Advances in Gastrointestinal Cancer
A topical collection in Gastroenterology Insights (ISSN 2036-7422). This collection belongs to the section "Gastrointestinal Disease".
Viewed by 30894Editors
Interests: urothelial cancer; sarcoma; molecular pathology; experimental therapeutics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: comorbidity; radiotherapy; cancer; population-based treatment studies; radiation oncology
2. Department of Oncology, National Cheng Kung University Hospital and National Cheng Kung University, Tainan 704, Taiwan
Interests: solid tumors; signaling transduction; molecular biology; Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST); biliary tract cancer; clinical research; pancreatic cacer
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
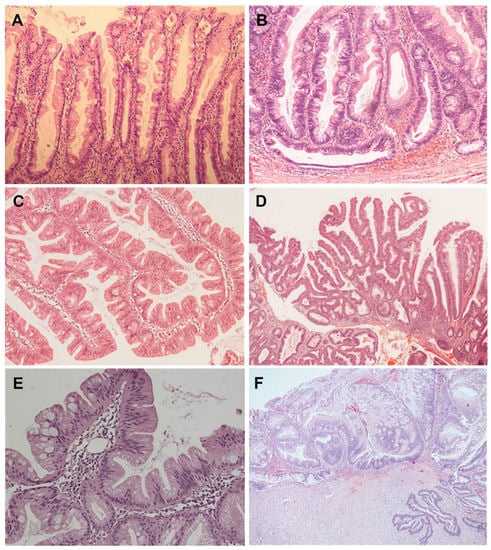
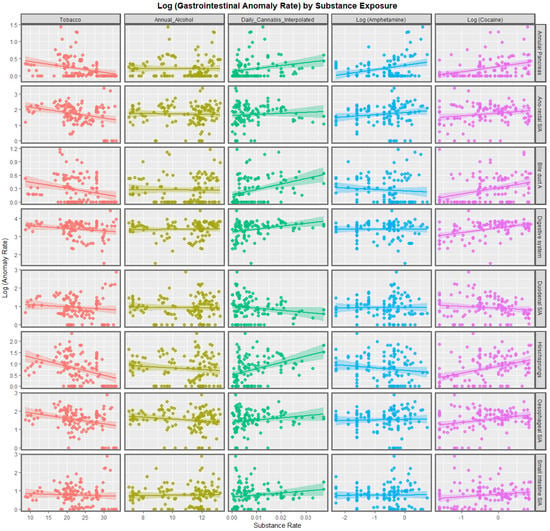
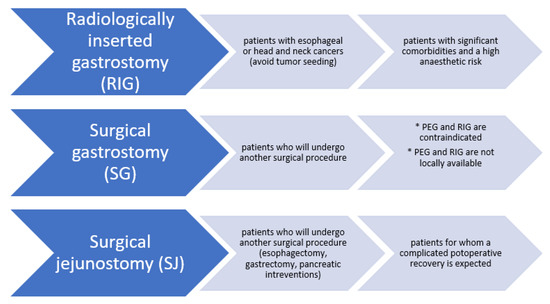
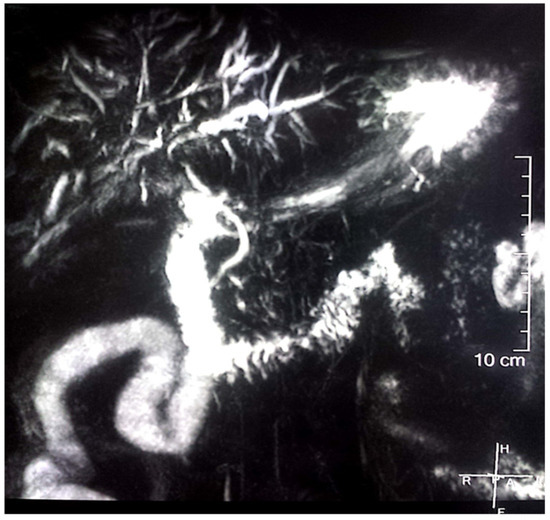
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is the fourth most common cancer, which leads to a considerable number of cancer-related deaths worldwide. GI cancer consists of a heterogeneous group of cancers with wide ranging anatomic sites, etiology, pathogenesis, molecular aberrations, histological features, and clinical outcomes. It mostly involves the esophagus, stomach, liver and biliary tract, gallbladder, pancreas, colon, and rectum. To date, surgery remains the mainstay of early-stage GI cancer; chemotherapy is the therapeutic cornerstone in unresectable and metastatic GI cancer. However, an increasing number of targeted therapy strategies have been developed based on recent studies that have disclosed the genetic and molecular biological and immune landscapes of various GI cancers. The emerging integration of multi-omic profiling will also lead to the identification of distinct molecular subtypes with diverse clinical behaviors. With the above-mentioned efforts, the management of GI cancer is now moving toward precision- and evidence-based personalized therapeutics.
Accordingly, the aim of this Special Issue is to deliver the most up-to-date concepts for GI cancer diagnosis, classification, prognostication, surgical and pharmaceutical treatment, and biomarker identification. With the scope to eliminate the gaps between clinical and basic research, studies conducted in a translational manner will be given priority for this issue.
Prof. Dr. Chien-Feng Li
Dr. Ching-Chieh Yang
Dr. Nai-Jung Chiang
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Gastroenterology Insights is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- gastrointestinal cancer
- pathology
- biomarker
- diagnosis
- surgery
- radiotherapy
- targeted therapy
- clinical trial