Journal Description
Dermato
Dermato
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on skin science published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 16 days; acceptance to publication in 5.8 days (median values for MDPI journals in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
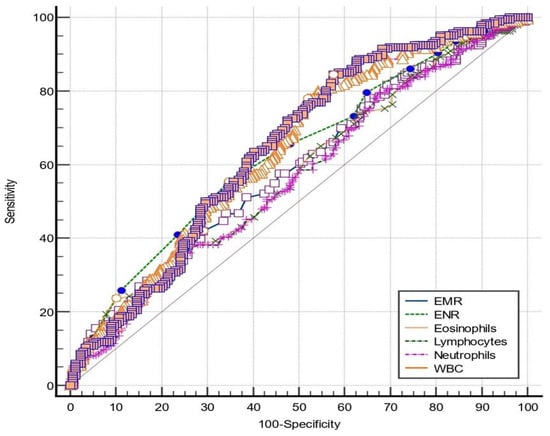
Eosinophil-Count-Derived Inflammatory Markers and Psoriasis Severity: Exploring the Link
Dermato 2024, 4(2), 25-36; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato4020004 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease, with various triggering factors, genetic predisposition, and an altered immune response concurring in the development of this disease. The eosinophil is a cell with an important role in various kinds of inflammatory processes. Scarce data are available regarding
[...] Read more.
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease, with various triggering factors, genetic predisposition, and an altered immune response concurring in the development of this disease. The eosinophil is a cell with an important role in various kinds of inflammatory processes. Scarce data are available regarding the role of the eosinophil in psoriasis. This study aims to address the overall relationship between eosinophil-count-derived inflammatory markers and psoriasis severity. There were 366 patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria included in this retrospective study and they were divided based on the body surface area (BSA) scale in mild and moderate-to-severe psoriasis. White blood cell (WBC), neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, and eosinophil count, along with eosinophil-to-monocyte ratio (EMR) and eosinophil-to-neutrophil ratio (ENR) differed significantly between the two study groups. Eosinophil count, EMR, and ENR negatively correlated with disease severity. ENR is the most reliable eosinophil-count-derived marker in assessing psoriasis severity with an AUC of 0.627 and a cut-off value of 0.03. Eosinophil-count-derived inflammatory markers’ usefulness in appreciating disease severity was assessed for the first time in the literature in this study and proved to be reliable for the eosinophil count, EMR, and ENR.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Interventions Impacting the Natural History of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessEditorial
The Updated Scope of Dermato
by
Thilo Gambichler and Chalid Assaf
Dermato 2024, 4(2), 23-24; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato4020003 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
We are very happy that Dermato has now entered its fourth year, having published notable papers covering the wide field of dermatology and other closely related disciplines [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
Considering Phytosphingosine-Based Ceramide Formulations for Atopic Skin Care
by
Dalibor Mijaljica, Joshua P. Townley, Angelina Hondros, Caroline Hewson, Ian P. Harrison and Fabrizio Spada
Dermato 2024, 4(1), 5-22; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato4010002 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review provides an overview of the structural and functional features of key phytosphingosine-based ceramides (CERs), notably CER[EOP], CER[NP], and CER[AP], and their role in atopic skin health. Herein, we discuss how these indispensable stratum corneum (SC) lipids maintain skin barrier homeostasis and
[...] Read more.
This review provides an overview of the structural and functional features of key phytosphingosine-based ceramides (CERs), notably CER[EOP], CER[NP], and CER[AP], and their role in atopic skin health. Herein, we discuss how these indispensable stratum corneum (SC) lipids maintain skin barrier homeostasis and contribute to the skin’s barrier function in terms of its cohesiveness and resilience. We also consider the usefulness of CER[EOP], CER[NP], and CER[AP] in preserving skin hydration and protecting and/or repairing dry, itchy, or sensitive skin. Next, we explore how and to what extent an imbalance or inadequate amounts of CER[EOP], CER[NP], and CER[AP] contribute to the hallmark characteristics of atopic skin diseases like eczema. Furthermore, we discuss the importance of complementary SC resident lipids such as cholesterol (CHOL) and free fatty acids (FFAs), which are crucial for optimal CER function. Studies have shown that delivering topical CERs in balanced and optimal combination with CHOL and FFAs—while supporting and boosting the endogenous biosynthesis of CERs using ingredients such as niacinamide and lactic acid—helps relieve symptoms of atopic diseases to provide some measure of relief. Finally, we look at some emerging ingredients that can complement the science of CERs in healthy and diseased skin.
Full article
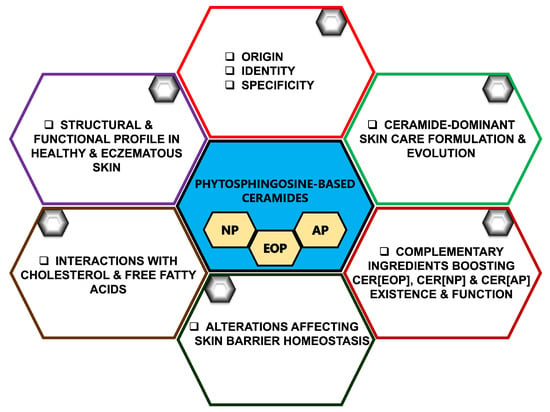
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Juvenile-Onset Non-Poikilodermatous CD8+CD56+ Mycosis Fungoides
by
Thilo Gambichler, Andrea Thiele, Hartmut Merz, Laura Susok and Stefanie Boms
Dermato 2024, 4(1), 1-4; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato4010001 - 08 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The most frequent primary cutaneous lymphomas observed in childhood and adolescence are mycosis fungoides (MF) and CD30-positive lymphoproliferative diseases. We report a 22-year-old female who presented with a 6-year history of multiple well-demarcated large roundish-oval scaly and reddish-brownish patches and plaques on the
[...] Read more.
The most frequent primary cutaneous lymphomas observed in childhood and adolescence are mycosis fungoides (MF) and CD30-positive lymphoproliferative diseases. We report a 22-year-old female who presented with a 6-year history of multiple well-demarcated large roundish-oval scaly and reddish-brownish patches and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Histopathology revealed the focal parakeratosis and prominent epidermotropism of atypical lymphocytes, which were positive for CD8, CD56, and TIA-1 and showed a loss of CD7 and CD5 expression. T-cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangement analysis (multiplex-PCR, BIOMED-2) of the lesional skin demonstrated the rearrangement of the gamma chain (tube A: 162 nt). Based on clinicopathological findings and a complete work-up, she was diagnosed with juvenile non-poikilodermatous C8+/CD56+ MF in stage IA. Resolution of the skin lesions was achieved by 16-week narrowband UVB phototherapy and clobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment. Juvenile-onset non-poikilodermatous CD8+CD56+ MF represents a very rare MF subtype and is associated with an indolent course. In order to avoid too aggressive diagnostics and treatments, clinicians should be aware of this rare and indolent MF variant in childhood and adolescence.
Full article
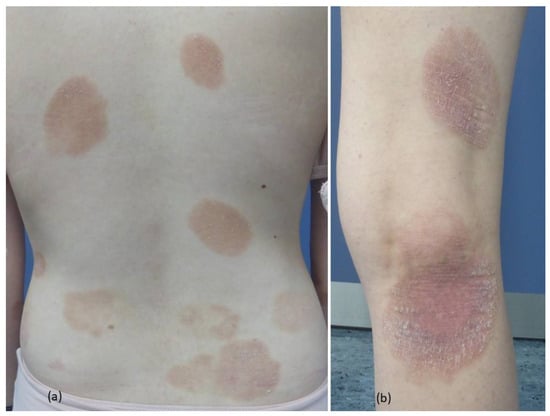
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Skin: A Case Report
by
Rim Jridi, Franziska Hartmann, Stefanie Boms, Andrea Tannapfel and Thilo Gambichler
Dermato 2023, 3(4), 263-266; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3040020 - 13 Dec 2023
Abstract
Adenosquamous carcinoma of the skin (ASCS) or primary cutaneous adenosquamous carcinoma is a rare malignant neoplasm. It is characterized by the presence of both glandular and squamous cell components and a propensity for aggressive clinical behavior. Due to its rarity, it continues to
[...] Read more.
Adenosquamous carcinoma of the skin (ASCS) or primary cutaneous adenosquamous carcinoma is a rare malignant neoplasm. It is characterized by the presence of both glandular and squamous cell components and a propensity for aggressive clinical behavior. Due to its rarity, it continues to pose diagnostic challenges. To date, only a few cases of this tumor have been reported, and even fewer have been thoroughly investigated via immunohistochemistry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue What Is Your Diagnosis?—Case Report Collection)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Rosacea: An Overview of Its Etiological Factors, Pathogenesis, Classification and Therapy Options
by
Serap Maden
Dermato 2023, 3(4), 241-262; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3040019 - 01 Nov 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rosacea is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition. It mainly affects the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead, causing flushing or transient erythema, persistent erythema, phymatous changes, papules, pustules, and telangiectasias, and the eyes may also be affected by rosacea. Rosacea is more common
[...] Read more.
Rosacea is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition. It mainly affects the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead, causing flushing or transient erythema, persistent erythema, phymatous changes, papules, pustules, and telangiectasias, and the eyes may also be affected by rosacea. Rosacea is more common in women than in men and can start at any age. Rosacea affects both fair-skinned and darker-skinned people. Physical changes in the face due to rosacea can cause embarrassment, leading to reduced quality of life and self-esteem. Rosacea has several triggers, and its pathogenesis involves multiple factors, which means there are several treatment options, and these options can be combined. A patient’s clinical findings and symptoms will help a doctor to diagnose and classify the condition. Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, topical medications, systemic antibiotics and light-based therapy. The best approach is to tailor the treatment to the individual’s condition and preferences. The aim of treatment is to manage symptoms and prevent the progression of the disease.
Full article
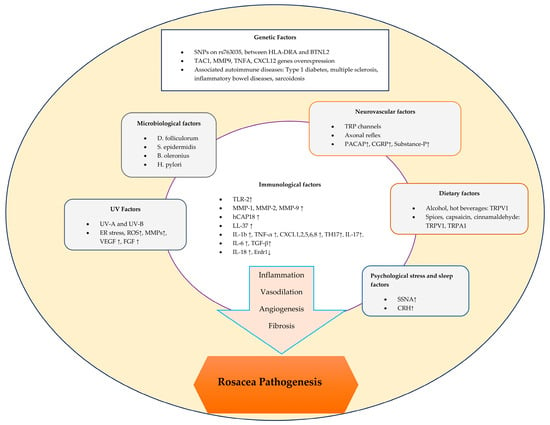
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Case of Paraneoplastic Anti-TIF1-γ Antibody-Positive Dermatomyositis Presenting with Generalized Edema and Associated with Aortic Aneurysm
by
Raven Bennett, Katherine Bradley, Iman Salem, David Weiner, Dhrumil Patel, Jeffrey Cloutier, Nicole Pace and Dorothea Barton
Dermato 2023, 3(4), 232-240; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3040018 - 18 Oct 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a rare autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by pathognomonic skin findings, often accompanied by myositis beginning with proximal weakness [...]
Full article
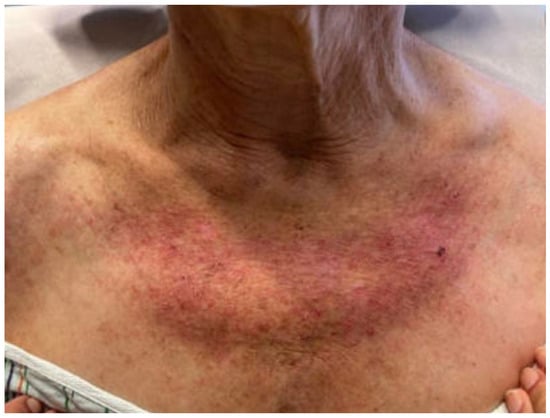
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Post-COVID Kawasaki-like Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Complicated by Herpes Simplex Virus-1 in a Two-Year-Old Child
by
Emma L. Hodson, Iman Salem, Katherine E. Bradley, Chiamaka L. Okorie, Arthur Marka, Nigel D. Abraham, Nicole C. Pace, Alicia T. Dagrosa, Ryan C. Ratts and Julianne A. Mann
Dermato 2023, 3(3), 224-231; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3030017 - 11 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare, systemic inflammation following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. We report a case of a 2-year-old male who presented with an exanthem and aberrant laboratory markers, mimicking Kawasaki disease but failing to
[...] Read more.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare, systemic inflammation following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. We report a case of a 2-year-old male who presented with an exanthem and aberrant laboratory markers, mimicking Kawasaki disease but failing to meet the full diagnostic criteria. His course was further complicated by herpes Simplex Virus-1 (HSV-1) stomatitis.
Full article
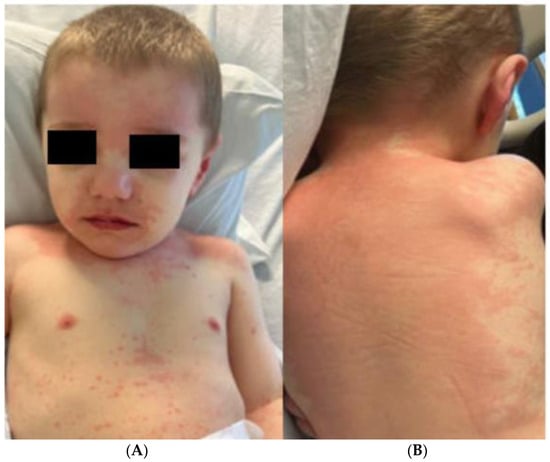
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Sex-Dependent Skin Aging and Rejuvenation Strategies
by
Marta Gerasymchuk, Gregory Ian Robinson, Nataliia Vardinska, Samuel Abiola Ayedun, Sandra Chinwe Alozie, John Wesley Robinson, Olga Kovalchuk and Igor Kovalchuk
Dermato 2023, 3(3), 196-223; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3030016 - 04 Aug 2023
Abstract
The skin, the largest external organ, serves as the primary defensive barrier against various environmental factors such as ultraviolet exposure, pollution, dietary habits, pathogens, and chemical compounds. Consequently, the skin reflects our age through visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles, age spots,
[...] Read more.
The skin, the largest external organ, serves as the primary defensive barrier against various environmental factors such as ultraviolet exposure, pollution, dietary habits, pathogens, and chemical compounds. Consequently, the skin reflects our age through visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles, age spots, dullness, and sagging. This review explores the gender-related aspects of cutaneous aging and the associated dermatological conditions. It highlights the different manifestations of aging in females and males that become evident after the age of 12, emphasizing the susceptibility to conditions such as seborrheic eczema, acne, and rosacea. Treatment strategies often vary between genders due to these disparities. While men tend to experience accelerated skin aging, most anti-aging products and strategies primarily target females. However, there has been a recent shift in men’s priorities, leading to increased interest in maintaining a youthful appearance and seeking cosmetic treatments. The manuscript covers a comprehensive range of modern dermal anti-aging and rejuvenation procedures, including plastic surgery, bio-revitalization methods, lasers, microneedling, and topical treatments. Additionally, it explores promising natural and synthetic therapeutics for combating age-related skin changes. The focus is on understanding the physiological aspects of gender-related cutaneous structure and aging to guide effective and tailored approaches in dermatological practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antioxidants and Skin Health)
►▼
Show Figures
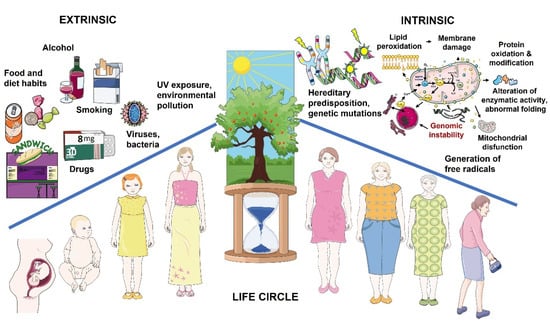
Figure 1
Open AccessLetter
BASCULE Syndrome Associated with Autoantibodies
by
Thilo Gambichler, Milan Barras, Rene Stranzenbach, Christina H. Scheel and Nessr Abu Rached
Dermato 2023, 3(3), 193-195; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3030015 - 15 Jul 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dear Editors: In 2016, Bessis and coworkers first reported Bier anemic spots, cyanosis, and urticaria-like eruption (BASCULE) syndrome [...]
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Laser Removal of Cosmetic Eyebrow Tattoos with a Picosecond Laser
by
Candice Menozzi-Smarrito and Stéphane Smarrito
Dermato 2023, 3(3), 182-192; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3030014 - 03 Jul 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This current retrospective study, including 98 patients aged 21 to 71 years, aims to assess the safety and the efficiency of a picosecond 755 nm/532 nm laser in the removal of complex eyebrows tattoos. Patients were treated with a picosecond laser at 755
[...] Read more.
This current retrospective study, including 98 patients aged 21 to 71 years, aims to assess the safety and the efficiency of a picosecond 755 nm/532 nm laser in the removal of complex eyebrows tattoos. Patients were treated with a picosecond laser at 755 nm with fluences ranging from 0.69 to 6.37 J/cm2 and at 532 nm with a fluence of 0.64 or 1.12 J/cm2. Analyses of Variance (ANOVA, single factor) and comparison tests (F-test) were conducted. A total of 70 subjects finished the full treatment. An average of three laser sessions were necessary to achieve the patients’ objective (total removal, attenuation for redo, or correction). The number of sessions was significantly higher if cosmetic tattoos contained visible warm pigments (red, orange, yellow). A total of 18 patients experienced immediate grey discoloration, although this was not found to significantly influence the number of laser sessions. The main side effects were redness, swelling, and bleeding points. One patient experienced a bruise immediately after laser shots. This retrospective study has shown the picosecond laser to be safe and efficient in removing complex cosmetic tattoos. Further investigation is ongoing to assess optimal parameters for treating red and white pigments.
Full article
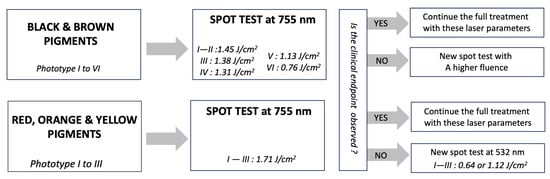
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review with a Focus on Contemporary Optical Imaging Diagnostic Modalities
by
Shazli Razi, Samavia Khan, Thu M. Truong, Shamail Zia, Farozaan Feroz Khan, Khalid Mahmood Uddin and Babar K. Rao
Dermato 2023, 3(2), 161-181; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3020013 - 19 Jun 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) arises from the abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes of the epidermis, most commonly due to UV-light-induced DNA damage. Although histopathological assessment is the gold standard for diagnosing cSCC, nascent optical imaging diagnostic modalities enable clinicians to perform “optical or
[...] Read more.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) arises from the abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes of the epidermis, most commonly due to UV-light-induced DNA damage. Although histopathological assessment is the gold standard for diagnosing cSCC, nascent optical imaging diagnostic modalities enable clinicians to perform “optical or virtual biopsy” in real-time. We aim to report advances in optical imaging diagnostics for cSCC, along with an updated review of the literature. A comprehensive literature review was performed using PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases for manuscripts published from 2008 to 2022. The search yielded a total of 9581 articles, out of which 136 relevant articles were included in the literature review after fulfilling screening and eligibility criteria. This review highlights the current optical imaging devices used for diagnosing cSCC and their diagnostic features. These devices include in vivo and ex vivo reflectance confocal microscopy, optical coherence tomography, line-field confocal optical coherence tomography, multiphoton tomography, and high-frequency ultrasonography. Although surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery is considered the gold standard, the latest developments in nonsurgical management of cSCC are discussed. Based on he review of the literature, we conclude that contemporary optical imaging devices such as confocal microscopy, optical coherence tomography, line-field confocal optical coherence tomography and multiphoton tomography have revolutionized real-time diagnostic imaging in dermatology, particularly within the realm of skin cancer. These devices enable rapid diagnoses and allow for a faster initiation of therapy. The application of newer imaging devices to cSCC management may benefit high-risk patients (e.g., chronic UV radiation exposure or organ transplant recipients) or patients with multifocal cSCC, for whom multiple biopsies would be impractical, thus avoiding unnecessary biopsies. Together with dermoscopy, optical imaging technologies can help to improve the efficiency of diagnosis by reducing the turnaround time and the need for extensive laboratory processing resources.
Full article
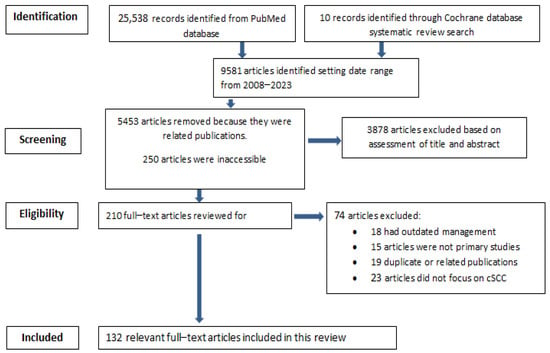
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A 63-Year-Old Female Presenting to the Emergency Department with Massive Facial Swelling and Dyspnea
by
Thilo Gambichler, Rosanna Schacht, Kathrin Noldes and Stefanie Boms
Dermato 2023, 3(2), 158-160; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3020012 - 01 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A 63-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with acute dyspnea and progressive swelling of the face (Figure 1), neck, and upper trunk [...]
Full article
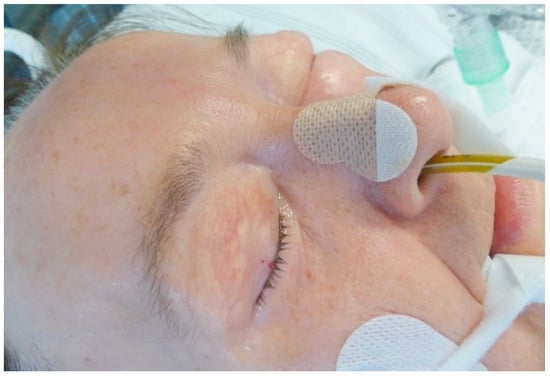
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Safety Concern and Regulatory Status of Chemicals Used in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
by
Manthan Kaushik, Uzma Farooq, Mohd Shoab Ali, Mohammad Javed Ansari, Zeenat Iqbal and Mohd Aamir Mirza
Dermato 2023, 3(2), 131-157; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3020011 - 24 May 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cosmetics and personal care products (PCPs) are a few of the most commonly used products across the globe with a whopping market share of approximately USD 500 billion. These products are used for cleansing purposes and for improving the quality and beauty of
[...] Read more.
Cosmetics and personal care products (PCPs) are a few of the most commonly used products across the globe with a whopping market share of approximately USD 500 billion. These products are used for cleansing purposes and for improving the quality and beauty of the face, hair, and skin. There are many chemical substances involved in the manufacturing of cosmetics and PCPs. These chemical substances incorporated in cosmetics or PCPs are crucial to develop high-quality products with superior appearance, applicability, and stability; however, excessive use of such chemicals in cosmetics and PCPs has become a safety concern as many of these are reported to cause severe health complications. Overuse of cosmetics and PCPs with hazardous material should be minimized, especially by pregnant women and children. Gynecologists advise pregnant women not to use cosmetics and PCPs with hazardous chemicals. The implementation of a lawful framework is crucial to establish the safety of cosmetics and PCPs. Cosmetic companies/industries must be strictly regulated and made compliant to the guidelines in order to protect human health and minimize safety concerns. In this review, hazardous chemicals incorporated in the personal care products/cosmetics and their related risk and health complications have been discussed in detail. Additionally, regulatory status and clinical trials of chemical substances that involve toxicity and causing severe complications have also been discussed.
Full article
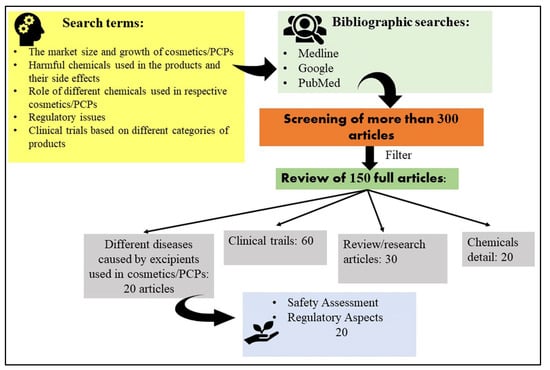
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Characterization of Novel Anisotropic Skin Graft Simulants
by
Vivek Gupta, Rohan Singla and Arnab Chanda
Dermato 2023, 3(2), 114-130; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3020010 - 10 May 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Split-thickness skin grafting is a well-known procedure for the treatment of small- and medium-sized burns. However, its effectiveness has been reported to be limited in the case of large and severe burns due to much lower real expansion offered by the grafts than
[...] Read more.
Split-thickness skin grafting is a well-known procedure for the treatment of small- and medium-sized burns. However, its effectiveness has been reported to be limited in the case of large and severe burns due to much lower real expansion offered by the grafts than the claimed expansion by graft mesh manufacturers. Recent computational studies have indicated that the collagen fiber orientation within the skin layers have a significant effect on the skin graft expansion. In this study, biofidelic anisotropic synthetic skin with one and two layers and all possible fiber orientations were developed, and incision patterns used in traditional graft meshing techniques were projected to fabricate novel synthetic skin grafts with a theoretical meshing ratio of 3:1. A biaxial tensile testing device was designed to simulate skin graft stretching in clinical settings, and a wide range of synthetic skin graft variants were mechanically tested. The measured quantities included induced nonlinear stress–strain, void area, and meshing ratio. In addition, the stress–strain responses were characterized using nonlinear hyperelastic models. The key observations include the generation of higher induced stresses in two-layer grafts. In the one-layer graft models, a 15° fiber orientation produced the highest expansion at a minimal stress value of 0.21 MPa. In the two-layer graft models, the 45°–15° fiber orientation generated the maximum expansion with minimum stress. A range of such findings were analyzed to determine the graft orientations that may allow enhanced expansion without generating much stress. This information would be indispensable not only for understanding the expansion potential of skin grafts, but also for further research and the development of skin grafts with enhanced expansion for severe burn injury treatment.
Full article
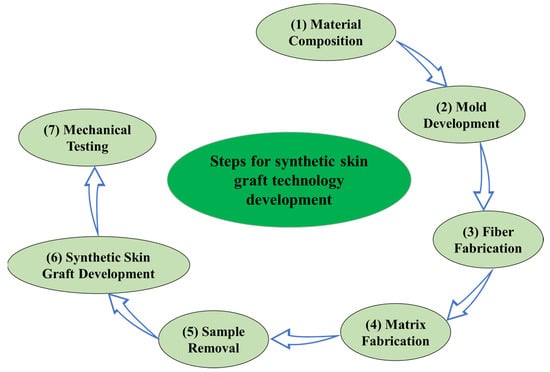
Figure 1
Open AccessLetter
Efficacy of Tofacitinib in the Treatment of Universal Alopecia Areata and Primary Sjögren Syndrome
by
Teresa Rodenas-Herranz, Marta Cebolla-Verdugo, Carlos Llamas-Segura, Ricardo Ruiz-Villaverde and Maria Teresa Herranz-Marín
Dermato 2023, 3(2), 109-113; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3020009 - 21 Apr 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dear Editor: Alopecia areata (AA) is a form of alopecia whose prevalence ranges from 0 [...]
Full article
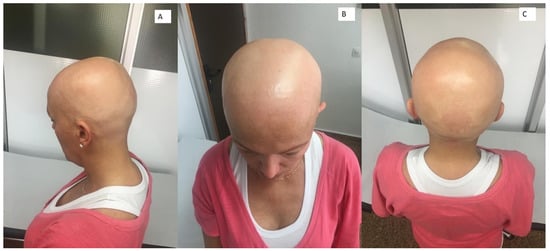
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Congenital Atrophic Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
by
Iman Salem, Katherine Bradley, Julianne A. Mann, Joseph H. Shin, Matthew LeBoeuf and Aravindhan Sriharan
Dermato 2023, 3(2), 97-108; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3020008 - 16 Apr 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare mesenchymal tumor of intermediate malignant potential. The neoplasm is locally aggressive with a high rate of recurrence. It typically presents in adults. Atrophic congenital DFSP is extremely rare. The few reported cases have presented as a morphea-like
[...] Read more.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare mesenchymal tumor of intermediate malignant potential. The neoplasm is locally aggressive with a high rate of recurrence. It typically presents in adults. Atrophic congenital DFSP is extremely rare. The few reported cases have presented as a morphea-like plaque that persists for years, before progressing into a nodular form. To our knowledge, congenital atrophic DFSP has been only reported fourteen times, and of those, only nine were confirmed by molecular studies. Herein we report a congenital case of atrophic DFSP, which initially presented as a bruise-like atrophic plaque on the dorsal forearm, initially mistaken for child abuse. The clinical appearance, histopathology, and molecular features of this rare form of DFSP are reviewed. Our case highlights the importance of early detection and adequate sampling of congenital DFSP; early treatment allows for treating small lesions without large, disfiguring, and potentially disabling excisions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An In Vitro Pilot Study Investigating the Antineoplastic Effects of GP-2250 on Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines: Preliminary Results
by
Milan Barras, Lutz Schmitz, Chris Braumann, Waldemar Uhl, Marina Skrygan, Marie Buchholz, Thomas Meyer, Eggert Stockfleth, Thomas Müller, Jürgen C. Becker and Thilo Gambichler
Dermato 2023, 3(1), 85-96; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3010007 - 14 Mar 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) can be a life-threatening disease for which effective and safe treatment in advanced stages is very limited. GP-2250 has been recently proven to have—in vitro and in vivo—antineoplastic effects on cancer cells. This study aims to investigate
[...] Read more.
Advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) can be a life-threatening disease for which effective and safe treatment in advanced stages is very limited. GP-2250 has been recently proven to have—in vitro and in vivo—antineoplastic effects on cancer cells. This study aims to investigate the potential anti-neoplastic effects of GP-2250 on the cSCC cell lines SCC13 and A431 through dose finding assessments, MTT cytotoxicity assays, cell migration assays, BrdU proliferation assays and FCM analysis. Our preliminary results have shown for the first time evidence for anti-neoplastic effects of GP-2250 on cSCC cells, enhancing cytotoxicity, attenuating cancer cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis and reducing tumour cell migration. Further investigations evaluating the modes of action of GP-2250 on cSCC cell lines are warranted in order to justify the use in vivo studies.
Full article
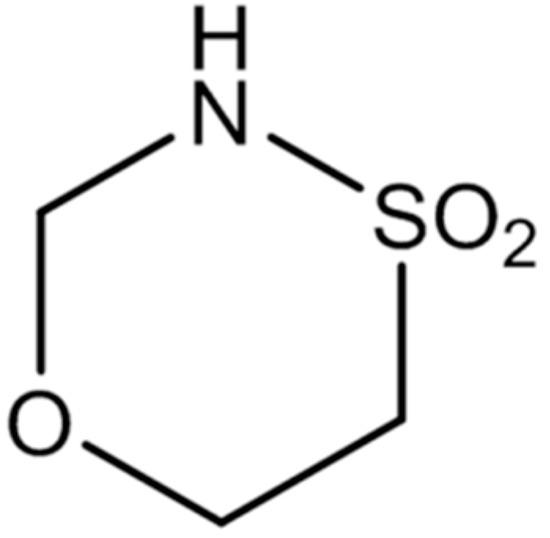
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
FDTD Simulations of Sweat Ducts and Hair at 0.45 THz
by
Zoltan Vilagosh, Negin Foroughimehr, Alireza Lajevardipour and Andrew W. Wood
Dermato 2023, 3(1), 69-84; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3010006 - 02 Mar 2023
Cited by 3
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Advances in Terahertz frequency electromagnetic radiation (THz) production technologies have produced an increasing interest in exploring possible applications. New applications will inevitably lead to increased incidental interaction of humans with THz radiation. Given that the wavelength of THz radiation is in the same
[...] Read more.
Advances in Terahertz frequency electromagnetic radiation (THz) production technologies have produced an increasing interest in exploring possible applications. New applications will inevitably lead to increased incidental interaction of humans with THz radiation. Given that the wavelength of THz radiation is in the same order of magnitude as the dimensions of skin structures such as hair and sweat ducts, the possibility of interaction among these structures is of interest. The interaction was studied utilizing Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) simulations using a far-field excitation of 0.45 THz. No antenna-like effects were detected. Regions of increased specific absorption rate (SAR) due to reactive near-field effects with both the hair and sweat ducts were found in the order of 0.01–0.05 mm and 0.001–0.002 mm, respectively. Simulations using unwound sweat ducts yielded the same penetration pattern as the helical structure, indicating that the helical structure has no impact on the propagation of THz radiation in skin.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Violaceous Lesions on the Leg: What Else Apart from Kaposi Sarcoma? Differential Diagnosis with a Narrative Review of the Literature
by
Alessandro Pileri, Gionathan Orioni, Corrado Zengarini, Vieri Grandi, Bianca Maria Piraccini and Valeria Gaspari
Dermato 2023, 3(1), 56-68; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato3010005 - 16 Feb 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With this work, we aimed to review the principal benign and malignant tumors (including vascular, keratinocytic/epidermal, melanocytic, hematopoietic, and lymphoid origin), primarily affecting the leg’s skin. The lesions’ location can also help focus on a spectrum of differential diagnoses in clinical practice. All
[...] Read more.
With this work, we aimed to review the principal benign and malignant tumors (including vascular, keratinocytic/epidermal, melanocytic, hematopoietic, and lymphoid origin), primarily affecting the leg’s skin. The lesions’ location can also help focus on a spectrum of differential diagnoses in clinical practice. All the diseases present the same clinical presentation characterized by erythematous to violaceous nodules. Despite the same clinical presentation, each disease’s prognostic outcome and therapeutic management can be somewhat different. Since clinical diagnosis may sometimes be challenging, histology and immunohistochemistry play a fundamental role in recognizing and staging these types of lesions. Molecular studies can help to determine the exact nature of lesions with no specific characteristics. Kaposi’s sarcoma is an angioproliferative neoplasm that typically occurs in the lower limbs and can enter into differential diagnosis with several other rarer skin diseases. The principal differential diagnosis concerns primary cutaneous lymphomas, of which mycosis fungoides represent the most frequent primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Other rare forms include primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas, which can be divided into indolent and aggressive forms, such as the primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type, and lymphomatoid papulomatosis (LyP). In the case of indolent lesions, skin-directed therapies, limited-field radiotherapy, and surgical approaches can be good options. At the same time, different management, with systemic chemotherapy and allogenic bone marrow transplant, is required with aggressive neoplasms, such as blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasia or advanced mycosis fungoides. The dermatologist’s role can be crucial in recognizing such diseases and avoiding misdiagnosis, giving the pathologist the correct clinical information for an accurate diagnosis, and starting the suitable therapy.
Full article
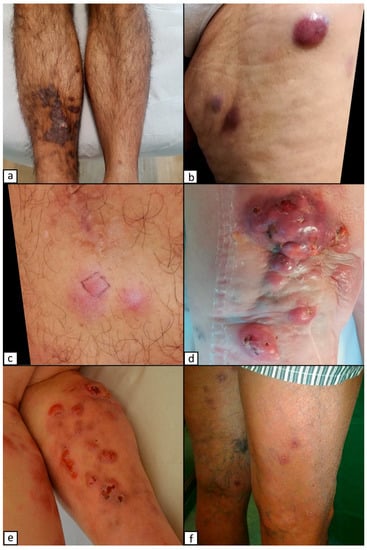
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Clinics and Practice, Dermato, Life, Current Oncology
Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Skin Cancer
Topic Editors: José Juan Pereyra-Rodríguez, Ricardo Ruiz-Villaverde, Jose-Carlos Armario-HitaDeadline: 30 September 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Dermato
Interventions Impacting the Natural History of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
Guest Editors: Francesco Bellinato, Paolo GisondiDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Dermato
What Is Your Diagnosis?—Case Report Collection
Guest Editors: Jose Manuel Lopes, Robert GniadeckiDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Dermato
Clinical Features and Molecular Pathology of Melanomas
Guest Editors: Paola Savoia, Elisa ZavattaroDeadline: 15 September 2024
Special Issue in
Dermato
Dermoscopy in Skin Cancer
Guest Editors: Elisa Zavattaro, Paola SavoiaDeadline: 14 February 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Dermato
Artificial Intelligence in Dermatology
Collection Editor: Alexander Navarini-Meury