Clinical Simulation in Health Sciences
A topical collection in Healthcare (ISSN 2227-9032). This collection belongs to the section "Nursing".
Viewed by 56737
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. José Luis Díaz Agea
Dr. José Luis Díaz Agea
 Dr. José Luis Díaz Agea
Dr. José Luis Díaz Agea
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Faculty of Nursing, Catholic University of Murcia, 30107 Guadalupe, Spain
Interests: nursing
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Special Issue encompassing all areas of applications and research in healthcare simulation technology and reflects its mission to advance the science of healthcare simulation. The journal is relevant to a broad range of health professionals. Priority will be given to research results related to safety and quality-oriented training programs, the development of educational and competency assessments, and reports of experience in the use of simulation technology and virtual reality.
Dr. Cesar Leal-Costa
Dr. José Luis Díaz Agea
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Healthcare is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Clinical simulation
- Safety and quality-oriented training programs
- Development of educational and competency assessment
- Non-technical skills, clinical skills
- Innovative teaching/learning strategies using simulation
- Clinical and academic uses of simulation
- Leadership for simulation
- Virtual reality
Published Papers (20 papers)
Open AccessArticle
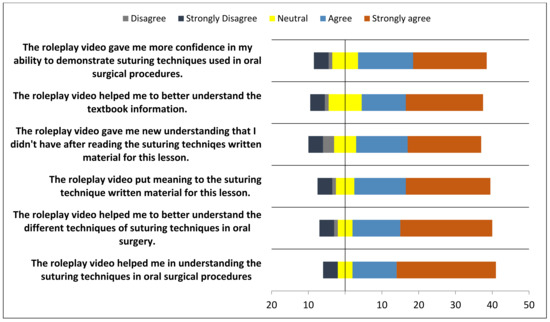
Quantitative Evaluation of Dental Students’ Perceptions of the Roleplay-Video Teaching Modality in Clinical Courses of Dentistry: A Pilot Study
by
Kiran Kumar Ganji, Anil Kumar Nagarajappa, Mohammed G Sghaireen, Kumar Chandan Srivastava, Mohammad Khursheed Alam, Shadi Nashwan, Ahmad Al-Qerem and Yousef Khader
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1328
Abstract
In the modern era of dentistry, role modeling/roleplaying is one of the most prevalent and recommended methods of dental education. Working on video production projects and using student-centred learning also help students create feelings of ownership and self-esteem. This study aimed to compare
[...] Read more.
In the modern era of dentistry, role modeling/roleplaying is one of the most prevalent and recommended methods of dental education. Working on video production projects and using student-centred learning also help students create feelings of ownership and self-esteem. This study aimed to compare students’ perceptions of roleplay videos among genders, different disciplines of dentistry, and different levels of dental students. This study included 180 third- and fourth-year dental students registered in courses such as ‘Introduction to Dental Practice’ and ‘Surgical management of oral and maxillofacial diseases’, respectively, at the College of Dentistry at Jouf University. Four groups of recruited participants were pre-tested using a questionnaire about their clinical and communication skills. The students were tested again using the same questionnaire at the end of the workshop to evaluate improvements in their skills. The students were then assigned to create roleplay videos with respect to demonstrated skills related to all three disciplines (Periodontics, Oral Surgery, and Oral Radiology) in a week’s time. Students’ perceptions of the roleplay video assignments were collected through a questionnaire survey. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare responses for each section of the questionnaire (
p < 0.05). Improvements in problem-solving and project management skills during video production were reported by 90% of the participants. No significant difference (
p > 0.05) in the mean scores of the responses was found with respect to the type of discipline involved in the process. There was a significant difference in the mean scores of the responses between male and female students (
p < 0.05). The fourth year participants demonstrated increased mean scores and significantly higher (
p < 0.05) mean scores than third-year participants. Students’ perceptions of roleplay videos differed by gender and the level of the students, but not by the type of discipline.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
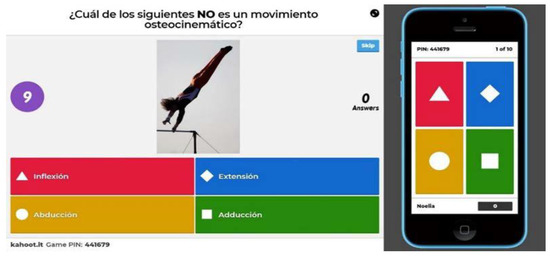
Study Based on Gamification of Tests through Kahoot!™ and Reward Game Cards as an Innovative Tool in Physiotherapy Students: A Preliminary Study
by
Irene Cortés-Pérez, Noelia Zagalaz-Anula, María del Carmen López-Ruiz, Ángeles Díaz-Fernández, Esteban Obrero-Gaitán and María Catalina Osuna-Pérez
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3417
Abstract
Background:
Kahoot! is an educational tool allowing teachers to create a series of gamified tests with the aim of reinforcing educational content, thus improving the teaching-learning process. The objective of this project is to evaluate the acquisition of content through gamified tests with
[...] Read more.
Background:
Kahoot! is an educational tool allowing teachers to create a series of gamified tests with the aim of reinforcing educational content, thus improving the teaching-learning process. The objective of this project is to evaluate the acquisition of content through gamified tests with
Kahoot! and reward cards compared to the traditional teaching methodology (contents not reinforced). Methods: This Physiotherapy Teaching Innovation Project (PTIP) was carried out in four subjects of the Degree in Physiotherapy at the University of Jaén (Spain). The teachers responsible for each subject were instructed in the use of
Kahoot! and reward cards. These teachers randomly selected the contents that were going to be reinforced with
Kahoot! while the other 50% of the contents would not be reinforced. In the final exam of each subject, the results related to the reinforced contents were compared with those non-reinforced and the degree of satisfaction of the students with the experience was evaluated. Results: A total of 313 students participated in this PTIP. In all subjects, we determined a significant increase in the number of correct answers in an improvement range from 7% (95% CI 3.85 to 9.38) to more than 20% (95% CI 17.61 to 26.86) in favor of the questions that alluded to reinforced content using
Kahoot! compared to the non-reinforced contents. More than 90% of the participants considered the use of
Kahoot! useful and motivating. Our findings showed that
Kahoot! motivated more than 65% of students to study daily. Conclusions: The students obtained better academic results in the questions related to contents reinforced with tests through
Kahoot! and reward cards compared to those non-reinforced, showing that this methodology can be an effective tool to promote retention and content assimilation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Competencies in Basic Life Support after a Course with or without Rescue Ventilation: Historical Cohort Study
by
Jordi Castillo, Adrián González-Marrón, Anna Llongueras, Laia Camós, Mireia Montané and Encarnación Rodríguez-Higueras
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1037
Abstract
Background: Simplifying the international guidelines to improve skills after training and their retention over time has been one of the top priorities in recent years. The objective of our study was to compare the results of the practical skills learned during training in
[...] Read more.
Background: Simplifying the international guidelines to improve skills after training and their retention over time has been one of the top priorities in recent years. The objective of our study was to compare the results of the practical skills learned during training in basic life support with and without pulmonary ventilation. Methods: This was a comparative study of historical cohorts consisting of undergraduate students in health sciences. In one cohort, rescue breathing was performed, and in the other, it was not. The same data collection instruments were used for both cohorts: a test type examination of knowledge, data from a smart mannequin and an instructor observation grid. The means of knowledge and practical skills scores collected by the mannequin were compared using independent sample t-tests. Results: 497 students were recruited without significant differences between the two cohorts. The mean scores for knowledge and skills determined by the instructor and the mannequin were statistically higher in the cohort that did not perform rescue breathing. Conclusion: Students who participated in basic life support training that did not include rescue breathing scored better than those who participated in training that included this skill. Training with only compressions simplifies the guidelines and increases learning and content retention.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Design and Validation of a Questionnaire to Measure the Perception of Nursing Degree Students about the Learning Process in Primary Care
by
Adrián Almazor-Sirvent, Maria Dolores Miguel-Ruiz, Anna Huguet-Miguel, Bárbara Hurtado-Pardos, Juan Francisco Roldán-Merino, María del Carmen Moreno-Arroyo, Ainoa Biurrún-Garrido, Manuel Vicente Garnacho-Castaño and Anna Escofet
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1155
Abstract
The aim of this study was to develop a tool for the evaluation of the learning process of the clinical practicum in primary care. The study was carried out in two phases: (1) identification of the categories that determine the perception of the
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to develop a tool for the evaluation of the learning process of the clinical practicum in primary care. The study was carried out in two phases: (1) identification of the categories that determine the perception of the nursing degree students about the learning process in the clinical practicum in primary care and the items for each category; and (2) cross-sectional study in a sample of 475 nursing degree students. The psychometric properties in terms of reliability (internal consistency) and construct validity were analyzed through a confirmatory factor analysis. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of internal consistency for the entire questionnaire was 0.93, and that for each of the categories was above 0.70 in all cases. The chi-squared test was statistically significant (2.84;
p < 0.001). The confirmatory factor analysis produced a model of 6 dimensions and 41 items. The parameters were estimated through the least squares method. All saturations were statistically significant (
p < 0.05). In view of the results of this study, it can be asserted that the questionnaire to measure the perception of the nursing degree students about the learning process in the community clinical practicum (QPCLP) presents good properties in terms of internal consistency and validity.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
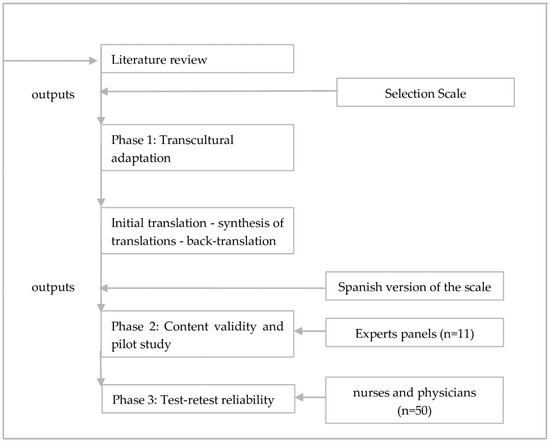
Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the Instrument “Nurse–Physician Relationship Survey: Impact of Disruptive Behavior in Patient Care” to the Spanish Context
by
Pedro Moreno-Leal, César Leal-Costa, José Luis Díaz-Agea, Ismael Jiménez-Ruiz, María Suarez-Cortés and Adriana Catarina De Souza Oliveira
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1340
Abstract
Disruptive behavior in the healthcare context has an impact on patient care, healthcare personnel, and the health organization, and it also influences the therapeutic relationship, communication process, and adverse events. However, there is a lack of instruments that could be used for its
[...] Read more.
