Feature Papers in Phylogeny and Evolution
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
As Diversity is a generalist journal, we hereby invite authors to submit articles outlining the state of the art of some special features concerning phylogeny and evolution, dealing with all aspects of the evolution and phylogeny of organisms, both living and extinct.
Specialized or local studies will be evaluated only if discussion leads to/illustrates general questions/conclusions relevant to evolution and phylogeny. Both descriptive studies and more theoretical papers are acceptable.
The following list includes some of the topics covered:
- Evolutionary biology;
- Phylogenetic reconstruction;
- Evolution of ecosystems;
- Palaeontology;
- Palaeobotany;
- Micropalaeontology;
- Invertebrate palaeontology;
- Vertebrate palaeontology;
- Palaeobiology;
- Fossil record;
- Macroevolution;
- Molecular phylogeny;
- Ancient DNA;
- Evolutionary biogeography;
- Palaeobiogeography;
- Island biogeography;
- Extinctions;
- Evolution of behavior;
- Evolutionary patterns;
- Mechanisms of evolution;
- Factors of evolutionary change;
- Climate change and evolution.
Submissions must represent a starting point for further research and be equally accessible to non-biologists and to specialists in the field.
Dr. Eric Buffetaut
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Diversity is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- phylogeny
- evolution
- palaeontology
- DNA
- molecular phylogeny
Published Papers (5 papers)
Open AccessArticle
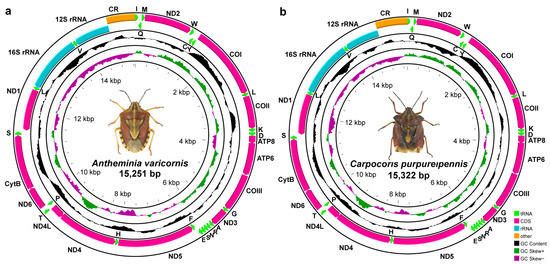
The Characterization and Phylogenetic Implications of the Mitochondrial Genomes of Antheminia varicornis and Carpocoris purpureipennis (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae)
by
Ying Wang, Ruijuan Yang, Xiuxiu Zhu, Chenguang Zheng and Wenjun Bu
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1220
Abstract
The mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) has been widely used for structural comparisons and phylogenetic analyses of Hemiptera groups at different taxonomic levels. However, little is known about the mitogenomic characteristics of species from
Antheminia and
Carpocoris, two morphologically similar genera in the Pentatomidae
[...] Read more.
The mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) has been widely used for structural comparisons and phylogenetic analyses of Hemiptera groups at different taxonomic levels. However, little is known about the mitogenomic characteristics of species from
Antheminia and
Carpocoris, two morphologically similar genera in the Pentatomidae family, and their phylogenetic relationships need to be further confirmed. In this study, the mitogenomes of
Antheminia varicornis (Jakovlev, 1874) and
Carpocoris purpureipennis (De Geer, 1773) were sequenced and analyzed. Coupled with previously published mitogenomes of Pentatomidae, we performed a phylogenetic analysis. The mitogenomes of
A. varicornis and
C. purpureipennis are conserved in terms of genomic structure, base composition, codon usage, and tRNA secondary structure. Each mitogenome contains the typical 37 genes and a control region and all genes are arranged in the same order as in the ancestral insect mitogenome. Nucleotide composition is highly biased with the third codon in PCGs displaying the highest A + T content. Phylogenetic analysis strongly supports the sister relationship between
A. varicornis and
C. purpureipennis. The phylogenetic trees show a strong support for the monophyly of Asopinae and Phyllocephalinae, while the monophyly of Pentatominae and Podopinae was rejected. Our study enriches the mitochondrial genome database of the genera
Antheminia and
Carpocoris and provides a valuable resource for further phylogenetic and evolutionary analyses of the Pentatomidae.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A New Basal Neornithischian Dinosaur from the Phu Kradung Formation (Upper Jurassic) of Northeastern Thailand
by
Sita Manitkoon, Uthumporn Deesri, Bouziane Khalloufi, Thanit Nonsrirach, Varavudh Suteethorn, Phornphen Chanthasit, Wansiri Boonla and Eric Buffetaut
Viewed by 10450
Abstract
An exceptional articulated skeleton of a new basal neornithischian dinosaur,
Minimocursor phunoiensis gen. et sp. nov., was discovered in the Late Jurassic Phu Kradung Formation at the Phu Noi locality, Kalasin Province, Thailand, a highly productive non-marine fossil vertebrate locality of the Khorat
[...] Read more.
An exceptional articulated skeleton of a new basal neornithischian dinosaur,
Minimocursor phunoiensis gen. et sp. nov., was discovered in the Late Jurassic Phu Kradung Formation at the Phu Noi locality, Kalasin Province, Thailand, a highly productive non-marine fossil vertebrate locality of the Khorat Plateau. It is one of the best-preserved dinosaurs ever found in Southeast Asia.
Minimocursor phunoiensis gen. et sp. nov. shows a combination of both plesiomorphic and apomorphic characters resembling those of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous small-bodied ornithischians from China: a low subtriangular boss is projected laterally on the surface of the jugal, the brevis shelf of the ilium is visible in lateral view along its entire length, a distinct supraacetabular flange is present on the pubic peduncle of the ilium, the prepubis tip extends beyond the distal end of the preacetabular process of the ilium, and the manus digit formula is ?-3-4-3-2. The phylogenetic analysis shows that this dinosaur is among the most basal neornithischians. This study provides a better understanding of the early evolution and taxonomic diversity of ornithischians in Southeast Asia.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
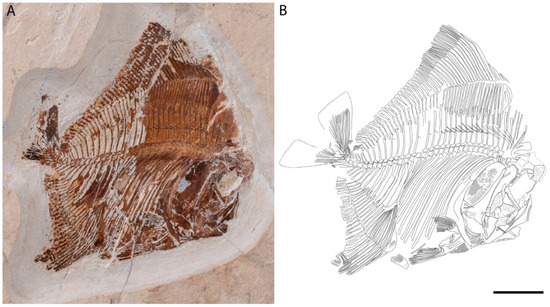
A New Enigmatic Teleost Fish from the Mid-Cretaceous of Lebanon
by
Tamara El Hossny and Lionel Cavin
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2058
Abstract
Teleosts form the largest clade among the extant actinopterygians, some extinct forms of which are still poorly positioned in the phylogeny. The Tselfatiiformes and Araripichthyidae are such examples. A newly discovered genus and species from the Cenomanian of Haqel, Lebanon, is described, and
[...] Read more.
Teleosts form the largest clade among the extant actinopterygians, some extinct forms of which are still poorly positioned in the phylogeny. The Tselfatiiformes and Araripichthyidae are such examples. A newly discovered genus and species from the Cenomanian of Haqel, Lebanon, is described, and its systematic affinities are discussed. It shares several characteristics (deep and compressed body with elongated and high dorsal and anal fins, edentulous maxilla, and sinusoidal vertebral column) with both the Tselfatiiformes and
Araripichthys, making it difficult to place within the teleosts. It shares with
Abisaadichthys, among the tselfatiiforms’ family Protobramidae, an autogenous retroarticular, and with
Araripichthys premaxillae with a long ascending process, well-developed maxillary articular condyle and two supramaxillae. Moreover, it shows some unique characteristics (a thin maxilla with two large supramaxillae, fused articular and angular bones, mandibular sensory canal opening on the external side of the anguloarticular, first dorsal pterygiophore having the same enlarged semi-circular plate as the first anal pterygiophore) justifying its generic status. Comments on some of the protobramids are presented, and the necessity for phylogenetic analysis to place the Tselfatiiformes,
Araripichthys and
Ypsiloichthys within the teleosts is outlined.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
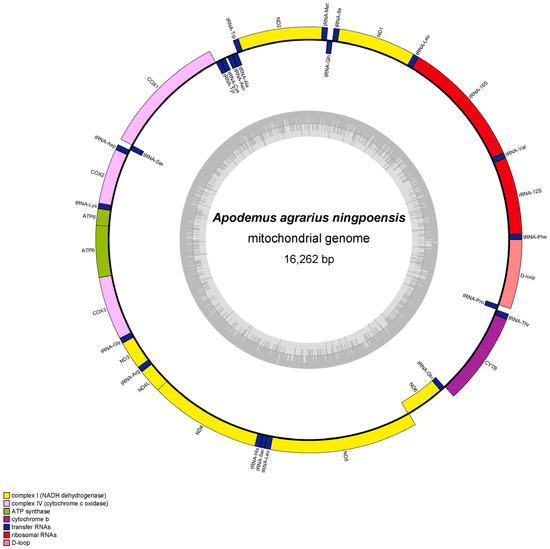
Characterization of Two New Apodemus Mitogenomes (Rodentia: Muridae) and Mitochondrial Phylogeny of Muridae
by
Di Wu, Lizhi Zhou, Jiezhong Xue, Qiliang Xia and Lei Meng
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1880
Abstract
Apodemus is the most common small rodent species in the Palearctic realm and an ideal species for biogeographical research and understanding environmental changes. Elucidating phylogenetic relationships will help us better understand species adaptation and genetic evolution. Due to its stable structure, maternal inheritance,
[...] Read more.
Apodemus is the most common small rodent species in the Palearctic realm and an ideal species for biogeographical research and understanding environmental changes. Elucidating phylogenetic relationships will help us better understand species adaptation and genetic evolution. Due to its stable structure, maternal inheritance, and rapid evolution, the mitogenome has become a hot spot for taxonomic and evolutionary studies. In this research, we determined the mitochondrial genome of
Apodemus agrarius ningpoensis and
Apodemus draco draco and studied the phylogeny of Muridae using ML and BI trees based on all known complete mitogenomes. The mitochondrial genome of
Apodemus agrarius ningpoensis was 16,262 bp, whereas that of
Apodemus draco draco was 16,222 bp, and both encoded 13 protein-coding genes, 2 ribosomal RNA genes, and 22 transfer RNA genes. Analysis of base composition showed a clear A-T preference. All tRNAs except tRNA
Ser and tRNA
Lys formed a typical trilobal structure. All protein-coding genes contained T- and TAA as stop codons. Phylogeny analysis revealed two main branches in the Muridae family.
Apodemus agrarius ningpoensis formed sister species with
Apodemus chevrieri, whereas
Apodemus draco draco with
Apodemus latronum. Our findings provide theoretical basis for future studies focusing on the mitogenome evolution of
Apodemus.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
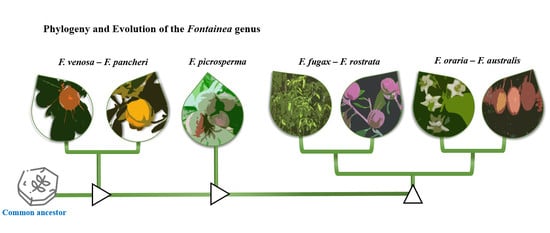
Phylogenetic Reconstruction of the Rainforest Lineage Fontainea Heckel (Euphorbiaceae) Based on Chloroplast DNA Sequences and Reduced-Representation SNP Markers
by
Aaron J. Brunton, Robert W. Lamont, Gabriel C. Conroy, Samantha Yap, Maurizio Rossetto, Alyce Taylor-Brown, Laurent Maggia, Paul W. Reddell and Steven M. Ogbourne
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2834
Abstract
Fontainea is a plant genus with nine recognised species that occur across the tropical and subtropical rainforests of Australia, Papua New Guinea, New Caledonia, and Vanuatu. One of these species is cultivated commercially as the source of a cancer therapeutic, and several other
[...] Read more.
Fontainea is a plant genus with nine recognised species that occur across the tropical and subtropical rainforests of Australia, Papua New Guinea, New Caledonia, and Vanuatu. One of these species is cultivated commercially as the source of a cancer therapeutic, and several other species are under threat of extinction. Despite this, the phylogenetic relationships of the genus have not been explored. Our study assessed the phylogeny of seven
Fontainea taxa from the Australian and Pacific Island complex using chloroplast DNA sequence data and reduced-representation genome sequencing. Maximum-likelihood and consensus network trees were used to infer the topology of phylogenetic relationships between species, which highlighted three distinct lineages and a number of sister species. Our results indicated that the geographically disjunct species
Fontainea venosa and
F. pancheri formed a sister group at the earliest position of divergence for the genus. The data also revealed that the vulnerable
Fontainea australis and the critically endangered
F. oraria form a sister subclade with evidence of some shared plastid genotypes. Generally, our phylogenetic reconstruction supports the modern taxonomical nomenclature. However, we suggest further accessions across several species may support improved genetic distinctions between the sister groups of
Fontainea within the genus.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures