Ageism, the Black Sheep of the Decade of Healthy Ageing
A topical collection in Geriatrics (ISSN 2308-3417). This collection belongs to the section "Healthy Aging".
Viewed by 31067
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Lydia Gimenez Llort
Prof. Dr. Lydia Gimenez Llort
 Prof. Dr. Lydia Gimenez Llort
Prof. Dr. Lydia Gimenez Llort
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Institut de Neurociències, Department of Psychiatry & Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Campus Bellaterra, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 08193 Cerdanyola del Vallès, Barcelona, Spain
Interests: Alzheimer's disease; neurodegenerative diseases; translational behavioral neuroscience and pharmacology; aging; behavioral neuroendocrinology; neuropharmacology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
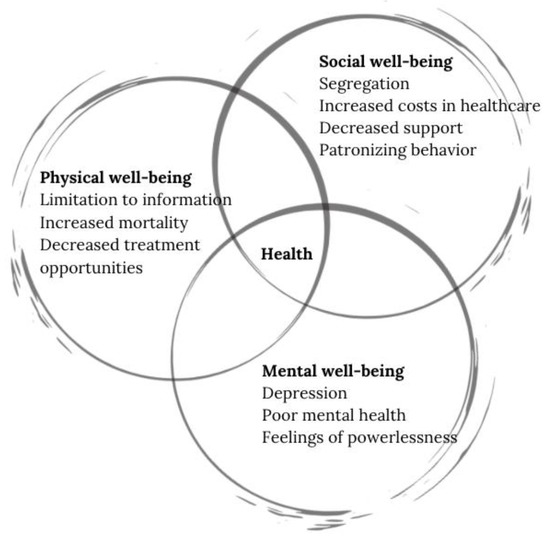
The first UN Global Report on Ageism (18th March 2021) has unveiled ageism as an old yet highly prevalent phenomenon, which extends worldwide and has a dramatic impact: "Ageism is associated with earlier death (by 7.5 years), poorer physical and mental health, and slower recovery from disability in older age." The Decade of Health Aging 2021–2030 does not just clash with the COVID-19 pandemic, insofar as its suddenly exhausted health and socioeconomic systems, but urgently needs to confront this old problem of stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination towards age and ageing. In response to the "Global Campaign to Combat Ageism" call for "A World for All Ages", this Topical Collection aims to provide selected contributions from quantitative and qualitative research or reviews, as well as promote new initiatives tackling ageism from different disciplines and perspectives. Potential topics include but are not limited to: stereotypes (how we think), prejudice (how we feel), and discrimination (how we act) towards others or oneself based on age. Its impact: culture's aging stereotypes; self-directed ageism; intersection and exacerbation of other disadvantages. Where it is seen: institutions; relationships; self-limiting behaviors; policies and practices. Strategies to combat it: (1) policies and laws; (2) educational activities; (3) intergenerational interventions; (4) other.
Prof. Dr. Lydia Gimenez Llort
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Geriatrics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1800 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- ageism
- stereotypes
- prejudice
- discrimination
- education
- policies
- intergenerational interventions
Published Papers (12 papers)
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Mitigating the Harmful Impact of Ageism among Older Individuals: The Buffering Role of Resilience Factors
by
Lotte P. Brinkhof, Sanne de Wit, Jaap M. J. Murre and K. Richard Ridderinkhof
Viewed by 1609
Abstract
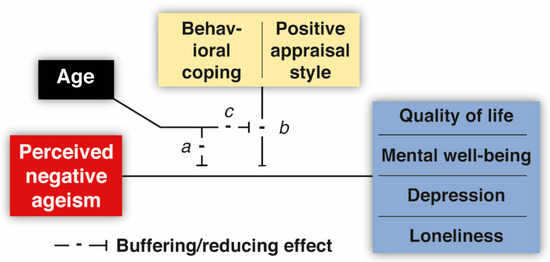
Frequent exposure to ageism has significant repercussions on the quality of life and mental well-being/health of older adults. Resilience may play a crucial role in mitigating these effects. The current study aimed to investigate the potential buffering roles of two types of coping
[...] Read more.
Frequent exposure to ageism has significant repercussions on the quality of life and mental well-being/health of older adults. Resilience may play a crucial role in mitigating these effects. The current study aimed to investigate the potential buffering roles of two types of coping variables—behavioral coping and a positive appraisal style—in older adults (N = 2000, aged 55–93). Confirming previous findings, higher levels of perceived negative ageism (PNA) were associated with diminished quality of life and mental well-being, increased depression and loneliness. However, individuals that tend to employ behavioral coping strategies when confronted with challenging/stressful situations showed a weaker relationship between PNA and quality of life, mental well-being, and depression. Embracing a positive appraisal style attenuated the negative impact of PNA on feelings of depression and loneliness. Interestingly, younger older adults appeared to benefit the most from these resilience factors. Despite considerable inter-individual variability, encouraging the utilization of behavioral coping strategies and nurturing a positive appraisal style could serve as effective approaches to mitigate the detrimental effects of PNA.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Institutionalisation of Brazilian Older Abused Adults: A Qualitative Study among Victims and Formal Carers
by
Dayane Ribeiro, Lígia Carreira, Maria Aparecida Salci, Francielle Renata Danielli Martins Marques, Adriana Gallo, Wanessa Baccon, Vanessa Baldissera and Carlos Laranjeira
Viewed by 1326
Abstract
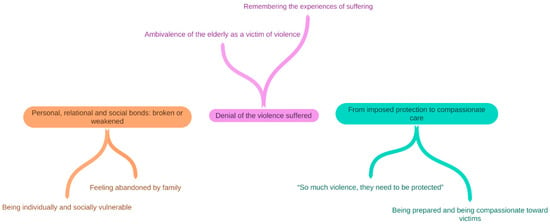
Abuse against elders is acknowledged as a severe and pervasive problem in society. If support services are not tailored to the victims’ knowledge or perceived needs, the intervention is likely to be unsuccessful. This study aimed to explore the experience of institutionalisation of
[...] Read more.
Abuse against elders is acknowledged as a severe and pervasive problem in society. If support services are not tailored to the victims’ knowledge or perceived needs, the intervention is likely to be unsuccessful. This study aimed to explore the experience of institutionalisation of abused older people from the perspective of the victims and their formal carers in a Brazilian social shelter. A qualitative descriptive study was performed with 18 participants, including formal carers and older abused persons admitted to a long-term care institution in the south of Brazil. Qualitative thematic analysis was used to analyse the transcripts of semi-structured qualitative interviews. Three themes were identified: (1) personal, relational, and social bonds: broken or weakened; (2) denial of the violence suffered; and (3) from imposed protection to compassionate care. Our findings provide insights for effective prevention and intervention measures in elder abuse. From a socio-ecological standpoint, vulnerability and abuse might be averted at the community and societal levels (e.g., education and awareness of elder abuse) by creating a minimum standard for the care of older individuals (e.g., law or economic incentives). Further study is needed to facilitate recognition and raise awareness among individuals in need and those offering assistance and support.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Population Older than 69 Had Similar Fatality Rates Independently If They Were Admitted in Nursing Homes or Lived in the Community: A Retrospective Observational Study during COVID-19 First Wave
by
Javier Martínez-Redondo, Carles Comas, Cristina García-Serrano, Montserrat Crespo-Pons, Pilar Biendicho Palau, Teresa Vila Parrot, Francisco Reventoz Martínez, Lídia Aran Solé, Neus Arola Serra, Eva Tarragona Tassies and Jesús Pujol Salud
Viewed by 1600
Abstract
The aim of this study is to assess the influence of living in nursing homes on COVID-19-related mortality, and to calculate the real specific mortality rate caused by COVID-19 among people older than 20 years of age in the Balaguer Primary Care Centre
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study is to assess the influence of living in nursing homes on COVID-19-related mortality, and to calculate the real specific mortality rate caused by COVID-19 among people older than 20 years of age in the Balaguer Primary Care Centre Health Area during the first wave of the pandemic. We conducted an observational study based on a database generated between March and May 2020, analysing COVID-19-related mortality as a dependent variable, and including different independent variables, such as living in a nursing home or in the community (outside nursing homes), age, sex, symptoms, pre-existing conditions, and hospital admission. To evaluate the associations between the independent variables and mortality, we calculated the absolute and relative frequencies, and performed a chi-square test. To avoid the impact of the age variable on mortality and to assess the influence of the “living in a nursing home” variable, we established comparisons between infected population groups over 69 years of age (in nursing homes and outside nursing homes). Living in a nursing home was associated with a higher incidence of COVID-19 infection, but not with higher mortality in patients over 69 years of age (
p = 0.614). The real specific mortality rate caused by COVID-19 was 2.27
0/
00. In the study of the entire sample, all the comorbidities studied were associated with higher mortality; however, the comorbidities were not associated with higher mortality in the infected nursing home patients group, nor in the infected community patients over 69 years of age group (except for neoplasm history in this last group). Finally, hospital admission was not associated with lower mortality in nursing home patients, nor in community patients over 69 years of age.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Health Consequences of Falls among Older Adults in India: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Isha Biswas, Busola Adebusoye and Kaushik Chattopadhyay
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2514
Abstract
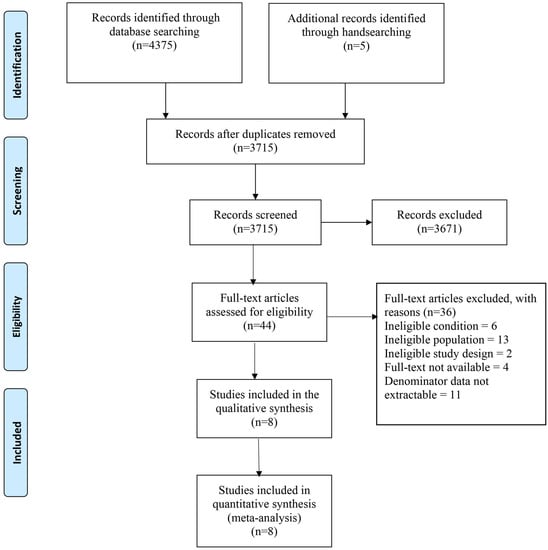
Research has been conducted on the prevalence of health consequences of falls among older adults (aged ≥60 years) in India, and our systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to synthe-size the existing evidence on this topic. The JBI guideline was followed for conducting this
[...] Read more.
Research has been conducted on the prevalence of health consequences of falls among older adults (aged ≥60 years) in India, and our systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to synthe-size the existing evidence on this topic. The JBI guideline was followed for conducting this review work. Several databases were searched, and eight studies were included. The critical appraisal scores (“yes” responses) for the included studies ranged from 56% to 78%. Among older adults in India who fell, the pooled prevalence of injuries was 65.63% (95% confidence interval [38.89, 87.96]). Similarly, head and/or neck injuries was 7.55% (4.26, 11.62), upper extremity injuries was 19.42% (16.06, 23.02), trunk injuries was 9.98% (2.01, 22.47), lower extremity injuries was 34.36% (24.07, 45.44), cuts, lacerations, abrasions, grazes, bruises and/or contusions was 37.95% (22.15, 55.16), fractures was 12.50% (7.65, 18.30), dislocations and/or sprains was 14.31% (6.03, 25.26), loss of consciousness was 5.96% (0.75, 15.08), disabilities was 10.79% (7.16, 15.02), and hospital admissions was 19.68% (15.54, 24.16). Some of the high figures indicate the need for prioritizing and addressing the problem. Furthermore, high-quality studies on this topic should be conducted, including on psychological health consequences, health-related quality of life, length of hospital stay, and death. PROSPERO registration: CRD42022332903.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
How Well Did the Healthcare System Respond to the Healthcare Needs of Older People with and without Dementia during the COVID-19 Pandemic? The Perception of Healthcare Providers and Older People from the SI4CARE Project in the ADRION Region
by
Stella Fragkiadaki, Dionysia Kontaxopoulou, Evangelia Stanitsa, Efthalia Angelopoulou, Dimosthenis Pavlou, Darja Šemrov, Simon Colnar, Mitja Lustrek, Bojan Blažica, Inga Vučica, Roberta Matković, Katarina Vukojevic, Ana Jelicic, Pietro Hiram Guzzi, Vlatka Martinović, Amina Pekmez Medina, Guido Piccoli, Margherita Menon, Srdjan Kozetinac, Miodrag Miljković, Chrysanthi Kiskini, Themis Kokorotsikos, Vasiliki Zilidou, Ivan Radević, John Papatriantafyllou, Eleftherios Thireos, Agis Tsouros, Vlado Dimovski and Sokratis G. Papageorgiouadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
| Viewed by 2064
Abstract
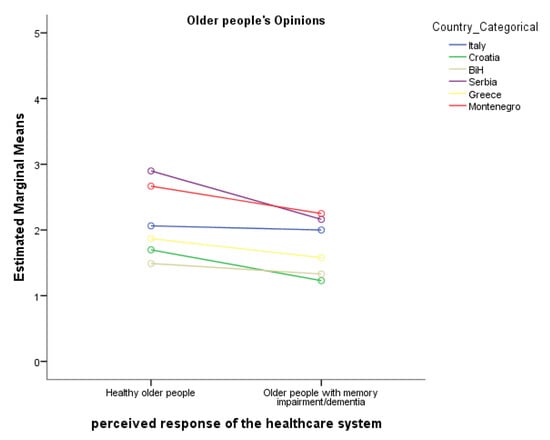
One major challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic was the limited accessibility to healthcare facilities, especially for the older population. The aim of the current study was the exploration of the extent to which the healthcare systems responded to the healthcare needs of the
[...] Read more.
One major challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic was the limited accessibility to healthcare facilities, especially for the older population. The aim of the current study was the exploration of the extent to which the healthcare systems responded to the healthcare needs of the older people with or without cognitive impairment and their caregivers in the Adrion/Ionian region. Data were collected through e-questionnaires regarding the adequacy of the healthcare system and were anonymously administered to older individuals and stakeholder providers in the following countries: Slovenia, Italy (Calabria), Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece, Montenegro, and Serbia. Overall, 722 older people and 267 healthcare stakeholders participated in the study. During the COVID-19 pandemic, both healthcare stakeholders and the older population claimed that the healthcare needs of the older people and their caregivers increased dramatically in all countries, especially in Italy (Calabria), Croatia and BiH. According to our results, countries from the Adrion/Ionian regions faced significant challenges to adjust to the special needs of the older people during the COVID-19 pandemic, which was possibly due to limited accessibility opportunities to healthcare facilities. These results highlight the need for the development of alternative ways of providing medical assistance and supervision when in-person care is not possible.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
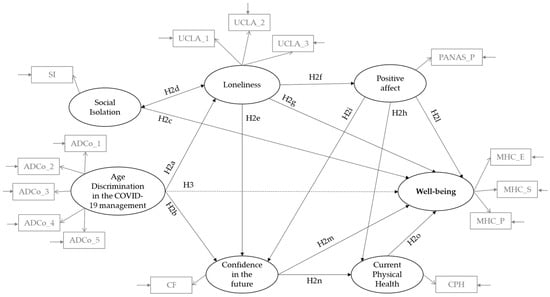
Ageism and the Pandemic: Risk and Protective Factors of Well-Being in Older People
by
Anna Rosa Donizzetti and Vincenza Capone
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2093
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has particularly affected the older population both in terms of the high number of victims and the psychological impact. Moreover, the pandemic has made older people more vulnerable to isolation and loneliness, and victims of ageism. The aim of the
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has particularly affected the older population both in terms of the high number of victims and the psychological impact. Moreover, the pandemic has made older people more vulnerable to isolation and loneliness, and victims of ageism. The aim of the present study was to investigate the risk and protective factors for the well-being of older people during the pandemic. The role of positive affect, confidence in the future, current physical health, social isolation, loneliness, and ageism were analysed. A self-report questionnaire was administered to 1301 participants (mean age: 77.3 years, DS: 5.46), almost equally distributed by gender (56.1% female). Descriptive and correlational analyses were performed, together with SEM. The results showed that perceived age discrimination positively predicts loneliness and negatively and indirectly predicts well-being. Furthermore, positive affect, confidence in the future, and current physical health are protective factors, while loneliness, social isolation, and ageism are risk factors. Future emergency policies must take into account the impact of such actions on the well-being of this segment of the population.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Attitude towards Older People According to Sociodemographic and Educational Variables in Students of a Chilean University
by
Rodrigo Yáñez-Yáñez, Maria Antonia Parra-Rizo, Nelson McArdle-Draguicevic, Nathalie Valdés-Valdés, Gabriel A. Rojas, Leslith Gamín, Paulina Lorca, Francisca Acevedo-Carrizo, Rafael Zapata-Lamana, Caterin Diaz-Vargas and Igor Cigarroa
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 4063
Abstract
Current evidence suggests that attitude towards older people may be associated with sociodemographic and educational variables; hence, a positive attitude towards older people is key when training new university professionals. However, there is little evidence of this association in Chilean university students. The
[...] Read more.
Current evidence suggests that attitude towards older people may be associated with sociodemographic and educational variables; hence, a positive attitude towards older people is key when training new university professionals. However, there is little evidence of this association in Chilean university students. The objective was to analyze students from a Chilean university’s attitudes towards older people, according to sociodemographic and educational variables. Analytical and cross-sectional study; 515 students from a Chilean university were consulted online about their attitude towards older people using Kogan’s Attitudes towards Old People scale. Additionally, sociodemographic and educational variables were recorded. The average score for positive attitude was 70.8 (±9.7), while the negative attitude score was 68.3 (±11.6). The total score was 139.1 (±16.6). Mostly, university students perceive themselves with a low-level positive attitude (61.2%). Additionally, older university students (26–42 years old); women; Chileans; students of law, speech therapy, and occupational therapy; students in their final years of the programs; and those who had training in older people outside the university have a more positive attitude towards older people. In Conclusion, a profile of sociodemographic and educational characteristics of students with a lower and higher attitude towards older age was investigated. These results are relevant since the way of seeing the aging process could regulate the training of future professionals and consequently generate changes in dealing with older people. Young people’s perception of ageing would affect the treatment and incorporation of the older people in society and the adaptation of policies in this age group.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Factors Influencing the Data Communication Equipment Competence in Korean Older People
by
HeeYoung Kim
Viewed by 1715
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to identify the most vulnerable group among older Korean adults regarding information literacy. Once that was identified, the study aimed to provide basic data for developing strategies to improve information literacy by investigating the factors that influence
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study was to identify the most vulnerable group among older Korean adults regarding information literacy. Once that was identified, the study aimed to provide basic data for developing strategies to improve information literacy by investigating the factors that influence the ability to utilize the Data Communication Equipment (DCE). The subjects included 10,073 older adults from the 10,299 participants of the 2017 Korean National Survey of Older Adults. The mean age of the older people was 74.06 years from a range of 65 to 106 years old. This study excluded the 216 individuals who did not complete the survey. The data were analyzed using the SPSS 18.0 program. A univariate analysis was performed to identify the most vulnerable group with regard to DCE competence. To investigate the factors that influence DCE competence, a logistic regression analysis was performed on the significant variables in the univariate analysis, while the nominal variables were treated as dummies. Senior citizens in Korea were less able to utilize DCE when they had higher ages, lower education levels, were women, lived alone, lower incomes, decreased sensory function, decreased cognitive function, negative value of learning, no lifelong learning, and smaller social networks. The factors influencing DCE competence in older adults were as follows: age, education level, income level, health status, cognitive function, social networks, lifelong learning, and the value of learning. For DCE competence in older adults to be effectively improved, adequate support must be provided to the vulnerable group. Furthermore, support for personalized DCE utilization seems essential and should consider a person’s age, education level, income, health status, cognitive function, social networks, lifelong learning and the value of learning.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
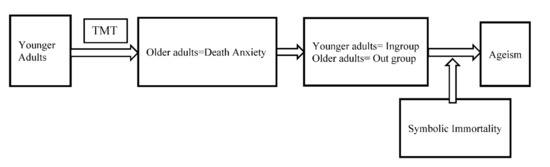
Nurses’ Death Anxiety and Ageism towards Older Adults Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Moderating Role of Symbolic Immortality
by
Mohammad Rababa, Shatha Al-Sabbah and Dania Bani-Hamad
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2758
Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected all aspects of individuals’ lives and behaviors, including the behaviors of nurses. Specifically, the pandemic has impacted the way that nurses treat older adults and has led to the spread of ageism among nurses. This
[...] Read more.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected all aspects of individuals’ lives and behaviors, including the behaviors of nurses. Specifically, the pandemic has impacted the way that nurses treat older adults and has led to the spread of ageism among nurses. This study was conducted using self-report tools on 163 nurses to examine the problem of ageism amid the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that critical care nurses have higher levels of death anxiety and ageism in comparison to medical/surgical nurses. After controlling for the work department, low levels of symbolic immortality were associated with high levels of ageism and death anxiety among nurses. These results might provide an insight into the development of a psychological intervention to reduce nurses’ death anxiety and ageism toward older adults.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
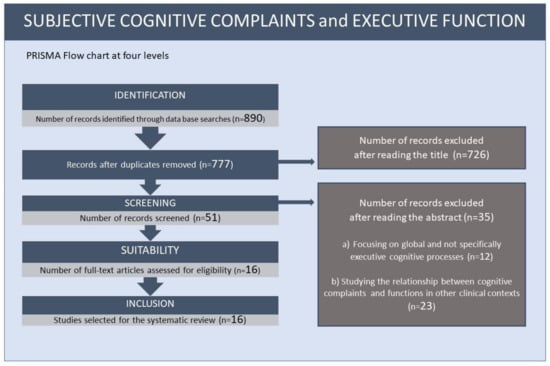
The Challenge of Subjective Cognitive Complaints and Executive Functions in Middle-Aged Adults as a Preclinical Stage of Dementia: A Systematic Review
by
Felipe Webster-Cordero and Lydia Giménez-Llort
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3324
Abstract
Subjective cognitive complaints correspond to a heterogeneous construct that frequently occurs in the early stages of older adult life. Despite being a common source of worry for middle-aged people, it can be underestimated when clinical and neuropsychological assessments discard any underlying pathological processes.
[...] Read more.
Subjective cognitive complaints correspond to a heterogeneous construct that frequently occurs in the early stages of older adult life. Despite being a common source of worry for middle-aged people, it can be underestimated when clinical and neuropsychological assessments discard any underlying pathological processes. Negative age stereotyping but also self-stereotyping can contribute to doing so. Although its diagnosis is a challenge, its implication as a possible predictor of mild cognitive impairment or dementia increases the interest in its early diagnosis and intervention. The present systematic review analyzes the empirical data on the relationship between these complaints and early executive dysfunction with possible predictive value for preclinical stages of dementia. The sixteen papers obtained from the PubMed and Embase databases were exploratory, cross-sectional and prospective in scope. The studies corroborated the relationship between subjective cognitive complaints and some executive processes, which is noteworthy since many people with subjective executive complaints progress to dementia. The relational studies confirmed that impaired executive performance is associated with CSF biomarkers and reduced cortical volume in specific brain regions. However, the heterogeneity of reports in these studies demands stronger efforts in future research with specific tools applied in clinical and neuropsychological assessments and analyzed under a gender perspective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Ageist No More: Interprofessional Training for Undergraduate Healthcare Students
by
Aniela Mendez, Mildred Lopez, Karina Rodriguez-Quintanilla and Belinda Carrion
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3066
Abstract
Ageism seeps deep into our society, whether in law, policies, or healthcare practices it segregates individuals based on their age. The aim of this work was to evaluate the impact of an educational strategy in ageist attitudes against older adults in healthcare undergraduate
[...] Read more.
Ageism seeps deep into our society, whether in law, policies, or healthcare practices it segregates individuals based on their age. The aim of this work was to evaluate the impact of an educational strategy in ageist attitudes against older adults in healthcare undergraduate students. A five-week intervention: Healthy environments and self-care for the older adults was implemented. To assess the impact of this strategy in ageist attitudes in participants, a simulated consultation with an older adult was conducted. Participants’ perspectives on the experience were collected using an online survey. One hundred and thirty-eight undergraduate students from health programs were included. They highlighted growth in the understanding of the normal aging process and the prejudices that surround aging. During the role-play activity, participants identified communication, empathy, and professionalism as the abilities developed with this strategy and the need to show empathy and avoid prejudice against older adults in their clinical interactions. Educational interventions are a great tool to promote cultural changes, diminish prejudices and misconceptions of ageism in future healthcare professionals.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Spanish Intergenerational Study: Beliefs, Stereotypes, and Metacognition about Older People and Grandparents to Tackle Ageism
by
Aida Muntsant, Paula Ramírez-Boix, Rocío Leal-Campanario, Francisco Javier Alcaín and Lydia Giménez-Llort
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2957
Abstract
Ageism can be seen as systematic stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination of people because of their age. For a long time, society has accepted negative stereotypes as a norm. When referring to older adults, the United Nations Global Report on Ageism warns about a
[...] Read more.
Ageism can be seen as systematic stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination of people because of their age. For a long time, society has accepted negative stereotypes as a norm. When referring to older adults, the United Nations Global Report on Ageism warns about a severe impact. The Intergenerational Study for a Healthy Aging, a questionnaire about believes, stereotypes, and knowledge about older people and grandparents, was administered to 326 Spanish biology and medical students. Here we report the results of stereotype analysis through adjective qualification of the youth and older people performed before the survey. Content analysis of two open questions about metacognition at the end of the survey is also presented. The results show that: (1) The questionnaire promoted metacognition; (2) Positive metacognition toward grandparents was higher than for the general old population; (3) Most participants were not conscious about ageism; (4) Gender was a key factor—male students were more ageist than females; (5) The feeling of guilt was higher in the questionnaire about older people; (6) The metacognition exercise elicited thoughts and, in few cases, the need to take action to tackle ageism. In conclusion, both activities promoted active thoughts about older people vs. grandparents and helped participants realize unconscious ageism—specifically toward the older population—serving as an awareness activity that may help tackle ageism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures