Frailty in Older Adults
A topical collection in Geriatrics (ISSN 2308-3417). This collection belongs to the section "Healthy Aging".
Viewed by 80743
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. David Hewson
Prof. Dr. David Hewson
 Prof. Dr. David Hewson
Prof. Dr. David Hewson
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Institute for Health Research, University of Bedfordshire, Luton LU1 3JU, Bedfordshire, UK
Interests: ageing; frailty; sarcopenia; fall prevention; exercise as medicine; geriatric screening tools; public health; sedentary behaviour
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Social factors, such as social exclusion, inequality, and socio-economic status, are recognised as playing an increasingly important role in the health of older people. Studies have shown that when older people have less social support, adverse health outcomes are more likely to occur, including increased mortality and disability. In addition to studies of single social factors, composite measures that combine many factors, such as the social vulnerability index, could be more effective at identifying adverse outcomes due to the complex interplay between social factors and health outcomes. For this Topical Collection of Geriatrics, articles that examine the link between social vulnerability and health outcomes are welcome, particularly articles of longitudinal studies and those including clinical assessment of social vulnerability. Submissions can include both reviews and original research.
Prof. Dr. David Hewson
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Geriatrics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1800 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (24 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Association of the Combination of Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Sleep Quality with Physical Frailty
by
Tsubasa Yokote, Harukaze Yatsugi, Tianshu Chu, Xin Liu, Lefei Wang and Hiro Kishimoto
Viewed by 998
Abstract
Background: The association of the individual and combined effects of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) and sleep quality with physical frailty in community-dwelling older adults is still unknown. Subjects and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with a sample of older adults who had
[...] Read more.
Background: The association of the individual and combined effects of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) and sleep quality with physical frailty in community-dwelling older adults is still unknown. Subjects and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with a sample of older adults who had not required nursing care or support services. Physical frailty was assessed using Liu’s definition based on Fried’s concept. MVPA was measured by a triaxial accelerometer, and individuals who met either moderate physical activity (MPA) for ≥300 min/week, vigorous physical activity (VPA) for ≥150 min/week, or both were defined as “MVA
+”. “SLP
+” was defined as a Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index score of <5.5 points. Results: A total of 811 participants were included in the final analysis. After adjusting for the multivariable confounding factors, the odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for physical pre-frailty and frailty in the MVA
−SLP
+ (OR, 2.56; 95%CI, 1.80–3.62) and the MVA
−SLP
− group (OR, 3.97; 95%CI, 2.33–6.74) were significantly higher compared with the MVA
+SLP
+ group. Conclusion: Community-dwelling older adults who did not meet the MVPA criteria, regardless of sleep quality, had a higher prevalence of physical frailty.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Frailty and Survivability of Polish Caucasian Nonagenarians and Centenarians
by
Agnieszka Skubiszewska, Katarzyna Broczek, Iwona Maruniak-Chudek, Gabriela Oledzka, Marta Izabela Jonas, Monika Puzianowska-Kuznicka and Malgorzata Mossakowska
Viewed by 1302
Abstract
Frailty is a major geriatric problem leading to an increased risk of disability and death. Prevention, identification, and treatment of frailty are important challenges in gerontology and public health. The study aimed to estimate the prevalence of the frailty phenotype (FP) among the
[...] Read more.
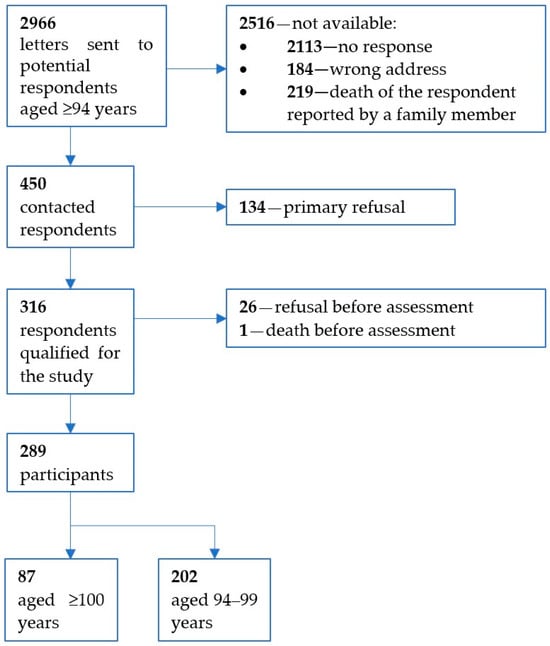
Frailty is a major geriatric problem leading to an increased risk of disability and death. Prevention, identification, and treatment of frailty are important challenges in gerontology and public health. The study aimed to estimate the prevalence of the frailty phenotype (FP) among the oldest-old Polish Caucasians and investigate the relationship between the FP and mortality. Baseline data were collected from 289 long-lived individuals, including 87 centenarians and 202 subjects aged 94–99. Mortality was obtained from population registers over the following 5 years. Sixty percent of subjects were classified as frail, 33% as prefrail, and 7% as robust. Frailty was more common in women than men and among centenarians than nonagenarians. During the 5-year observation period, 92.6% of the frail women and all frail men died, while mortality rates were lower among prefrail, 78.8% and 66.7%, and robust individuals, 60% and 54.5%, respectively. In the survival analysis, frailty was the strongest negative risk factor: HR = 0.328 (95% CI: 0.200–0.539). The inability to perform handgrip strength measurement was an additional predictor of short survival. In conclusion, the FP is prevalent in nonagenarians and centenarians and correlates with lower survivability. Future studies should address differences between unavoidable age-associated frailty and reversible disability in long-lived individuals.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Unmet Needs for Support in Activities of Daily Living among Older Persons: The Effects of Family and Household Structures in a Low- and Middle-Income Context
by
Jacob Wale Mobolaji
Viewed by 1334
Abstract
The unmet need for assistance in activities of daily living (ADLs) accentuates older persons’ risk of falls, ill health, hospitalisation, and mortality. In Nigeria, the family arrangements through which older persons derive support are changing due to modernisation, migration, and economic challenges. How
[...] Read more.
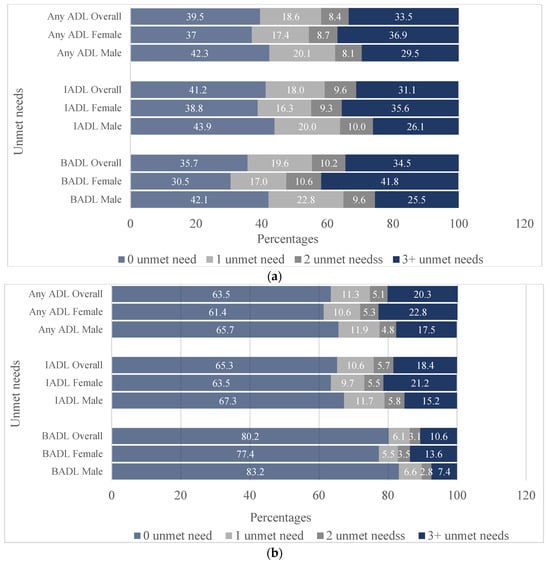
The unmet need for assistance in activities of daily living (ADLs) accentuates older persons’ risk of falls, ill health, hospitalisation, and mortality. In Nigeria, the family arrangements through which older persons derive support are changing due to modernisation, migration, and economic challenges. How the family dynamics explain the unmet needs is poorly understood. This study investigates the influence of family and household structures on older persons’ unmet needs in ADLs in southwestern Nigeria. The study analysed the data of 827 older adults aged ≥65 years selected from Oyo State, southwestern Nigeria, using a multi-stage sampling design. Associations were examined using the Poisson–logit hurdle regression model. From the results, 65% of older persons with difficulties had unmet needs in instrumental ADLs and 59% in basic ADLs. Increased unmet needs were associated with older persons living with non-family members (β = 0.19;
p < 0.01; 95% C.I. = 0.05–0.32) and widows (β = 0.27;
p < 0.01; 95% C.I. = 0.13–0.42). Conversely, unmet needs decreased with higher family size (β = −0.06;
p < 0.001; 95% C.I. = −0.08–−0.03), living in rich households (β = −0.29;
p < 0.001; 95% C.I. = −0.42–−0.17), not being the household head (β = −0.27;
p < 0.001; 95% C.I. = −0.40–−0.15), close family bonds, and proximity to children/caregivers. The study recommends alternative or complementary home-based support mechanisms for seniors with vulnerable family settings in southwestern Nigeria.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Frailty and Diminished Human Relationships Are Associated with Poor Sleep Quality in Japanese Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Hitomi Matsuda, Thomas Mayers, Naoki Maki, Akihiro Araki and Sachie Eto
Viewed by 1889
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to examine the association between sleep quality, frailty, and human relationships in Japanese older adults (aged 65 years and above, excluding those certified as requiring long-term care). This cross-sectional study used a questionnaire survey to gather demographic
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study was to examine the association between sleep quality, frailty, and human relationships in Japanese older adults (aged 65 years and above, excluding those certified as requiring long-term care). This cross-sectional study used a questionnaire survey to gather demographic information, data on frequency of conversation and conversation partners, and employed the following validated instruments: Kihon Checklist (KCL), a Japanese instrument used to determine the care needs and frailty of older adults; the Dysphagia Risk Assessment for Community-Dwelling Elderly (DRACE) scale; Japanese versions of Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J); the Geriatric Depression Scale-15 (GDS-15-J); and the University of California Los Angeles Scale (UCLA-J), an instrument to assess loneliness in older adults. The 500 respondents were divided into two groups based on sleep quality (PSQI-J): low sleep quality group (
n = 167, 33.4%) and high sleep quality group
(n = 333, 66.6%). Our analyses showed that the low sleep quality group had a KCL score of 5.55 ± 2.47, which indicated frailty. Binomial logistic regression analysis identified age, number of diseases under treatment, DRACE, GDS-15-J, and conversation frequency and discussion partner for important matters as factors (
p < 0.05) associated with poor sleep quality. These factors could help enhance the detection of frailty and predictability of caregiving needs.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Fragility Fractures of the Hip: An Interrupted Time-Series Analysis of the Lockdown Periods in Western Greece and Review of the Literature
by
Ilias D. Iliopoulos, Ioanna Lianou, Angelos Kaspiris, Dimitrios Ntourantonis, Christine Arachoviti, Christos P. Zafeiris, George I. Lambrou and Efstathios Chronopoulos
Viewed by 1740
Abstract
Since December 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on healthcare systems worldwide, prompting policymakers to implement measures of isolation and eventually adopt strict national lockdowns, which affected mobility, healthcare-seeking behavior, and services, in an unprecedented manner. This study aimed to
[...] Read more.
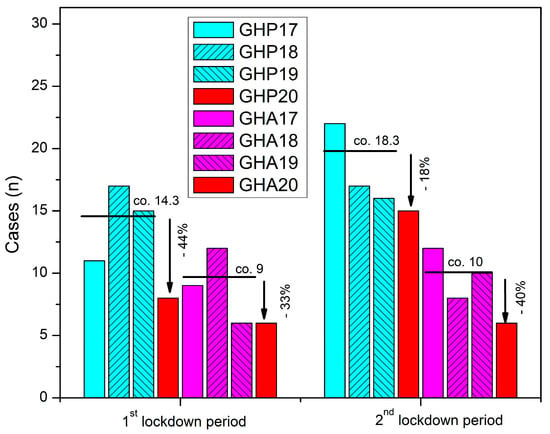
Since December 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on healthcare systems worldwide, prompting policymakers to implement measures of isolation and eventually adopt strict national lockdowns, which affected mobility, healthcare-seeking behavior, and services, in an unprecedented manner. This study aimed to analyze the effects of these lockdowns on hip-fracture epidemiology and care services, compared to nonpandemic periods in previous years. We retrospectively collected data from electronic patient records of two major hospitals in Western Greece and included patients who suffered a fragility hip fracture and were admitted during the two 5-week lockdown periods in 2020, compared to time-matched patients from 2017–2019. The results showed a drop in hip-fracture incidence, which varied among hospitals and lockdown periods, and conflicting impacts on time to surgery, time to discharge after surgery, and total hospitalization time. The study also found that differences between the two differently organized units were exaggerated during the COVID-19 lockdown periods, highlighting the impact of compliance with social-distancing measures and the reallocation of resources on the quality of healthcare services. Further research is needed to fully understand the specific variations and patterns of geriatric hip-fracture care during emergency health crises characterized by limited resources and behavioral changes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
In Situ Simulation Training for Frailty
by
Liam Dunnell, Anna Nicole Barnard, Katie Chu, Ania Barling, Jonathan Birns and Grace Walker
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1515
Abstract
Background: People living with frailty account for a significant proportion of hospital inpatients and are at increased risk of adverse events during admission. The understanding of frailty remains variable among hospital staff, and there is a need for effective frailty training across multidisciplinary
[...] Read more.
Background: People living with frailty account for a significant proportion of hospital inpatients and are at increased risk of adverse events during admission. The understanding of frailty remains variable among hospital staff, and there is a need for effective frailty training across multidisciplinary teams. Simulation is known to be advantageous for improving human factor skills in multidisciplinary teams. In situ simulation can increase accessibility and promote ward team learning, but its effectiveness with respect to frailty has not been explored. Method: A single-centre, multi-fidelity, inter-professional in situ frailty simulation programme was developed. One-hour sessions were delivered weekly using frailty-based clinical scenarios. Mixed-method evaluation was used, with data collected pre- and post-session for comparison. Results: In total, 86 multidisciplinary participants attended 19 sessions. There were significant improvements in self-efficacy rating across 10 of 12 human factor domains and in all frailty domains (
p < 0.05). The common learning themes were situational awareness, communication and teamwork. Participants commented on the value of learning within ward teams and having the opportunity to debrief. Conclusion: In situ simulation can improve the self-efficacy of clinical and human factor skills related to frailty. The results are limited by the nature of self-reporting methods, and further studies assessing behavioural change and clinical outcomes are warranted.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Severe Periodontitis Increases the Risk of Oral Frailty: A Six-Year Follow-Up Study from Kashiwa Cohort Study
by
Misa Nishimoto, Tomoki Tanaka, Hirohiko Hirano, Yutaka Watanabe, Yuki Ohara, Maki Shirobe and Katsuya Iijima
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2007
Abstract
Oral frailty, overlapping a decline in multi-faceted oral functions and often seen in older adults, increases risks of adverse health outcomes, thereby necessitating earlier measures. Tooth loss, a major element of oral frailty, is mainly caused by periodontal disease and is an irreversible
[...] Read more.
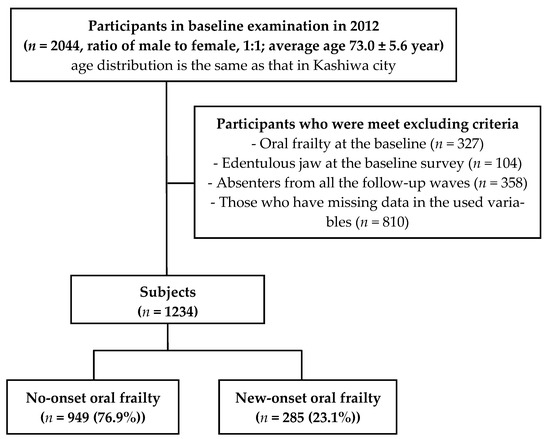
Oral frailty, overlapping a decline in multi-faceted oral functions and often seen in older adults, increases risks of adverse health outcomes, thereby necessitating earlier measures. Tooth loss, a major element of oral frailty, is mainly caused by periodontal disease and is an irreversible event. Therefore, this study aimed to clarify whether advanced periodontal disease increases the risks of “new-onset” oral frailty through a longitudinal analysis based on the 2012 baseline survey of the Kashiwa cohort and the follow-up assessments conducted in 2013, 2014, 2016, and 2018. The participants were disability-free, non-orally frail older adults living in Kashiwa City. Of the 1234 participants (72.2 ± 5.1 years old; 50.8% men) analyzed in this study, oral frailty occurred in 23.1% within the six-year period. The group with Community Periodontal Index (CPI) ≥ 3 at baseline had no significant difference in the risk of oral frailty compared with CPI ≤ 2; however, CPI4 at baseline was related to the increased risk of oral frailty compared with CPI ≤ 3 (an adjusted hazard ratio (95% confidence interval): 1.42 (1.12–1.81). Conclusively, severe periodontitis (CPI4) might be associated with new-onset oral frailty, suggesting that prevention of periodontal disease could contribute to oral frailty prevention.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
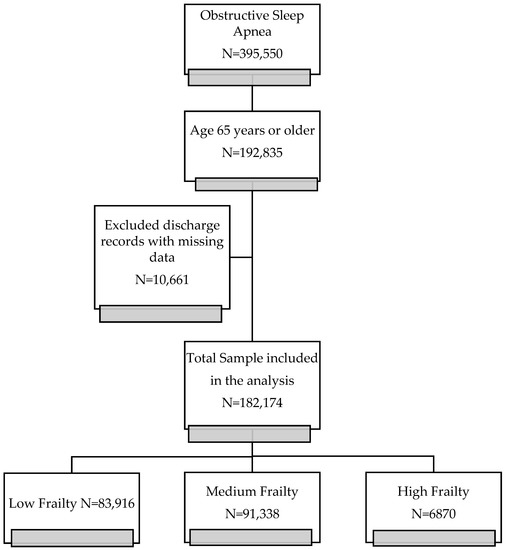
Higher Hospital Frailty Risk Score Is an Independent Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Hospitalized Older Adults with Obstructive Sleep Apnea
by
Temitope Ajibawo and Oluwatimilehin Okunowo
Viewed by 1607
Abstract
Background: Frailty predisposes individuals to stressors, increasing morbidity and mortality risk. Therefore, this study examined the impact of frailty defined by the Hospital Frailty Risk Score (HFRS) and other characteristics in older hospitalized patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA). Methods: We conducted a
[...] Read more.
Background: Frailty predisposes individuals to stressors, increasing morbidity and mortality risk. Therefore, this study examined the impact of frailty defined by the Hospital Frailty Risk Score (HFRS) and other characteristics in older hospitalized patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA). Methods: We conducted a retrospective study using the National Inpatient Sample 2016 in patients ≥65 years old with OSA. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the impact of frailty on inpatient mortality. A Kaplan-Meier curve with a log-rank test was used to estimate survival time between frailty groups. Results: 182,174 discharge records of elderly OSA were included in the study. 54% of the cohort were determined to be a medium/high frailty risk, according to HFRS. In multivariable analysis, frailty was associated with a fourfold (medium frailty, adjusted odd ratio (aOR): 4.12, 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 3.76–4.53,
p-value < 0.001) and sixfold (high frailty, OR: 6.38, 95% CI: 5.60–7.27,
p-value < 0.001) increased odds of mortality. Hospital survival time was significantly different between the three frailty groups (Log-rank test,
p < 0.0001). Comorbidity burden defined by Charlson comorbidity Index (CCI) was associated with increased mortality (
p < 0.001). Conclusion: More than half of the whole cohort was determined to be at medium and high frailty risk. Frailty was a significant predictor of in-hospital deaths in hospitalized OSA patients. Frailty assessment may be applicable for risk stratification of older hospitalized OSA patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
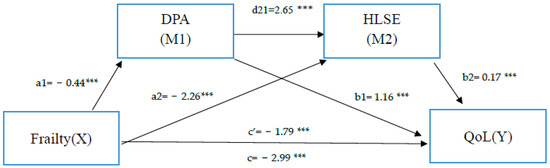
Frailty and Quality of Life among Older Adults in Communities: The Mediation Effects of Daily Physical Activity and Healthy Life Self-Efficacy
by
Chia-Hui Lin, Chieh-Yu Liu, Chun-Ching Huang and Jiin-Ru Rong
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2197
Abstract
As the global population ages, frailty, which has been shown to affect and predict the quality of life (QoL) of older adults, has become a central issue. The aim of this study was to explore the mediating effects of daily physical activity (DPA)
[...] Read more.
As the global population ages, frailty, which has been shown to affect and predict the quality of life (QoL) of older adults, has become a central issue. The aim of this study was to explore the mediating effects of daily physical activity (DPA) and healthy life self-efficacy (HLSE) on the relationship between frailty and QoL in older adults using a serial multiple mediation model. The cross-sectional study was conducted among 210 community-dwelling older adults in Taiwan. Data were collected using the Taiwanese version of the Tilburg Frailty Indicator, the EuroQoL visual analog scale, the Kihon Checklist, and the Chronic Disease Self-Efficacy Scales. The PROCESS macro for SPSS based on the bootstrap method was used to determine the mediating effects of DPA and HLSE on the relationship between frailty and QoL. The results showed that frailty was found to have both direct and indirect effects on QoL. As predicted, DPA and HLSE partially mediated the relationship between frailty and quality of life (DPA: B = −0.71,
p < 0.001; HLSE: B = −0.32,
p < 0.001). In addition, serial mediation analyses indicated that the association between frailty and QoL was partially mediated by DPA and HLSE in a sequential manner (B = −0.16,
p < 0.001). The serial mediation has a causal chain linking DPA and HLSE, with a specified direction of causal flow. According to the results of the serial multiple mediation model, the elderly should be encouraged to continue their activities in daily life, which not only improves self-efficacy and confidence in maintaining health but also reduces the negative impact of frailty on QoL.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
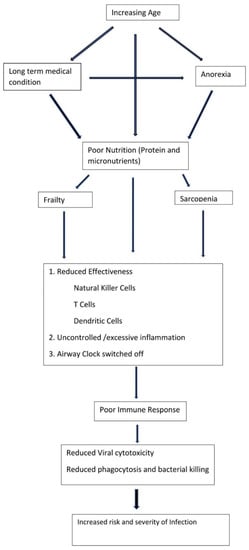
Pneumonia, Aspiration Pneumonia, or Frailty-Associated Pneumonia?
by
David G. Smithard and Yuki Yoshimatsu
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 5516
Abstract
Pneumonia is a common reason for admission afflicting frail older adults. Those who are the frailest are more likely to be provided with a diagnosis of aspiration pneumonia. This diagnosis has no clear definition and no clinical consensus. It is therefore time to
[...] Read more.
Pneumonia is a common reason for admission afflicting frail older adults. Those who are the frailest are more likely to be provided with a diagnosis of aspiration pneumonia. This diagnosis has no clear definition and no clinical consensus. It is therefore time to stop attempting to differentiate between pneumonia type and use the term frailty-associated pneumonia.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
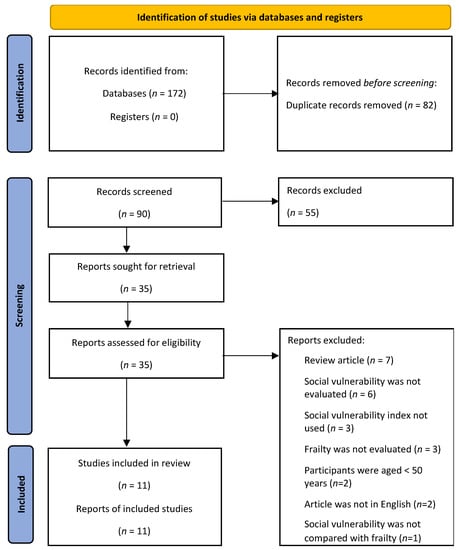
The Association between Social Vulnerability and Frailty in Community Dwelling Older People: A Systematic Review
by
Ayodele Ayeni, Adrienne Sharples and David Hewson
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2322
Abstract
The aim of this systematic literature review was to determine whether social vulnerability is associated with frailty in older people. Databases were searched for literature from January 2001 to March 2022. Hand searches of reference lists of the selected articles were also used
[...] Read more.
The aim of this systematic literature review was to determine whether social vulnerability is associated with frailty in older people. Databases were searched for literature from January 2001 to March 2022. Hand searches of reference lists of the selected articles were also used to identify other relevant studies. Studies that met the inclusion criteria were selected. Two independent reviewers assessed the methodological quality using an established tool. Eleven eligible studies from Canada, Europe, USA, Tanzania, Mexico, and China were selected. The level of social vulnerability measured by the Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) from a meta-analysis was 0.300 (95% CI: 0.242, 0.358), with the highest SVI in Tanzania (0.49), while the lowest level of SVI was reported in China (0.15). The highest frailty level of 0.32 was observed in both Tanzania and Europe, with the lowest frailty reported in a USA study from Hawaii (0.15). In all studies, social vulnerability was a significant predictor of mortality for both sexes at subsequent data collection points. The association between SVI and frailty was high in Tanzania (r = 0.81), with other studies reporting stronger correlations for females compared to males, but at small to moderate levels. In one study, an increase of 1SD in SVI was linked to a 20% increase in frailty score at a subsequent evaluation. Additional study is warranted to determine a potential causality between social vulnerability and frailty.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
Dental Pain in Care Homes: Is It a Phenomenon? A Systematic Review of the Literature
by
Pat Schofield, Nicole Thomas, Ewen McColl and Robert Witton
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1668
Abstract
Background: Evidence suggests that 80% of residents living in nursing homes have moderate to severe pain, could dental causes be an under reported contributory factor. The evidence suggests that this is an under-researched area. Our project aims were to explore and consolidate the
[...] Read more.
Background: Evidence suggests that 80% of residents living in nursing homes have moderate to severe pain, could dental causes be an under reported contributory factor. The evidence suggests that this is an under-researched area. Our project aims were to explore and consolidate the current literature and conduct some stakeholder groups with care home managers and dentists. Our stakeholder group will be reported elsewhere. Methods: We used the SPIDER framework to set out key search terms. Which included “dementia” OR “cognitively-impaired” OR “carehome residents” AND “dental pain” OR “oralfacial pain” OR “mouth pain” AND “pain assessment” OR “pain identification”. A literature search was carried out on 8 and 9 March 2022 in the electronic databases: Cochrane, PubMed, Medline, Dental & Oral Sciences Source, CINAHL, Global Health, SocINDEX, Ovid (Medline) and Scopus. Restrictions were placed on dates and language (2012–2022 and English only). Results: The search yielded 775 papers up to the year 2020. After screening and exclusion, we were left with five papers: four quantitative and one qualitative. Conclusions: This review demonstrates that there has been very little research into oral health and/or dental pain in adults with dementia. Furthermore, the recommendations have yet to be taken forward. Identifying pain in older adults with dementia remains challenging. There is a need to develop an algorithm in conjunction with care home staff and dental practitioners in order to identify and address the pain associated with dental disease in adults with dementia.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Frailty as a Predictor of Hospitalization and Low Quality of Life in Geriatric Patients at an Internal Medicine Outpatient Clinic: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Panita Limpawattana, Chudapha Khammak, Manchumad Manjavong and Apichart So-ngern
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1760
Abstract
Frailty is an aging-associated state that increases patients’ vulnerability to disease, and can lead to various adverse outcomes. It is classified as either physical frailty alone or physical frailty in combination with cognitive impairment (cognitive frailty). There are currently limited data available regarding
[...] Read more.
Frailty is an aging-associated state that increases patients’ vulnerability to disease, and can lead to various adverse outcomes. It is classified as either physical frailty alone or physical frailty in combination with cognitive impairment (cognitive frailty). There are currently limited data available regarding the prevalence and adverse outcomes of frailty in Thailand. This was a cross-sectional study aimed at determining the prevalence of physical and cognitive frailty and their effects on hospitalization and quality of life. Participants were older patients who attended an internal medicine outpatient clinic. Frailty was diagnosed using the Thai Frailty Index. The Thai version of the MoCA was used to evaluate cognitive status. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to compare adverse outcomes in terms of poor quality of life and history of admission to hospital between patients with frailty and non-frail patients, and among patients with physical frailty, cognitive frailty, cognitive impairment, and robust (non-frail and non-cognitively impaired) patients. We enrolled 198 participants. The prevalence of physical and cognitive frailty was 28.78% and 20.70%, respectively. When compared with non-frail patients, frailty was associated with hospitalization (adjusted OR 3.01,
p = 0.002) but was not significantly related to quality of life (adjusted OR = 1.98,
p = 0.09). However, physical and cognitive frailty were associated with fair quality of life when compared with normal patients (adjusted OR = 4.34,
p = 0.04 and adjusted OR = 4.28,
p = 0.03, respectively). The prevalence of frailty—particularly cognitive frailty—was high. Frailty was associated with adverse outcomes in terms of hospitalization and quality of life.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Frailty and Associated Factors among the Elderly in Vietnam: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Trung Quoc Hieu Huynh, Thi Lan Anh Pham, Van Tam Vo, Ha Ngoc The Than and Tan Van Nguyen
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2377
Abstract
Background: Frailty syndrome is common among older people and can lead to various adverse consequences such as falls, cognitive decline, disability, dependent living, increased mortality, excessive drug use, and prolonged hospital stays. Objectives: This research determined the prevalence of frailty and associated factors
[...] Read more.
Background: Frailty syndrome is common among older people and can lead to various adverse consequences such as falls, cognitive decline, disability, dependent living, increased mortality, excessive drug use, and prolonged hospital stays. Objectives: This research determined the prevalence of frailty and associated factors among older adults in Vietnam. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 584 older adults across five Ho Chi Minh City wards from November 2020 to January 2021. Based on the modified Fried frailty scale, the participants were divided into three categories: robust, pre-frail, and frail. A chi-square test (or Fisher’s test) examined the relationship between frailty categories and other variables. Multivariable logistic regression used variates with a cut-off of
p ≤ 0.05 in the univariate analysis. Results: The prevalence rates of frailty and pre-frailty were 19% and 64%, respectively. The most common frailty component was weak grip strength (63.9%), followed by slowness (36.1%), weight loss (21.6%), low physical activity (19.5%), and exhaustion (18.5%). In addition, the prevalence of frailty was significantly associated with age, BMI levels, living alone, and sarcopenia. Conclusion: The community’s prevalence of frailty among older adults is high. Frailty can lead to many adverse consequences for the elderly. As there were some modifiable factors associated with frailty, it should be assessed in older people through community-based healthcare programs for early diagnosis and management.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence Rates and Characteristics of Malnutrition, Frailty, and Other Nutrition and Muscle Mass-Related Conditions Document Potential Quality of Care Gap for Medicare Patients in US Skilled Nursing Facilities
by
Mary Beth Arensberg, Cory Brunton, Susan Drawert and Brenda Richardson
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2369
Abstract
Changes to the payment structure of the United States (U.S.) healthcare system are leading to an increased acuity level of patients receiving short-term skilled nursing facility care. Most skilled nursing facility patients are older, and many have medical conditions that cannot be changed.
[...] Read more.
Changes to the payment structure of the United States (U.S.) healthcare system are leading to an increased acuity level of patients receiving short-term skilled nursing facility care. Most skilled nursing facility patients are older, and many have medical conditions that cannot be changed. However, conditions related to nutrition/muscle mass may be impacted if there is early identification/intervention. To help determine the diagnosis and potential impact of nutrition/muscle mass-related conditions in skilled nursing facilities, this study evaluated 2016–2020 US Medicare claims data. Methods aimed to identify a set of skilled nursing facility claims with one or more specific diagnoses (COVID-19, malnutrition, sarcopenia, frailty, obesity, diabetes, and/or pressure injury) and then to determine length of stay, discharge status, total charges, and total payments for each claim. Mean values per beneficiary were computed and between–group comparisons were performed. Results documented that each year, the total number of Medicare skilled nursing facility claims declined, whereas the percentage of claims for each study diagnosis increased significantly. For most conditions, potentially related to nutrition/muscle mass, Medicare beneficiaries had a shorter length of skilled nursing facility stays compared to those without the condition(s). Furthermore, a lower percentage of these Medicare beneficiaries were discharged home (except for those with claims for sarcopenia and obesity). Total claim charges for those with nutrition/muscle mass-related conditions exceeded those without (except for those with sarcopenia). We conclude that although the acuity level of patients in skilled nursing facilities continues to increase, skilled nursing facility Medicare claims for nutrition/muscle mass-related conditions are reported at lower levels than their likely prevalence. This represents a potential care gap and requires action to help improve patient health outcomes and skilled nursing facility quality metrics.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
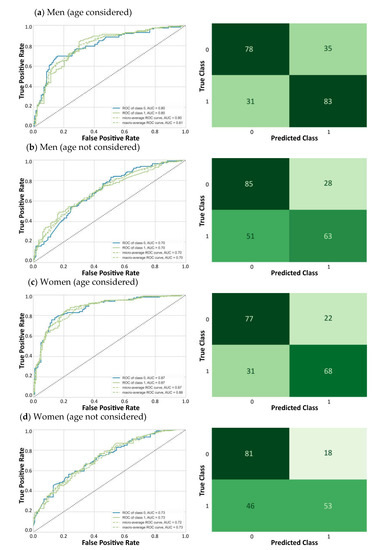
The Importance of Age in the Prediction of Mortality by a Frailty Index: A Machine Learning Approach in the Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing
by
Sebastian Moguilner, Silvin P. Knight, James R. C. Davis, Aisling M. O’Halloran, Rose Anne Kenny and Roman Romero-Ortuno
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3994
Abstract
The quantification of biological age in humans is an important scientific endeavor in the face of ageing populations. The frailty index (FI) methodology is based on the accumulation of health deficits and captures variations in health status within individuals of the same age.
[...] Read more.
The quantification of biological age in humans is an important scientific endeavor in the face of ageing populations. The frailty index (FI) methodology is based on the accumulation of health deficits and captures variations in health status within individuals of the same age. The aims of this study were to assess whether the addition of age to an FI improves its mortality prediction and whether the associations of the individual FI items differ in strength. We utilized data from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing to conduct, by sex, machine learning analyses of the ability of a 32-item FI to predict 8-year mortality in 8174 wave 1 participants aged 50 or more years. By wave 5, 559 men and 492 women had died. In the absence of age, the FI was an acceptable predictor of mortality with AUCs of 0.7. When age was included, AUCs improved to 0.8 in men and 0.9 in women. After age, deficits related to physical function and self-rated health tended to have higher importance scores. Not all FI variables seemed equally relevant to predict mortality, and age was by far the most relevant feature. Chronological age should remain an important consideration when interpreting the prognostic significance of an FI.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Seniors’ Community Hub: An Integrated Model of Care for the Identification and Management of Frailty in Primary Care
by
Marjan Abbasi, Sheny Khera, Julia Dabravolskaj, Bernadette Chevalier and Kelly Parker
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2947
Abstract
(1) Background: Integrated models of primary care deliver the comprehensive and preventative approach needed to identify and manage frailty in older people. Seniors’ Community Hub (SCH) was developed to deliver person-centered, evidence-informed, coordinated, and integrated care services to older community dwelling adults living
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Integrated models of primary care deliver the comprehensive and preventative approach needed to identify and manage frailty in older people. Seniors’ Community Hub (SCH) was developed to deliver person-centered, evidence-informed, coordinated, and integrated care services to older community dwelling adults living with frailty. This paper aims to describe the SCH model, and to present patient-oriented results of the pilot. (2) Methods: SCH was piloted in an academic clinic with six family physicians. Eligible patients were community dwelling, 65 years of age and older, and considered to be at risk of frailty (eFI > 0.12). Health professionals within the clinic received training in geriatrics and interprofessional teamwork to form the SCH team working with family physicians, patients and caregivers. The SCH intervention consisted of a team-based multi-domain assessment with person-centered care planning and follow-up. Patient-oriented outcomes (EQ-5D-5L and EQ-VAS) and 4-metre gait speed were measured at initial visit and 12 months later. (3) Results: 88 patients were enrolled in the pilot from April 2016–December 2018. No statistically significant differences in EQ-5D-5L/VAS or the 4-metre gait speed were detected in 38 patients completing the 12-month assessment. (4) Conclusions: Future larger scale studies of longer duration are needed to demonstrate impacts of integrated models of primary care on patient-oriented outcomes for older adults living with frailty.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Associations between Pet Ownership and Frailty: A Systematic Review
by
Gotaro Kojima, Reijiro Aoyama and Yu Taniguchi
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3771
Abstract
Frailty is defined as a state of increased vulnerability due to age-related decline in reserve and function across multiple physiological systems. Increasing physical activity level is considered to be a measure to counteract frailty. Some studies have indicated that pet owners are more
[...] Read more.
Frailty is defined as a state of increased vulnerability due to age-related decline in reserve and function across multiple physiological systems. Increasing physical activity level is considered to be a measure to counteract frailty. Some studies have indicated that pet owners are more engaged in physical activity than non-owners. We conducted a systematic review regarding associations between pet ownerships and frailty among community-dwelling older adults and critically assessed the findings. PubMed was searched in April 2020 according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines for cross-sectional or prospective studies examining associations between pet ownership and frailty in community-dwelling older adults with a mean age of 60 or above. A supplementary search was done using Google Scholar. Identified articles were reviewed by two investigators independently and assessed for methodological quality. The search identified 48 studies, among which three studies (two cross-sectional and one prospective) were included in this review. These studies suggested that pet ownership may be associated with a lower risk of frailty. This systematic review found only a limited amount of relevant research. More research is needed to establish the link between pet ownership and frailty as well as healthy aging and well-being.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Inter-Relationships between Frailty, Sarcopenia, Undernutrition and Dysphagia in Older People Who Are Admitted to Acute Frailty and Medical Wards: Is There an Older Adult Quartet?
by
David Smithard, Dharinee Hansjee, Darrien Henry, Laura Mitchell, Arjun Sabaharwal, Jo Salkeld, Eirene Yeung, Osman Younus and Ian Swaine
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3987
Abstract
Introduction: With increasing age the prevalence of frailty, sarcopenia, undernutrition and dysphagia increases. These are all independent markers of outcome. This study explores the prevalence of these four and explores relationships between them.
Methods: A convenience sample of 122 patients admitted
[...] Read more.
Introduction: With increasing age the prevalence of frailty, sarcopenia, undernutrition and dysphagia increases. These are all independent markers of outcome. This study explores the prevalence of these four and explores relationships between them.
Methods: A convenience sample of 122 patients admitted to acute medical and frailty wards were recruited. Each was assessed using appropriate screening tools; Clinical Frailty Score (CFS) for frailty, SARC-F for sarcopenia, Nutritional Risk Tool (NRT) for nutritional status and 4QT for dysphagia.
Results: The mean age of the participants was 80.53 years (65–99 years), and 50.37% (68) were female. Overall, 111 of the 122 (91.0%) reported the presence of at least one of the quartet. The median CFS was 5 (1–9), with 84 patients (68.9%) having a score of ≥5 (moderate or severely frail); The median SARC-F was 5 (0–10), with 64 patients (52.5%) having a score of ≥5; The median NRT was 0 (0–8) and 33 patients (27.0%) scored ≥ 1. A total of 77 patients (63.1%) reported no difficulty with swallowing/dysphagia (4QT ≥ 1) and 29 (23.7%) had only one factor. Sixteen patients (13.1%) had all four. There was a significant correlation between nutritional status and dysphagia, but not with frailty or sarcopenia. There were significant correlations between frailty and both sarcopenia and dysphagia.
Conclusions: In our sample of acute medical and frailty ward patients, there was a much higher prevalence than expected (91%) of either: frailty, sarcopenia, undernutrition or dysphagia. The prevalence of all four was present in 13% of patients. We suggest that frailty, sarcopenia, nutritional risk and dysphagia comprise an “Older Adult Quartet”. Further study is required to investigate the effect of the “Older Adult Quartet” on morbidity and mortality.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
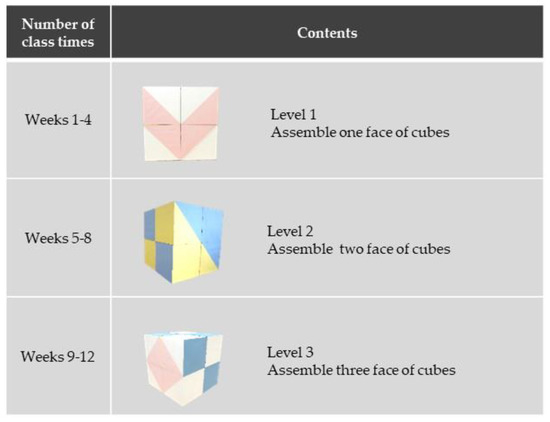
A Novel Exercise for Enhancing Visuospatial Ability in Older Adults with Frailty: Development, Feasibility, and Effectiveness
by
Miyuki Nemoto, Hiroyuki Sasai, Noriko Yabushita, Keito Tsuchiya, Kazushi Hotta, Yoshihiko Fujita, Taeho Kim, Takehiko Tsujimoto, Tetsuaki Arai and Kiyoji Tanaka
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 5230
Abstract
We aimed to develop a novel exercise to improve visuospatial ability and evaluate its feasibility and effectiveness in older adults with frailty. A non-randomized preliminary trial was conducted between June 2014 and March 2015. We recruited 35 adults with frailty (24 women), aged
[...] Read more.
We aimed to develop a novel exercise to improve visuospatial ability and evaluate its feasibility and effectiveness in older adults with frailty. A non-randomized preliminary trial was conducted between June 2014 and March 2015. We recruited 35 adults with frailty (24 women), aged 66–92 years. Participants were assigned to either locomotive- or visuospatial-exercise groups. All participants exercised under the supervision of physiotherapists for 90 min/week for 12 weeks. The visuospatial exercise participants used cubes with six colored patterns and were instructed to “reproduce the same colored pattern as shown in the photo”, using the cubes. In the locomotive exercise group, lower extremity functional training was provided. Rates of retention and attendance measured feasibility. Most participants completed the intervention (77.3%, locomotive; 84.6%, visuospatial) and had good attendance (83.8%, locomotive; 90.7%, visuospatial). Mini-mental state examination (MMSE), clock drawing test (CDT), and seven physical performance tests were conducted before and after interventions. The improvement in the MMSE score, qualitative analysis of CDT, grip strength, and sit and reach assessments were significantly greater in the visuospatial exercise group than in the locomotive exercise group. The cube exercise might be a feasible exercise program to potentially improve visuospatial ability and global cognition in older adults with frailty.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Screening for Frailty in Older Emergency Patients and Association with Outcome
by
Siobhan Lewis, Louis Evans, Timothy Rainer and Jonathan Hewitt
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3500
Abstract
Older people have a high incidence of adverse outcomes after urgent care presentation. Identifying high-risk older patients early is key to targeting interventions at those patients most likely to benefit. This study used the Frailsafe three-point screening questions amongst older Emergency Department (ED)
[...] Read more.
Older people have a high incidence of adverse outcomes after urgent care presentation. Identifying high-risk older patients early is key to targeting interventions at those patients most likely to benefit. This study used the Frailsafe three-point screening questions amongst older Emergency Department (ED) attendees. Consecutive unplanned ED attendances in patients aged ≥75 were assessed for Frailsafe status. The primary outcome was mortality at 180 days. A Frailsafe screen was completed in 356 patients, of whom 194/356 (54.5%) were Frailsafe positive. The mean age was 85.8 for Frailsafe screen positive and 82.2 for Frailsafe screen negative patients (
p < 0.001). A positive Frailsafe screen was a predictor of death within 180 days of presentation to the ED and remained so after adjustment (AOR = 3.23, 95% CI 1.45–7.19,
p = 0.004). A positive Frailsafe screen was an independent predictor of a new care home admission at 180 days (AOR = 8.95, 95% CI 2.01–39.83,
p = 0.004). A positive Frailsafe screen was also predictive of a number of secondary outcomes, such as length of stay of >28 days (AOR 3.42, 95% CI 1.41–8.31,
p = 0.007) and re-attendance within 30 days of discharge after admission (OR = 2.73, 95% CI 1.27–5.88,
p = 0.01). Frailsafe screen results independently predict a range of outcomes amongst older ED attendees.
Full article
Open AccessBrief Report
Frailty Confers High Mortality Risk across Different Populations: Evidence from an Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
by
Richard Ofori-Asenso, Ken Lee Chin, Berhe W. Sahle, Mohsen Mazidi, Andrew R. Zullo and Danny Liew
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4166
Abstract
We performed an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses to summarize available data regarding the association between frailty and all-cause mortality. Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Web of Science, PsycINFO, and AMED (Allied and Complementary Medicine) databases were searched until February 2020 for meta-analyses examining
[...] Read more.
We performed an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses to summarize available data regarding the association between frailty and all-cause mortality. Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Web of Science, PsycINFO, and AMED (Allied and Complementary Medicine) databases were searched until February 2020 for meta-analyses examining the association between frailty and all-cause mortality. The AMSTAR2 checklist was used to evaluate methodological quality. Frailty exposure and the risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR] or relative risk [RR]) were displayed in forest plots. We included 25 meta-analyses that pooled data from between 3 and 20 studies. The number of participants included in these meta-analyses ranged between <2000 and >500,000. Overall, 56%, 32%, and 12% of studies were rated as of moderate, low, and critically low quality, respectively. Frailty was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality in 24/24 studies where the HR/RRs ranged from 1.35 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.05–1.74] (patients with diabetes) to 7.95 [95% CI 4.88–12.96] (hospitalized patients). The median HR/RR across different meta-analyses was 1.98 (interquartile range 1.65–2.67). Pre-frailty was associated with a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality in 7/7 studies with the HR/RR ranging from 1.09 to 3.65 (median 1.51, IQR 1.38–1.73). These data suggest that interventions to prevent frailty and pre-frailty are needed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
The Attitudes Towards the Use of Restraint and Restrictive Intervention Amongst Healthcare Staff on Acute Medical and Frailty Wards—A Brief Literature Review
by
Ramith Gunawardena and David G. Smithard
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 11786
Abstract
Restraint in modern non-psychiatric-based healthcare is often regarded as a rare occurrence. It is deemed to be used as a last resort to prevent patients from directly harming themselves. However, techniques are used in modern day practice which are considered direct and indirect
[...] Read more.
Restraint in modern non-psychiatric-based healthcare is often regarded as a rare occurrence. It is deemed to be used as a last resort to prevent patients from directly harming themselves. However, techniques are used in modern day practice which are considered direct and indirect restraints with the justification of maintaining patient safety, but they are often not classified as “restraints”. Examples of these include the use of bed rails or tables to prevent patients from “wandering” and to reduce the risk of falls and injuries. More indirect techniques would involve passive interactions with patients or leaving mobility aids out of reach. Staff subconsciously restrain patients and reduce their liberties despite agreeing that patient autonomy should be upheld—a necessary evil to maintain a duty of care. Whilst the use of restraints is often justified to ensure patient care and prevent injury, it is not without consequence. There are physical and psychological health risks such as pressure sores from the inability to mobilise, or the brewing of anger and frustration when denied access to everyday actions. The reasons why restraints are used, whilst stemming from maintaining patient safety, are often due to low staffing levels and the inability to constantly watch at-risk patients due to a large workload. Inadequate training is another factor; by improving education in direct and indirect restraint and providing alternative methods, more ethical decisions and positive outcomes can be implemented. Healthcare professionals are reluctant to use restraint but often conduct it without realising it; assessing their understanding of restraint and providing education to raise awareness of the consequences of direct and indirect methods would result in positive steps toward reducing their use at the same time as looking to provide alternatives to uphold patient care whilst maintaining their dignity and liberty.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Review of Frailty Syndrome and Its Physical, Cognitive and Emotional Domains in the Elderly
by
Mina Khezrian, Phyo K. Myint, Christopher McNeil and Alison D. Murray
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 9532
Abstract
Background: Frailty, a very important complication of increasing age, is a well-recognised concept although it has not been accurately measured in the clinical setting. The aim of this literature review is to summarise commonly used frailty screening tools, and to describe how new
[...] Read more.
Background: Frailty, a very important complication of increasing age, is a well-recognised concept although it has not been accurately measured in the clinical setting. The aim of this literature review is to summarise commonly used frailty screening tools, and to describe how new measurement methods have been developed recently. Methods: Several frailty measurement tools including the most cited and newly developed scales have been described in this review. We searched the MEDLINE using the search terms; “frailty score, scale, tool, instrument, index, phenotype” and then summarised selected tools for physical, cognitive, emotional and co-morbidity domains. Results: The most cited frailty measurement methods developed from 1999 to 2005 are primarily criteria for physical frailty (e.g., frailty phenotype). More recently developed tools (e.g., triad of impairment and multidimensional frailty score) consider cognitive and emotional domains in addition to physical deficit in measuring frailty. Co-morbidity has also been considered as a domain of frailty in several measurement tools. Conclusion: Although frailty tools have traditionally assessed physical capability, cognitive and emotional impairment often co-exist in older adults and may have shared origins. Therefore, newer tools which provide a composite measure of frailty may be more relevant for future use.
Full article