"Electric Vehicles" Section: Review Papers
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Pedro Roncero-Sanchez
Prof. Dr. Pedro Roncero-Sanchez
 Prof. Dr. Pedro Roncero-Sanchez
Prof. Dr. Pedro Roncero-Sanchez
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Control Systems, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain
Interests: control of grid connected converters; power quality; renewable energy systems; energy storage devices; wireless power transfer
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Trung Van Nguyen
Prof. Dr. Trung Van Nguyen
 Prof. Dr. Trung Van Nguyen
Prof. Dr. Trung Van Nguyen
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
School of Engineering, University of Kansas, 1530 W 15th Street, Lawrence, Kansas, KS, USA
Interests: battery; fuel cells; design engineering; energy storage; electrochemical analysis; material characterization; materials; nanomaterials; nanomaterials synthesis; electrodes; modeling of electrochemical systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. João Paulo Carvalho Lustosa da Costa
Prof. Dr. João Paulo Carvalho Lustosa da Costa
 Prof. Dr. João Paulo Carvalho Lustosa da Costa
Prof. Dr. João Paulo Carvalho Lustosa da Costa
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Electric Engineering, Hamm-Lippstadt University of Applied Sciences, Marker Allee 76-78, 59063 Hamm, Germany
Interests: autonomous driving; electric vehicles; wireless communication; electrical engineering; signal processing
 Prof. Dr. Caiping Zhang
Prof. Dr. Caiping Zhang
 Prof. Dr. Caiping Zhang
Prof. Dr. Caiping Zhang
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
School of Electrical Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, No.3 Shangyuancun, Haidian District, Beijing 100044, China
Interests: battery modeling and states estimation; aging mechanisms and RUL prediction; charging optimizations; battery fault diagnosis and early warning
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Kaamran Raahemifar
Prof. Dr. Kaamran Raahemifar
 Prof. Dr. Kaamran Raahemifar
Prof. Dr. Kaamran Raahemifar
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue W, Waterloo, ON N2L 3G1, Canada
Interests: application of optimization in engineering; data analytics and artificial intelligence; reliability and prediction analysis
 Dr. Roberto Villafafila-Robles
Dr. Roberto Villafafila-Robles
 Dr. Roberto Villafafila-Robles
Dr. Roberto Villafafila-Robles
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
CITCEA-UPC, Department of Electrical Engineering (DEE), ETS d’Enginyeria Industrial de Barcelona, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Av. Diagonal 647, 2nd floor, 08028 Barcelona, Spain
Interests: integration of renewable energy-storage-electric vehicles into power systems; electricity markets; energy and territory
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Electric vehicles (EVs) are impacting the aerial, terrestrial, and marine transportation sectors due to energy conservation, emission reduction, and pollution prevention. However, the transition from fossil fuels to electric propulsion is a complex task, involving many open challenges, such as the design of advanced EV, the production of energy storage systems (ESS), and the development of adequate aviation, land, and naval infrastructure. In order to enable more scholars to quickly understand cutting-edge technologies in the field of EVs, this collection focuses on review papers in the field, including but not limited to:
- Ground EVs;
- Airborne EVs;
- Seaborne EVs;
- Electrically powered spacecraft;
- Autonomous and connected vehicles;
- Battery/ultracapacitor/fuel cell;
- Charging technologies;
- Energy and battery management systems;
- EV market and policy;
- Electric drive systems and component technologies;
- Grid integration of EVs;
- Safety aspects and information security issues of EVs.
Prof. Dr. Pedro Roncero-Sanchez
Prof. Dr. Trung Van Nguyen
Prof. Dr. João Paulo Carvalho Lustosa da Costa
Prof. Dr. Caiping Zhang
Prof. Dr. Kaamran Raahemifar
Dr. Roberto Villafafila-Robles
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- hybrid and electric vehicles
- energy storage systems
- powertrain technology
- economic and environmental issues
- lifecycle assessment
- power electronic converters
- energy conversion
- energy management
- EV market and policy
Published Papers (5 papers)
Open AccessReview
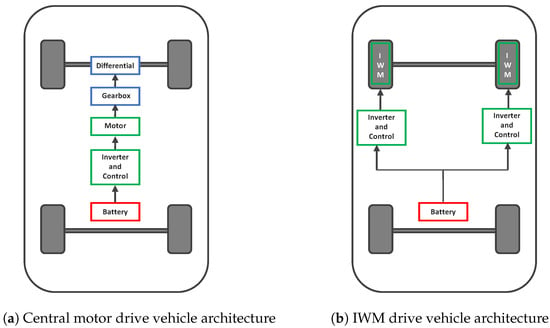
In-Wheel Motor Drive Systems for Electric Vehicles: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Trends
by
Kritika Deepak, Mohamed Amine Frikha, Yassine Benômar, Mohamed El Baghdadi and Omar Hegazy
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 5776
Abstract
Recently, there has been significant attention given to the electrification of transportation due to concerns about fossil fuel depletion and environmental pollution. Conventional drive systems typically include a clutch, reduction gear, and mechanical differential, which results in power loss, noise, vibration, and additional
[...] Read more.
Recently, there has been significant attention given to the electrification of transportation due to concerns about fossil fuel depletion and environmental pollution. Conventional drive systems typically include a clutch, reduction gear, and mechanical differential, which results in power loss, noise, vibration, and additional maintenance. However, in-wheel motor drive technology eliminates the need for these components, providing benefits such as higher system efficiency, improved wheel control, and increased passenger comfort. This article offers a comprehensive review of the technology and development of in-wheel motor drives. It begins with an overview of in-wheel motor drives in electric vehicles, followed by an exploration of the types of electric motors suitable for in-wheel motor drives. The paper then presents an industrial state of the art of in-wheel motors, comparing them with conventional motor drives, and reviews the implemented power electronics, control system, and cooling systems. Finally, the paper concludes by providing an outlook on the challenges and future trends of in-wheel drive systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
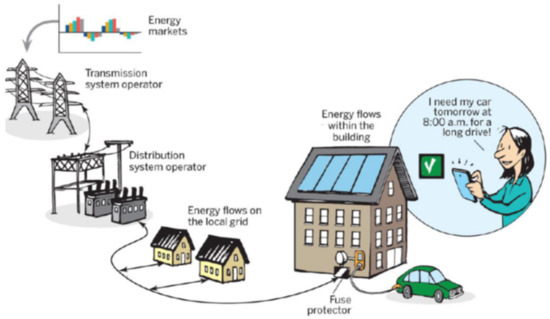
A Review of Tariffs and Services for Smart Charging of Electric Vehicles in Europe
by
Julia Hildermeier, Jaap Burger, Andreas Jahn and Jan Rosenow
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 5215
Abstract
Smart charging of electric vehicles (EVs) is an essential approach to reduce the costs and maximise the benefits of increasing numbers of EVs being connected to the power grid. This article analyses 139 tariffs and services for smart EV charging available in Europe.
[...] Read more.
Smart charging of electric vehicles (EVs) is an essential approach to reduce the costs and maximise the benefits of increasing numbers of EVs being connected to the power grid. This article analyses 139 tariffs and services for smart EV charging available in Europe. It finds that while the market for smart EV charging services is growing, there is a lack of consumer information on the savings and broader environmental benefits it offers, such as integration of renewables. Offers are also unevenly distributed across the continent, resulting in unequal access to smart EV charging. The article outlines six strategies to establish framework conditions in energy markets that would address these gaps and establish smart charging as a standard means of charging, to ensure the beneficial integration of EVs into power grids.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
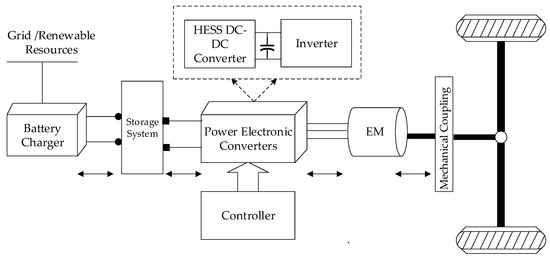
Different Topologies of Electrical Machines, Storage Systems, and Power Electronic Converters and Their Control for Battery Electric Vehicles—A Technical Review
by
Elango Sangeetha and Vijayapriya Ramachandran
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3679
Abstract
Electric vehicles (EVs) are emerging as an alternative transportation system owing to a reduction in depleting lubricates usage and greenhouse gas emissions. This paper presents a technical review of each and every sub-system and its feasible control of battery EV (BEV) propulsion units.