Disruptive behavior in the healthcare context has an impact on patient care, healthcare personnel, and the health organization, and it also influences the therapeutic relationship, communication process, and adverse events. However, there is a lack of instruments that could be used for its analysis in the hospital care environment in the Spanish context. The objective of the study was to culturally adapt and perform a content validation of the tool “Nurse–Physician Relationship Survey: Impact of Disruptive Behavior on Patient Care”, to the Spanish content (Spain). An instrumental study was conducted, which included an analysis of conceptual and semantic equivalence. A panel of experts analyzed the translations, by analyzing the Content Validity Index (CVI) of the group of items in the scale through the Relevance Index (RI) and the Pertinence Index (PI). Only a single item obtained an RI value of 0.72, although with PI value of 0.81, with consensus reached for not deleting this item. The CVI of all the items was >0.80 for the mean value of the RI, as well as the PI. The instrument was adapted to the Spanish context and is adequate for evaluating the disruptive behaviors on nurse–physician relationships and its impact on patient care. However, the importance of continuing the analysis of the rest of the psychometric properties in future studies is underlined.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
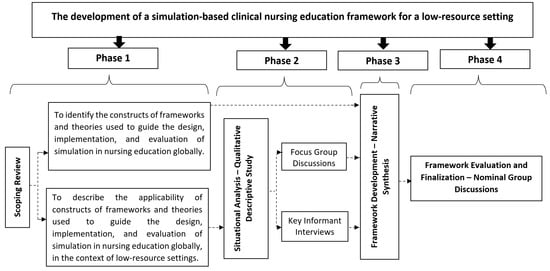
A Simulation-Based Clinical Nursing Education Framework for a Low-Resource Setting: A Multimethod Study
by
David Abdulai Salifu, Yolande Heymans and Christmal Dela Christmals
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 3644
Abstract
Simulation-based clinical education is a useful strategy for teaching, learning, and assessing clinical competence in health professions education. However, the use of simulation-based clinical nursing education (SBCNE) in low-resource settings such as Ghana has been hampered by the lack of a context-specific framework
[...] Read more.
Simulation-based clinical education is a useful strategy for teaching, learning, and assessing clinical competence in health professions education. However, the use of simulation-based clinical nursing education (SBCNE) in low-resource settings such as Ghana has been hampered by the lack of a context-specific framework to guide its design, implementation, and evaluation. This study sought to develop a context-specific framework to guide the design, implementation, and evaluation of SBCNE in a low-resource setting. The study employed a sequential multimethod design, comprising a scoping review; qualitative descriptive design (situational analysis) made up of two parts–focus group discussions (FGDs) with post-registration nurses and nursing students, and semi-structured interviews with nurse educators; and narrative synthesis of the scoping review and situational analysis data, used to develop a draft SBCNE framework for a low-resource setting. The draft SBCNE framework was evaluated by stakeholders of nursing education and practice using nominal group discussions. The framework is comprised of five constructs (context, planning, design, community of learning, and outcomes). The user-centric, comprehensive, context-specific SBCNE framework has the potential to enhance the implementation of simulation in nursing education and the development of clinical competence in a low-resource setting. As a result, we urge nursing leaders and nurse educator unions to take the lead in lobbying regulatory bodies, the central government, and their development partners to provide the necessary financial support and resources for the implementation of the framework and adoption of SBCNE in low-resource settings.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Use of the Ultrasound Technique as Compared to the Standard Technique for the Improvement of Venous Cannulation in Patients with Difficult Access
by
Ángeles Rodríguez-Herrera, Álvaro Solaz-García, Enrique Mollá-Olmos, Dolores Ferrer-Puchol, Francisca Esteve-Claramunt, Silvia Trujillo-Barberá, Pedro García-Bermejo and Jorge Casaña-Mohedo
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3670
Abstract
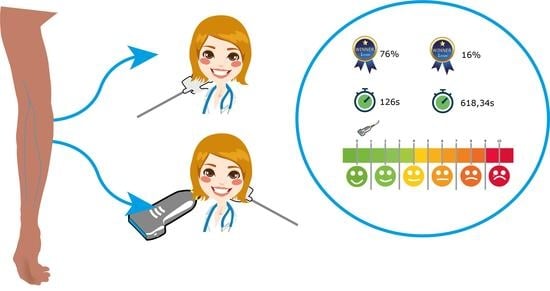
(1) Objective. We aimed to demonstrate that the use of the ultrasound-guided technique facilitates peripheral venous cannulation as compared to the standard technique in patients with difficult access at emergency services. (2) Method. A case–control study, randomized research. Variables were collected from a
[...] Read more.
(1) Objective. We aimed to demonstrate that the use of the ultrasound-guided technique facilitates peripheral venous cannulation as compared to the standard technique in patients with difficult access at emergency services. (2) Method. A case–control study, randomized research. Variables were collected from a population with non-palpable or not visible veins, classified into size risk groups for 6 months. In the comparative analysis, the patients were divided into two groups: the cases group was composed of patients to whom the peripheral venous cannulation was performed with the ultrasound-guided technique (UST), while the control was composed of patients with whom the standard technique (ST) was performed. The ultrasound LOGIQ P5 750VA from General Electric Healthcare, with an 11 mHz linear probe, was utilized, along with peripheral venous catheters model Insyte
TM Autoguard
TM with gauges of 14G to 26G. (3) Results. Seventy-two cases. The use of the ultrasound decreased the time (618.34s ST, 126s UST) and the number of punctures (2.92 ST, 1.23 UST); about 25% of the patients did not have complications with the UST, as compared to 8% with the ST. The use of the ultrasound decreased the pain experienced by 1.44 points in the visual analog scale, as compared to 0.11 points with the ST. The rate of success of the first try with the UST was 76%, as compared to 16% of the ST. The gauge of the catheter increased with the UST, with successful cannulations obtained with 20G (56%) and 18G (41%) gauges. (4) Conclusions. The use of ultrasound facilitates venous cannulation according to the variables of the study. The ultrasound visualization of the vessels is associated with the selection of the catheter gauge. There was no relation between the complications and the depth of the blood vessels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
Disruptive Behavior at Hospitals and Factors Associated to Safer Care: A Systematic Review
by
Pedro Moreno-Leal, César Leal-Costa, José Luis Díaz-Agea, Ismael Jiménez-Ruiz, Antonio Jesús Ramos-Morcillo, María Ruzafa-Martínez and Adriana Catarina De Souza Oliveira
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3461
Abstract
Disruptive behavior creates a dysfunctional culture that has a negative impact on work relations and influences the quality of care and safety of the patient. The objective of the present work is to provide the best methodological quality scientific evidence available on disruptive
[...] Read more.
Disruptive behavior creates a dysfunctional culture that has a negative impact on work relations and influences the quality of care and safety of the patient. The objective of the present work is to provide the best methodological quality scientific evidence available on disruptive behavior at a hospital, the aspect associated with the safety of the patient, and its impact on quality of care. For this, we included studies that addressed the prevalence of disruptive behaviors observed in the area of hospital health and its professionals. The selection, eligibility, data extraction and evaluation of the risk of bias stages were conducted by two researchers, and any discrepancies were solved by a third researcher. The data presented show that disruptive behaviors are frequently observed in the daily life of health professionals, and compromise the quality of care, the safety of the patient, and can lead to adverse effects. The results presented indicate that the appearance of disruptive behaviors compromises the quality of care, the safety of the patient, and the appearance of adverse effects, and can also affect the physical and mental health of the health professionals. PROSPERO registration number: CRD42021248798.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Bedsores Management: Efficiency Simulation of a New Mattress Design
by
Abdullatif Alwasel, Bandar Alossimi, Maha Alsadun and Khalid Alhussaini
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3150
Abstract
Bedsores, also known as pressure ulcers, are wounds caused by the applied external force (pressure) on body segments, thereby preventing blood supply from delivering the required elements to the skin tissue. Missing elements hinder the skin’s ability to maintain its health. It poses
[...] Read more.
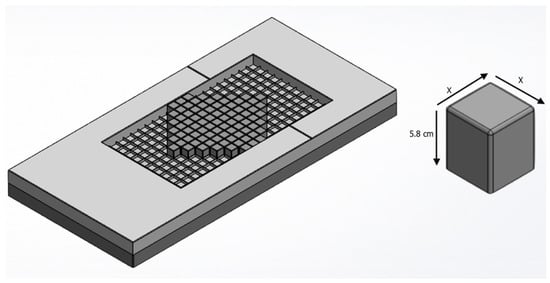
Bedsores, also known as pressure ulcers, are wounds caused by the applied external force (pressure) on body segments, thereby preventing blood supply from delivering the required elements to the skin tissue. Missing elements hinder the skin’s ability to maintain its health. It poses a significant threat to patients that have limited mobility. A new patented mattress design and alternative suggested designs aimed to reduce pressure are investigated in this paper for their performance in decreasing pressure. A simulation using Ansys finite element analysis (FEA) is carried out for comparison. Three-dimensional models are designed and tested in the simulation for a mattress and human anthropometric segments (Torso and Hip). All designs are carried out in solidworks. Results show that the original design can redistribute the pressure and decrease it up to 17% less than the normal mattress. The original design shows better ability to decrease the absolute amount of pressure on the body. However, increasing the surface area of the movable parts results in less pressure applied to the body parts. Thus, this work suggests changing the surface area of the cubes from 25 to 100 cm
2.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Training with High Fidelity Simulation in the Care of Patients with Coronavirus—A Learning Experience in Native Health Care Multi-Professional Teams
by
Andrés Rojo-Rojo, Maria Belén Soto-Castellón, Juan Antonio García-Méndez, César Leal-Costa, Maria Gracia Adánez-Martínez, María José Pujalte-Jesús and José Luis Díaz-Agea
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2370
Abstract
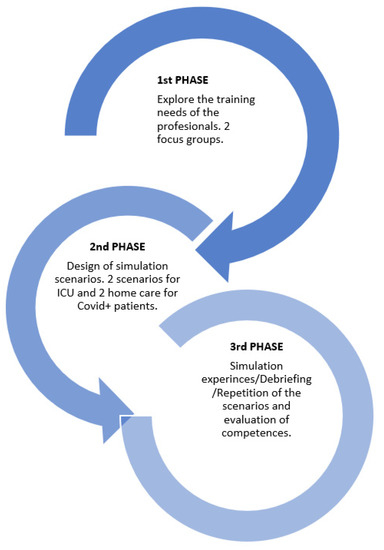
The training of emergency and intensive care teams in technical and non-technical skills is fundamental. The general aim of this study was to evaluate the training of various professional teams with simulations based on the care of COVID-19 patients using Zone 3 simulations
[...] Read more.
The training of emergency and intensive care teams in technical and non-technical skills is fundamental. The general aim of this study was to evaluate the training of various professional teams with simulations based on the care of COVID-19 patients using Zone 3 simulations (native emergency medical services and intensive care units-ICU teams) in the Region of Murcia (Spain). A mixed pilot study was designed (qualitative/quantitative) comprised of three phases: Phase 1: detection of needs (focus groups), Phase 2: design of simulation scenarios, and Phase 3: training with high-fidelity simulation and evaluation of competences. The results were used to determine the real training needs of these health professionals, which were used to design four simulation scenarios in line with these needs. The team competences were evaluated before and after the training session, with increases observed after the training sessions, especially in non-technical skills such as communication. Training with zone 3 simulation, with multi-professional native emergency and intensive care teams who provided care to patients with coronavirus was shown to be an effective method, especially for training in non-technical skills. We should consider the training needs of the professionals before the start of any training program to stay one-step ahead of crisis situations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Korean Advanced Life Support Education on Non-Technical and Technical Skills of Nursing Students: A Pilot Study
by
Yon Hee Seo and Kyong Ah Cho
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1784
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effect of the Korean Advanced Life Support (KALS) education program on the non-technical skills and technical skills of nursing students. This one-group pretest–posttest experimental study included 46 participants who were fourth year nursing students at Shinsung University
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to investigate the effect of the Korean Advanced Life Support (KALS) education program on the non-technical skills and technical skills of nursing students. This one-group pretest–posttest experimental study included 46 participants who were fourth year nursing students at Shinsung University located in Dangjin-si, Chungcheongnam-do Province, Republic of Korea. Data were collected in April 2021 and analyzed via SPSS/WIN 25.0, using a paired samples
t-test. The current study results report a significant improvement in the non-technical skills from 30.58 to 47.16 points (
t = −5.892,
p < 0.001). Furthermore, KALS training improved communication confidence from 23.45 to 35.77 points (
t = −6.563,
p < 0.001), critical thinking tendency from 96.71 to 107.16 points (
t = −3.352,
p = 0.002), and self-efficacy in performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation from 33.56 to 49.81 points (
t = −13.242,
p < 0.001). Lastly, technical skills also improved from 18.35 to 27.94 points (
t = −28.439,
p < 0.001). Therefore, the findings indicate that KALS education was effective in improving the non-technical and technical skills of these nursing students. However, this study did not analyze the effect of the stress level experienced by the study participants in emergency situations on their non-technical and technical skill performance. Thus, future studies should verify the effect of external stressors, caused by unpredictable emergencies, on non-technical and technical skill performance.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
A New Tool for Assessment of Professional Skills of Occupational Therapy Students
by
Dulce Romero-Ayuso, Araceli Ortiz-Rubio, Paz Moreno-Ramírez, Lydia Martín-Martín, José Matías Triviño-Juárez, María Serrano-Guzmán, Enrique Cano-Detell, Erika Novoa-Casasola, Miguel Gea and Patrocinio Ariza-Vega
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2556
Abstract
The assessment of the acquisition of professional skills is an essential process in occupational therapy students. Until now, there has been no standardized and validated instrument for evaluating these skills in Spanish occupational therapy students. This study reports the development and testing of
[...] Read more.
The assessment of the acquisition of professional skills is an essential process in occupational therapy students. Until now, there has been no standardized and validated instrument for evaluating these skills in Spanish occupational therapy students. This study reports the development and testing of the psychometric properties of the professional skills in students of occupational therapy during their practical training. Methods: A new instrument was developed to assess the professional skills of occupational therapy students, called CPTO. A total of 69 occupational therapists participated in evaluating 295 occupational therapy students from the University of Granada, between the 2018 and 2021 academic years. Results: Of a total of 79 items, the factor analysis yielded a final solution of 33 items, which explains 70.22% of the variance with the following three dimensions: (1) self-appraisal and professional responsibility (α = 0.951); (2) communication skills and delivering intervention (α = 0.944); and (3) clinical reasoning for assessing and planning the intervention (α = 0.947). The instrument allows students with low, medium, high and excellent clinical skills to be differentiated according to the cutting points established by the quartiles. Conclusion: the instrument has good psychometric properties, and is a useful tool to assess professional competencies in occupational therapy students during their practice placement education.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
High-Fidelity Virtual Objective Structured Clinical Examinations with Standardized Patients in Nursing Students: An Innovative Proposal during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Oscar Arrogante, Eva María López-Torre, Laura Carrión-García, Alberto Polo and Diana Jiménez-Rodríguez
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 3812
Abstract
In response to the cancellation of in-person objective structured clinical examinations (OSCEs) prompted by confinement due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we designed a solution to adapt our traditional OSCEs to this new reality in nursing education. We implemented an innovative teaching proposal based
[...] Read more.
In response to the cancellation of in-person objective structured clinical examinations (OSCEs) prompted by confinement due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we designed a solution to adapt our traditional OSCEs to this new reality in nursing education. We implemented an innovative teaching proposal based on high-fidelity virtual OSCEs with standardized patients. The purposes of our study were to describe this innovative teaching proposal and compare nursing competence acquisition in final year nursing students through virtual and in-person OSCE modalities. The study included 234 undergraduate students: 123 students were assessed through high-fidelity virtual OSCEs during May 2020, whereas 111 students were assessed through in-person OSCEs during May 2019. The structure of OSCEs, including its stations, clinical simulated scenarios, and checklists, was the same in both OSCE modalities. The effect size of the differences among the competence categories of checklists, including their total scores, was small. Regarding our virtual OSCEs was similarly successful to in-person OSCEs, this online format was found to be useful, feasible, and cost-saving when in-person OSCE was not possible. Therefore, high-fidelity virtual OSCEs with standardized patients could be considered as another choice of OSCE not only in the current COVID-19 pandemic but could also be extended to normal situations, even post-pandemic.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Does Multidisciplinary Team Simulation-Based Training Improve Obstetric Emergencies Skills?
by
Encarna Hernández, Marcos Camacho, César Leal-Costa, María Ruzafa-Martínez, Antonio Jesús Ramos-Morcillo, Eduardo Cazorla and José Luis Díaz-Agea
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3664
Abstract
Clinical simulation in obstetrics has turned out to be a tool that can reduce the rate of perinatal morbidity and mortality. The objective of this study was to analyze the impact and evaluate the effects of training with high-fidelity simulation of obstetric emergencies
[...] Read more.
Clinical simulation in obstetrics has turned out to be a tool that can reduce the rate of perinatal morbidity and mortality. The objective of this study was to analyze the impact and evaluate the effects of training with high-fidelity simulation of obstetric emergencies on a multidisciplinary group. The quasi-experimental research study was structured in three phases: a first phase where the most important obstetric emergencies were determined, a second phase of design and development of the selected cases for simulation training, and a third and final phase where the abilities and satisfaction of the multidisciplinary team were analyzed. Three scenarios and their respective evaluation tools of obstetric emergencies were selected for simulation training: postpartum hemorrhage, shoulder dystocia, and breech delivery. The health professionals significantly improved their skills after training, and were highly satisfied with the simulation experience (
p < 0.05). An inter-observer agreement between good and excellent reliability was obtained. Regarding conclusions, we can state that high-fidelity obstetric emergency simulation training improved the competencies of the health professionals.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Debriefing and Learning Strategies: A Comparison between Two Reflective Analysis Styles with/without a Graphical Record of Strengths/Weaknesses
by
Guillermo Escribano Sánchez, María Ruzafa-Martínez, César Leal-Costa, José Luis Díaz-Agea, Antonio Jesús Ramos-Morcillo and Alfonso García Sánchez
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2419
Abstract
Background: Clinical simulation efficiently complements the training of Nursing Degree students. The debriefing phase is the most important feature of simulation-based learning, where the students are able to acquire the necessary competences. It is at this stage where learning strategies and motivation play
[...] Read more.
Background: Clinical simulation efficiently complements the training of Nursing Degree students. The debriefing phase is the most important feature of simulation-based learning, where the students are able to acquire the necessary competences. It is at this stage where learning strategies and motivation play a crucial role. The objective of the study was to analyze the relationship between the style of debriefing utilized in the simulation sessions, and the learning strategies of Nursing Degree students who participated in a high-fidelity clinical simulation. Method: This was a quasi-experimental study conducted with a sample of 200 students in their third and fourth years at university. To obtain the data, an evaluation Questionnaire for the Evaluation of Learning Strategies of University Students (CEVEAPEU) was utilized, as well as two different types of structured debriefing styles, namely, with or without a graphical representation of the strengths/weaknesses during the analytical phase. The data analysis was performed with the SPSS
® v25 program. Results: Statistically significant differences were found, with higher scores obtained when utilizing debriefing with a graphical representation, on both scales of the questionnaire (affective and cognitive), on the motivational, metacognitive and processing, and use of information subscales, and twelve learning strategies mostly belonging to the subscales of motivation; searching, collecting, and selecting information; and processing and using information. Conclusion: Debriefing with a graphical representation is deemed, a priori, as the most adequate approach for our context, based on the greater number of learning strategies utilized by our students. The use of a written graphical record of the strengths and weaknesses in the analytical phase is recommended.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Developing an Innovative Medical Training Simulation Device for Peripheral Venous Access: A User-Centered Design Approach
by
Constanza Miranda, Fernando Altermatt, Ignacio Villagrán and Julián Goñi
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2412
Abstract
Nurses and other health students may lack the proper time for training procedural tasks, such as peripheral venous access. There is a need to develop these abilities in novices so that errors can be avoided when treating real patients. Nonetheless, from an experiential
[...] Read more.
Nurses and other health students may lack the proper time for training procedural tasks, such as peripheral venous access. There is a need to develop these abilities in novices so that errors can be avoided when treating real patients. Nonetheless, from an experiential point of view, the simulation devices offered in the market do not always make sense for educators and trainees. This could make the adoption of new technology difficult. The purpose of this case study is to describe the development of an innovative simulation device and to propose concrete tactics for the involvement of the educators and trainees. We used a participative design based approach, with an ethnographic basis, where incremental cycles of user testing, development and iteration were involved. The study showcases methods from the field of design and anthropology that can be used to develop future simulation devices that resonate with students and educators to achieve a long term learning experience. Results could shed a light on new ways for the involvement of educators and students to create devices that resonate with them, making learning significant and effective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Nursing Students’ Perception on the Effectiveness of Emergency Competence Learning through Simulation
by
Ignacio Manuel Guerrero-Martínez, Francisco Javier Portero-Prados, Rocío Cándida Romero-González, Rocío Romero-Castillo, Manuel Pabón-Carrasco and José Antonio Ponce-Blandón
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2329
Abstract
(1)
Background: Simulation is a part of the day-to-day of the learning method in health sciences. The objective is to determine if the clinical simulation is useful for learning in the emergency setting, from the point of view of the nursing students.
[...] Read more.
(1)
Background: Simulation is a part of the day-to-day of the learning method in health sciences. The objective is to determine if the clinical simulation is useful for learning in the emergency setting, from the point of view of the nursing students. (2)
Methods: A pre- and post-test exploratory study with an analytical and quasi-experimental design was used. The population is made up of nursing students from the Seville Red Cross Nursing Centre, who conducted a simulation exercise in the form of a drill for the care of multiple victims. A specific questionnaire was employed as a tool to analyse the dimensions of satisfaction, confidence and motivation, clinical experience, and decision making and technical abilities. (3)
Results: There were favourable significant differences in the set of global responses, with
p < 0.0001 for the “satisfaction” dimension and d = 1.25 for the “large” size of the effect, and
p < 0.0069 for the “confidence and motivation” dimension and d = 0.58 for the “moderate–large” size of the effect. (4)
Conclusions: The results are similar to those obtained in other studies in the scope of the 4 dimensions studied, thus coming to the conclusion that the perception of the nursing students on learning through clinical simulation is positive and favourable.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Simulated Video Consultations as a Learning Tool in Undergraduate Nursing: Students’ Perceptions
by
Diana Jiménez-Rodríguez and Oscar Arrogante
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 4467
Abstract
Simulated video consultations, a teaching tool based on high-fidelity simulations, were implemented in response to the necessary adaptation of high-fidelity clinical simulation sessions to the online or virtual modality during the university closure due to the COVID-19 confinement. The purpose of our study
[...] Read more.
Simulated video consultations, a teaching tool based on high-fidelity simulations, were implemented in response to the necessary adaptation of high-fidelity clinical simulation sessions to the online or virtual modality during the university closure due to the COVID-19 confinement. The purpose of our study was to explore the undergraduate nursing students’ satisfaction and perceptions about simulated video consultations using the high-fidelity simulation methodology. A mixed-method was utilized with 93 undergraduate nursing students using a validated satisfaction questionnaire (quantitative data), which included an observations section (qualitative data). Of the total sample, 97.8% of the students expressed a high overall satisfaction with simulated video consultations, highlighting their practical utility and positive learning outcomes. From the students’ comments, two main themes and their related categories emerged: advantages (satisfaction and enjoyment, learning, and calmness during simulated scenarios), and disadvantages (technical issues and technical skills development). Simulated video consultations may be considered as one more high-fidelity simulation teaching option. Nursing students should be trained in this modality of healthcare to face the challenge brought on by its increased use in healthcare services, beyond the specific adaptation of clinical simulation sessions due to the closure of universities during this pandemic.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Using High-Fidelity Simulation to Introduce Communication Skills about End-of-Life to Novice Nursing Students
by
Rebeca Abajas-Bustillo, Francisco Amo-Setién, Mar Aparicio, Noelia Ruiz-Pellón, Rosario Fernández-Peña, Tamara Silio-García, César Leal-Costa and Carmen Ortego-Mate
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3068
Abstract
Background: High-fidelity simulation is being considered as a suitable environment for imparting the skills needed to deal with end-of-life (EOL) situations. The objective was to evaluate an EOL simulation project that introduced communication skills to nursing students who had not yet begun
[...] Read more.
Background: High-fidelity simulation is being considered as a suitable environment for imparting the skills needed to deal with end-of-life (EOL) situations. The objective was to evaluate an EOL simulation project that introduced communication skills to nursing students who had not yet begun their training in real healthcare environments.
Methods: A sequential approach was used. The “questionnaire for the evaluation of the end-of-life project” was employed.
Results: A total of 130 students participated. Increasing the time spent in high-fidelity simulation significantly favored the exploration of feelings and fears regarding EOL (t = −2.37,
p = 0.019), encouraged dialogue (t = −2.23,
p = 0.028) and increased the acquisition of communication skills (t = −2.32,
p = 0.022).
Conclusions: High-fidelity simulation promotes communication skills related to EOL in novice nursing students.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Korean Nursing Students’ First Experiences of Clinical Practice in Psychiatric Nursing: A Phenomenological Study
by
Sunkyung Cha, Hyunjung Moon and Eunyoung Park
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2869
Abstract
Nursing students have a more negative attitude toward psychiatric practice than other practices. In particular, Korean nursing students experience increased pressure during clinical practice in psychiatric nursing due to sociocultural and institutional influences, such as prejudices, fear, and anxiety towards mental illnesses. This
[...] Read more.
Nursing students have a more negative attitude toward psychiatric practice than other practices. In particular, Korean nursing students experience increased pressure during clinical practice in psychiatric nursing due to sociocultural and institutional influences, such as prejudices, fear, and anxiety towards mental illnesses. This study aimed to conduct an investigation on students’ first experiences of clinical practice in psychiatric nursing. Participants were 12 fourth year nursing students in South Korea. The data were collected through semi-structured interviews, and data analysis was done using Colaizzi’s phenomenological method. The students’ experiences of clinical practice in psychiatric nursing could be categorized into emotional fluctuation, burnout, transformation, and growth. The results of this study show that nursing students experienced emotional fluctuation and burnout at the beginning of their clinical practice in psychiatric nursing. At the end of the clinical practice, they experienced transformation and growth. The study suggests that nursing instructors and on-site staff need to interact with nursing students to understand the nature of these first experiences and support them through teaching and field guidance.
Full article