Innovative People-Centered Solutions Applied to Industries, Cities and Societies
A topical collection in Future Internet (ISSN 1999-5903). This collection belongs to the section "Techno-Social Smart Systems".
Viewed by 55719Editors
Interests: information society; smart cities; e-government; e-mobility; smart mission critical systems; remote-sensing systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. IOTECH—Innovation on Technology, 4785-588 Trofa, Portugal
Interests: knowledge discovery; data science; progressive web apps; research and development
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
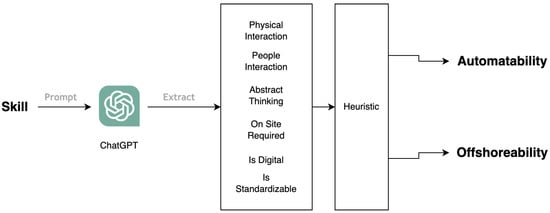
This Topical Collection on innovative people-centered solutions in industry has the goal of disseminating works following the IO paradigm. The IO paradigm means the application of people-centered technological innovation to industry or to a societal area. It represents innovation (I) on (O) the use of technologies able to solve specific issues/concerns of citizens, business or society. This paradigm was created by a technological start-up, IOTECH—Innovation on Technology. IOTech (https://iotech.pt) researches and develops pervasive, innovative and intelligent web/mobile solutions to address the concerns of industry, business, citizens and society.
The paradigm is materialised in an artefact, typical an ioSolution through the application of the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) concept. The artefact must be responsive and allow the operation of services, and the resolution of real problems of the industry without it being necessary to buy new equipment. The user can consume a set of services through their own device (mobile phone, tablet, computer, television, among others).
The ioSolution must be pervasive, innovative and use concepts associated with machine-learning, artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality, enabling the development of smart progressive web apps.
This Topical Collection intends to link researchers and professionals able to explore new solutions applied to society and industry. It will further explore and present paradigms, solutions or best practices able to be implemented in the real world. It represents a new era of disseminating knowledge by showing how scientific knowledge can be transferred to society and applied in industry.
In order to contribute to addressing this paradigm, this Topical Collection intends to collect the current developments and future directions of people-centered solutions applied to industry. Hence, we encourage authors to submit original papers related to these fields and disseminate their knowledge to society. All the articles must be people-centered and/or focus on industry.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
- Internet of Things
- Progressive web app
- Pervasive and cloud computing
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) solutions
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Web/mobile solutions
- Big data, open data and analytical tools
- Smart cities
- Wellbeing solutions
- Smart solutions
- Augmented reality
- System interoperability
- Blockchain
- System and applications security
- Industry 4.0
Prof. Dr. Dino Giuli
Prof. Dr. Carlos Filipe Da Silva Portela
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Future Internet is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- People-centered
- IOT
- Industry 4.0
- BYOD
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Data Science
- Web/Mobile
- smart cities
- sustainable societies
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Internet of Services-based business models: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract: The relevance of the Internet of Services (IoS) comes from the global reach of the Internet into everyone´s home and daily activities and from the move from a manufacturing-based economy to a service-based economy. The IoS is seen as a new ecosystem where service providers and consumers explore their business networks for service provision and consumption. The scientific literature refers to IoS as an important cornerstone for Industry 4.0 and Future Internet; thus, it becomes relevant to study how IoS interacts with business models. Nevertheless, there is a lack of clarity on such an intersection. Moreover, a systematic review of Internet of Services-based business models is still missing. This paper aims to review current studies and highlight state-of-the-art for IoS, identifying which have been business application fields through an interlocking analysis between IoS and business models. Twenty-three different studies are presented, examining the problem they address and proposed solutions. Concluding, the review highlights the opportunities of IoS applications in different fields, offering directions for future research on this new arena.