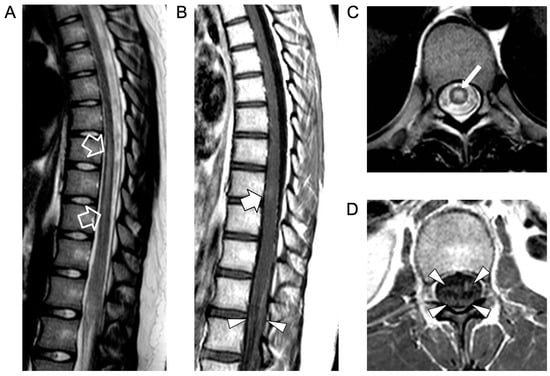
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
A Vulnerability Index to Assess the Risk of SARS-CoV-2-Related Hospitalization/Death: Urgent Need for an Update after Diffusion of Anti-COVID Vaccines
by
Francesco Lapi, Ettore Marconi, Alexander Domnich, Iacopo Cricelli, Alessandro Rossi, Ignazio Grattagliano, Giancarlo Icardi and Claudio Cricelli
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 260-268; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020021 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: There are algorithms to predict the risk of SARS-CoV-2-related complications. Given the spread of anti-COVID vaccination, which sensibly modified the burden of risk of the infection, these tools need to be re-calibrated. Therefore, we updated our vulnerability index, namely, the Health
[...] Read more.
Background: There are algorithms to predict the risk of SARS-CoV-2-related complications. Given the spread of anti-COVID vaccination, which sensibly modified the burden of risk of the infection, these tools need to be re-calibrated. Therefore, we updated our vulnerability index, namely, the Health Search (HS)-CoVulnerabiltyIndex (VI)d (HS-CoVId), to predict the risk of SARS-CoV-2-related hospitalization/death in the primary care setting. Methods: We formed a cohort of individuals aged ≥15 years and diagnosed with COVID-19 between 1 January and 31 December 2021 in the HSD. The date of COVID-19 diagnosis was the study index date. These patients were eligible if they had received an anti-COVID vaccine at least 15 days before the index date. Patients were followed up from the index date until one of the following events, whichever came first: COVID-19-related hospitalization/death (event date), end of registration with their GPs, and end of the study period (31 December 2022). To calculate the incidence rate of COVID-19-related hospitalization/death, a patient-specific score was derived through linear combination of the coefficients stemming from a multivariate Cox regression model. Its prediction performance was evaluated by obtaining explained variation, discrimination, and calibration measures. Results: We identified 2192 patients who had received an anti-COVID vaccine from 1 January to 31 December 2021. With this cohort, we re-calibrated the HS-CoVId by calculating optimism-corrected pseudo-R2, AUC, and calibration slope. The final model reported a good predictive performance by explaining 58% (95% CI: 48–71%) of variation in the occurrence of hospitalizations/deaths, the AUC was 83 (95% CI: 77–93%), and the calibration slope did not reject the equivalence hypothesis (p-value = 0.904). Conclusions: Two versions of HS-CoVId need to be differentially adopted to assess the risk of COVID-19-related complications among vaccinated and unvaccinated subjects. Therefore, this functionality should be operationalized in related patient- and population-based informatic tools intended for general practitioners.
Full article
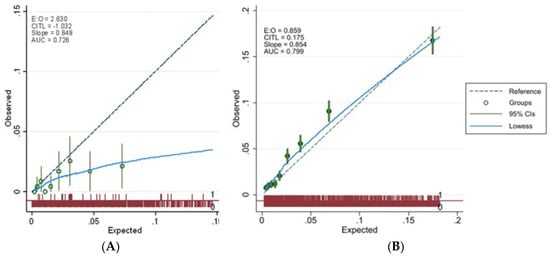
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
An Aminoglycoside-Sparing Regimen with Double Beta-Lactam to Successfully Treat Granulicatella adiacens Prosthetic Aortic Valve Endocarditis—Time to Change Paradigm?
by
Alberto Pagotto, Floriana Campanile, Paola Conti, Francesca Prataviera, Paola Della Siega, Sarah Flammini, Simone Giuliano, Luca Martini, Davide Pecori, Assunta Sartor, Maria Screm, Tosca Semenzin and Carlo Tascini
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 249-259; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020020 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
(1) Background: Granulicatella adiacens is a former nutritionally variant streptococci (NVS). NVS infective endocarditis (IE) is generally characterized by a higher rate of morbidity and mortality, partially due to difficulties in choosing the most adequate microbiological culture method and the most effective treatment
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Granulicatella adiacens is a former nutritionally variant streptococci (NVS). NVS infective endocarditis (IE) is generally characterized by a higher rate of morbidity and mortality, partially due to difficulties in choosing the most adequate microbiological culture method and the most effective treatment strategy, and partially due to higher rates of complications, such as heart failure, peripheral septic embolism, and peri-valvular abscess, as well as a higher rate of valve replacement. Depending on the affected valve (native valve endocarditisNVE, or prosthetic valve endocarditisPVE), the American Heart Association (AHA) 2015 treatment guidelines (GLs) suggest penicillin G, ampicillin, or ceftriaxone plus gentamicin (2 weeks for NVE and up to 6 weeks for PVE), while vancomycin alone may be a reasonable alternative in patients who are intolerant of β-lactam therapy. The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2023 GLs recommend treating NVE with penicillin G, ceftriaxone, or vancomycin for 6 weeks, suggesting combined with an aminoglycoside (AG) for at least the first 2 weeks only for PVE; likewise, the same recommendations for IE due to Enterococcus faecalis. (2) Methods: Starting from the case of a 51-year-old man with G. adiacens aortic bio-prosthesis IE who was successfully treated with aortic valve replacement combined with double beta-lactams, an AG-sparing regimen, we performed microbiology tests in order to validate this potential treatment change. (3) Results: As for E. faecalis IE, we found that the combination of ampicillin plus cephalosporines (like ceftriaxone or ceftobiprole) showed a synergistic effect in vitro, probably due to wider binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), thus contributing to enhanced bacterial killing and good clinical outcome, as well as avoiding the risk of nephrotoxicity due to AG association therapy. (4) Conclusions: Further studies are required to confirm this hypothesis, but double beta-lactams and an adequate sourcecontrol could be a choice in treating G. adiacens IE.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bacterial Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
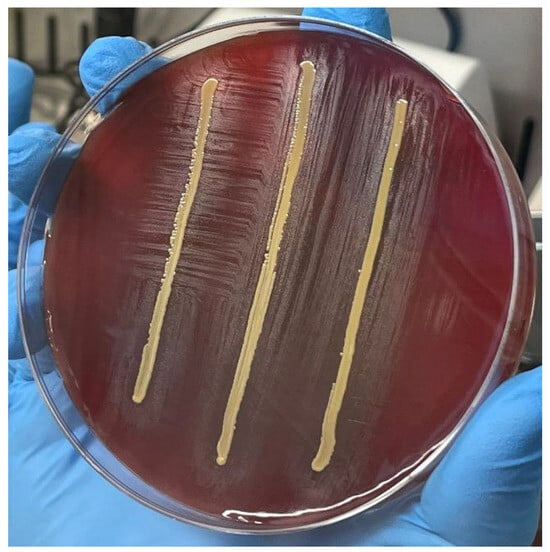
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Risk Factors for Late HIV Presentation in Patients Treated at a Single Belgian Reference Centre from 2018 to 2022
by
Damien Scaia, Karine Fombellida, Nathalie Maes, Majdouline El Moussaoui and Gilles Darcis
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 239-248; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020019 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
A late HIV diagnosis is associated with increased mortality and morbidity, increased healthcare costs and increased onward viral transmission. In this regard, we retrospectively analysed the characteristics of patients who presented for care at our centre from January 2018 to December 2022 to
[...] Read more.
A late HIV diagnosis is associated with increased mortality and morbidity, increased healthcare costs and increased onward viral transmission. In this regard, we retrospectively analysed the characteristics of patients who presented for care at our centre from January 2018 to December 2022 to assess the proportion of patients and factors associated with late HIV presentation. We collected data from the Liège University Hospital database, and we used binary logistic regression models to analyse the impact of individuals’ characteristics on late presentation. Among 167 participants, 38.3% were late presenters (LPs) (presenting for care with a CD4+ T-cell count < 350 cells/mm3 or after an AIDS-defining event), and 21.6% were late presenters with advanced disease (LPs-AD) (presenting for care with a CD4+ T-cell count < 200 cells/mm3 or after an AIDS-defining event). The risk of being an LPs-AD was increased in older individuals (OR on log-transformed age: 7.5) and individuals of sub-Saharan African origin compared to individuals of Belgian or other origin (ORs of 0.30 and 0.25, respectively). The results of this study suggest that broadening the focus beyond the previously common risk groups is essential to prevent late diagnosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section HIV-AIDS)
►▼
Show Figures
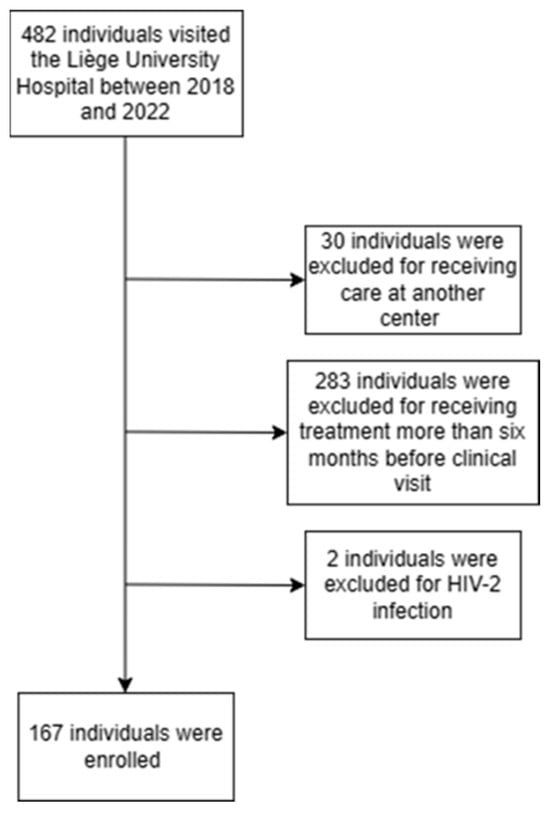
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adverse Outcomes of Patients with Non-Ventilator-Associated Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (nvHAP)—A Single Centre Cohort Study
by
Enrica Amodio, Peter W. Schreiber, Mirjam Faes Hesse and Aline Wolfensberger
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 228-238; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020018 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
Non-ventilator associated hospital-acquired pneumonia (nvHAP) is a common nosocomial infection, but little is known about the outcomes of patients with nvHAP and the risk factors for adverse outcomes. In this retrospective study conducted in a Swiss tertiary care centre, adverse outcomes like in-hospital
[...] Read more.
Non-ventilator associated hospital-acquired pneumonia (nvHAP) is a common nosocomial infection, but little is known about the outcomes of patients with nvHAP and the risk factors for adverse outcomes. In this retrospective study conducted in a Swiss tertiary care centre, adverse outcomes like in-hospital mortality, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and mechanical ventilation, both all-cause and nvHAP-associated, were investigated. Of 244 patients with nvHAP, 72 (30%) died, 35 (14%) deaths were attributed to nvHAP. While 36 (15%) patients acquired nvHAP on the ICU, another 173 patients were eligible for ICU-transferral, and 76 (43.9%) needed ICU-admission. Of all patients hospitalized on the ICU 58 (51.8%) needed intubation due to nvHAP. Multivariable logistic regression analysis identified lower body mass index (OR per unit increase: 0.90, 95%CI: 0.82–0.98) and lower haemoglobin on admission (OR per unit in g/l increase: 0.98, 95%CI: 0.97–1.00) as patient specific factors independently associated with nvHAP-associated mortality. Given the frequency of nvHAP adverse outcomes, hospitals should evaluate increasing nvHAP prevention efforts, especially for patients at high risk for nvHAP mortality. To what extent pneumonia prevention interventions do lower nvHAP mortality in these patients is still to be evaluated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Infection Prevention and Control)
►▼
Show Figures
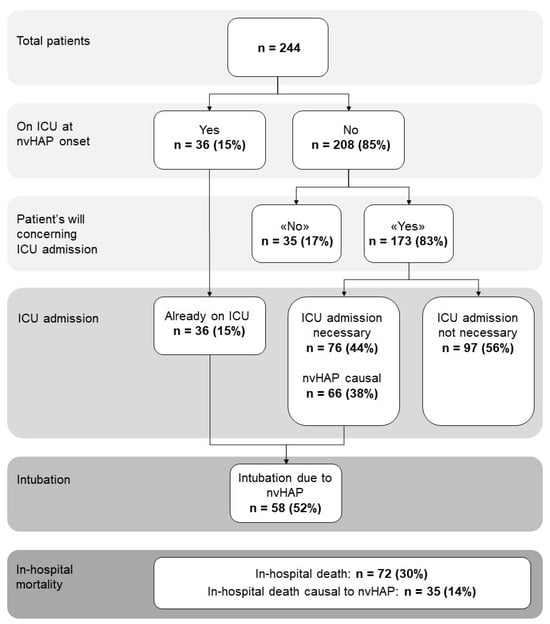
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Tackling Infectious Diseases with Rapid Molecular Diagnosis and Innovative Prevention
by
Rabeea F. Omar, Maurice Boissinot, Ann Huletsky and Michel G. Bergeron
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 216-227; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020017 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
Infectious diseases (IDs) are a leading cause of death. The diversity and adaptability of microbes represent a continuing risk to health. Combining vision with passion, our transdisciplinary medical research team has been focussing its work on the better management of infectious diseases for
[...] Read more.
Infectious diseases (IDs) are a leading cause of death. The diversity and adaptability of microbes represent a continuing risk to health. Combining vision with passion, our transdisciplinary medical research team has been focussing its work on the better management of infectious diseases for saving human lives over the past five decades through medical discoveries and innovations that helped change the practice of medicine. The team used a multiple-faceted and integrated approach to control infectious diseases through fundamental discoveries and by developing innovative prevention tools and rapid molecular diagnostic tests to fulfill the various unmet needs of patients and health professionals in the field of ID. In this article, as objectives, we put in context two main research areas of ID management: innovative infection prevention that is woman-controlled, and the rapid molecular diagnosis of infection and resistance. We also explain how our transdisciplinary approach encompassing specialists from diverse fields ranging from biology to engineering was instrumental in achieving success. Furthermore, we discuss our vision of the future for translational research to better tackle IDs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pulmonary Involvement in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Systematic Review
by
Illari Sechi, Narcisa Muresu, Biagio Di Lorenzo, Laura Saderi, Mariangela Puci, Stefano Aliberti, Ivana Maida, Michele Mondoni, Andrea Piana and Giovanni Sotgiu
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 200-215; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020016 - 28 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a non-malignant disease, characterized by the production of wart-like growths in the respiratory tract, affecting both young people and adults (juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, JORRP, and adult-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, AORRP, respectively). Infection caused by human papillomavirus (HPV)
[...] Read more.
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a non-malignant disease, characterized by the production of wart-like growths in the respiratory tract, affecting both young people and adults (juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, JORRP, and adult-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, AORRP, respectively). Infection caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) is known as the main factor involved in RRP development. Complications of RRP may rarely occur, including lung involvement and malignant transformation. The present systematic review aimed to evaluate the prevalence of severe complications, such as lung involvement and lung tumor in JORRP and AORRP patients, and assess the role of HPV genotypes in the progression of disease severity following the guideline for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA Statement). A total of 378 studies were found on PubMed and Scopus using the following MESH terms: “recurrent respiratory papillomatosis and lung tumor” and “pulmonary tumor and recurrent respiratory papillomatosis”. Basing on inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 11 studies were included in the systematic review. We found a pooled prevalence of 8% (95% CI: 4–14%; I2: 87.5%) for lung involvement in RRP patients. In addition, we found a pooled risk difference of 5% in lung involvement between JORRP and AORRP (95% CI: −7–18%; I2: 85.6%, p-value: 0.41). Among patients with lung involvement, we observed a pooled prevalence of lung tumor of 4% (95% CI:1–7%; I2: 67.1%) and a pooled prevalence mortality for this group of 4% (95% CI:2–6%; I2: 0%). Overall, the positivity rate for HPV-6 and -11 in patients with RRP was 91%. Considering only cases with pulmonary involvement, the pooled prevalence for HPV-11 was 21% (95% CI: 5–45%; I2: 77.2%). Our results evidenced a low/middle risk of pulmonary involvement and lung tumor in JORRP and AORRP patients, with an increased risk for HPV-11-positive patients. Further studies should be performed to improve knowledge and adopt preventive measures to contrast the progression to severe diseases in RRP patients.
Full article
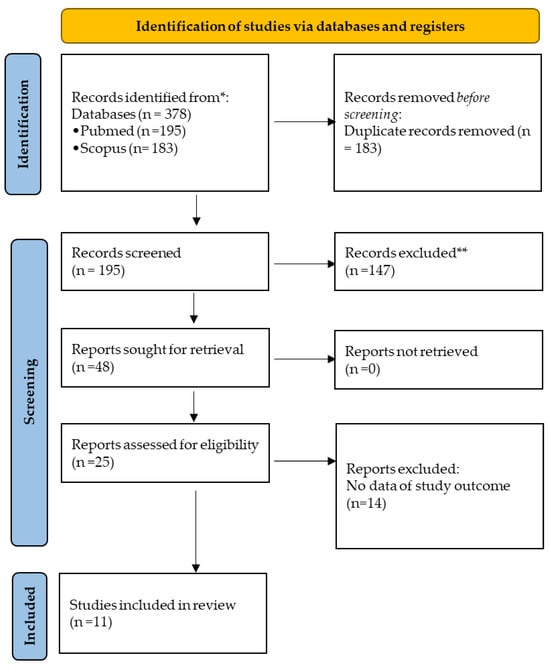
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Radiological Explorations of Patients with Upper or Febrile Urinary Tract Infection
by
Katia Vanolli, Mike Libasse Jost, Olivier Clerc, Daniel Genné and Gregor John
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 189-199; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020015 - 23 Feb 2024
Abstract
Recent European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines and a clinical prediction rule developed by Van Nieuwkoop et al. suggest simple criteria for performing radiological imaging for patients with a febrile urinary tract infection (UTI). We analysed the records of patients with a UTI
[...] Read more.
Recent European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines and a clinical prediction rule developed by Van Nieuwkoop et al. suggest simple criteria for performing radiological imaging for patients with a febrile urinary tract infection (UTI). We analysed the records of patients with a UTI from four hospitals in Switzerland. Of 107 UTI patients, 58% underwent imaging and 69% (95%CI: 59–77%) and 64% (95%CI: 54–73%) of them were adequately managed according to Van Nieuwkoop’s clinical rule and EAU guidelines, respectively. However, only 47% (95%CI: 33–61%) and 57% (95%CI: 44–69%) of the imaging performed would have been recommended according to their respective rules. Clinically significant imaging findings were associated with a history of urolithiasis (OR = 11.8; 95%CI: 3.0–46.5), gross haematuria (OR = 5.9; 95%CI: 1.6–22.1) and known urogenital anomalies (OR = 5.7; 95%CI: 1.8–18.2). Moreover, six of 16 (38%) patients with a clinically relevant abnormality displayed none of the criteria requiring imaging according to Van Nieuwkoop’s rule or EAU guidelines. Thus, adherence to imaging guidelines was suboptimal, especially when imaging was not recommended. However, additional factors associated with clinically significant findings suggest the need for a new, efficient clinical prediction rule.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bacterial Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
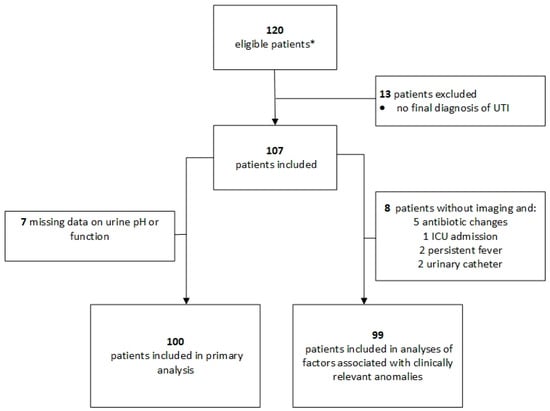
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
The Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Helicobacter pylori Detected in Dyspeptic Patients in North–Central Bangladesh
by
Syeda Jannatul Ferdaus, Shyamal Kumar Paul, Syeda Anjuman Nasreen, Nazia Haque, Mohammad Sadekuzzaman, Mohammad Reazul Karim, Syed Mahmudul Islam, Abdullah Al Mamun, Fardousi Akter Sathi, Proma Basak, Rifat Binte Nahid, Suraiya Aktar and Nobumichi Kobayashi
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 181-188; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020014 - 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
Chronic infection of Helicobacter pylori represents a key factor in the etiology of gastrointestinal diseases, with high endemicity in South Asia. The present study aimed to determine the prevalence of H. pylori among dyspeptic patients in north–central Bangladesh (Mymensingh) and analyze risk factors
[...] Read more.
Chronic infection of Helicobacter pylori represents a key factor in the etiology of gastrointestinal diseases, with high endemicity in South Asia. The present study aimed to determine the prevalence of H. pylori among dyspeptic patients in north–central Bangladesh (Mymensingh) and analyze risk factors of infection and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) determinants in the pathogen. Endoscopic gastrointestinal biopsy samples were collected from dyspeptic patients for a one-year period from March 2022 and were checked for the presence of H. pylori via the rapid urease test and PCR and further analyzed for the status of virulence factors vacA/cagA and genetic determinants related to AMR via PCR with direct sequencing or RFLP. Among a total of 221 samples collected, 80 (36%) were positive for H. pylori, with the vacA+/cagA+ genotype being detected in almost half of them. H. pylori was most prevalent in the age group of 41–50-year-olds, with it being more common in males and rural residents with a lower economic status and using nonfiltered water, though the rates of these factors were not significantly different from those of the H. pylori-negative group. Relatively higher frequency was noted for the A2147G mutation in 23S rRNA, related to clarithromycin resistance (18%, 7/39). Amino acid substitutions in PBP-1A (T556S) and GyrA (N87K and D91N) and a 200 bp deletion in rdxA were detected in samples from some patients with recurrence after treatment with amoxicillin, levofloxacin, and metronidazole, respectively. The present study describes the epidemiological features of H. pylori infection in the area outside the capital in Bangladesh, revealing the spread of AMR-associated mutations.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Monkeypox (MPOX) Knowledge and Vaccination Intention among Health and Life Sciences Students in Algeria: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Mohamed Lounis, Ahmed Hamimes and Ali Dahmani
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 170-180; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020013 - 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
Monkeypox (MPOX) is a viral zoonotic disease affecting endemically the Central and Western regions of Africa. The ongoing outbreak in non-endemic countries has made this disease a global concern. While no cases have been reported in Algeria, it is important to raise awareness
[...] Read more.
Monkeypox (MPOX) is a viral zoonotic disease affecting endemically the Central and Western regions of Africa. The ongoing outbreak in non-endemic countries has made this disease a global concern. While no cases have been reported in Algeria, it is important to raise awareness about the disease to prepare for a potential outbreak, especially in light of the cases reported in neighboring Middle East and North African (MENA) countries. This study aimed to evaluate the knowledge and attitude of Algerian Health and Life Sciences students toward MPOX and its vaccine through an anonymous online survey. A total of 196 students participated in this study. Students of medicine (64.3%), females (85.7%), and those under 20 years of age (55.1%) were the most represented. The results revealed a low level of knowledge represented by a score of only 42.8% for correct answers with multiple gaps in epidemiology, etiology, and clinical manifestations of MPOX. Students of veterinary sciences showed the highest levels of knowledge (OR: 6.71; CI95%: 1.23–36.77), while those aged between 20 and 30 years old (OR: 0.11; CI95%: 0.02–0.79) and those vaccinated against seasonal flu (OR: 0.42; CI95%: 0.21–0.85) were associated with low levels of knowledge. Regarding MPOX vaccination, the study found a moderate level of acceptance (48.5%) among the surveyed students with Natural and Life Sciences students and those having a high vaccine conspiracy belief score (VCBS) showing the lowest level of acceptance. These findings highlight the need for educational programs and intensified public awareness campaigns to improve knowledge about MPOX and emphasize the importance of vaccination in preventing outbreaks and overcoming vaccine reluctance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Human Monkeypox Research)
►▼
Show Figures
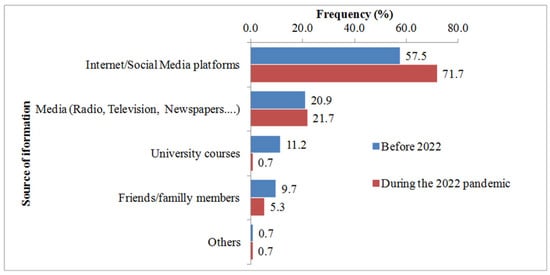
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in Patients with Tick-Borne Illness: A Scoping Review of 98 Cases
by
Dorde Jevtic, Marilia Dagnon da Silva, Alberto Busmail Haylock, Charles W. Nordstrom, Stevan Oluic, Nikola Pantic, Milan Nikolajevic, Nikola Nikolajevic, Magdalena Kotseva and Igor Dumic
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 154-169; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020012 - 21 Feb 2024
Abstract
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) secondary to tick-borne infections is a rare but potentially life-threatening syndrome. We performed a scoping review according to PRISMA guidelines to systematically analyze the existing literature on the topic. A total of 98 patients were included, with a mean age
[...] Read more.
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) secondary to tick-borne infections is a rare but potentially life-threatening syndrome. We performed a scoping review according to PRISMA guidelines to systematically analyze the existing literature on the topic. A total of 98 patients were included, with a mean age of 43.7 years, of which 64% were men. Most cases, 31%, were reported from the USA. Immunosuppression was present in 21.4%, with the most common cause being previous solid organ transplantation. Constitutional symptoms were the most common, observed in 83.7% of the patients, while fever was reported in 70.4% of cases. Sepsis was present in 27.6%. The most common laboratory abnormalities in this cohort were thrombocytopenia in 81.6% of patients, while anemia, leukopenia, and leukocytosis were observed in 75.5%, 55.1%, and 10.2%, respectively. Liver enzyme elevation was noted in 63.3% of cases. The H-score was analyzed in 64 patients, with the mean value being 209, and bone marrow analysis was performed in 61.2% of patients. Ehrlichia spp. was the main isolated agent associated with HLH in 45.9%, followed by Rickettsia spp. in 14.3% and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in 12.2%. Notably, no patient with Powassan virus infection or Lyme borreliosis developed HLH. The most common complications were acute kidney injury (AKI) in 35.7% of patients, shock with multiple organ dysfunction in 22.5%, encephalopathy/seizure in 20.4%, respiratory failure in 16.3%, and cardiac complications in 7.1% of patients. Treatment included antibiotic therapy alone in 43.9%, while 5.1% of patients were treated with immunosuppressants alone. Treatment with both antibiotics and immunosuppressants was used in 51% of patients. Appropriate empiric antibiotics were used in 62.2%. In 43.9% of cases of HLH due to tick-borne disease, patients received only antimicrobial therapy, and 88.4% of those recovered completely without the need for immunosuppressive therapy. The mortality rate in our review was 16.3%, and patients who received inappropriate or delayed empiric therapy had a worse outcome. Hence, we suggest empiric antibiotic treatment in patients who are suspected of having HLH due to tick-borne disease or in whom diagnostic uncertainty persists due to diagnostic delay in order to minimize mortality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bacterial Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
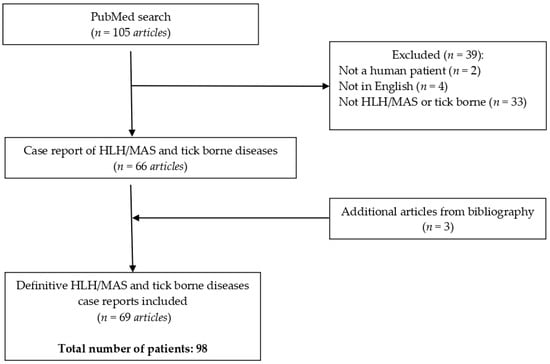
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Excess Mortality Stratified by Age and Sex for Croatia and Croatian Counties during the 2020–2021 COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Mara Šošić, Zvonimir Boban, Marijan Erceg and Nataša Boban
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 142-153; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16020011 - 20 Feb 2024
Abstract
Excess mortality is often used to estimate the effect of a certain crisis on the population. It is defined as the number of deaths during a crisis exceeding the expected number based on historical trends. Here, we calculated excess mortality due to the
[...] Read more.
Excess mortality is often used to estimate the effect of a certain crisis on the population. It is defined as the number of deaths during a crisis exceeding the expected number based on historical trends. Here, we calculated excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic for Croatia in the 2020–2021 period. The excess was calculated on the national and county level for different age and sex categories. In addition to the absolute number, the excess mortality was also expressed as a ratio of excess deaths to the predicted baseline and excess mortality rate. We showed that using both measures is necessary to avoid incorrect conclusions. The estimated excess mortality on the national level was 14,963, corresponding to an excess percentage of 14.3%. With respect to sex, there was a higher excess mortality rate for men compared to women. An exponential relationship was observed between age and the excess mortality rate.These trends wee representative of most counties as well, with large variations in the magnitude of the effect. However, there were also exceptions to the general rule. The reasons for these deviations were discussed in terms of between-county differences in demographic structure, population density and special events that took place during the pandemic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Infections: Epidemiology, Diagnostics, Clinics and Evolution)
►▼
Show Figures
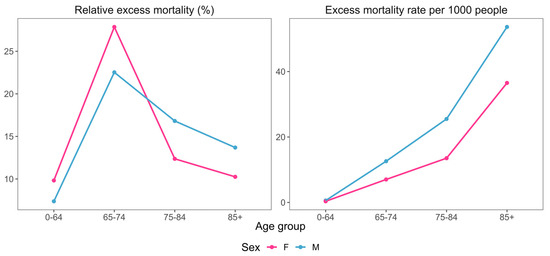
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Intention to Recommend RSV Vaccination: A Cross-Sectional Survey of Cardiologists and Cardiac Nurses in Southern Italy
by
Domenico Ponticelli, Lorenzo Losa, Ippazio Cosimo Antonazzo, Anna Zampella, Fabio Di Marino, Gaetano Mottola, Mara Noemi Fede, Fortuna Gallucci, Roberto Magliuolo, Antonio Rainone, Antonella Arcari, Carmine Del Giudice and Pietro Ferrara
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 128-141; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16010010 - 15 Feb 2024
Abstract
As respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine distribution gains traction in Europe and Italy, healthcare workers (HCWs) can strategize about vaccine promotion to increase uptake among patients at risk of RSV consequences, such cardiac patients. This cross-sectional survey investigated the knowledge about and attitude
[...] Read more.
As respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine distribution gains traction in Europe and Italy, healthcare workers (HCWs) can strategize about vaccine promotion to increase uptake among patients at risk of RSV consequences, such cardiac patients. This cross-sectional survey investigated the knowledge about and attitude towards RSV and RSV vaccines, and the intention to recommend vaccination within a cardiological hospital in Italy. To explore factors associated with the outcomes of interest, multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted. Of 197 invited HCWs, 78.2% returned the survey. The knowledge about market authorisation for new RSV vaccines for older adults (present in 46.9% of respondents) was significantly associated with the HCWs’ age, education, and previous update on vaccinations. HCWs with a higher educational level and those with a positive attitude towards RSV vaccines safety reported a higher attitude towards the importance of vaccinating people at risk. The willingness of recommending RSV vaccination to patients (70.5% of respondents) was more likely in HCWs who were knowledgeable about market authorisation for RSV vaccines and in physicians. This tempestive research sheds light on current factors influencing the strategies of cardiac HCWs regarding RSV vaccination. The results suggest the need for training events on the protective role of RSV vaccination in cardiac patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Global Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus)
►▼
Show Figures
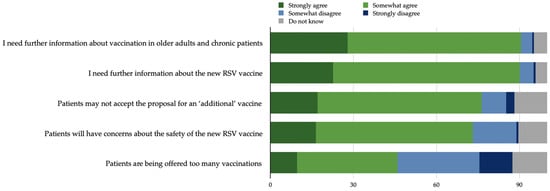
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Diseases, Infectious Disease Reports, Pathogens, Viruses, TropicalMed
Human Monkeypox Research
Topic Editors: Shailendra K. Saxena, Ahmed Sayed Abdel-MoneimDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Diagnostics, Diseases, Healthcare, Infectious Disease Reports, JCM
Post COVID-19: Latest Advances, Challenges and Methodologies
Topic Editors: Yudong Zhang, Juan Manuel GorrizDeadline: 4 September 2024
Topic in
Gastroenterology Insights, Infectious Disease Reports, Life, Microbiology Research, Microorganisms
High-Throughput Analyses as a Multi-Faceted Approach for Characterizing the Human Microbiota
Topic Editors: Simone Filardo, Rosa Sessa, Andrea Carolina EntrocassiDeadline: 30 October 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Zoonotic Viruses Responsible for Encephalitis: New Advanced Research
Guest Editor: Philippe PérotDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
Guest Editors: Sachiko Sato, Marc Ouellette, Rabeea OmarDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Emerging and Reemerging Infections of the Central Nervous System
Guest Editor: Sofia R. ValdoleirosDeadline: 30 September 2024
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Emerging Infections: Epidemiology, Diagnostics, Clinics and Evolution
Guest Editors: Massimo Ciccozzi, Marta GiovanettiDeadline: 31 October 2024






