-
 Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor
Overview of Pharmacological Therapies for Diffuse Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor -
 Erythrocyte Folyl Polyglutamate Synthetase Activity Profiling as a Potential Tool for the Prediction of Methotrexate Efficacy and Toxicity in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Erythrocyte Folyl Polyglutamate Synthetase Activity Profiling as a Potential Tool for the Prediction of Methotrexate Efficacy and Toxicity in Rheumatoid Arthritis -
 Evaluations of NSAIDs and Opioids as Analgesics in Pediatric Oncology
Evaluations of NSAIDs and Opioids as Analgesics in Pediatric Oncology -
 Carrier-Mediated Delivery of Low-Molecular-Weight N-Containing Drugs across the Blood–Brain Barrier or the Blood–Retinal Barrier Using the Proton-Coupled Organic Cation Antiporter
Carrier-Mediated Delivery of Low-Molecular-Weight N-Containing Drugs across the Blood–Brain Barrier or the Blood–Retinal Barrier Using the Proton-Coupled Organic Cation Antiporter
Journal Description
Future Pharmacology
Future Pharmacology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on pharmacology, drug discovery, and therapeutics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Future Pharmacology is a companion journal of Pharmaceutics.
Latest Articles
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling of UGT Substrate Drugs Lamotrigine and Raltegravir during Pregnancy
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(2), 317-335; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4020018 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Pregnancy is associated with various physiological changes that can significantly impact the disposition of drugs. To further the insight into how pregnancy affects the pharmacokinetics of drugs at different stages, clinical studies can be simulated using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic modelling. PBPK modelling of
[...] Read more.
Pregnancy is associated with various physiological changes that can significantly impact the disposition of drugs. To further the insight into how pregnancy affects the pharmacokinetics of drugs at different stages, clinical studies can be simulated using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic modelling. PBPK modelling of drugs metabolised by Phase I enzymes (CYPs) in pregnant population models had been reported in the past, while its use in Phase II (UGTs) is not known. In this study, based on the results of a recent meta-analysis, lamotrigine (UGT1A4) and raltegravir (UGT1A1) were selected as candidate drugs, and pregnancy-specific models were developed for both using the Simcyp v.21 simulator. A middle-out strategy was used where previously published drug parameters were adapted from a minimal to a full PBPK model to allow their application for the pregnancy population models using Simcyp PBPK software. Adapted models were successfully validated against observed clinical data both qualitatively (visual overlay of plasma concentrations on graphs) and quantitatively (calculating the predicted/observed ratios for AUC, Cmax and CL as well as statistical analysis using model prediction power metrics). They were then applied to predict the PKs of both drugs in pregnancy population models. The temporal changes in maternal enzymatic activities during gestation were modelled based on in vitro data reported in literature and default relationships encoded in the Simcyp platform for UGT1A1 and UGT1A4, respectively. Our study demonstrates the successful development and validation of a PBPK model for LTG and RTG in pregnancy population models. Future work with additional UGT1A4 substrate drugs using the proposed changes in UGT1A4 activity may enable validating the pregnancy population model and its subsequent use for the prospective prediction of PK.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Biologics, Small Molecules and More in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The Present and the Future
by
Manish Manrai, Atul Abhishek Jha, Saurabh Dawra and Aditya Vikram Pachisia
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 279-316; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010017 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of heterogeneous chronic inflammatory diseases of the gut presenting with intestinal and extraintestinal manifestations. Most cases fit in predominantly two types, namely, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The incidence of IBD has been increasing steadily in
[...] Read more.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of heterogeneous chronic inflammatory diseases of the gut presenting with intestinal and extraintestinal manifestations. Most cases fit in predominantly two types, namely, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The incidence of IBD has been increasing steadily in the past three decades. Focused research has resulted in many therapeutic options. Biologics (derived from humans or animals) and small molecules have emerged as the cornerstone in the management of IBD and have become widely available. Currently, monoclonal antibodies against tumor necrosis factor-alpha (infliximab, adalimumab, certolizumab, and golimumab), integrins (vedolizumab and natalizumab), and interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonists (ustekinumab), along with small molecules (tofacitinib), are approved for use. This article summarizes various aspects of these drugs, like clinical pharmacology, indications for use in IBD, safety in pregnancy and lactation, and the adverse effects profile based on the studies leading to their approval. This review also focuses on the recent advances and future perspectives specific to biologics in IBD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Study of the Effects of Curcuminoids and Tetrahydrocurcuminoids on Melanogenesis: Role of the Methoxy Groups
by
Shilpi Goenka
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 256-278; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010016 - 08 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Curcuminoids are naturally occurring yellow-colored compounds that, when hydrogenated to remove their conjugated double bond, become colorless and are referred to as tetrahydrocurcuminoids. Curcuminoids consist of pure curcumin (PC) in major amounts and demethoxycurcumin (DC) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDC) in minor amounts. Tetrahydrocurcuminoids similarly
[...] Read more.
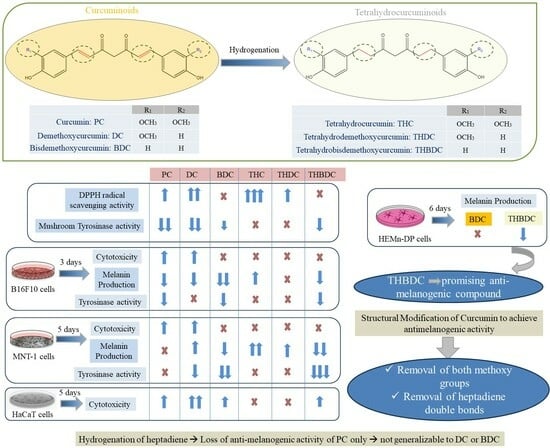
Curcuminoids are naturally occurring yellow-colored compounds that, when hydrogenated to remove their conjugated double bond, become colorless and are referred to as tetrahydrocurcuminoids. Curcuminoids consist of pure curcumin (PC) in major amounts and demethoxycurcumin (DC) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDC) in minor amounts. Tetrahydrocurcuminoids similarly consist mainly of tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), along with minor amounts of tetrahydrodemethoxycurcumin (THDC) and tetrahydrobisdemethoxycurcumin (THBDC). Previous studies have shown the inhibitory effects of PC, DC, and BDC on melanin production, but there are contradictory findings about THC. In addition, there are currently no reports on the effects of THDC and THBDC on melanogenesis. Our previous report described that, in contrast to PC, which suppressed melanin production, THC stimulated melanin production in B16F10 and MNT-1 cells; this effect was ascribed to the loss of the conjugated heptadiene moiety of PC. However, whether this finding can be generalized to the two curcumin derivatives (DC and BDC), such that THDC and THBDC might also stimulate melanogenesis, has not been addressed. Herein, a comparative study of six curcumin derivatives (PC, DC, BDC, THC, THDC, and THBDC) was undertaken to identify their effects on melanogenesis with the goal of elucidating the structure–activity relationships (SARs) focused on assessing the two regions of the parent curcumins’ structure: (i) the hydrogenation of the two double bonds bridging the phenyl rings to the β-diketone moiety, and (ii) the effect of the ortho-methoxy substituent (-OCH3) on the two phenyl rings. To determine the direct effects of the six compounds, antioxidant activity and tyrosinase activity were assessed in cell-free systems before cellular experiments utilizing the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells, MNT-1 human melanoma cells, and primary cells. Evaluations were made on cytotoxicity, melanin concentration, and cellular tyrosinase activity. The results showed that BDC inhibited melanogenesis in B16F10 and MNT-1 cells. However, it was ineffective in primary human melanocytes, while THBDC continued to exhibit anti-melanogenic capacity in normal human melanocytes. Moreover, these findings provide a novel perspective into the role of the methoxy groups of PC on the biological effects of melanogenesis and also confirm that the removal of the conjugated double bonds abolishes the anti-melanogenic capacity of PC and DC only, but not BDC, as THBDC maintained anti-melanogenic activity that was greater than BDC. However, the outcome is contingent upon the specific kind of cell involved. To the best of our knowledge, this work presents novel findings indicating that the anti-melanogenic capacity of the colored BDC is not only intact but enhanced after its hydrogenation as observed in THBDC. The findings show potential for using colorless THBDC as a pharmacological candidate to diminish the increased pigmentation characteristic of skin hyperpigmentation disorders. Future pharmacological therapeutics that incorporate pure THBDC or THBDC-enriched extracts, which retain both a colorless appearance and potent anti-melanogenic activity, can be applied to compounds for anti-melanoma therapeutics where the demand for nontoxic novel molecules is desired for established efficacies.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Using 5-Nitroimidazole Derivatives against Neglected Tropical Protozoan Diseases: Systematic Review
by
Micheel M. Vichi-Ramírez, Edgar López-López, Catalina Soriano-Correa and Carolina Barrientos-Salcedo
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 222-255; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010015 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a significant global health problem. Additionally, anti-protozoan treatments are toxic, and their therapeutic regimens require prolonged treatment times and high concentrations of the drugs. Additionally, multi-resistant protozoan strains represent an important global emergency that must be addressed. For
[...] Read more.
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a significant global health problem. Additionally, anti-protozoan treatments are toxic, and their therapeutic regimens require prolonged treatment times and high concentrations of the drugs. Additionally, multi-resistant protozoan strains represent an important global emergency that must be addressed. For these reasons, global efforts are being made to identify new drug candidates that are capable of combating these kinds of diseases. This systematic review shows that 5-nitroimidazole derivatives have been successfully used against neglected tropical protozoan diseases (NTPDs), with a specific focus on three diseases: malaria, leishmaniasis, and human trypanosomiasis. Some nitroimidazole derivatives have been repurposed, and an important group of new drugs is available for the treatment of NTPDs. Finally, we address 5-nitroimidazoles using chemoinformatics and medicinal chemistry tools to describe the most recent and promising 5-nitroimidazole derivatives associated with anti-protozoal activity using their published in vitro and in vivo data. We show that 5-nitroimidazoles offer a broader spectrum of activity against a variety of protozoal pathogens. More importantly, these compounds demonstrate a significantly reduced systemic toxicity compared to other nitroimidazoles. This makes them a more favorable option in the treatment of protozoal infections, particularly in scenarios where the patient’s tolerance to drug side effects is a critical concern.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
The Role of Lysophosphatidic Acid in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders
by
Simona Dedoni, Chiara Camoglio, Carlotta Siddi, Maria Scherma, Walter Fratta and Paola Fadda
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 199-221; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010014 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Individuals suffering from diverse neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders often have comparable symptoms, which may underline the implication of shared hereditary influences and the same biological processes. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a bioactive phospholipid and a crucial regulator of the development of adult neuronal
[...] Read more.
Individuals suffering from diverse neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders often have comparable symptoms, which may underline the implication of shared hereditary influences and the same biological processes. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a bioactive phospholipid and a crucial regulator of the development of adult neuronal systems; hence, it may play an important role in the onset of certain diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, and schizophrenia. During development, LPA signaling regulates many cellular processes such as proliferation, survival, migration, differentiation, cytoskeleton reorganization, and DNA synthesis. So far, six lysophosphatidic acid receptors that respond to LPA have been discovered and categorized based on their homology. Despite the abundance of evidence relating LPA cellular activities to different pathological conditions, little is known about the involvement of LPA in the field of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases. The purpose of this review is to define LPA activities related to the illnesses stated above in order to better understand these pathologies and provide future novel treatment strategies based on the latest data.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Target-Based 6-5 Fused Ring Heterocyclic Scaffolds Display Broad Antiparasitic Potency In Vitro
by
Darline Dize, Mariscal Brice Tchatat Tali, Cyrille Armel Njanpa Ngansop, Rodrigue Keumoe, Eugenie Aimée Madiesse Kemgne, Lauve Rachel Tchokouaha Yamthe, Patrick Valere Tsouh Fokou, Boniface Pone Kamdem, Katsura Hata and Fabrice Fekam Boyom
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 188-198; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010013 - 28 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Malaria, leishmaniasis, and African trypanosomiasis are protozoan diseases that constitute major global health problems, especially in developing countries; however, the development of drug resistance coupled with the toxicity of current treatments has hindered their management. The involvement of certain enzymes (dihydrofolate reductase [DHFR])
[...] Read more.
Malaria, leishmaniasis, and African trypanosomiasis are protozoan diseases that constitute major global health problems, especially in developing countries; however, the development of drug resistance coupled with the toxicity of current treatments has hindered their management. The involvement of certain enzymes (dihydrofolate reductase [DHFR]) or proteins (potassium channels) in the pathogenesis of these protozoan diseases is undeniable. In this study, a series of three DHFR inhibitors (6-5 fused heterocyclic derivatives X, Y, and Z) and one K+ channel blocker (E4031) were screened for their inhibitory effects on Leishmania donovani, Plasmodium falciparum, and Trypanosoma brucei. A resazurin assay was used to assess the antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial activities of the test compounds, whereas the antiplasmodial activity was evaluated through the SYBR Green I test. Moreover, the cytotoxicities of the test compounds were evaluated in Vero, Raw 264.7, and HepG-2 cells using a resazurin-based test, while their pharmacokinetic properties were predicted using the online tool, pkCSM. As a result, compound Y exhibited selective (selectivity index range: from 2.69 to >61.4; Vero, Raw 264.7, and HepG-2 cells) and broad-spectrum antiprotozoal activity against L. donovani promastigotes (IC50: 12.4 µM), amastigotes (IC50: 4.28 µM), P. falciparum (IC50: 0.028 µM), and T. brucei brucei (IC50: 0.81 µM). In addition, compound X inhibited the growth of P. falciparum (IC50: 0.0052 µM) and T. brucei brucei (IC50: 6.49 µM). In silico screening of the active antiprotozoal compounds revealed positive drug likeness scores, as none of the criteria for Lipinski’s rule were violated by these compounds. However, in-depth pharmacokinetic and mechanistic studies are warranted to support the discovery of novel antiprotozoal agents against malaria, leishmaniasis, and African trypanosomiasis by repurposing K+ channel blockers and DHFR inhibitors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Low-Impact Ampakine CX1739 Exerts Pro-Cognitive Effects and Reverses Opiate-Induced Respiratory Depression in Rodents
by
Daniel Pierce Radin, Sheng Zhong, Rok Cerne, Mohammed Shoaib, Jeffrey M. Witkin and Arnold Lippa
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 173-187; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010012 - 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
AMPA-glutamate receptors (AMPARs) are expressed throughout the CNS and mediate the majority of fast excitatory synaptic transmission. Ampakines are orally available small molecules that bind allosterically to AMPARs and enhance excitatory currents elicited by the endogenous agonist glutamate. In preclinical studies, ampakines are
[...] Read more.
AMPA-glutamate receptors (AMPARs) are expressed throughout the CNS and mediate the majority of fast excitatory synaptic transmission. Ampakines are orally available small molecules that bind allosterically to AMPARs and enhance excitatory currents elicited by the endogenous agonist glutamate. In preclinical studies, ampakines are effective in ameliorating symptoms in a battery of neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases in which excitatory transmission is compromised. However, the development of ampakines as medicines was slowed by the emergence of neurotoxicity and seizures in rodents due to some ampakines. Here, we describe the preclinical pharmacology of a novel ampakine, N-methyl-N-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)benzo[c][1,2,5] oxadiazole-5-carboxamide (CX1739), that does not induce seizures in animals or humans at efficacious doses. CX1739 dose-dependently enhanced long-term potentiation in vivo in rats, a process thought to be a molecular substrate of learning and memory. Correspondingly, CX1739 dose-dependently enhanced performance in assays that probed multiple aspects of cognition—the novel object recognition test, the win shift radial arm maze, and the five-choice serial reaction time task in rats. CX1739 also abrogated amphetamine-induced locomotor activity, demonstrating that it may be given in conjunction with stimulants for pro-cognitive gains while mitigating the side effects of stimulant-based ADHD medications. CX1739 also rapidly reversed opioid-induced respiratory depression. While efficacy in these tests occurred at doses of 0.03–18 mg/kg, there were no adverse events detected in safety studies in rats up to 2000 mg/kg. These preclinical findings suggest that CX1739 can be translated safely into the clinical setting to potentially treat dementia, neuropsychiatric disorders, and the life-threatening complication of opiate-induced suppression of endogenous inspiratory breathing rhythms.
Full article
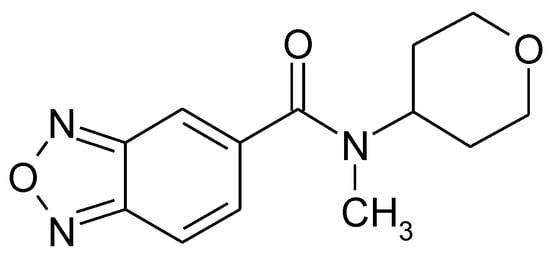
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Atazanavir/Ritonavir Increased Tizoxanide Exposure from Oral Nitazoxanide through Pharmacokinetic Interaction in Healthy Volunteers
by
Abdulafeez Akinloye, Timothy Oyedeji, Oluwasegun Eniayewu, Babatunde Adeagbo, Oluseye Bolaji, Steve Rannard, Andrew Owen and Adeniyi Olagunju
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 163-172; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010011 - 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nitazoxanide use is limited by gastrointestinal side effects associated with increasing dose. In this drug repurposing study, we investigated the possibility of enhancing the exposure of its active metabolite, tizoxanide, through pharmacokinetic interaction with atazanavir/ritonavir. In this crossover drug–drug interaction study, 18 healthy
[...] Read more.
Nitazoxanide use is limited by gastrointestinal side effects associated with increasing dose. In this drug repurposing study, we investigated the possibility of enhancing the exposure of its active metabolite, tizoxanide, through pharmacokinetic interaction with atazanavir/ritonavir. In this crossover drug–drug interaction study, 18 healthy participants received a single dose of 1000 mg of nitazoxanide alone and in combination with 300/100 mg atazanavir/ritonavir in period 1 and 2 respectively. On both days, blood samples for intensive pharmacokinetic analyses were collected at 0–12 h post-dose. To explore the utility of dried blood spots (DBS) as an alternative to plasma for tizoxanide quantification, 50 µL of blood from some participants was spotted on DBS cards and correlated with plasma concentrations. Pharmacokinetic parameters were derived by non-compartmental analysis and compared between both periods. Co-administration of nitazoxanide with atazanavir/ritonavir resulted in a significant increase in tizoxanide plasma exposure [GMR (90% CI) of AUC0–12h, Cmax and C12h being 1.872 (1.870–1.875), 2.029 (1.99–2.07) and 3.14 (2.268–4.352), respectively]. DBS concentration (%CV) was 46.3% (5.6%) lower than plasma concentrations, and there was strong correlation (R = 0.95, p < 0.001) between DBS-derived plasma concentration and plasma concentrations. Co-administration with atazanavir/ritonavir enhanced tizoxanide exposure with no report of adverse events in healthy volunteers.
Full article
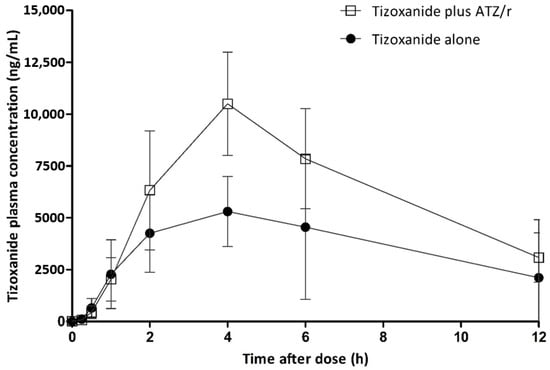
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Human Serum Albumin Grafted by Monomeric and Polymeric β-Cyclodextrin as Drug Delivery System for Levofloxacin with Improved Pharmacological Properties
by
Tatiana Yu Kopnova, Linara R. Yakupova, Natalya Georgievna Belogurova and Elena Vadimovna Kudryashova
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 139-162; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010010 - 13 Feb 2024
Abstract
Human serum albumin (HSA) is a multifunctional protein, known to be a natural carrier for a number of endogenous and exogenous compounds, including drugs. HSA-based drugs formulation is a clinically validated approach to improve pharmacological properties and biodistribution (such as in Abraxane). Based
[...] Read more.
Human serum albumin (HSA) is a multifunctional protein, known to be a natural carrier for a number of endogenous and exogenous compounds, including drugs. HSA-based drugs formulation is a clinically validated approach to improve pharmacological properties and biodistribution (such as in Abraxane). Based on this, one might like to modify HSA in a way that its distribution is more favorable for certain therapeutic purposes. Levofloxacin (LV), a broad-spectrum antibiotic drug, could benefit from extended systemic exposure, and stronger interactions with plasma proteins could be useful for this purpose. We engrafted monomeric or polymeric cyclodextrins (CDs) on the surface of HSA molecules to strengthen the LV adsorption (the CD−LV dissociation constant is three orders of magnitude lower than that of HSA−LV). We found that (HSA−HPolS)conj+LV exhibited the highest activity against E. coli, whereas (HSA−HPCD)conj+LV was the most effective against B. subtilis, and both HSA conjugates were more potent than LV alone or LV with HSA. Further fine-tuning of HSA could yield an improvement in biodistribution and thus a more favorable risk/benefit ratio.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Drug Delivery Systems Using Polymeric Nanocarriers)
►▼
Show Figures
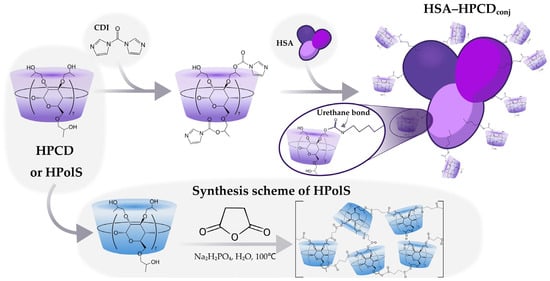
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
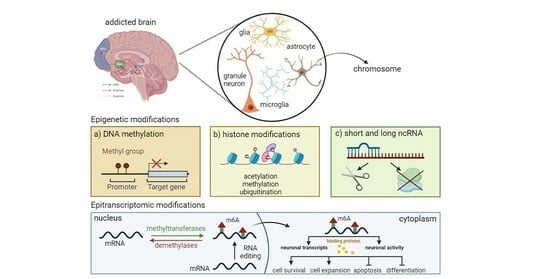
Breaking the Chains: Advances in Substance Addiction Research through Single-Cell Sequencing, Epigenetics, and Epitranscriptomic
by
Ana Filošević Vujnović, Ivana Stanković Matić, Lara Saftić Martinović and Sanja Dević Pavlić
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 115-138; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010009 - 29 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Addiction is a complex brain disease influenced by genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Psychostimulants, cocaine, and methamphetamine influence different cell types in different brain regions, with a focus on the neurons responsible for rewarding effects in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and ventral tegmental
[...] Read more.
Addiction is a complex brain disease influenced by genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Psychostimulants, cocaine, and methamphetamine influence different cell types in different brain regions, with a focus on the neurons responsible for rewarding effects in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA). Known markers for psychostimulant-induced neuronal plasticity in combination with droplet-based high-throughput single-cell sequencing divided the heterogeneity of cell populations in NAc and VTA into clusters, where all cells of the same type do not respond equally to exposure to psychostimulants. To explain psychostimulant-induced neuronal plasticity as changes in the amplitude and phase shifts of gene expression, we focused on epigenetic mechanisms of DNA and chromatin modifications, as well as DNA accessibility. We also comment on epitranscriptomics as a novel approach in the study of messenger RNA posttranslational modification, which regulates translation and potentially localized transcription in synapses in order to address the molecular chains that connect addiction from changes in gene expression to synaptic and, finally, neuronal plasticity.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Pharmacokinetics Profile and Genetics of Double Antiviral Therapy with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for Prolonged COVID-19 in Patients Treated with Rituximab: A Real-Life Study and Literature Review
by
Ilaria De Benedetto, Silvia Corcione, Carlotta Giambra, Matteo Ferrante, Simone Mornese Pinna, Elisa Zanotto, Alice Palermiti, Francesca Sidoti, Luca Scaglione, Cecilia Grosso, Martina Billi, Tommaso Lupia, Sara Soloperto, Jessica Cusato, Cristina Costa, Antonio D’Avolio and Francesco Giuseppe De Rosa
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 103-114; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010008 - 24 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Patients with hematologic malignancies are more likely to develop severe and prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection, often showing viral persistence despite the use of authorized antivirals. Herein, we report the cases of four patients who received rituximab for different conditions and developed persistent COVID-19
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Patients with hematologic malignancies are more likely to develop severe and prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection, often showing viral persistence despite the use of authorized antivirals. Herein, we report the cases of four patients who received rituximab for different conditions and developed persistent COVID-19 treated with an extended course of dual antivirals, Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir. Moreover, we describe the pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics (PK/PG) characteristics of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir treatment in two of these patients. Methods: Plasma specimens for evaluation of trough concentrations (Ctrough) were collected 10 min before the daily dose administration, in addition to 3 h (Cmax), 4 h (C4h), 6 h (C6h) and 1 h (Cmax) after the administration of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir, respectively. The following gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were investigated: ABCB1 3435 (rs1045642) C > T, ABCB1 1236 (rs1128503) C > T, PXR 63396 (rs2472667) T > C, CYP2D6 (rs1135840) G > C, and CYP3A4*1B (rs2740574) G > A. Results: Double antiviral treatment was successful in terms of symptoms resolution, whereas three out of four patients achieved microbiological eradication. Based on our results, concentrations of Nirmatrelvir ranging from 50 to 5000 ng/mL were effective, whereas a higher concentration (range 1068–3377 ng/mL), compared to that previously reported in patients with similar weight and BMI, was evidenced for Ritonavir. Considering the genetic variant analysis, ABCB1 3435 CT and 1236 CT genotypes were found in patient 1; and ABCB1 3435 CC and 1236 CC in patient 2. In conclusion, this real-life study supports the usefulness of TDM and genetics in immunocompromised patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection, a challenging setting for clinicians in which personalized medicine may improve outcome.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
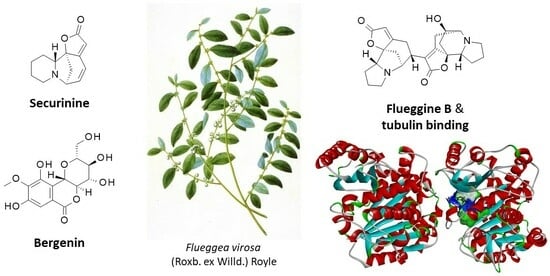
Traditional Uses, Pharmacology and Phytochemistry of the Medicinal Plant Flueggea virosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) Royle
by
Christian Bailly
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 77-102; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010007 - 18 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The white berry bush, officially Flueggea virosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) Royle is a medicinal plant distributed throughout tropical areas and traditionally used in Africa, India and China. Root decoctions are used to treat abdominal pain, whereas extracts from the aerial parts serve to
[...] Read more.
The white berry bush, officially Flueggea virosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) Royle is a medicinal plant distributed throughout tropical areas and traditionally used in Africa, India and China. Root decoctions are used to treat abdominal pain, whereas extracts from the aerial parts serve to treat liver and urinary diseases, inflammatory pathologies and diabetes, among other pathologies. Plant extracts have revealed antiparasitic, antimicrobial, antiepilepsy, antidiabetic, anticancer and analgesic effects. Three main categories of phytochemicals were isolated from F. virosa: polyphenols, with the lead product bergenin; terpenoids, such as the flueggenoids and related podocarpane-type diterpenoids; and many alkaloids derived from securinine and norsecurinine. A remarkable feature of S. virosa is the production of norsecurinine oligomers, including macromolecular tetramers and pentamers, such as fluevirosinines. The most potent anticancer alkaloid in the family is the dimeric indolizidine flueggine B, which was identified as a potential binder to α/β-tubulin dimer, which is a known target for securinine. This review highlights the diversity of phytochemicals identified from S. virosa and the potential therapeutic benefits of dimeric alkaloids. Studies are encouraged to further investigate the therapeutic properties of the lead compounds but also define and finesse the nutritional profile of the edible fruit.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Monoketone Curcuminoids: An Updated Review of Their Synthesis and Biological Activities
by
Tatiana M. Vieira, Lívia S. Tanajura, Vladimir C. G. Heleno, Lizandra G. Magalhães and Antônio E. M. Crotti
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 54-76; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010006 - 17 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Curcumin (or diferuloylmethane), a component of Curcuma longa L. rhizomes, displays various biological and pharmacological activities. However, it is poorly bioavailable and unstable in physiological pH. In this review, we cover papers published between 2019 and 2023 on the synthesis and biological activities
[...] Read more.
Curcumin (or diferuloylmethane), a component of Curcuma longa L. rhizomes, displays various biological and pharmacological activities. However, it is poorly bioavailable and unstable in physiological pH. In this review, we cover papers published between 2019 and 2023 on the synthesis and biological activities of more stable and effective curcumin analogs known as monoketone curcuminoids (MKCs) or “monocarbonyl curcuminoids.” Recent advances in Claisen–Schmidt condensation, the standard procedure to synthesize MKCs, including the use of ionic liquids, are addressed. MKCs’ antimicrobial, anticancer, antioxidant, and antiparasitic actions, as well as other less common MKC biological and pharmacological activities, have been shown to be similar or higher than curcumin. The promising biological and pharmacological activities, combined with the attractive synthetic aspects (e.g., good yields and an easiness of product isolation) to obtain MKCs, make this class of compounds an interesting prospect for further antimicrobial, anticancer, and antiparasitic drug discovery.
Full article
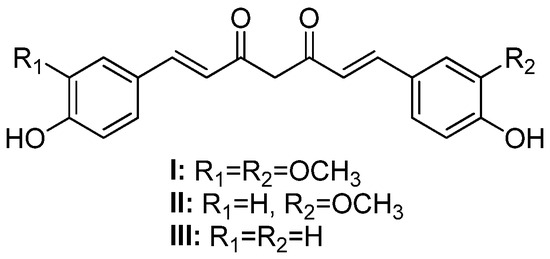
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hereditary Angioedema: Novel Molecules for Treatment of Acute Attacks and Long-Term Prophylaxis
by
Bianca Covella, Marica Giliberti, Adriano Montinaro, Luigi Rossi and Vincenzo Montinaro
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 41-53; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010005 - 12 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare disease caused by a genetic alteration of the SERPING1 gene and characterized by recurrent attacks of angioedema that involve the skin, and the mucosae of the gastrointestinal tract and upper airways, which significantly affect the quality of
[...] Read more.
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare disease caused by a genetic alteration of the SERPING1 gene and characterized by recurrent attacks of angioedema that involve the skin, and the mucosae of the gastrointestinal tract and upper airways, which significantly affect the quality of life of patients. Nowadays there are effective drugs for both 1. treating acute attacks and 2. preventing attacks with a long-term prophylaxis. However, there are some unmet needs for HAE treatment, and therefore several novel molecules are under active testing for this clinical condition. Novel drugs will simplify the mode of administration (oral versus parenteral for both on demand treatment or long-term prophylaxis), prolong the interval between administrations (up to 3–6 months of efficacy with a single administration), target more specifically the central enzymes involved in the generation of bradykinin, the ultimate mediator of angioedema (prekallikrein, activated plasma kallikrein or activated factor XII), and potentially determine a definitive cure for the disease by genetic manipulation of the altered gene (SERPING1) or other downstream genes (KLKB1). In this review we provide a panoramic view of all new medications that are under active experimentation and will probably transform and enrich all of the therapeutic armamentarium for treating this disease.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Real-World Data Study on Risk Factors Associated with Acute Kidney Damage in Patients Treated with Anti-MRSA Antibiotics
by
Ivan Maray, Cristina Álvarez-Asteinza, Lola Macía-Rivas, Clara Luz Fernández-Laguna, Miguel Alaguero-Calero, Pablo Valledor and Javier Fernández
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 30-40; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010004 - 09 Jan 2024
Abstract
The objective was to evaluate the incidence of nephrotoxicity related to vancomycin and other anti-MRSA antibiotics (linezolid and daptomycin). Patients receiving any of these drugs between July 2014 and December 2020 at a tertiary hospital were included. Renal failure was evaluated using the
[...] Read more.
The objective was to evaluate the incidence of nephrotoxicity related to vancomycin and other anti-MRSA antibiotics (linezolid and daptomycin). Patients receiving any of these drugs between July 2014 and December 2020 at a tertiary hospital were included. Renal failure was evaluated using the acute renal injury (AKIN) system. Univariate analysis was conducted on the 5806 patients who were included. Among them, 1023 patients (17.62%) developed renal failure. The renal damage incidence was 14.74% (496/3365) for vancomycin, 19.13% (367/1918) for linezolid, and 30.59% (160/523) for daptomycin. Patients with lower basal glomerular filtration had a higher risk of AKIN. In the vancomycin group, the risk factors were high creatinine and urea serum basal values, duration of treatment (DOT), body mass index (BMI), ICU stay, age, and low CKDEPI and albumin levels. In the linezolid group, AKIN was linked to high creatinine and urea levels, BMI, age, and ICU stay and to low CKDEPI levels; for daptomycin, AKIN was associated with low CKDEPI and albumin levels and a long DOT. Patients with AKIN showed higher mortality rates. Vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity remains a great concern. However, linezolid and daptomycin could also cause nephrotoxicity. Bearing in mind risk factors that may prompt nephrotoxicity in hospitalized patients taking anti-staphylococcal antibiotics will result in better pharmacotherapeutic management.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Dual Cardiovascular Effect of Centrally Administered Clonidine: A Comparative Study between Pentobarbital- and Ketamine/Xylazine-Anesthetized Rats
by
Natália Kimie Matsubara and José Eduardo da Silva-Santos
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 17-29; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010003 - 09 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The administration of the α2-adrenergic receptor agonist clonidine via intracerebroventricular route produces hypotension in pentobarbital-anesthetized rats and pressor responses in conscious normotensive rats. We explored the impact of different anesthetics on the central nervous system-dependent cardiovascular effects of clonidine. Normotensive male
[...] Read more.
The administration of the α2-adrenergic receptor agonist clonidine via intracerebroventricular route produces hypotension in pentobarbital-anesthetized rats and pressor responses in conscious normotensive rats. We explored the impact of different anesthetics on the central nervous system-dependent cardiovascular effects of clonidine. Normotensive male Wistar rats with guide cannulas previously implanted in the cerebroventricular system were anesthetized with pentobarbital or ketamine/xylazine and prepared for blood pressure measurement. The animals received intracerebroventricular injections of 10 μg clonidine or 0.6 μg dexmedetomidine, and the effects on the systolic, diastolic, mean arterial pressure, and heart rate were evaluated. The influence of 5 μg yohimbine, a selective α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, was also assessed. The i.c.v. microinjection of clonidine decreased all three components of systemic arterial pressure and the heart rate of pentobarbital-anesthetized rats. On the other hand, clonidine increased the blood pressure and generated a less intense reduction in the heart rate of ketamine/xylazine-anesthetized rats. The pressor and bradycardic effects of clonidine in ketamine/xylazine-anesthetized animals were reproduced by dexmedetomidine, a more selective α2-adrenergic receptor agonist. Notably, the previous intracerebroventricular injection of yohimbine significantly inhibited the hypertensive effect of clonidine and dexmedetomidine. This study discloses that while normotensive rats anesthetized with pentobarbital show hypotensive responses, the stimulation of α2-adrenergic receptors increases the blood pressure in rats under ketamine/xylazine-induced anesthesia, reproducing the effects seen in conscious normotensive animals. Recognizing the mechanisms involved in these differences may allow us to understand better the final effects of clonidine and other α2-adrenergic receptor agonists in the central nervous system, contributing to the repurposing of these drugs.
Full article
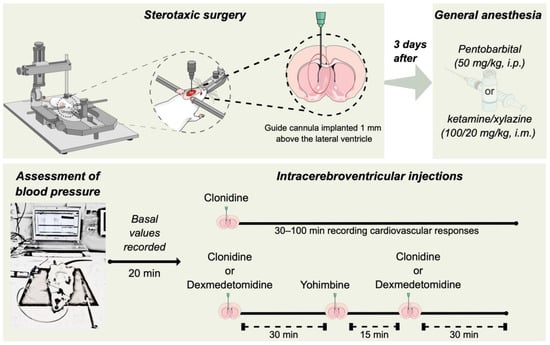
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation through Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin
by
Ana Carolina Furian da Silva, Sindy Magri Roque, Marta Cristina Teixeira Duarte, Gerson Nakazato, Nelson Durán and Karina Cogo-Müller
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 3-16; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010002 - 05 Jan 2024
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a causative agent of nosocomial infections and its antibiotic-resistant strains give cause for concern. Solutions are being explored to improve treatment for these infections, including repositioning drugs such as statins and using nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties. This study evaluated the
[...] Read more.
Staphylococcus aureus is a causative agent of nosocomial infections and its antibiotic-resistant strains give cause for concern. Solutions are being explored to improve treatment for these infections, including repositioning drugs such as statins and using nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties. This study evaluated the antimicrobial effects of simvastatin (SIM) and biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles (bio-AgNPs) in isolate form and in combination using assays of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), an in vitro biofilm model, and the association of antimicrobials against clinical strains of S. aureus. Bio-AgNPs showed a 53.8 ± 1.23 nm mean diameter and standard deviation, a 0.23 polydispersity index, and a −25.66 ± 2.19 mV mean potential and standard deviation. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed the formation of nanoparticles, and the presence of Ag0 and AgCl. S. aureus strains were sensitive to bio-AgNPs and SIM, showing 31.88–187.5 and 74.66–149.32 μM concentrations, respectively. The association assay showed 2.0 fractional inhibitory concentration indices (i.e., indifferent for clinical strains) and 0.32 values for the standard ATCC 29213 strain (synergy). Biofilm inhibition assays with isolated SIM and bio-AgNPs showed decreased biofilm formation 4× to ⅛ MICs concentrations, showing no synergism in association. These findings evince that simvastatin and bio-AgNPs at subinhibitory concentrations can serve as antimicrobial agents against S. aureus biofilm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
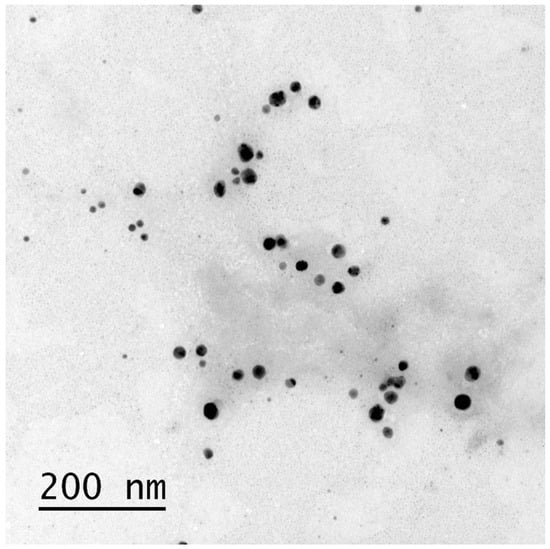
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
2023: The Best Year Ever for Future Pharmacology (and Even Better Years to Come)
by
Fabrizio Schifano
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(1), 1-2; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010001 - 02 Jan 2024
Abstract
The end of any year provides an opportunity to reflect on the past, and in particular, the past twelve months [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
Therapeutic Use of Palmitoylethanolamide as an Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulator
by
Maria Clara Inácio de Sá and Marina Gomes Miranda Castor
Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3(4), 951-977; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3040058 - 15 Dec 2023
Abstract
Palmitoylethanolamine (PEA) is an endocannabinoid-like compound first encountered within the lipid fractions of specific foods and has intrigued researchers since the 1950s due to its therapeutic effects. This survey aims to explore the therapeutic promise held by PEA as an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory
[...] Read more.
Palmitoylethanolamine (PEA) is an endocannabinoid-like compound first encountered within the lipid fractions of specific foods and has intrigued researchers since the 1950s due to its therapeutic effects. This survey aims to explore the therapeutic promise held by PEA as an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agent. The therapeutic impact of PEA reverberates across diverse physiological systems, such as the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, vascular network, and the digestive and respiratory system. Additionally, it is effective in pain management and reducing inflammation and immune responses. These attributes have fostered collaborations targeting conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, cerebral ischemia, neuroinflammation, general inflammation, pain, coagulopathy, steatohepatitis, and acute lung injury. PEA operates both independently and in synergy with other compounds, like paracetamol, luteolin, and oxymetazoline. This efficacy stems from its interactions with pivotal targets, including PPARα, PPAR-δ, PPAR-γ, CB1, CB2, GPR55, and TRPV1. Additionally, PEA exerts a direct influence on the inflammatory cascade, orchestrating precise adjustments in immune responses. Numerous animal studies have elucidated the inherent potential of PEA. Nevertheless, the imperative of reinforcing clinical investigation is evident. This review notably underscores the pivotal necessity for methodologically rigorous clinical trials to definitively establish the translational efficacy of PEA in ameliorating diverse inflammatory pathologies within the human milieu.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Gene-Based Therapy: A New Approach to Feline Induced Sterilization?
by
Rita Payan-Carreira
Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3(4), 938-950; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3040057 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Feline population control remains a concern as to whether it is intended for the short- or long-term. Induced sterilization of felids is critical in the case of feral, free-roaming cats, or the management of wild populations in Zoos or sanctuaries. This narrative review
[...] Read more.
Feline population control remains a concern as to whether it is intended for the short- or long-term. Induced sterilization of felids is critical in the case of feral, free-roaming cats, or the management of wild populations in Zoos or sanctuaries. This narrative review explores the shifting paradigm in induced sterilization methods, driven by the development of gene editing approaches recently applied to control felid reproductive activity. Although gene therapy approaches have gained attention as alternatives to more traditional methods, their clinical applications remain in the realm of thought. The objective of this study was to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state and most recent advances in gene-based contraception options, consolidate current research and evidence, and share some considerations on its potential effectiveness, advantages or limitations, and implications for animal welfare and population control strategies. Gene-based contraception therapy tested in felines, targeting the AMH pathway, was unable to suppress the estrous cycle and follicular development. However, at an experimental level, preliminary results hint at the need to change towards different molecular targets. Moreover, their side effects remain largely unknown, and several questions remain unanswered, such as the regularity of treatment applications or cost.
Full article
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Future Pharmacology, Pharmaceutics, Current Oncology
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 30 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Unveiling New Insights and Treatment Options for Ocular Surface Diseases
Guest Editors: Paola Tirassa, Pamela Rosso, Fabiana MalloneDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Antiviral Drug Discovery and Development: Current Innovations and Future Trends
Guest Editor: Peng ZhanDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Biomaterials and Stem/Stromal Cell-Based Pharmaceuticals in Tissue Engineering
Guest Editor: Natasha MaurmannDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024
Guest Editor: Fabrizio SchifanoDeadline: 31 August 2024




