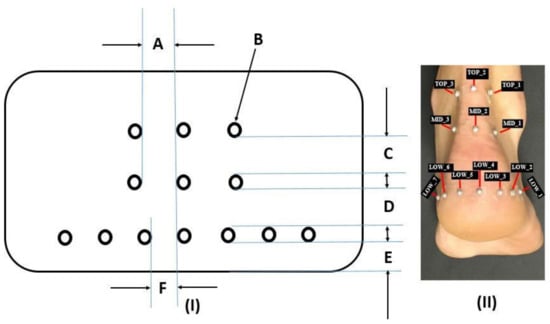
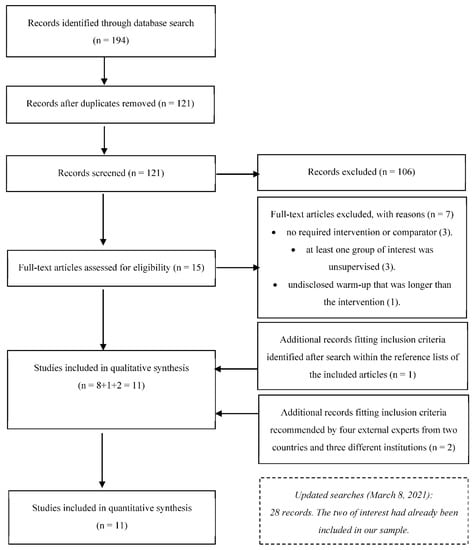
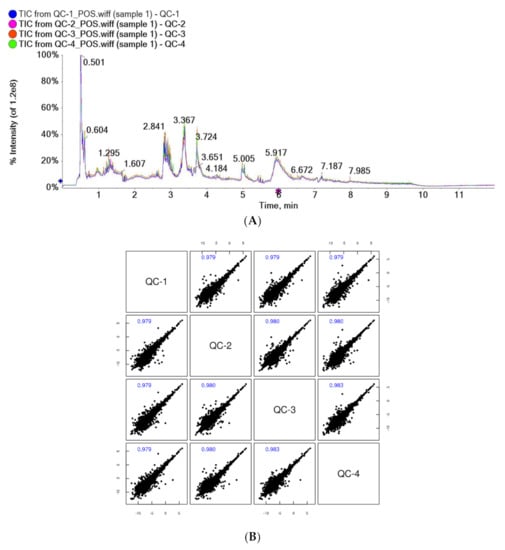
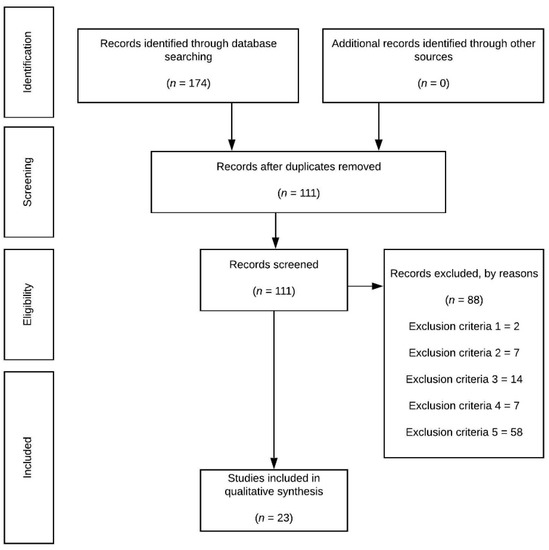
Sport and Exercise Medicine
A topical collection in Healthcare (ISSN 2227-9032).
Viewed by 177794Editors
Interests: children health; school health; quality of life; body composition; exercise training; health; physical activity; sport performance; soccer training; reliability and validity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: health sciences; active methodologies; physical education
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Practicing sports and exercise is one of the most effective non-pharmacological approaches for improving physical and mental health. Additionally, there is consistent evidence about the beneficial effect of sports and exercise on the clinical population which may meaningfully benefit from regular practice, contributing toward regulating the progression of specific diseases or even reducing drug need. Due to the importance of sports and exercise, it is essential to improve the clinical practice that may include this non-pharmacological strategy as part of a multidisciplinary approach. Interactions with drugs, nutrition, or other strategies also need to be further researched for a great overview of the impact of all of them, acting together to benefit health.
Therefore, this Special Issue’s focus is to open a window of opportunity to publish articles that reveal the effects of using sports and exercises as a single or combined approach for healthcare in clinical and non-clinical populations. Considering that more research should be conducted and published about such important topics, the aim of the Special Issue “Sport and Exercise Medicine” is to publish original, high-quality investigations and narrative and systematic reviews in the field of health care, sports, and exercise. We look forward to receiving contributions related (but not limited) to the following topics: (i) experimental studies and interventions using sports and exercise in healthy or clinical populations; (ii) observational analytic studies identifying the effects of practicing sport and exercise on health and quality of life; (iii) systematic reviews and meta-analyses that may summarize the evidence about the effects of sport and exercise on healthy and clinical populations.
Prof. Dr. Jorge Pérez-Gómez
Dr. Jorge Carlos-Vivas
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Healthcare is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- sports medicine
- clinical Exercise
- recreational sport
- preventive health
- health care