Journal Description
Compounds
Compounds
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on chemical compounds published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Compounds is a companion journal of Metals.
Latest Articles
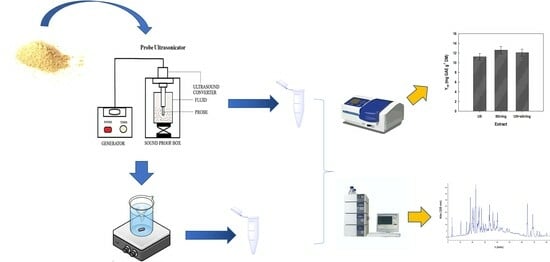
Ultrasonication-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Waste Orange Peel Polyphenols: Optimization of Process Variables and Effect on Extract Composition
Compounds 2024, 4(2), 301-314; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4020016 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
The citrus processing industry is responsible for the generation of large volumes of waste side streams, represented principally by fruit peels. These tissues are exceptionally rich in polyphenolic bioactive phytochemicals, and there has been a great industrial interest for their valorization. The examination
[...] Read more.
The citrus processing industry is responsible for the generation of large volumes of waste side streams, represented principally by fruit peels. These tissues are exceptionally rich in polyphenolic bioactive phytochemicals, and there has been a great industrial interest for their valorization. The examination presented herein targeted at developing a fast and straight-forward aqueous extraction process, based on ultrasonication, for the efficacious recovery of polyphenolic compounds from waste orange peels. After an initial single-factor examination, the response surface optimization showed that a maximum total polyphenol yield of 12.81 mg chlorogenic acid equivalents (GAE) per g−1 dry mass could be achieved by setting sonicator amplitude at 80%, for 15 min, using a duty cycle of 2/2 (2 s on/2 s off). Comparison of this methodology with a stirred-tank extraction demonstrated that the ultrasonication technique was equally effective, requiring ambient temperature and considerably shorter resident time. The combination of both techniques using the ultrasonication process as a pretreatment step did not boost extraction yield, and the extracts produced had similar polyphenolic composition and antioxidant activity. However, a slight enhancement of the recovery of individual constituents was noted. It is proposed that efficient extraction of polyphenolic substances from waste orange peels may be accomplished using the present methodology, which is a low-cost (ambient temperature, short time) and sustainable (water as solvent) process.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
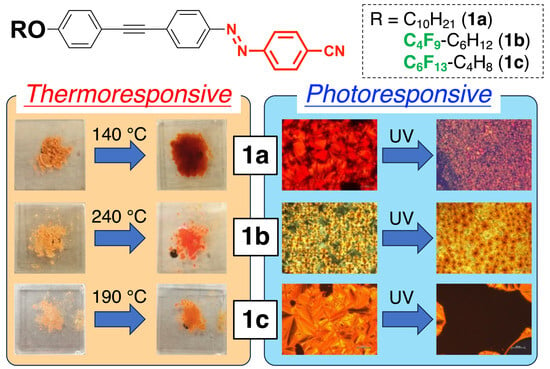
(1E)-1,2-Diaryldiazene Derivatives Containing a Donor–π-Acceptor-Type Tolane Skeleton as Smectic Liquid–Crystalline Dyes
by
Shigeyuki Yamada, Keigo Yoshida, Yuto Eguchi, Mitsuo Hara, Motohiro Yasui and Tsutomu Konno
Compounds 2024, 4(2), 288-300; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4020015 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
Considerable attention has been paid to (1E)-1,2-diaryldiazenes (azo dyes) possessing liquid–crystalline (LC) and optical properties because they can switch color through thermal phase transitions and photoisomerizations. Although multifunctional molecules with both LC and fluorescent properties based on a donor–π-acceptor (D-π-A)-type tolane
[...] Read more.
Considerable attention has been paid to (1E)-1,2-diaryldiazenes (azo dyes) possessing liquid–crystalline (LC) and optical properties because they can switch color through thermal phase transitions and photoisomerizations. Although multifunctional molecules with both LC and fluorescent properties based on a donor–π-acceptor (D-π-A)-type tolane skeleton have been developed, functional molecules possessing LC and dye properties have not yet been developed. Therefore, this study proposes to develop LC dyes consisting of (1E)-1,2-diaryldiazenes with a D–π-A-type tolane skeleton as the aryl moiety. The (1E)-1,2-diaryldiazene derivatives exhibited a smectic phase, regardless of the flexible-chain structure, whereas the melting temperature was significantly increased by introducing fluoroalkyl moieties into the flexible chain. Evaluation of the optical properties revealed that compounds with decyloxy chains exhibited an orange color, whereas compounds with semifluoroalkoxy chains absorbed at a slightly blue-shifted wavelength, which resulted in a pale orange color. The thermal phase transition caused a slight color change accompanied by a change in the absorption properties, photoisomerization-induced shrinkage, and partial disappearance of the LC domain. These results indicate that (1E)-1,2-diaryldiazenes with a D–π-A-type tolane skeleton can function as thermo- or photoresponsive dyes and are applicable to smart windows and in photolithography.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Compounds (2024))
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
NOx Storage and Reduction (NSR) Performance of Sr-Doped LaCoO3 Perovskite Prepared by Glycine-Assisted Solution Combustion
by
Xinru Luan, Xudong Wang, Tianfei Zhang, Liangran Gan, Jianxun Liu, Yujia Zhai, Wei Liu, Liguo Wang and Zhongpeng Wang
Compounds 2024, 4(2), 268-287; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4020014 - 08 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Here, we successfully synthesized Sr-doped perovskite-type oxides of La1−xSrxCo1−λO3−δ, “LSX” (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7), using the glycine-assisted solution combustion method. The effect of strontium doping on the catalyst structure, NO to NO
[...] Read more.
Here, we successfully synthesized Sr-doped perovskite-type oxides of La1−xSrxCo1−λO3−δ, “LSX” (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7), using the glycine-assisted solution combustion method. The effect of strontium doping on the catalyst structure, NO to NO2 conversion, NOx adsorption and storage, and NOx reduction performance were investigated. The physicochemical properties of the catalysts were studied by XRD, SEM-EDS, N2 adsorption–desorption, FTIR, H2-TPR, O2-TPD, and XPS techniques. The NSR performance of LaCoO3 perovskite was improved after Sr doping. Specifically, the perovskite with 50% of Sr doping (LS5 sample) exhibited excellent NOx storage capacity within a wide temperature range (200–400 °C), and excellent stability after hydrothermal and sulfur poisoning. It also displayed the highest NOx adsorption–storage capacity (NAC: 1889 μmol/g; NSC: 1048 μmol/g) at 300 °C. This superior performance of the LS5 catalyst can be attributed to its superior reducibility, better NO oxidation capacity, increased surface Co2+ concentration, and, in particular, its generation of more oxygen vacancies. FTIR results further revealed that the LSX catalysts primarily store NOx through the “nitrate route”. During the lean–rich cycle tests, we observed an average NOx conversion rate of over 50% in the temperature range of 200–300 °C, with a maximum conversion rate of 61% achieved at 250 °C.
Full article
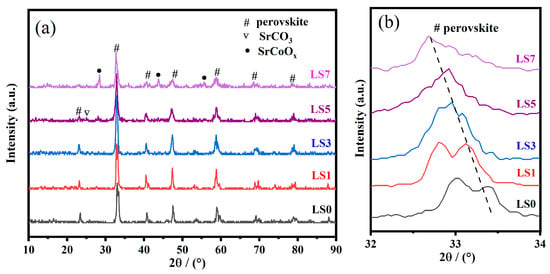
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
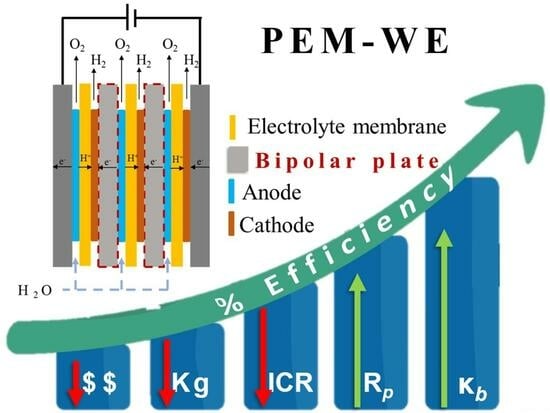
Performance of Stainless-Steel Bipolar Plates (SS-BPPs) in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Water Electrolyser (PEMWE): A Comprehensive Review
by
Eirini Zagoraiou, Soorya Krishan, Amal Siriwardana, Anastasia Maria Moschovi and Iakovos Yakoumis
Compounds 2024, 4(2), 252-267; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4020013 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bipolar Plates (BPPs) play a critical role in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Water Electrolysers (PEMWEs) for effective hydrogen generation. The performance and longevity of the system can be considerably impacted by choosing the suitable material for these components. Polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis technology
[...] Read more.
Bipolar Plates (BPPs) play a critical role in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Water Electrolysers (PEMWEs) for effective hydrogen generation. The performance and longevity of the system can be considerably impacted by choosing the suitable material for these components. Polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis technology relies on cost-effective and corrosion-resistant BPPs. Tantalum, niobium, and titanium are low-cost, easy-to-machine materials that have good electrical and thermal conductivity; however, they exhibit low corrosion resistance. Noble metal and metal nitride coatings are usually investigated to minimize corrosion and interfacial contact resistance. Because of its performance-to-cost ratio, Stainless Steel (SS) based materials are among the most popular materials for BPP development. This study recommends material and operating parameters to improve PEMWE systems for sustainable hydrogen production’s efficiency, durability, and economic viability.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
AlH3 as High-Energy Fuels for Solid Propellants: Synthesis, Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Stabilization
by
Youhai Liu, Fusheng Yang, Yang Zhang, Zhen Wu and Zaoxiao Zhang
Compounds 2024, 4(2), 230-251; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4020012 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aluminum hydride (AlH3) has attracted wide attention due to its high gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen capacity. AlH3 can easily release hydrogen when heated at relatively low temperature. Such high hydrogen density and low dehydrogenation temperature make it one of the
[...] Read more.
Aluminum hydride (AlH3) has attracted wide attention due to its high gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen capacity. AlH3 can easily release hydrogen when heated at relatively low temperature. Such high hydrogen density and low dehydrogenation temperature make it one of the most promising high-energy fuels for solid propellants. In particular, AlH3 as a component of solid propellants may greatly increase the specific impulse of rocket engines. However, AlH3 exhibits low chemical and thermal stability in an ambient atmosphere. In this paper, the research progress about the synthesis, dehydrogenation thermodynamics, and kinetics, the stabilization of AlH3 over the past decades are reviewed, with the aim of exploring more a economical synthesis and suitable stabilization methods for large-scale use in solid propellants. Finally, some suggestions regarding future research directions in this filed are proposed.
Full article
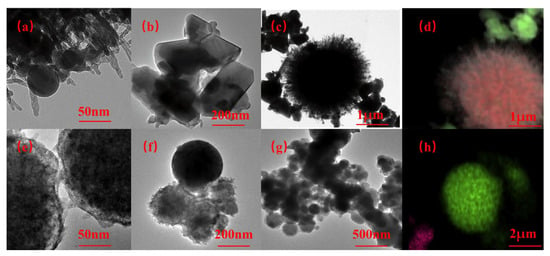
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Antimicrobial Activity of Dimeric Flavonoids
by
Inês Lopes, Carla Campos, Rui Medeiros and Fátima Cerqueira
Compounds 2024, 4(2), 214-229; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4020011 - 22 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Distributed throughout the environment are various microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. Although many are part of the human microbiome, many are pathogenic and cause infections ranging from mild to severe. In recent years, the identification of multidrug-resistant microorganisms has become
[...] Read more.
Distributed throughout the environment are various microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. Although many are part of the human microbiome, many are pathogenic and cause infections ranging from mild to severe. In recent years, the identification of multidrug-resistant microorganisms has become a serious public health problem. The resulting infections call into question the therapeutic capacity of health systems and lead to approximately 70,000 deaths annually worldwide. The progressive resistance to antibiotics and antifungals has been a major challenge for the medical and pharmaceutical community, requiring the search for new compounds with antimicrobial properties. Several studies have demonstrated the potential of natural and synthesized flavonoids, especially the dimers of these molecules. In this review are presented many examples of dimeric flavonoids that have demonstrated antimicrobial activity against viruses, like influenza and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), protozoal infections, such as Leishmaniasis and Malaria, fungal infections by Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans, and bacterial infections caused, for example, by Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. In the pursuit to find potential safe agents for therapy in microbial infections, natural dimeric flavonoids are an option not only for the antimicrobial activity, but also for the low toxicity usually associated with these compounds when compared to classic antimicrobials.
Full article
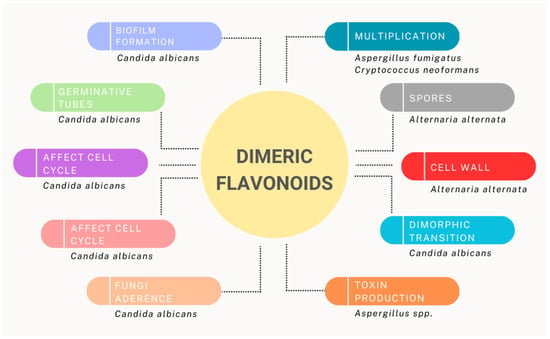
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Synthesis and Biological Activities of Some Metal Complexes of 2-Thiouracil and Its Derivatives: A Review
by
Petja Emilova Marinova and Kristina Dimova Tamahkyarova
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 186-213; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010010 - 27 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The thionamide antithyroid agents were discovered largely through observations carried out by various researchers in the 1940s that found that sulfhydryl-containing substances were goitrogenic in animals. Prof. Edwin B. Astwood started using these drugs to treat hyperthyroidism. In the current paper, we summarize
[...] Read more.
The thionamide antithyroid agents were discovered largely through observations carried out by various researchers in the 1940s that found that sulfhydryl-containing substances were goitrogenic in animals. Prof. Edwin B. Astwood started using these drugs to treat hyperthyroidism. In the current paper, we summarize the development background of these agents and the coordination possibility of 2-thiouracil and its derivatives, as well as the biological activities of some of its complexes. Some of them are used as agents for the treatment of tuberculosis, and arthritis, others have bactericidal and fungicidal activity, the third cytotoxic properties, and could be used to treat various types of cancer.
Full article
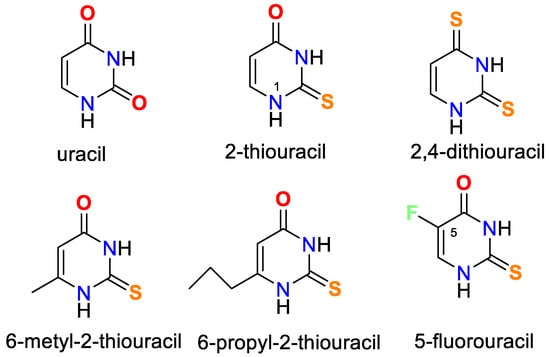
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Milestones and New Challenges in Compounds
by
Juan C. Mejuto
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 182-185; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010009 - 21 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Since 2021, we have been immersed in the challenge of publishing a journal that constitutes a form of communication of scientific achievements in the field of the synthesis and characterization of chemical compounds from a theoretical and experimental point of view [...]
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Chloride Solutions Using Mixtures of P507 and Cyanex 272
by
Mikhail A. Afonin, Andrey V. Nechaev, Ilya A. Yakimenko and Vera V. Belova
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 172-181; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010008 - 20 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, the extraction of rare earth elements (REEs) from chloride solutions after leaching REE carbonate concentrate with solutions of the mixtures of P507 (2-ethylhexylphosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester) and Cyanex 272 (bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid) (1:1) at various concentrations was experimentally studied. It was
[...] Read more.
In this study, the extraction of rare earth elements (REEs) from chloride solutions after leaching REE carbonate concentrate with solutions of the mixtures of P507 (2-ethylhexylphosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester) and Cyanex 272 (bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid) (1:1) at various concentrations was experimentally studied. It was shown that the distribution ratios of all REEs decrease with the increasing concentration of these metals in the initial solution, which is associated with the loading of the organic phase. The most significant improvement in the extraction is observed for the heavy group of rare earth elements. The extractability of REEs increases with the increasing atomic number of the element, as is typical for the extraction of these metals with acidic organophosphorus extractants. The data obtained show that the separation factors of adjacent rare earth elements decrease slightly with the increasing concentration of metals in the initial aqueous solution. Increasing the concentration of the extractant mixture does not have a significant effect on the values of the adjacent REE separation factors. The data obtained on the distribution ratios and separation factors made it possible to propose a flow sheet for the separation of rare earth elements with the production of Y, Ho, Tb and Dy.
Full article
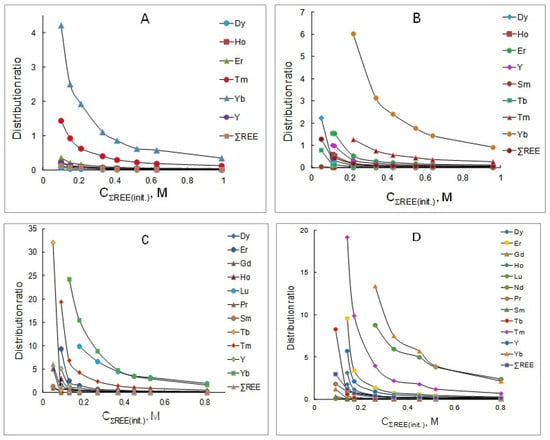
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Recent Progress and Challenges in the Field of Metal–Organic Framework-Based Membranes for Gas Separation
by
Shunsuke Tanaka, Kojiro Fuku, Naoki Ikenaga, Maha Sharaf and Keizo Nakagawa
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 141-171; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010007 - 02 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) represent the largest class of materials among crystalline porous materials ever developed, and have attracted attention as core materials for separation technology. Their extremely uniform pore aperture and nearly unlimited structural and chemical characteristics have attracted great interest and promise
[...] Read more.
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) represent the largest class of materials among crystalline porous materials ever developed, and have attracted attention as core materials for separation technology. Their extremely uniform pore aperture and nearly unlimited structural and chemical characteristics have attracted great interest and promise for applying MOFs to adsorptive and membrane-based separations. This paper reviews the recent research into and development of MOF membranes for gas separation. Strategies for polycrystalline membranes and mixed-matrix membranes are discussed, with a focus on separation systems involving hydrocarbon separation, CO2 capture, and H2 purification. Challenges to and opportunities for the industrial deployment of MOF membranes are also discussed, providing guidance for the design and fabrication of future high-performance membranes. The contributions of the underlying mechanism to separation performance and adopted strategies and membrane-processing technologies for breaking the selectivity/permeability trade-off are discussed.
Full article
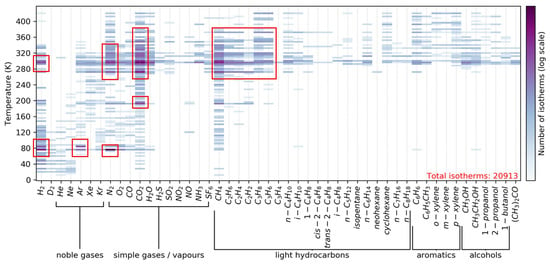
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Particle Size on the Physical Properties of PLA/Potato Peel Composites
by
Katharina Miller, Corina L. Reichert, Myriam Loeffler and Markus Schmid
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 119-140; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010006 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
In recent years, agricultural by-product fillers have been investigated in composites to influence the physical properties of the packaging material, increase biodegradability, and reduce costs. In general, the properties of composites are mainly influenced by the type, amount, and size of fillers. The
[...] Read more.
In recent years, agricultural by-product fillers have been investigated in composites to influence the physical properties of the packaging material, increase biodegradability, and reduce costs. In general, the properties of composites are mainly influenced by the type, amount, and size of fillers. The aim of this study was to characterize potato peel particles as a filler in a poly(lactic acid) (PLA) matrix and to determine the effect of particle size on the physical properties of the composite. Therefore, different fractions of potato peel powder (0–53 μm, 125–250 μm, and 315–500 μm) were incorporated into PLA matrix via compounding and injection-molding. Microscopic analysis of the injection-molded samples revealed that the average particle shape did not differ between the different fractions. Overall, increasing the particle size of potato peel particles resulted in increased stiffness and decreased ductility. The cold crystallization temperature and water vapor transmission rate of the composites were independent of particle size but increased upon the incorporation of potato peel particles. In conclusion, the effect of particle incorporation on packaging-related properties was higher than the effect of using different particle size fractions. This means that potato peel particles, regardless of their particle size distribution, are promising fillers for composites, with the potential to improve biodegradability, maintain some level of protection for the packaged product, and reduce the cost of the composites.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Polymeric Substrates Modification with Biobased Functional Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Designing and Manufacturing of Biocompatible Hydroxyapatite and Sodium Trisilicate Scaffolds by Ordinary Domestic Microwave Oven
by
Giorgio Luciano, Maurizio Vignolo, Denise Galante, Cristina D’Arrigo, Franco Furlani, Monica Montesi and Silvia Panseri
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 106-118; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010005 - 30 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this work, we present a versatile, rapid, and low-cost manufacturing technique to develop bioceramic scaffolds that could enhance bone tissue regeneration via microwave preparation using a domestic microwave oven. The scaffolds were prepared by combining hydroxyapatite and water glass (sodium trisilicate solution),
[...] Read more.
In this work, we present a versatile, rapid, and low-cost manufacturing technique to develop bioceramic scaffolds that could enhance bone tissue regeneration via microwave preparation using a domestic microwave oven. The scaffolds were prepared by combining hydroxyapatite and water glass (sodium trisilicate solution), foamed by using a microwave oven, and then characterized by means of Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX), mechanical properties, infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), and a density and stability test in water. Furthermore, in vitro tests were performed to verify the affinity of the scaffold for osteoclast cells. The morphology of the samples showed interconnected pores suitable for promoting tissue regeneration and vascularization, while specific mechanical properties were preserved. The physicochemical characterization and the in vitro tests presented promising results for bone regenerative applications. The scaffolds we obtained exhibited comparable properties to those fabricated using a laboratory microwave oven, including the ability to induce the formation of bone-like tissue in vitro.
Full article
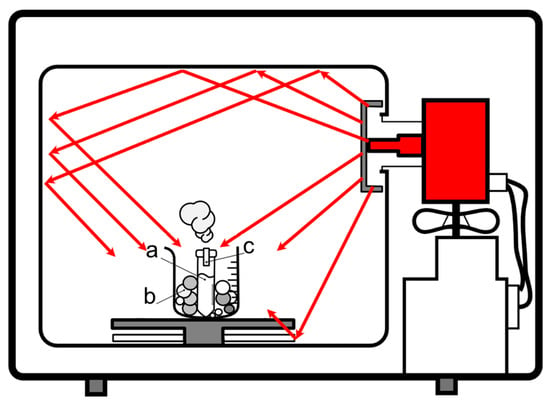
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
An Approach to 3D Printing Techniques, Polymer Materials, and Their Applications in the Production of Drug Delivery Systems
by
Pedro H. N. Cardoso and Evando S. Araújo
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 71-105; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010004 - 17 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Three-dimensional printing (3DP) technologies are characterized as a set of innovative manufacturing techniques that allow for the creation of complex and/or personalized three-dimensional physical objects on the work surface of a 3D printing machine (based on the computer-aided design (CAD) project designs of
[...] Read more.
Three-dimensional printing (3DP) technologies are characterized as a set of innovative manufacturing techniques that allow for the creation of complex and/or personalized three-dimensional physical objects on the work surface of a 3D printing machine (based on the computer-aided design (CAD) project designs of these parts). Three-dimensional printing techniques are widely used in various areas of knowledge, such as education, engineering, and biomedicine. Polymeric materials are widely used for these applications, mainly due to their desirable workability during part manufacturing, compatibility with other chemical materials, the wide range of polymers with different physical and chemical characteristics, and the possibility for recycling. The development of polymeric drug delivery systems (DDSs) by 3D printing is currently an active field of research, both in academia and industry, given the potential of this technique for medical purposes. In this context, this work reviews potential polymers for the production of drug delivery systems via 3D printing techniques. The demonstrations of the main 3DP techniques used for drug delivery applications include their working principles and advantages and how the technologies develop the final product. In addition, potential synthetic and natural polymers that are currently used in 3DP drug delivery devices are presented and discussed based on recent scientific studies.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Chemical Compositions and Essential Fatty Acid Analysis of Selected Vegetable Oils and Fats
by
Pawan Kumar Ojha, Darbin Kumar Poudel, Anil Rokaya, Salina Maharjan, Sunita Timsina, Ambika Poudel, Rakesh Satyal, Prabodh Satyal and William N. Setzer
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 37-70; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010003 - 17 Jan 2024
Abstract
The fatty acid (FA) compositions of thirty-nine vegetable oils and fats, including nangai nut, pili nut, shea butter, tamanu oil, baobab, sea buckthorn berry, Brazil nut, grape seed, black seed, evening primrose, passion fruit, milk thistle, sunflower, pumpkin seed, sesame, soybean, flax seed,
[...] Read more.
The fatty acid (FA) compositions of thirty-nine vegetable oils and fats, including nangai nut, pili nut, shea butter, tamanu oil, baobab, sea buckthorn berry, Brazil nut, grape seed, black seed, evening primrose, passion fruit, milk thistle, sunflower, pumpkin seed, sesame, soybean, flax seed, kukui, red raspberry seed, walnut, chia seed, hemp seed, rosehip, almond, avocado, carrot seed, moringa, apricot kernel, camellia seed, macadamia, olive, marula, argan, castor, jojoba, pomegranate seed, medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) coconut, roasted coconut, canola, and mustard oil, were analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Vegetable oils and fats have different profiles in terms of their fatty acid composition, and their major constituents vary significantly. However, we categorized them into different classes based on the percentages of different fatty acids they contain. The saturated fatty acids, such as palmitic acid and stearic acid, and the unsaturated fatty acids, including oleic acid, linoleic acid, and linolenic acid, are the main categories. Among them, roasted coconut oil contained the greatest amount of saturated fatty acids followed by nangai nut (45.61%). Passion fruit oil contained the largest amount of linoleic acid (66.23%), while chia seed oil had the highest content of linolenic acid (58.25%). Oleic acid was exclusively present in camellia seed oil, constituting 78.57% of its composition. Notably, mustard oil had a significant presence of erucic acid (54.32%), while pomegranate seed oil exclusively contained punicic acid (74.77%). Jojoba oil primarily consisted of (Z)-11-eicosenoic acid (29.55%) and (Z)-docos-13-en-1-ol (27.96%). The major constituent in castor oil was ricinoleic acid (89.89%). Compared with other vegetable oils and fats, pili nut oil contained a significant amount of (E)-FA (20.62%), followed by sea buckthorn berry oil with a content of 9.60%. FA compositions from sources may be problematic in the human diet due to no labeling or the absence of essential components. Therefore, consumers must cast an eye over some essential components consumed in their dietary intake.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Compounds (2022–2023))
►▼
Show Figures
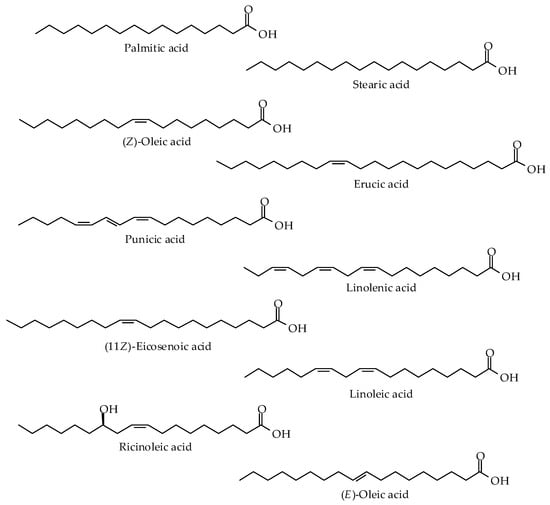
Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Hydroxyhydroquinone and Quassinoids as Promising Compounds with Hypoglycemic Activity through Redox Balance
by
Paulo R. dos Santos, Sidinéia Danetti, A. Joseph Rastegar, Wellington V. de Souza, Rafaele Frassini, Fernando J. Scariot, Sidnei Moura and Mariana Roesch-Ely
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 17-36; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010002 - 03 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the present study, an insulin-resistant cell model (human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line: HepG2) was chosen to investigate the efficacy of two compound classes and their common molecular motif for glycemic control and insulin sensitization. The two compounds’ classes were flavonoid extracts from
[...] Read more.
In the present study, an insulin-resistant cell model (human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line: HepG2) was chosen to investigate the efficacy of two compound classes and their common molecular motif for glycemic control and insulin sensitization. The two compounds’ classes were flavonoid extracts from Rourea cuspidata and quassinoid extracts from Picrasma crenata. The flavonoid-like hydroxyhydroquinone (HHQ) was synthesized. HepG2 cells were tested in a high-glucose environment (HepG2/IRM) by monitoring ROS activity, the concentration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and the measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). The expression of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) protein, which mediates gluconeogenesis and insulin resistance, was also investigated using indirect immunocytochemistry and Western blot techniques. A significant increase in glucose uptake and well-regulated ATP concentrations were observed in the treated cells. The downregulation of FOXO1 expression was seen in cells treated with HHQ and quassinoids in comparison to cells treated with flavonoids. This study provides a pharmacological basis for the application of HHQ, quassinoids from P. crenata, and flavonoids from R. cuspidata in the treatment of metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Full article
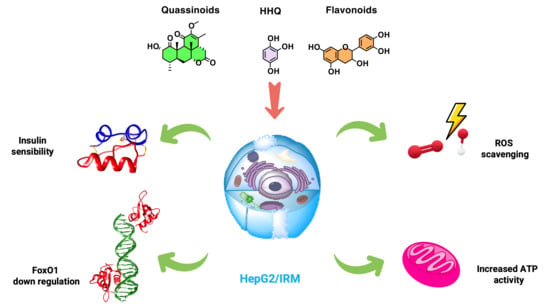
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Bio-Based Tannin Foams: Comparing Their Physical and Thermal Response to Polyurethane Foams in Lightweight Sandwich Panels
by
Marlon Bender Bueno Rodrigues, Ronan Côrrea, Pedro Henrique G. De Cademartori, Ana C. R. Ribeiro, Rodrigo Coldebella, Rafael A. Delucis, Nayara Lunkes and André L. Missio
Compounds 2024, 4(1), 1-16; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds4010001 - 25 Dec 2023
Abstract
Rigid polyurethane foams are the better-performing material for the most common insulation purposes, like sandwich panels. Nevertheless, they are highly flammable materials, release toxic gases, and are manufactured from fossil sources. As an alternative, tannin foams are bio-based materials that work as innovative
[...] Read more.
Rigid polyurethane foams are the better-performing material for the most common insulation purposes, like sandwich panels. Nevertheless, they are highly flammable materials, release toxic gases, and are manufactured from fossil sources. As an alternative, tannin foams are bio-based materials that work as innovative alternatives thanks to their great fire resistance, as well as lower smoke and harmful gases emissions. In the present study, lab-made foams of both materials were compared through morphology, thermal and fire degradation, mechanical properties, and water affinity in order to fill the technological gap between them and their related sandwich panels. It was observed that tannin foams are still relatively inhomogeneous (since formaldehyde was not used) and present a high affinity for water but have higher thermal and fire resistance. The flat compression strength of the polyurethane sandwiches was greater than that of tannin sandwiches (3.61 and 3.09 MPa, respectively) thanks, mainly, to the crosslinking degree difference between the resins. Also, tannin foams presented a lower weight loss (−70.684% lower weight loss in flammability tests than polyurethane foams) and the ability to self-extinguish the flame. Therefore, sandwich panels with tannin foam cores could be successful materials in areas that require protection against fire, such as the building engineering and automotive industries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue (Bio)molecules from Natural Extracts: An Infinite World of Opportunities)
►▼
Show Figures
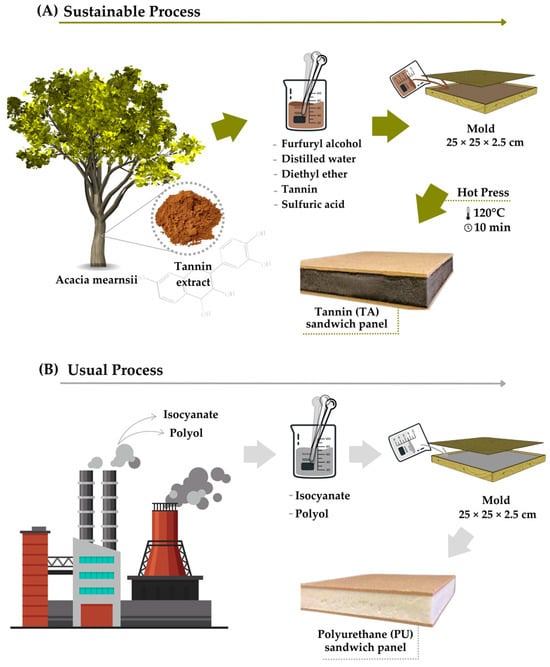
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antimicrobial Activity of Bovine Bone Scaffolds Impregnated with Silver Nanoparticles on New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacilli Biofilms
by
Geiziane Aparecida Gonçalves, Victoria Stadler Tasca Ribeiro, Leticia Ramos Dantas, Ana Paula de Andrade, Paula Hansen Suss, Maria Alice Witt and Felipe Francisco Tuon
Compounds 2023, 3(4), 584-595; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds3040042 - 15 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: The antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles has been extensively investigated in common bacteria. Metallo-β-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacteria are hard-to-treat microorganisms with few therapeutic options, and silver nanoparticles were not evaluated on the biofilm of these bacteria. Objectives: The aim of this study was
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles has been extensively investigated in common bacteria. Metallo-β-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacteria are hard-to-treat microorganisms with few therapeutic options, and silver nanoparticles were not evaluated on the biofilm of these bacteria. Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the antibiofilm activity of a bone scaffold impregnated with silver nanoparticles in NDM-producing Gram-negative bacilli. Methods: Bone scaffolds from bovine femur were used for the tests and impregnated with silver nanoparticles (50 nm) by physical adsorption. Silver nitrate minimal inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations (MIC and MBC) were performed on NDM-producing Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Disc diffusion tests for silver nanoparticles’ susceptibility and the quantification of biofilm production on plate and bone with sessile cell count were performed. Results: The MIC results demonstrated that silver nitrate had an antimicrobial effect on all microorganisms, inactivating the growth of isolates from a concentration of 8 µg/mL. MBC results showed that E. coli 16.211 was the only isolate to present MIC that were different from MBC, with a value of 16 µg/mL. Conclusion: Bone scaffolds impregnated with silver nanoparticles can significantly reduce the biofilm of multidrug-resistant bacteria. This is a strategical material that can be used as bone implant in different clinical conditions.
Full article
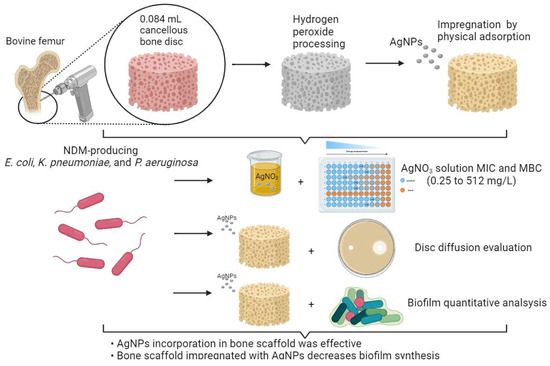
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Composition of the Scent in Some Ophrys Orchids Growing in Basilicata (Southern Italy): A Solid-Phase Microextraction Study Coupled with Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
by
Maurizio D’Auria, Richard Lorenz, Marisabel Mecca, Rocco Racioppi and Vito Antonio Romano
Compounds 2023, 3(4), 573-583; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds3040041 - 14 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Several methods have been used to determine the volatile organic compounds emitted by Ophrys orchids. The use of different methods results in incomparable data. Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) has not been used extensively on Ophrys orchids. The main components found in the SPME analysis
[...] Read more.
Several methods have been used to determine the volatile organic compounds emitted by Ophrys orchids. The use of different methods results in incomparable data. Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) has not been used extensively on Ophrys orchids. The main components found in the SPME analysis of the scent in Ophrys orchids were as follows: O. apifera: benzyl benzoate and α-copaene; O. crabronifera subsp. biscutella: pentadecane, heptadecane, and nonadecane; O. bertolonii subsp. bertolonii: pentadecane and heptadecane; O. passionis subsp. garganica: i-propyl palmitate and heptadecane; O. holosericea subsp. apulica: α-copaene, pentadecane, and heptadecane; O. lacaitae: α-copaene, pentadecane, and heptadecane; O. bombyliflora: cyclosativene, pentadecane, and ethyl dodecanoate; O. insectifera: 8-heptadecene and pentadecane; O. lutea: heptadecane and docosane; O. tenthredinifera subsp. neglecta: α-copaene, caryophyllene, and i-propyl palmitate.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of Impregnation Approach of Zinc Oxide Nano-Dispersions for Potential UV Stabilization in Abies alba and Fagus sylvatica
by
Lukas Sommerauer, Alexander Petutschnigg and Thomas Schnabel
Compounds 2023, 3(4), 561-572; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds3040040 - 01 Nov 2023
Abstract
As biological material, wood is distinctly affected by to various environmental influences during use. Reductions in durability can come from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, insects, fungi, and microorganisms in both exterior and interior applications. Wood can be easily protected from living organisms via the
[...] Read more.
As biological material, wood is distinctly affected by to various environmental influences during use. Reductions in durability can come from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, insects, fungi, and microorganisms in both exterior and interior applications. Wood can be easily protected from living organisms via the control of moisture content; however, UV radiation is not so easily managed. Wood components subject to this degradation are damaged and decomposed at a molecular level leading to deterioration of surface quality, especially in visible application areas. A potential remedy to this is using the UV-stabilizing properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Zinc oxide nano-dispersions based on propylene glycol (PG) were introduced into the microscopic structure of fir (Abies alba) and beech (Fagus sylvatica) wood by whole-cell impregnation to overcome problems associated with surface coatings. In this work the material uptake of ZnO nano-dispersions in concentrations of 1%, 2%, and 3% w/v were investigated and their effect on the stability of the optical appearance to UV exposure in short-term weathering were evaluated. Untreated reference samples showed significant photo-yellowing. A 1% w/v ZnO dispersion significantly increased the UV stability of treated surfaces. It was found that the uptake of the nano-dispersions was independent of the proportion of ZnO, and that the impregnating agents penetrated fir wood (about 200%) stronger than beech wood (about 70%). Already, a 2% w/v ZnO nano-dispersion led to a saturation of ZnO in the cell structure of the treated wood, for fir as well as beech, and no further ZnO uptake was achieved with 3% w/v nano-dispersions. Scanning electron microscopy shows an agglomeration of ZnO-NP in the cellular pathways impacting penetration, reducing leachability at higher concentrations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Compounds (2022–2023))
►▼
Show Figures
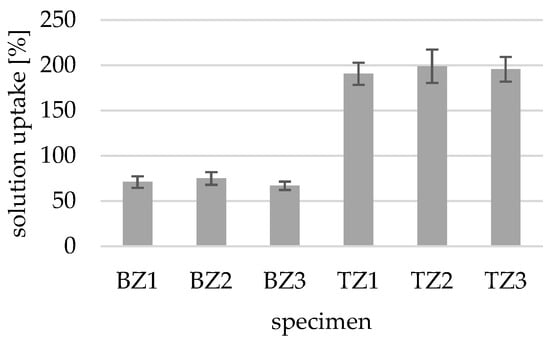
Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceCommunication
Identifying the Structural Components Responsible for the Antiproliferative Properties of Hydroxychavicol
by
Joshua Jackson, Gerome M. Romero, Diana Hawkins, Richard G. Cornwall and Georgi L. Lukov
Compounds 2023, 3(4), 552-560; https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds3040039 - 25 Oct 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Betel leaves are widely used as herbal medicine in Asia due to their antimicrobial properties. These properties have been attributed to the phenolic compound eugenol and its derivative, hydroxychavicol. Hydroxychavicol has also been shown to inhibit cancer cell proliferation. The main objective of
[...] Read more.
Betel leaves are widely used as herbal medicine in Asia due to their antimicrobial properties. These properties have been attributed to the phenolic compound eugenol and its derivative, hydroxychavicol. Hydroxychavicol has also been shown to inhibit cancer cell proliferation. The main objective of this study was to investigate which structural components of hydroxychavicol are responsible for the antiproliferative property of this compound. Jurkat-E6 cells (JE6) were treated with increasing concentrations (5, 15, and 45 µM) of hydroxychavicol and structural variants of it for 48 h. The results of this study demonstrate that the catechol structure in hydroxychavicol is the structural component that exhibits the highest antiproliferative effect. More specifically, the data show that the six-carbon ring must be aromatic with the two hydroxyl groups attached in an ortho position. Furthermore, this study establishes that the oxygen in the hydroxyl groups has a vital role in the antiproliferative properties of catechol and hydroxychavicol.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue (Bio)molecules from Natural Extracts: An Infinite World of Opportunities)
►▼
Show Figures
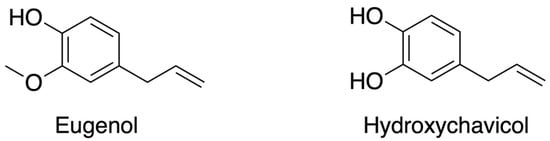
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Compounds
Organic Compounds with Biological Activity
Guest Editors: Enrique Domínguez-Álvarez, Małgorzata Anna MarćDeadline: 30 September 2024
Special Issue in
Compounds
(Bio)molecules from Natural Extracts: An Infinite World of Opportunities
Guest Editors: Jorge F. B. Pereira, Cassamo U. MussagyDeadline: 30 November 2024
Special Issue in
Compounds
Feature Papers in Compounds (2024)
Guest Editor: Juan C. MejutoDeadline: 31 December 2024