[...] Read more.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are emerging as an alternative transportation system owing to a reduction in depleting lubricates usage and greenhouse gas emissions. This paper presents a technical review of each and every sub-system and its feasible control of battery EV (BEV) propulsion units. The study includes the possible combination of electrical machines (EMs), storage system, and power electronic converters and their associated control strategies. The primary unit, i.e., EM, is the heart of the EV, which is used to drive the vehicle at the desired speed as well as to restore the regenerative braking (RB) energy that is generated to enhance the overall system reliability. To electrify the transportation sector, it is necessary to include new options of power electronic converter topologies and their associated control strategies for numerous reasons, which include extracting maximum power from sources in case the EV is powered from renewable energy resources, boosting the energy storage capability for longer electric range, managing power flow from the source to battery or battery to vehicle or vehicle to battery, and regulating the speed of the vehicle and braking control. Based on the survey, the suitable combination of sub-systems and their control for three and four-wheeler EVs are summarized in this paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
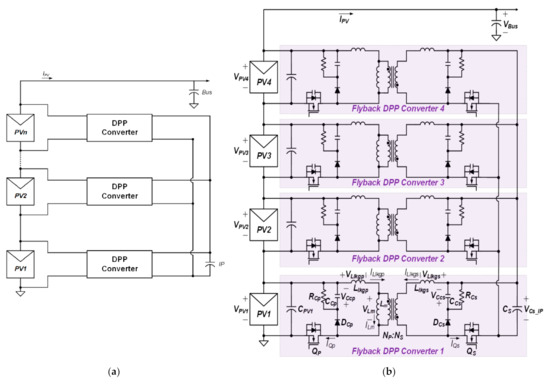
Differential Power Processing Converter with an Integrated Transformer and Secondary Switch for Power Generation Optimization of Multiple Photovoltaic Submodules
by
Ji-Hoon Lim, Dong-In Lee, Ye-Ji Hyeon, Jae-Hyuk Choi and Han-Shin Youn
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1609
Abstract
In recent years, to increase the fuel efficiency of environment-friendly vehicles, a large volume of research is ongoing regarding applying photovoltaic (PV) systems. However, in PV systems, a power imbalance between submodules is common due to shading or pollution, and this degrades the
[...] Read more.
In recent years, to increase the fuel efficiency of environment-friendly vehicles, a large volume of research is ongoing regarding applying photovoltaic (PV) systems. However, in PV systems, a power imbalance between submodules is common due to shading or pollution, and this degrades the power generation efficiency of the system. To solve this problem, various differential power processing (DPP) converters have been developed. In order to adopt the DPP converter to environment-friendly vehicles, the DPP converter must have a small volume, high efficiency, and high price competitiveness. In this regard, we propose a DPP converter with a single multi-winding transformer by integrating multiple transformers and secondary sides of the conventional flyback DPP converter. Since the proposed DPP converter can be applied to battery balancing circuits as well as photovoltaic systems, the proposed circuit is a valuable converter. In the PV system, the maximum output power of each submodule is 60 W, and the total PV system is 240 W by connecting four submodules in series. To verify the validity of the proposed DPP converter, a prototype with 8 V input and 60 W/30 V output specification was built and tested, and the effectiveness of the proposed converter is supported by the experimental results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
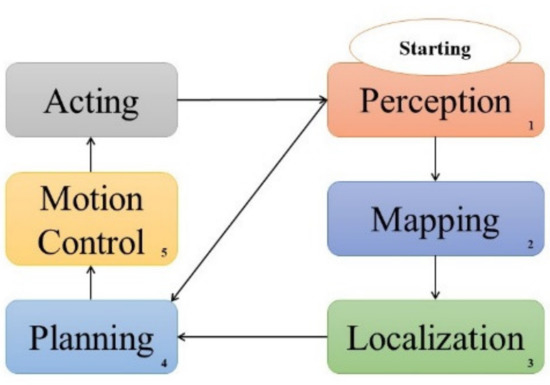
An Investigation into the Energy-Efficient Motion of Autonomous Wheeled Mobile Robots
by
Mohammad Mohammadpour, Lotfi Zeghmi, Sousso Kelouwani, Marc-André Gaudreau, Ali Amamou and Massinissa Graba
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 2627
Abstract
In recent years, the use of electric Autonomous Wheeled Mobile Robots (AWMRs) has dramatically increased in transport of the production chain. Generally, AWMRs must operate for several hours on a single battery charge. Since the energy density of the battery is limited, energy
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the use of electric Autonomous Wheeled Mobile Robots (AWMRs) has dramatically increased in transport of the production chain. Generally, AWMRs must operate for several hours on a single battery charge. Since the energy density of the battery is limited, energy efficiency becomes a key element in improving material transportation performance during the manufacturing process. However, energy consumption is influenced by the navigation stages, because the type of motion necessary for the AWMR to perform during a mission is totally defined by these stages. Therefore, this paper analyzes methods of energy efficiency that have been studied recently for AWMR navigation stages. The selected publications are classified into planning and motion control categories in order to identify research gaps. Unlike other similar studies, this work focuses on these methods with respect to their implications for the energy consumption of AWMRs. In addition, by using an industrial Self-Guided Vehicle (SGV), we illustrate the direct influence of the motion planning stage on global energy consumption by means of several simulations and experiments. The results indicate that the reaction of the SGV in response to unforeseen obstacles can affect the amount of energy consumed. Hence, energy constraints must be considered when developing the motion planning of AWMRs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures