Journal Description
Chemistry Proceedings
Chemistry Proceedings
is an open access journal dedicated to publishing findings resulting from conferences, workshops, and similar events, in all areas of chemistry. The conference organizers and proceedings editors are responsible for managing the peer review process and selecting papers for conference proceedings.
Latest Articles
Correction: Kumar et al. Numerical and Experimental Modeling of Paper-Based Actuators. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 15
Chem. Proc. 2021, 5(1), 92; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2021005092 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
Text Correction [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 1st International Electronic Conference on Chemical Sensors and Analytical Chemistry)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Preparation and Characterization of Different Types of Eggshells Acidified with Acetic Acid
by
Eliza-Gabriela Brettfeld, Daria-Gabriela Popa, Raluca Somoghi, Cristian Andi Nicolae, Adrian Birtas, Diana Constantinescu-Aruxandei and Florin Oancea
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013032 - 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper investigates the acidification of eggshells of different origins with acetic acid. The acidification process was investigated for conventional and organic eggshells generated from the production of liquid eggs in the food industry and hatched eggshells from egg incubators. The acidified eggshell
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates the acidification of eggshells of different origins with acetic acid. The acidification process was investigated for conventional and organic eggshells generated from the production of liquid eggs in the food industry and hatched eggshells from egg incubators. The acidified eggshell materials were characterized using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results demonstrate that each type of investigated eggshell generates different nanostructures due to slight variations in their composition and this indicates potential applications: as a source of calcium supplements or to produce a snow-melting agent or CO2 adsorbent.
Full article
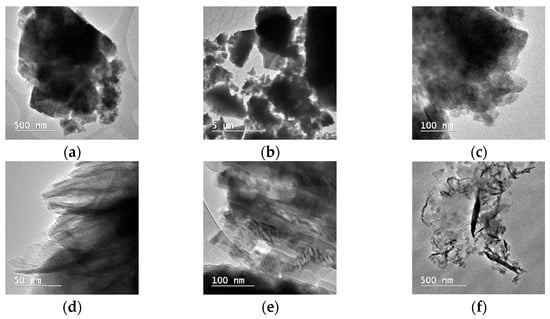
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Preparation of Ceramic Granules Enriched with Silicon Extracted from Reeds
by
Mălina Deșliu-Avram, Luiza Capră, Ioana Tudor, Carmen Lupu, Diana Constantinescu-Aruxandei, Orsolya Csilla Raduly, Mariana Pătrașcu and Florin Oancea
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013031 - 20 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article presents the microwave-assisted extraction of biosilica from common reed (Phragmites australis) biomass and the utilization of the resulting aqueous extract to enrich porous ceramic granules based on diatomaceous earth and bentonite from white wine cleaning. The enriched porous ceramic
[...] Read more.
This article presents the microwave-assisted extraction of biosilica from common reed (Phragmites australis) biomass and the utilization of the resulting aqueous extract to enrich porous ceramic granules based on diatomaceous earth and bentonite from white wine cleaning. The enriched porous ceramic granule generated a solution of soluble silicon that was +23.4 ± 2.2 more concentrated than the porous ceramic granules not enriched with reed extract. The water reactivity of Si-O-Si groups is higher in the polysilicic acid formed via the polycondensation of silicic acid extracted from reed, compared to the Si-O-Si group from diatomaceous earth or bentonite.
Full article
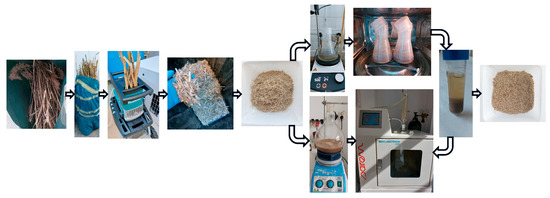
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Optimization of an Experimental Model for Microalgae Cultivation with CO2 Fixation
by
Eliza-Gabriela Brettfeld, Daria-Gabriela Popa, Corina-Ioana Moga, Diana Constantinescu-Aruxandei and Florin Oancea
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013030 - 20 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microalgae cultivation is a promising approach for sustainable CO2 fixation. This work describes the optimization of a laboratory-scale experimental model for microalgae cultivation under CO2 supplementation. The experimental model was developed using a stirred clear glass reactor, white LED strips, connection
[...] Read more.
Microalgae cultivation is a promising approach for sustainable CO2 fixation. This work describes the optimization of a laboratory-scale experimental model for microalgae cultivation under CO2 supplementation. The experimental model was developed using a stirred clear glass reactor, white LED strips, connection system caps with three ports, tubes, valves, regulators, and N2-CO2 compressed gas cylinder. Three microalgae strains were used: Raphidocelis subcapitata ATCC22662, Desmodesmus communis NIVA-CHL 7, and Chlorella sorokiniana NIVA-CHL 176. The appropriate medium for cultivation of each of these strains was selected. The optimized experimental model demonstrated the positive influence of CO2 supplementation on microalgae growth, particularly for Chlorella sorokiniana.
Full article
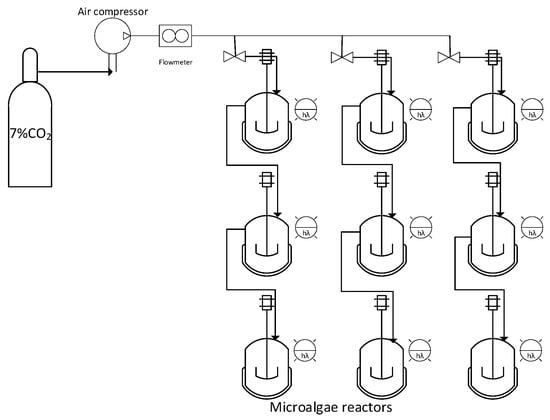
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Bioaugmentation Performance of a Bacterial Consortium for Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Treating Municipal Wastewater
by
Eliza-Gabriela Brettfeld, Oana-Andreea Cheoafa, Diana Constantinescu-Aruxandei and Florin Oancea
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013029 - 20 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A compatible microbial consortium with a high organic pollutant degradation ability, which includes a gram-positive Brevibacillus parabrevis B50 NCAIM B 001413 bacterial strain and a gram-negative Pseudoxanthomonas mexicana P32 NCAIM (P) B 001414 bacterial strain, was selected using high-throughput screening techniques. The compatible
[...] Read more.
A compatible microbial consortium with a high organic pollutant degradation ability, which includes a gram-positive Brevibacillus parabrevis B50 NCAIM B 001413 bacterial strain and a gram-negative Pseudoxanthomonas mexicana P32 NCAIM (P) B 001414 bacterial strain, was selected using high-throughput screening techniques. The compatible microbial consortium, encapsulated in alginate beds, was used to inoculate moving bed biofilm reactors from a small municipal wastewater treatment plant. The bioaugmentation performance of the inoculated consortium was evaluated by determining the water quality parameters before inoculation and one month after bioaugmentation treatment. The removal of organic matter was enhanced after treatment with the selected microbial consortium.
Full article
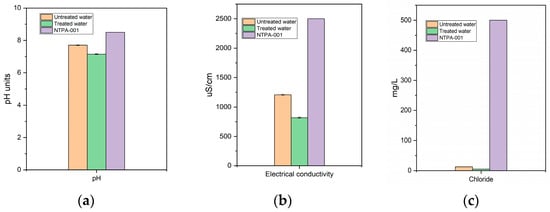
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Preparation of a Veterinary Supplement That Reduces Aflatoxin B1 Availability
by
Mălina Deșliu-Avram, Carmen Lupu, Simona Rotaru, Diana Constantinescu-Aruxandei, Radian Nicolae Negrilă and Florin Oancea
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013028 - 20 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work describes the preparation of a veterinary supplement based on diatomaceous earth, chemically hydrolyzed proteins, and essential oils, which are applicable for protecting monogastric animals against the mycotoxin contamination of cereal-based feeds. The veterinary supplement comprises 54.5–55% diatomaceous earth, 40.5–41% hydrolyzed proteins
[...] Read more.
This work describes the preparation of a veterinary supplement based on diatomaceous earth, chemically hydrolyzed proteins, and essential oils, which are applicable for protecting monogastric animals against the mycotoxin contamination of cereal-based feeds. The veterinary supplement comprises 54.5–55% diatomaceous earth, 40.5–41% hydrolyzed proteins (whey protein concentrate and soybean protein isolate), 2.4–2.5% oregano essential oils, 0.6–0.7% NaCl, and 1.6% CaCl2. The preparation process includes alkaline thermal hydrolysis of proteins, followed by emulsification of the essential oil with protein hydrolysate and granulation with diatomaceous earth. The veterinary supplement prepared in this work reduces the availability of aflatoxin B1 in a simulated gastric fluid by 82.7 ± 4.43%.
Full article
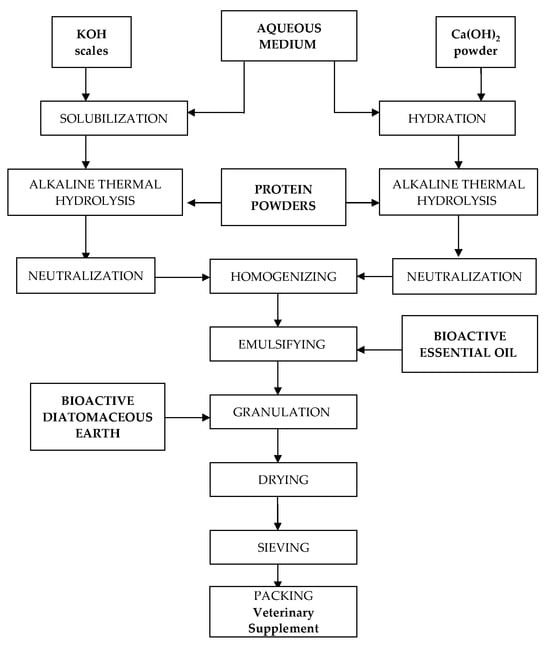
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
99mTc-Selenium-NPs as SPECT Tracers: Radio Synthesis and Biological Evaluation
by
Akhilesh Kumar Singh, Mohd. Faheem, Amit Jaiswal, Malleswari Ponnala, Sanjay Gambhir and Manish Dixit
Chem. Proc. 2023, 14(1), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16172 - 14 Dec 2023
Abstract
As the usage of nano-sized complexes in biomedical applications has grown significantly over the past ten years, nanoparticles are now playing a significant role in the enhancement and revolution of medical applications. It may be due primarily to the novel and exceptional electrical,
[...] Read more.
As the usage of nano-sized complexes in biomedical applications has grown significantly over the past ten years, nanoparticles are now playing a significant role in the enhancement and revolution of medical applications. It may be due primarily to the novel and exceptional electrical, optical, photo-responsive, and catalytic capabilities displayed by particles with sizes ranging from 1 to 100 nm. The radiolabelled nanoparticles refer to the process of incorporating radioactive isotopes into nanoparticles. This technique enables the nanoparticles to be tracked, imaged and monitored using various imaging techniques, such as Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT/CT) or Positron Emission Tomography (PET). They play a crucial role in understanding the biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and targeted delivery of nanoparticles to biological systems. In this study, selenium-based nanoparticles (Se-NPs) were explored for imaging potential as these are usable due to their size, surface, and kinetics, as well as their ability to be functionalised. The 99mTechnicium (99mTc) radionuclide was used to radiolabel the bio-inspired highly dispersed over grown endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum selenium NP using conventional radiochemistry protocol. The radiolabelling yield was found to be 94.5 ± 3% and analysed by various analytical tools. The synthesized 99mTc-Se-NPs were assessed through In-vitro stability, and their In-vivo biodistribution was performed. The accumulation of post six-hour data was primarily seen in the liver (around 3.4% ID/g) and lungs (about 2.2% ID/g). These Se-NPs can be used as an imaging agent for lung and liver disorders because these NPs quickly pass through the kidneys are expelled via urine and show a long retention time in the body. These properties of 99mTc-Se-NPs can be used for non-invasive imaging via SPECT.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 27th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
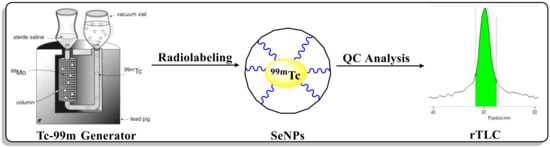
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Reaction of 1,6-Diamino-4-aryl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine- 3,5-Dicarbonitriles with Certain Electrophilic Agents
by
Alexei A. Dolganov, Alexandra R. Chikava and Victor V. Dotsenko
Chem. Proc. 2023, 14(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16081 - 06 Dec 2023
Abstract
The reaction of 1,6-diamino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarbonitriles, which are easily available through the reaction of cyanoacetohydrazide with arylmethylene malononitriles, with ninhydrin leads to the formation of novel dihydroindeno[1,2-e]pyrido[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazines. Another active carbonyl compound, glyoxal, reacts with 1,6-diamino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarbonitriles under mild conditions to give functionalized 6-oxo-6H-pyrido[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazine-7,9-dicarbonitriles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 27th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Scheme 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
In Vitro and In Silico Antioxidant Activity of Hydrazones and Semicarbazones Derived from Aldehydes Found in Essential Oils
by
Leandro G. Gutierrez, Carla M. Ormachea, Ana P. Reinick, Vanina A. Guntero and Cristián A. Ferretti
Chem. Proc. 2023, 14(1), 100; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16577 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the in vitro and in silico antioxidant properties of four hydrazones and semicarbazones derived from vanillin and cinnamaldehyde, aromatic aldehydes found in essential oils. They were synthesized by condensation of these aldehydes with the corresponding
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to investigate the in vitro and in silico antioxidant properties of four hydrazones and semicarbazones derived from vanillin and cinnamaldehyde, aromatic aldehydes found in essential oils. They were synthesized by condensation of these aldehydes with the corresponding phenylhydrazine and semicarbazide in good yields. The antioxidant properties of the target molecules were determined using the Reducing Power assay (RP) and the hydrogen peroxide scavenging method (HP), and the results were compared with thermodynamic descriptors obtained from theoretical calculations using the DFT method. The target molecules were shown to be highly active for the total antioxidant assay and the results of theoretical calculations were consistent with the antioxidant activity observed experimentally, making them a useful tool to understand the mechanism of action. This would also allow theoretical tests of new antioxidant compounds to be carried out in a predictive manner.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 27th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
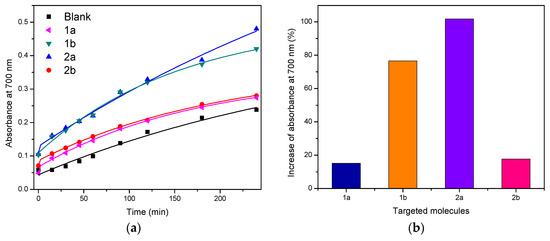
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Selective Synthesis of Fatty Alcohols over Mild Reaction Conditions via Non-Catalytic Liquid-Phase Fatty Acid Methyl Esters’ Reduction
by
Alejandro Vallejo Orrego, Cristián A. Ferretti and Verónica K. Díez
Chem. Proc. 2023, 14(1), 87; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16384 - 30 Nov 2023
Abstract
The upgrading of fatty alcohols synthesis from natural fatty acid methyl esters’ reduction using alumina-supported NaBH4 without H2 supply was investigated. It was possible to synthesize fatty alcohols efficiently with high yields. By using pure NaBH4 or alumina-supported NaBH4
[...] Read more.
The upgrading of fatty alcohols synthesis from natural fatty acid methyl esters’ reduction using alumina-supported NaBH4 without H2 supply was investigated. It was possible to synthesize fatty alcohols efficiently with high yields. By using pure NaBH4 or alumina-supported NaBH4 and methanol as co-reactants, 100% selectivity towards fatty alcohols was achieved. The purpose of supporting the metal hydride is to increase its stability and ensure the recovery of the product at the end of the reaction. A high final fatty alcohol yield was obtained when alumina-supported NaBH4 was used. The use of more than stoichiometric amounts of methanol and NaBH4 is important to produce alkoxyborohydride anions that act as better reducing species than NaBH4. The reaction conditions effect was investigated and the role of short carbon chain alcohol structure was explained. The effect of fatty acid methyl ester structure was also examined. Saturated fatty acid methyl esters (methyl laurate, methyl myristate) with short carbon chains can be easily reduced using NaBH4/Al2O3 and methanol, thus obtaining high conversion and selectable fuel alcohol. Unsaturated fatty acid methyl ester (methyl oleate) with longer carbon shows steric hindrance, which is not suitable for the interaction of esters and reduces the surface area, meaning that the conversion of fatty acid methyl ester is lower.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 27th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
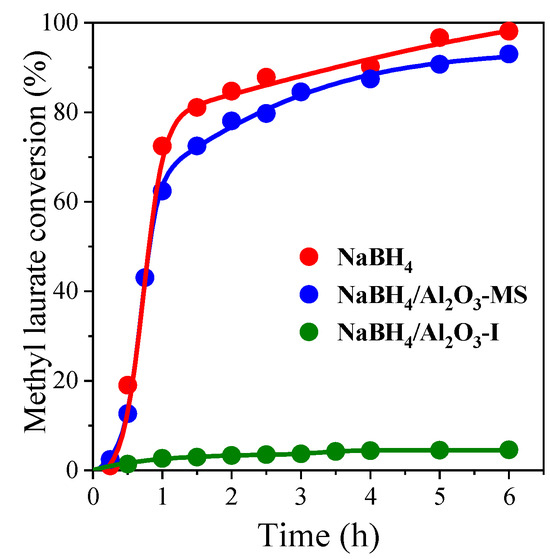
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Synthesis and Characterisation of Thymol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents
by
Deborah Oluwatomilola Adeoye, Zaharaddeen Sani Gano, Omar Umar Ahmed, Suleiman Mohammed Shuwa, Abdulazeez Yusuf Atta and Baba Yakubu Jubril
Chem. Proc. 2023, 14(1), 96; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16380 - 29 Nov 2023
Abstract
The evolution of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents (HDESs) has expanded the applications of the new generation of solvents, known as Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES), to include water-based operations. How stable they are in aqueous media qualifies them to be categorised as hydrophobic. This
[...] Read more.
The evolution of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents (HDESs) has expanded the applications of the new generation of solvents, known as Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES), to include water-based operations. How stable they are in aqueous media qualifies them to be categorised as hydrophobic. This also determines whether they are appropriate materials for water-based industrial processes or not or whether they end up constituting a greater pollution load than those processes due to the leaching of their precursors into the aqueous media when used. This work sought to prepare HDESs from a monoterpene (thymol), and three long-chain organic acids (octanoic acid, decanoic acid, and dodecanoic acid). The physicochemical characteristics of the prepared HDESs were investigated. Thereafter, their moisture absorption capacity and stability in an aqueous environment were determined to ascertain whether they are hydrophobic as predicted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 27th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
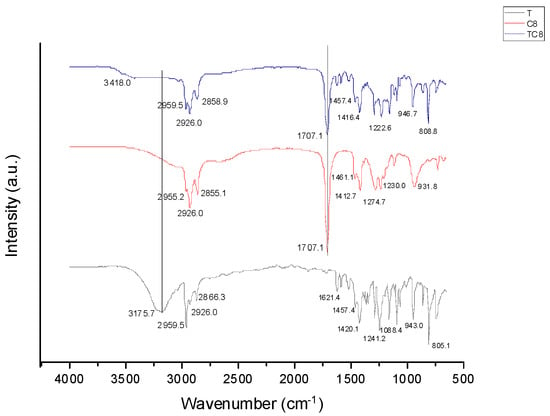
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Bioavailability Computations for Natural Phenolic Derivatives for Druglikeness Assessment
by
Amalia Stefaniu, Lucia Camelia Pirvu, Lucia Pintilie and Sorin Constantin Godeanu
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013026 - 24 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The main phenolic compounds in the Hippophae rhamnoides fruit with potential therapeutic activities are quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside, quercetin-3-O-galactoside, myricetin, rutin, luteolin, kaempferol, vitexin, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, 7-methoxycoumarin, p-coumaric acid, and ferulic acid. Their general features recommend them for
[...] Read more.
The main phenolic compounds in the Hippophae rhamnoides fruit with potential therapeutic activities are quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside, quercetin-3-O-galactoside, myricetin, rutin, luteolin, kaempferol, vitexin, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, 7-methoxycoumarin, p-coumaric acid, and ferulic acid. Their general features recommend them for nutritional and therapeutic purposes, exploiting their neuroprotective and radioprotective effects. This study aims to investigate the potency of polyphenol-derived structures against dual tyrosine-regulated kinase, modulating neuroblastomas and glioblastomas in humans. Structural insights from the point of view of drug-like property assessment are also provided by Density Functional Theory (DFT) predictions on the lowest energy conformers, using the B3LYP/6-311G (d,p) method.
Full article
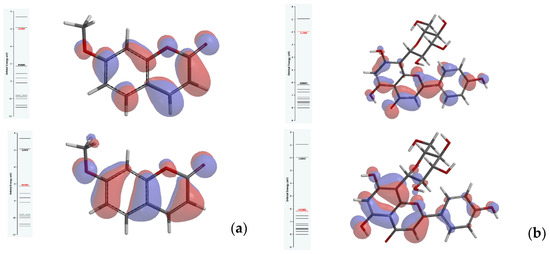
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Synthesis of a Bio-Based Methacrylic Polymer Using Camphor Terpene as a Renewable Resource
by
Naziha Chabane, Fayçal Dergal, Hervé Pata and Ilyas Chikhi
Chem. Proc. 2023, 14(1), 89; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16336 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
Sustainable polymers derived from biomass have the potential to reduce environmental impacts while offering significant performance and cost advantages over petrochemical-derived macromolecules. We present here a facile and efficient approach to the synthesis of a biomethacrylic monomer, isobornyl/bornyl methacrylate (IBOMA/BOMA), using the naturally
[...] Read more.
Sustainable polymers derived from biomass have the potential to reduce environmental impacts while offering significant performance and cost advantages over petrochemical-derived macromolecules. We present here a facile and efficient approach to the synthesis of a biomethacrylic monomer, isobornyl/bornyl methacrylate (IBOMA/BOMA), using the naturally available camphor terpene in the essential oil of the Algerian plant Artemisia arborescens (Absinthe) as a key intermediate. The essential oil of the aerial part of the Artemisia arborescens plant naturally distributed in northwest Algeria was isolated by hydrodistillation and analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC/MS) techniques. Nine components were identified, representing 90.7% of the total content. The main constituent of Artemisia arborescens essential oil is camphor (71.8%). Camphor was purified and modified to produce an 80% renewable-carbon-based methacrylic monomer. This terpene-derived methacrylic monomer was free radically polymerized to create a biosourced methacrylic polymer. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) was used to characterize the structure of camphor terpene, isobornyl/bornyl methacrylate, and poly (isobornyl/bornyl methacrylate) (PIBOMA)/(PBOMA).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 27th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
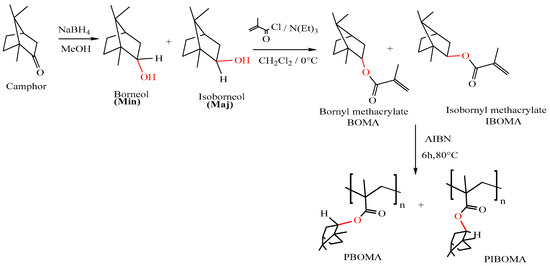
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Proteogenomic Tools in the Assessment of Pharmacological Effects of Natural Compounds
by
Radu Albulescu, Adrian Albulescu, Georgeta Caraene, Corina Bubueanu, Alice Grigore, Maria Petrescu and Roxana-Mădălina Stoica
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013027 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
Proteogenomics is a recently developed omics application, adding enhancing the sensitivity of proteomics, and thus making possible the detection of proteome markers in very tiny amounts of samples. Even if the filed developed only in the last 10 years, the technology is very
[...] Read more.
Proteogenomics is a recently developed omics application, adding enhancing the sensitivity of proteomics, and thus making possible the detection of proteome markers in very tiny amounts of samples. Even if the filed developed only in the last 10 years, the technology is very intensely applied in clinical diagnostics, and more recently, efforts are made to use it in non-clinical, in vitro and in vivo studies. The aim of this study was to investigate the applicability of single-plex and multiplex assays in the evaluation of proteome changes generated in vitro by the exposure to several standard compounds. The extracts demonstrated weak cytotoxic effects. The detection of cytokines Performing the same assays on tissue lysates permitted only the detection of low levels of cytokines.
Full article
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Diagnosis, Photogrammetry and Conservation Treatment with Nanomaterials of Sacidava Fortress
by
Rodica-Mariana Ion, Lorena Iancu, Ramona Marina Grigorescu, Sorin Marcel Colesniuc, Verginica Schroder, Raluca Andreea Trandafir, Silviu Ionita, Anca Irina Gheboianu and Sofia Slamnoiu-Teodorescu
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013025 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The diagnosis, thermography, aerial photogrammetry, and conservation treatment with nanomaterials (CHAp) for some samples from Sacidava Fortress, Romania, are analyzed and the results are discussed accordingly in this paper.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Practical Aspects of Biogenic Amines Detection
by
Petru Epure, Ana-Maria Gurban and Lucian-Gabriel Zamfir
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013024 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents a method for monitoring food freshness and quality through the early detection of biogenic amines, which are indicators of food spoilage/degradation. The urge to monitor food quality has led to a growing interest in the detection of toxic compounds, such
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a method for monitoring food freshness and quality through the early detection of biogenic amines, which are indicators of food spoilage/degradation. The urge to monitor food quality has led to a growing interest in the detection of toxic compounds, such as biogenic amines (BAs), as chemical indicators of food degradation by using different bioanalytical tools. The bioanalytical platform includes several parts and modules useful for food hazard evaluation. This paper presents how electrochemical and spectrometric detection works for biogenic amine monitoring in food and how the communication interface provides useful data.
Full article
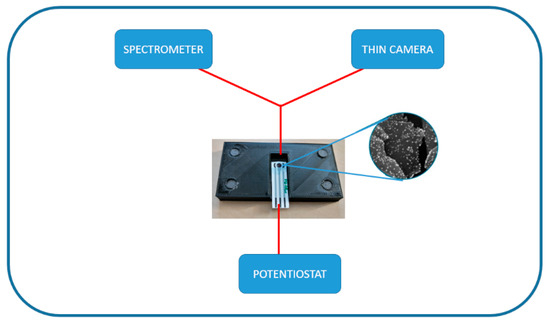
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Assessment of Pullulan, a Microbial Polysaccharide, as a Matrix for Senotherapeutics Delivery
by
Ramona-Daniela Pavaloiu, Fawzia Sha’at, Corina Bubueanu, Maria Petrescu and Claudia Sevcenco
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013023 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
This study’s objective was to assess pullulan, in the form of pullulan acetate, as a matrix for senotherapeutics delivery. Polymeric nanoparticles loaded with various senotherapeutics (metformin, quercitin, kaempferol, curcumin, and luteolin) were prepared via nanoprecipitation or double emulsion methods using pullulan acetate as
[...] Read more.
This study’s objective was to assess pullulan, in the form of pullulan acetate, as a matrix for senotherapeutics delivery. Polymeric nanoparticles loaded with various senotherapeutics (metformin, quercitin, kaempferol, curcumin, and luteolin) were prepared via nanoprecipitation or double emulsion methods using pullulan acetate as a biodegradable polymeric matrix. Quercitin, kaempferol, curcumin, and luteolin nanoparticles showed good yield (<70%), satisfactory values of entrapment efficiency (<60%), and nanometric sizes ranging between 205 and 270 nm, with narrow dispersity and good stability at 4 °C. The formulations demonstrated that pullulan showed great potential for producing nanoparticles with application in senotherapeutics delivery.
Full article
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Durability of Multifunctional Coatings Made with Additions of Animal Waste and Agro-Industrial By-Products
by
Irina Popa, Cristian Petcu and Alexandrina Mureșanu
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013022 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Agriculture and agriculture-related industries generate many different forms of by-products and waste, whose integration into the circular economy still requires experimental studies and research. This research aimed to obtain innovative coatings containing agro-industrial by-products and animal waste, characterizing the thermal insulation potential of
[...] Read more.
Agriculture and agriculture-related industries generate many different forms of by-products and waste, whose integration into the circular economy still requires experimental studies and research. This research aimed to obtain innovative coatings containing agro-industrial by-products and animal waste, characterizing the thermal insulation potential of the resulting products, and determining the durability of the respective coatings by exposing them to the action of an aggressive environment with large temperature variations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Impact on Indoor Air of Multifunctional Materials Made with Animal Waste and Agro-Industrial By-Products
by
Vasilica Vasile, Irina Popa, Cristian Petcu, Alina Dima and Mihaela Ion
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013021 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
One severe public health problem globally is air pollution, as exposure to air pollutants threatens the health of people everywhere in the world. Agriculture generates waste, the improper disposal of such waste producing adverse environmental effects like air pollution, etc. In this context,
[...] Read more.
One severe public health problem globally is air pollution, as exposure to air pollutants threatens the health of people everywhere in the world. Agriculture generates waste, the improper disposal of such waste producing adverse environmental effects like air pollution, etc. In this context, our research focused on capitalizing on animal waste (wool) and agro-industrial by-products (sunflower seed husks) as additives in two types of aqueous dispersion finishing/protection products, serving as binders. The paper presents the results from the monitoring of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions of four types of innovative multi-layer finishes made with such types of waste.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Combined Alkaline and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Eggshell Membranes for Obtaining Ingredients for Food and Cosmetic Applications
by
Diana Pasarin, Cristina Emanuela Enascuta, Cristian Enache-Preoteasa, Catalin Bogdan Matei and Andra-Ionela Ghizdareanu
Chem. Proc. 2023, 13(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2023013020 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigated the combined alkaline and enzymatic hydrolysis of eggshell membranes for obtaining ingredients for food and cosmetic applications. 1.25 N NaOH and Alcalase 2.4 L protease were used for eggshell membrane hydrolysis. The characterization of the hydrolysates consisted of the determination
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the combined alkaline and enzymatic hydrolysis of eggshell membranes for obtaining ingredients for food and cosmetic applications. 1.25 N NaOH and Alcalase 2.4 L protease were used for eggshell membrane hydrolysis. The characterization of the hydrolysates consisted of the determination of the degree of hydrolysis, oligopeptides, and free amino acids obtained through eggshell membrane hydrolysis. The degree of hydrolysis was 14.23%. Analytical techniques such as reversed-phase liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry, hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography, and FT-IR spectroscopy revealed the presence of oligopeptides, dipeptides, and amino acids, including alanine, lysine/glutamine, glutamic acid, histidine, proline, valine, hydroxyproline, and phenylalanine. Electrophoretic analysis demonstrated protein fractions within the molecular weight range of approximately 14 kDa to 70 kDa in all samples.
Full article
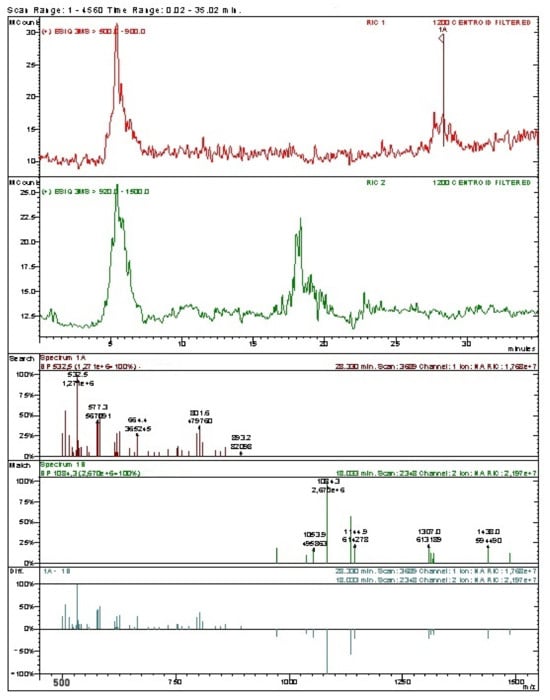
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics










