Researches on Normal and Cancer Stem Cells
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Stem Cells".
Viewed by 69389
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Umberto Galderisi
Prof. Umberto Galderisi
 Prof. Umberto Galderisi
Prof. Umberto Galderisi
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Experimental Medicine, University of Campania "Vanvitelli", 80138 Naples, Italy; Temple University, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Interests: stem cell; MUSE cells; cellular biology
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Stem cells are characterized by the ability to differentiate into specialized cells and by their self-renewal capacity. Many tissues have the ability to regenerate in physiological conditions or response to injury, this is due to the presence of resident stem cells into specialized areas called niches. Like all other cells, stem cells are subject to genotoxic stress and DNA damage accumulation. These events may have profound consequences on the body’s health. Damaged stem cells may be eliminated by apoptosis or they can survive and become senescent cells with a loss of the cell’s functions. The senescence of stem cells contributes to organismal aging by reducing tissue homeostasis.
Alternatively, following a DNA damage occurrence, stem cells could experience a neoplastic transformation. Emerging evidence has demonstrated the presence within tumors of a subpopulation of stem-like cells, which exhibit characteristics of both embryonic stem cells and cancer cells associated with a more aggressive cancer phenotype. These cells are named cancer stem cells (CSCs). The CSCs show characteristics associated with normal stem cells, specifically the ability to give rise to all cell types found in a particular tumor and to self-renew. Current anti-cancer therapies aim to target CSCs to promote tumor regression.
Knowing the mechanisms governing stem cell functions in normal and pathological conditions is of paramount importance for human health.
This Topical Collection will highlight current knowledge on “normal” and cancer stem cells properties in physiological and pathological conditions. Both original research articles and reviews are welcome.
Prof. Umberto Galderisi
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Stem cells
- cancer stem cells
- senescence
- drugs discovery
- aging
- cancer therapy
- mesenchymal stromal cells
- embryonic stem cells
- DNA damage
- oxidative stress
Published Papers (22 papers)
Open AccessReview
Metabolic Profiles of Cancer Stem Cells and Normal Stem Cells and Their Therapeutic Significance
by
Ioannis Stouras, Maria Vasileiou, Panagiotis F. Kanatas, Eleni Tziona, Christina Tsianava and Stamatis Theocharis
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2159
Abstract
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a rare cancer cell population, responsible for the facilitation, progression, and resistance of tumors to therapeutic interventions. This subset of cancer cells with stemness and tumorigenic properties is organized in niches within the tumor microenvironment (TME) and presents
[...] Read more.
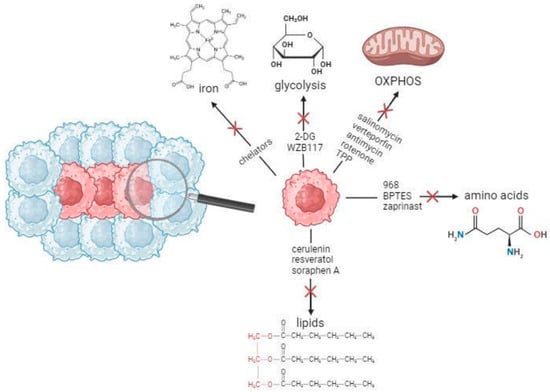
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a rare cancer cell population, responsible for the facilitation, progression, and resistance of tumors to therapeutic interventions. This subset of cancer cells with stemness and tumorigenic properties is organized in niches within the tumor microenvironment (TME) and presents altered regulation in a variety of metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), as well as lipid, amino acid, and iron metabolism. CSCs exhibit similarities as well as differences when comparedto normal stem cells, but also possess the ability of metabolic plasticity. In this review, we summarize the metabolic characteristics of normal, non-cancerous stem cells and CSCs. We also highlight the significance and implications of interventions targeting CSC metabolism to potentially achieve more robust clinical responses in the future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Label-Free Cell Sorting Approach to Highlight the Impact of Intratumoral Cellular Heterogeneity and Cancer Stem Cells on Response to Therapies
by
Céline Hervieu, Mireille Verdier, Elodie Barthout, Gaëlle Bégaud, Niki Christou, Magali Sage, Julie Pannequin, Serge Battu and Muriel Mathonnet
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2039
Abstract
Cancer stem cells play a crucial role in tumor initiation, metastasis, and resistance to treatment. Cellular heterogeneity and plasticity complicate the isolation of cancer stem cells. The impact of intra-tumor cellular heterogeneity using a label-free approach remains understudied in the context of treatment
[...] Read more.
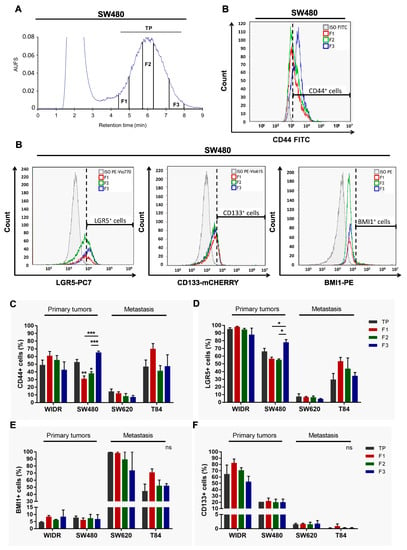
Cancer stem cells play a crucial role in tumor initiation, metastasis, and resistance to treatment. Cellular heterogeneity and plasticity complicate the isolation of cancer stem cells. The impact of intra-tumor cellular heterogeneity using a label-free approach remains understudied in the context of treatment resistance. Here, we use the sedimentation field–flow fractionation technique to separate, without labeling, cell subpopulations of colorectal cancer cell lines and primary cultures according to their biophysical properties. One of the three sorted cell subpopulations exhibits characteristics of cancer stem cells, including high tumorigenicity in vivo and a higher frequency of tumor-initiating cells compared to the other subpopulations. Due to its chemoresistance, two- and three-dimensional in vitro chemosensitivity assays highlight the therapeutic relevance of this cancer stem cell subpopulation. Thus, our results reveal the major implication of intra-tumor cellular heterogeneity, including cancer stem cells in treatment resistance, thanks to our label-free cell sorting approach. This approach enables—by breaking down the tumor—the study the individualized response of each sorted tumor cell subpopulation and to identify chemoresistance, thus offering new perspectives for personalized therapy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Angiotensin 1–7 Stimulates Proliferation of Lung Bronchoalveolar Progenitors—Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Infection
by
Andrzej K. Ciechanowicz, Wen Xin Lay, Jefte Prado Paulino, Erika Suchocki, Susanne Leszczak, Christian Leszczak and Magdalena Kucia
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1952
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to severe lung damage due to pneumonia and, in more severe cases, leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS. This affects the viability of bronchoalveolar cells. An important role in the pathogenesis of these complications is the hyperactivation of
[...] Read more.
SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to severe lung damage due to pneumonia and, in more severe cases, leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS. This affects the viability of bronchoalveolar cells. An important role in the pathogenesis of these complications is the hyperactivation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) pathway and induction of cytokine storm that occurs in an Nlrp3 inflammasome-dependent manner. To shed more light on the susceptibility of lung tissue to SARS-CoV-2 infection, we evaluated murine bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASC), alveolar type II cells (AT2), and 3D-derived organoids expression of mRNA encoding genes involved in virus entry into cells, components of RAA, and genes that comprise elements of the Nlrp3 inflammasome pathway. We noticed that all these genes are expressed by lung alveolar stem cells and organoids-derived from these cells. Interestingly, all these cells express a high level of ACE2 that, on the one hand, serves as an entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and, on the other, converts angiotensin II into its physiological antagonist, angiotensin 1–7 (Ang 1–7), which has been reported to have a protective role in lung damage. To shed more light on the role of Ang 1–7 on lung tissue, we exposed lung-derived BASC and AT2 cells to this mediator of RAA and noticed that it increases the proliferation of these cells. Based on this, Ang 1–7 could be employed to alleviate the damage to lung alveolar stem/progenitor cells during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Comparative Study on the Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in 2D and 3D Culture
by
Anne Wolff, Marcus Frank, Susanne Staehlke and Kirsten Peters
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3005
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSC) are capable of renewing the progenitor cell fraction or differentiating in a tissue-specific manner. Adipogenic differentiation of adipose-tissue-derived MSC (adMSC) is important in various pathological processes. Adipocytes and their progenitors are metabolically active and secrete molecules (adipokines) that have
[...] Read more.
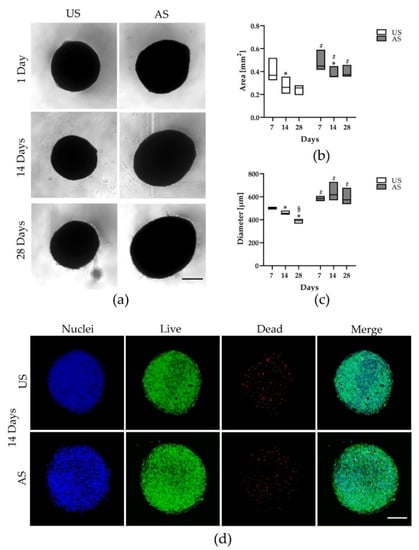
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSC) are capable of renewing the progenitor cell fraction or differentiating in a tissue-specific manner. Adipogenic differentiation of adipose-tissue-derived MSC (adMSC) is important in various pathological processes. Adipocytes and their progenitors are metabolically active and secrete molecules (adipokines) that have both pro- and anti-inflammatory properties. Cell culturing in 2D is commonly used to study cellular responses, but the 2D environment does not reflect the structural situation for most cell types. Therefore, 3D culture systems have been developed to create an environment considered more physiological. Since knowledge about the effects of 3D cultivation on adipogenic differentiation is limited, we investigated its effects on adipogenic differentiation and adipokine release of adMSC (up to 28 days) and compared these with the effects in 2D. We demonstrated that cultivation conditions are crucial for cell behavior: in both 2D and 3D culture, adipogenic differentiation occurred only after specific stimulation. While the size and structure of adipogenically stimulated 3D spheroids remained stable during the experiment, the unstimulated spheroids showed signs of disintegration. Adipokine release was dependent on culture dimensionality; we found upregulated adiponectin and downregulated pro-inflammatory factors. Our findings are relevant for cell therapeutic applications of adMSC in complex, three-dimensionally arranged tissues.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
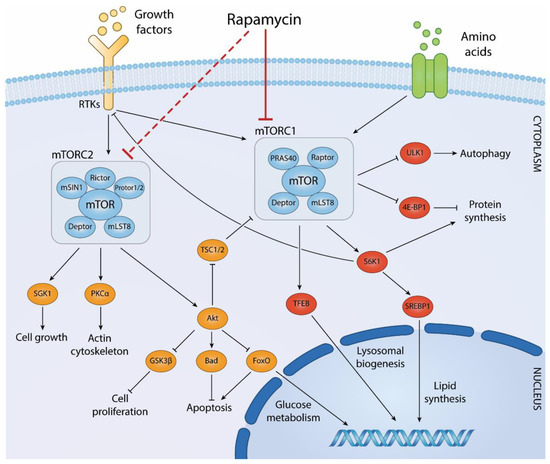
ROCK ‘n TOR: An Outlook on Keratinocyte Stem Cell Expansion in Regenerative Medicine via Protein Kinase Inhibition
by
Giorgia Centonze, Sara Centonze, Luca Ponzone and Enzo Calautti
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3800
Abstract
Keratinocyte stem cells play a fundamental role in homeostasis and repair of stratified epithelial tissues. Transplantation of cultured keratinocytes autografts provides a landmark example of successful cellular therapies by restoring durable integrity in stratified epithelia lost to devastating tissue conditions. Despite the overall
[...] Read more.
Keratinocyte stem cells play a fundamental role in homeostasis and repair of stratified epithelial tissues. Transplantation of cultured keratinocytes autografts provides a landmark example of successful cellular therapies by restoring durable integrity in stratified epithelia lost to devastating tissue conditions. Despite the overall success of such procedures, failures still occur in case of paucity of cultured stem cells in therapeutic grafts. Strategies aiming at a further amplification of stem cells during keratinocyte ex vivo expansion may thus extend the applicability of these treatments to subjects in which endogenous stem cells pools are depauperated by aging, trauma, or disease. Pharmacological targeting of stem cell signaling pathways is recently emerging as a powerful strategy for improving stem cell maintenance and/or amplification. Recent experimental data indicate that pharmacological inhibition of two prominent keratinocyte signaling pathways governed by apical mTOR and ROCK protein kinases favor stem cell maintenance and/or amplification ex vivo and may improve the effectiveness of stem cell-based therapeutic procedures. In this review, we highlight the pathophysiological roles of mTOR and ROCK in keratinocyte biology and evaluate existing pre-clinical data on the effects of their inhibition in epithelial stem cell expansion for transplantation purposes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
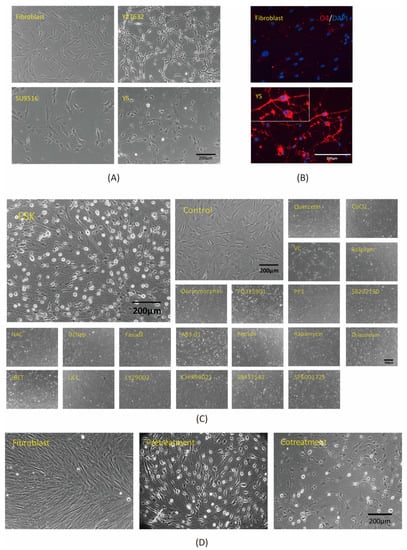
Development of a Chemical Cocktail That Rescues Mouse Brain Demyelination in a Cuprizone-Induced Model
by
Pei-Lun Lai, Chi-Hou Ng, Chia-Hsin Wu, Chien-Ying Lai, Scott C. Schuyler, Vicki Wang, Hsuan Lin, Yueh-Chang Lee, Ming-Hsi Chuang, Chang-Huan Yang, Wei-Ju Chen, Hsiao-Chun Huang and Jean Lu
Viewed by 3384
Abstract
Oligodendrocytes are glial cells located in the central nervous system (CNS) that play essential roles in the transmission of nerve signals and in the neuroprotection of myelinated neurons. The dysfunction or loss of oligodendrocytes leads to demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS).
[...] Read more.
Oligodendrocytes are glial cells located in the central nervous system (CNS) that play essential roles in the transmission of nerve signals and in the neuroprotection of myelinated neurons. The dysfunction or loss of oligodendrocytes leads to demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS). To treat demyelinating diseases, the development of a therapy that promotes remyelination is required. In the present study, we established an in vitro method to convert human fibroblasts into induced oligodendrocyte-like cells (iOLCs) in 3 days. The induced cells displayed morphologies and molecular signatures similar to oligodendrocytes after treatment with valproic acid and exposure to the small molecules Y27632, SU9516, and forskolin (FSK). To pursue the development of a cell-free remyelination therapy in vivo, we used a cuprizone-induced demyelinated mouse model. The small molecules (Y27632, SU9516, and FSK) were directly injected into the demyelinated corpus callosum of the mouse brain. This combination of small molecules rescued the demyelination phenotype within two weeks as observed by light and electron microscopy. These results provide a foundation for exploring the development of a treatment for demyelinating diseases via regenerative medicine.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
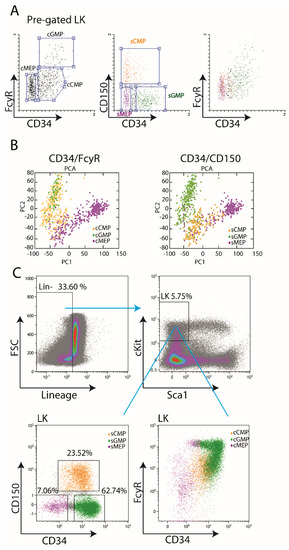
Isolation of Murine Myeloid Progenitor Populations by CD34/CD150 Surface Markers
by
Leonid Olender, Roshina Thapa and Roi Gazit
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2527
Abstract
Myeloid progenitors are intermediates between Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) and Myeloid effector progeny. In mouse bone marrow, they are part of the Lineage
− cKit
+ Sca1
− (LK) compartment. To date, most researchers used CD34 and FcγR surface markers for the dissection
[...] Read more.
Myeloid progenitors are intermediates between Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) and Myeloid effector progeny. In mouse bone marrow, they are part of the Lineage
− cKit
+ Sca1
− (LK) compartment. To date, most researchers used CD34 and FcγR surface markers for the dissection of this compartment into various populations. Surprisingly, however, this approach does not provide distinct separation by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). In this study, we suggest using CD150 instead of FcγR. We re-analyzed published single-cell RNA-Seq data and found that CD34/CD150 provides better sub-populations separation, compared to the “classical” CD34/FcγR-based approach. We confirm our findings by independent FACS analysis. We demonstrate comparable differentiation potential of the newly-obtained LK sub-populations, like previous “classical” ones. Therefore, we suggest the CD34/CD150 gating strategy, utilizing commonly-used surface markers, as a robust and reproducible separation of the LK compartment into distinct sub-populations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
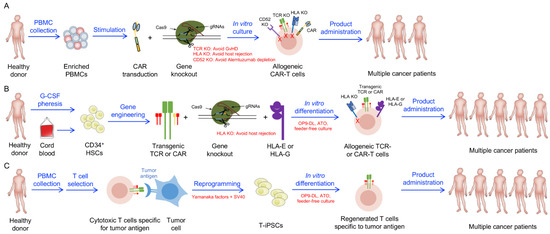
Development of Stem Cell-Derived Immune Cells for Off-the-Shelf Cancer Immunotherapies
by
Yan-Ruide Li, Zachary Spencer Dunn, Yang Zhou, Derek Lee and Lili Yang
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 5094
Abstract
Cell-based cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of hematological malignancies. Specifically, autologous chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T (CAR-T) cell therapies have received approvals for treating leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma following unprecedented clinical response rates. A critical barrier to the widespread usage of current
[...] Read more.
Cell-based cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of hematological malignancies. Specifically, autologous chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T (CAR-T) cell therapies have received approvals for treating leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma following unprecedented clinical response rates. A critical barrier to the widespread usage of current CAR-T cell products is their autologous nature, which renders these cellular products patient-selective, costly, and challenging to manufacture. Allogeneic cell products can be scalable and readily administrable but face critical concerns of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), a life-threatening adverse event in which therapeutic cells attack host tissues, and allorejection, in which host immune cells eliminate therapeutic cells, thereby limiting their antitumor efficacy. In this review, we discuss recent advances in developing stem cell-engineered allogeneic cell therapies that aim to overcome the limitations of current autologous and allogeneic cell therapies, with a special focus on stem cell-engineered conventional αβ T cells, unconventional T (iNKT, MAIT, and γδ T) cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Muscle Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Activity of the Free and the Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET)-Bond Myeloperoxidase
by
Thierry Franck, Justine Ceusters, Hélène Graide, Ange Mouithys-Mickalad and Didier Serteyn
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2267
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known to migrate to tissue injury sites to participate in immune modulation, tissue remodelling and wound healing, reducing tissue damage. Upon neutrophil activation, there is a release of myeloperoxidase (MPO), an oxidant enzyme. But little is known about
[...] Read more.
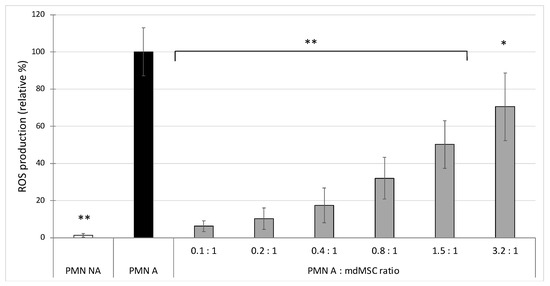
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known to migrate to tissue injury sites to participate in immune modulation, tissue remodelling and wound healing, reducing tissue damage. Upon neutrophil activation, there is a release of myeloperoxidase (MPO), an oxidant enzyme. But little is known about the direct role of MSCs on MPO activity. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of equine mesenchymal stem cells derived from muscle microinvasive biopsy (mdMSC) on the oxidant response of neutrophils and particularly on the activity of the myeloperoxidase released by stimulated equine neutrophils. After specific treatment (trypsin and washings in phosphate buffer saline), the mdMSCs were exposed to isolated neutrophils. The effect of the suspended mdMSCs was studied on the ROS production and the release of total and active MPO by stimulated neutrophils and specifically on the activity of MPO in a neutrophil-free model. Additionally, we developed a model combining adherent mdMSCs with neutrophils to study total and active MPO from the neutrophil extracellular trap (NET). Our results show that mdMSCs inhibited the ROS production, the activity of MPO released by stimulated neutrophils and the activity of MPO bound to the NET. Moreover, the co-incubation of mdMSCs directly with MPO results in a strong inhibition of the peroxidase activity of MPO, probably by affecting the active site of the enzyme. We confirm the strong potential of mdMSCs to lower the oxidant response of neutrophils. The novelty of our study is an evident inhibition of the activity of MPO by MSCs. The results indicated a new potential therapeutic approach of mdMSCs in the inhibition of MPO, which is considered as a pro-oxidant actor in numerous chronic and acute inflammatory pathologies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Nestin-Expressing Cells in the Lung: The Bad and the Good Parts
by
Gilberto Jaramillo-Rangel, María-de-Lourdes Chávez-Briones, Adriana Ancer-Arellano and Marta Ortega-Martínez
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2640
Abstract
Nestin is a member of the intermediate filament family, which is expressed in a variety of stem or progenitor cells as well as in several types of malignancies. Nestin might be involved in tissue homeostasis or repair, but its expression has also been
[...] Read more.
Nestin is a member of the intermediate filament family, which is expressed in a variety of stem or progenitor cells as well as in several types of malignancies. Nestin might be involved in tissue homeostasis or repair, but its expression has also been associated with processes that lead to a poor prognosis in various types of cancer. In this article, we review the literature related to the effect of nestin expression in the lung. According to most of the reports in the literature, nestin expression in lung cancer leads to an aggressive phenotype and resistance to chemotherapy as well as radiation treatments due to the upregulation of phenomena such as cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Furthermore, nestin may be involved in the pathogenesis of some non-cancer-related lung diseases. On the other hand, evidence also indicates that nestin-positive cells may have a role in lung homeostasis and be capable of generating various types of lung tissues. More research is necessary to establish the true value of nestin expression as a prognostic factor and therapeutic target in lung cancer in addition to its usefulness in therapeutic approaches for pulmonary diseases.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Iron Metabolism as a Potential Mechanism for Inducing TRAIL-Mediated Extrinsic Apoptosis Using Methylsulfonylmethane in Embryonic Cancer Stem Cells
by
Nipin Sp, Dong Young Kang, Eun Seong Jo, Jin-Moo Lee and Kyoung-Jin Jang
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2385
Abstract
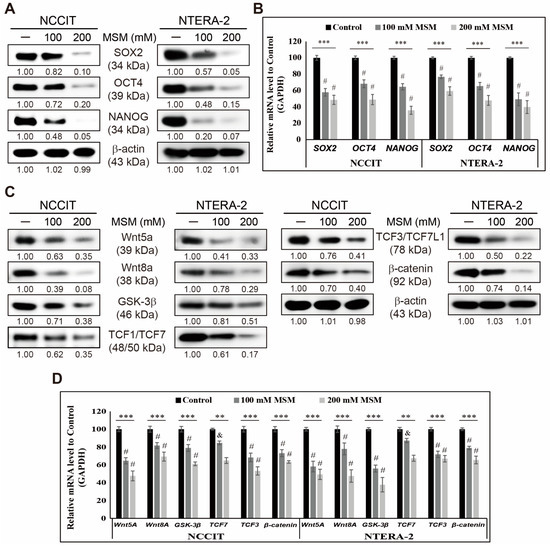
Embryonic cancer stem cells (CSCs) can differentiate into any cancer type. Targeting CSC using natural compounds is a good approach as it suppresses cancer recurrence with fewer adverse effects, and methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is a sulfur-containing compound with well-known anticancer activities. This study determined
[...] Read more.
Embryonic cancer stem cells (CSCs) can differentiate into any cancer type. Targeting CSC using natural compounds is a good approach as it suppresses cancer recurrence with fewer adverse effects, and methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is a sulfur-containing compound with well-known anticancer activities. This study determined the mechanistic aspects of the anticancer activity of MSM. We used Western blotting and real-time qPCR for molecular signaling studies and conducted flow cytometry for analyzing the processes in cells. Our results suggested an inhibition in the expression of CSC markers and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. MSM induced TRAIL-mediated extrinsic apoptosis in NCCIT and NTERA-2 cells rather than an intrinsic pathway. Inhibition of iron metabolism-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation takes part in TRAIL-mediated apoptosis induction by MSM. Suppressing iron metabolism by MSM also regulated p38/p53/ERK signaling and microRNA expressions, such as upregulating miR-130a and downregulating miR-221 and miR-222, which resulted in TRAIL induction and thereby extrinsic pathway of apoptosis. Hence, MSM could be a good candidate for neoadjuvant therapy by targeting CSCs by inhibiting iron metabolism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Spontaneous Calcium Oscillations through Differentiation: A Calcium Imaging Analysis of Rat Cochlear Nucleus Neural Stem Cells
by
Johannes Voelker, Christine Voelker, Jonas Engert, Nikolas Goemann, Rudolf Hagen and Kristen Rak
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2896
Abstract
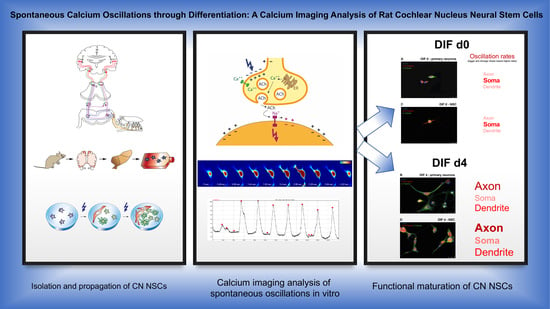
Causal therapies for the auditory-pathway and inner-ear diseases are still not yet available for clinical application. Regenerative medicine approaches are discussed and examined as possible therapy options. Neural stem cells could play a role in the regeneration of the auditory pathway. In recent
[...] Read more.
Causal therapies for the auditory-pathway and inner-ear diseases are still not yet available for clinical application. Regenerative medicine approaches are discussed and examined as possible therapy options. Neural stem cells could play a role in the regeneration of the auditory pathway. In recent years, neural stem and progenitor cells have been identified in the cochlear nucleus, the second nucleus of the auditory pathway. The current investigation aimed to analyze cell maturation concerning cellular calcium activity. Cochlear nuclei from PND9 CD rats were microscopically dissected and propagated as neurospheres in free-floating cultures in stem-cell medium (Neurobasal, B27, GlutaMAX, EGF, bFGF). After 30 days, the dissociation and plating of these cells took place under withdrawal of the growth factors and the addition of retinoic acid, which induces neural cell differentiation. Calcium imaging analysis with BAPTA-1/Oregon Green was carried out at different times during the differentiation phase. In addition, the influence of different voltage-dependent calcium channels was analyzed through the targeted application of inhibitors of the L-, N-, R- and T-type calcium channels. For this purpose, comparative examinations were performed on CN NSCs, and primary CN neurons. As the cells differentiated, a significant increase in spontaneous neuronal calcium activity was demonstrated. In the differentiation stage, specific frequencies of the spontaneous calcium oscillations were measured in different regions of the individual cells. Initially, the highest frequency of spontaneous calcium oscillations was ascertainable in the maturing somata. Over time, these were overtaken by calcium oscillations in the axons and dendrites. Additionally, in the area of the growth cones, an increasing activity was determined. By inhibiting voltage-dependent calcium channels, their expression and function in the differentiation process were confirmed. A comparable pattern of maturation of these channels was found in CN NSCs and primary CN neurons. The present results show that neural stem cells of the rat cochlear nucleus differentiated not only morphologically but also functionally. Spontaneous calcium activities are of great relevance in terms of neurogenesis and integration into existing neuronal structures. These functional aspects of neurogenesis within the auditory pathway could serve as future targets for the exogenous control of neuronal regeneration.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Stem Cell Research Tools in Human Metabolic Disorders: An Overview
by
Serena Ricci and Pietro Cacialli
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3037
Abstract
Metabolic disorders are very common in the population worldwide and are among the diseases with the highest health utilization and costs per person. Despite the ongoing efforts to develop new treatments, currently, for many of these disorders, there are no approved therapies, resulting
[...] Read more.
Metabolic disorders are very common in the population worldwide and are among the diseases with the highest health utilization and costs per person. Despite the ongoing efforts to develop new treatments, currently, for many of these disorders, there are no approved therapies, resulting in a huge economic hit and tension for society. In this review, we recapitulate the recent advancements in stem cell (gene) therapy as potential tools for the long-term treatment of both inherited (lysosomal storage diseases) and acquired (diabetes mellitus, obesity) metabolic disorders, focusing on the main promising results observed in human patients and discussing the critical hurdles preventing the definitive jump of this approach from the bench to the clinic.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
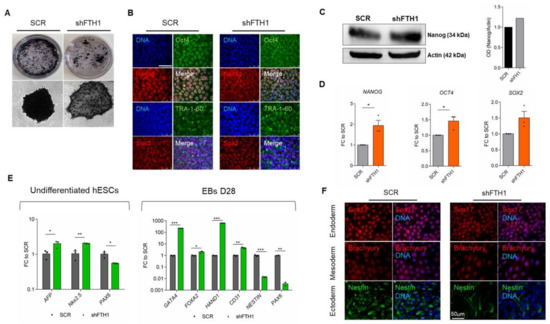
Uncovering the Metabolic and Stress Responses of Human Embryonic Stem Cells to FTH1 Gene Silencing
by
Luana Scaramuzzino, Valeria Lucchino, Stefania Scalise, Michela Lo Conte, Clara Zannino, Alessandro Sacco, Flavia Biamonte, Elvira Immacolata Parrotta, Francesco Saverio Costanzo and Giovanni Cuda
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3459
Abstract
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent cells with indefinite self-renewal ability and differentiation properties. To function properly and maintain genomic stability, ESCs need to be endowed with an efficient repair system as well as effective redox homeostasis. In this study, we investigated different
[...] Read more.
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent cells with indefinite self-renewal ability and differentiation properties. To function properly and maintain genomic stability, ESCs need to be endowed with an efficient repair system as well as effective redox homeostasis. In this study, we investigated different aspects involved in ESCs’ response to iron accumulation following stable knockdown of the ferritin heavy chain (FTH1) gene, which encodes for a major iron storage protein with ferroxidase activity. Experimental findings highlight unexpected and, to a certain extent, paradoxical results. If on one hand FTH1 silencing does not correlate with increased ROS production nor with changes in the redox status, strengthening the concept that hESCs are extremely resistant and, to a certain extent, even refractory to intracellular iron imbalance, on the other, the differentiation potential of hESCs seems to be affected and apoptosis is observed. Interestingly, we found that FTH1 silencing is accompanied by a significant activation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived-2)-like 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), which crosstalk in driving hESCs antioxidant cascade events. These findings shed new light on how hESCs perform under oxidative stress, dissecting the molecular mechanisms through which Nrf2, in combination with PPP, counteracts oxidative injury triggered by FTH1 knockdown.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
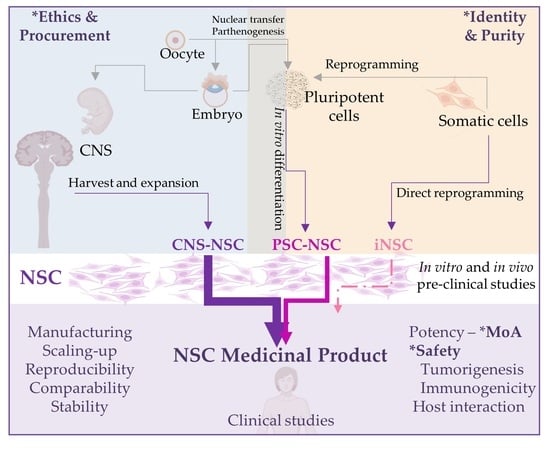
Human Neural Stem Cells for Cell-Based Medicinal Products
by
Beatriz Fernandez-Muñoz, Ana Belen Garcia-Delgado, Blanca Arribas-Arribas and Rosario Sanchez-Pernaute
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3577
Abstract
Neural stem cells represent an attractive tool for the development of regenerative therapies and are being tested in clinical trials for several neurological disorders. Human neural stem cells can be isolated from the central nervous system or can be derived in vitro from
[...] Read more.
Neural stem cells represent an attractive tool for the development of regenerative therapies and are being tested in clinical trials for several neurological disorders. Human neural stem cells can be isolated from the central nervous system or can be derived in vitro from pluripotent stem cells. Embryonic sources are ethically controversial and other sources are less well characterized and/or inefficient. Recently, isolation of NSC from the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with spina bifida and with intracerebroventricular hemorrhage has been reported. Direct reprogramming may become another alternative if genetic and phenotypic stability of the reprogrammed cells is ensured. Here, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of available sources of neural stem cells for the production of cell-based therapies for clinical applications. We review available safety and efficacy clinical data and discuss scalability and quality control considerations for manufacturing clinical grade cell products for successful clinical application.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
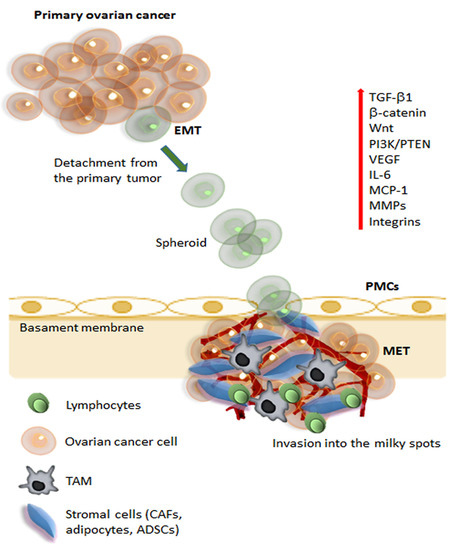
Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Adipose Tissue and Extracellular Vesicles in Ovarian Cancer Patients: A Bridge toward Metastatic Diffusion or a New Therapeutic Opportunity?
by
Gabriele Storti, Maria Giovanna Scioli, Bong-Sung Kim, Sonia Terriaca, Elena Fiorelli, Augusto Orlandi and Valerio Cervelli
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3697
Abstract
Ovarian cancer is one of the deadliest malignancies among women. Approximately 75% of the patients with ovarian cancer are diagnosed with advanced disease that already has metastasis, particularly to the omentum. The omentum constitutes the ideal soil for ovarian cancer metastasis due to
[...] Read more.
Ovarian cancer is one of the deadliest malignancies among women. Approximately 75% of the patients with ovarian cancer are diagnosed with advanced disease that already has metastasis, particularly to the omentum. The omentum constitutes the ideal soil for ovarian cancer metastasis due to a complex intraperitoneal milieu that favors and supports the whole metastatic process. Adipose-derived stem/stromal cells (ADSCs) are part of this microenvironment and foster tumor progression via sustained paracrine secretion, including extracellular vesicles (EVs). Nonetheless, the preferential relationship between ADSCs, ADSC-derived EVs, and ovarian cancer cells could be exploited to use ADSCs and EVs as a vehicle for anti-cancer therapies. This review will analyze the strict relations between tumor progression, metastatic disease, and adipose tissue with its staminal components. In addition, we will describe the crosstalk and biologic relationship between ADSCs and tumor cells, the role of EVs in intercellular communication, the establishment of drug resistance, metastatic capacity, and ovarian cancer progression. We will analyze the new therapeutic opportunities in treating ovarian cancer offered by ADSCs and EVs as a vehicle for therapeutic molecules to target precisely tumor cells and limit the systemic adverse effects. Finally, we will discuss the limitations of these therapeutic approaches.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
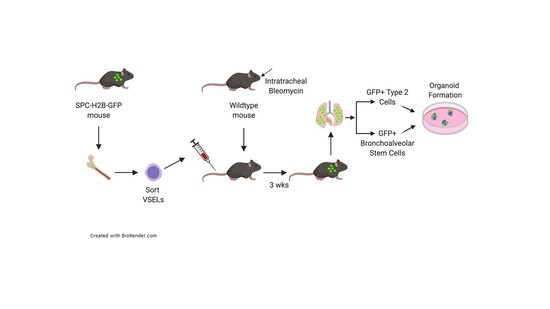
Bone Marrow-Derived VSELs Engraft as Lung Epithelial Progenitor Cells after Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury
by
Andrzej K. Ciechanowicz, Katarzyna Sielatycka, Monika Cymer, Marta Skoda, Malwina Suszyńska, Kamila Bujko, Mariusz Z. Ratajczak, Diane S. Krause and Magdalena Kucia
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3013
Abstract
Background: Alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells and bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASC) perform critical regenerative functions in response to lung damage. Published data show that nonhematopoietic, bone marrow-derived “very small embryonic-like stem cells” (VSELs) can differentiate in vivo into surfactant protein C (SPC)-producing AT2
[...] Read more.
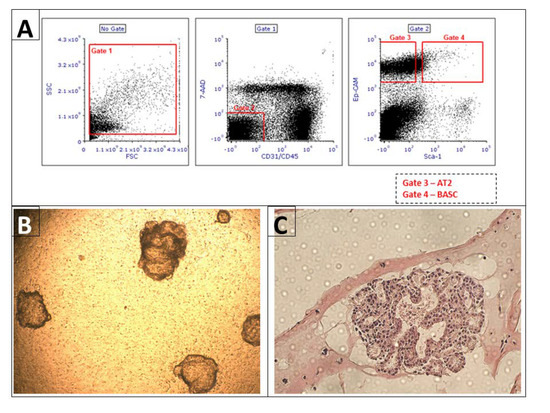
Background: Alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells and bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASC) perform critical regenerative functions in response to lung damage. Published data show that nonhematopoietic, bone marrow-derived “very small embryonic-like stem cells” (VSELs) can differentiate in vivo into surfactant protein C (SPC)-producing AT2 cells in the lung. Here, we test directly whether VSEL-derived BASC and AT2 cells function to produce differentiated progeny. Methods: using a reporter mouse in which the H2B-GFP fusion protein is driven from the murine SPC promoter, we tested whether bone marrow-derived VSELs or non-VSEL/nonhematopoietic stem cells (non-VSEL/non-HSCs) can differentiate into AT2 and BASC cells that function as progenitor cells. Immediately following bleomycin administration, WT recipient mice underwent intravenous administration of VSELs or non-VSEL/non-HSCs from SPC H2B-GFP mice. GFP+ AT2 and BASC were isolated and tested for progenitor activity using in vitro organoid assays. Results: after 21 days in vivo, we observed differentiation of VSELs but not non-VSEL/non-HSCs into phenotypic AT2 and BASC consistent with previous data in irradiated recipients. Subsequent in vitro organoid assays revealed that VSEL-derived AT2 and BASC maintained physiological potential for differentiation and self-renewal. Conclusion: these findings prove that VSELs produce functional BASC and AT2 cells, and this may open new avenues using VSELs to develop effective cell therapy approaches for patients with lung injury.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
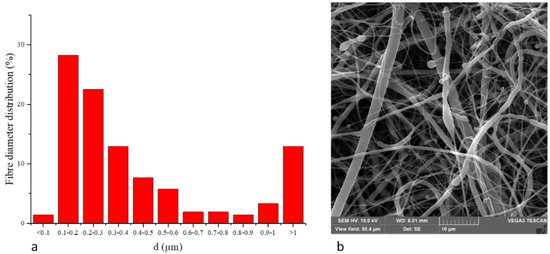
Natural Compounds and PCL Nanofibers: A Novel Tool to Counteract Stem Cell Senescence
by
Emanuela Bellu, Sara Cruciani, Giuseppe Garroni, Francesca Balzano, Rosanna Satta, Maria Antonia Montesu, Angela Fadda, Maurizio Mulas, Giorgia Sarais, Pasquale Bandiera, Carlo Ventura, Martin Kralovič, Jan Sabo, Evzen Amler and Margherita Maioli
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2633
Abstract
Tissue homeostasis mainly depends on the activity of stem cells to replace damaged elements and restore tissue functions. Within this context, mesenchymal stem cells and fibroblasts are essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis in skin, in particular in the dermis. Modifications in collagen fibers
[...] Read more.
Tissue homeostasis mainly depends on the activity of stem cells to replace damaged elements and restore tissue functions. Within this context, mesenchymal stem cells and fibroblasts are essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis in skin, in particular in the dermis. Modifications in collagen fibers are able to affect stem cell features. Skin properties can be significantly reduced after injuries or with aging, and stem cell niches, mainly comprising extracellular matrix (ECM), may be compromised. To this end, specific molecules can be administrated to prevent the aging process induced by UV exposure in the attempt to maintain a youngness phenotype. NanoPCL-M is a novel nanodevice able to control delivery of Mediterranean plant myrtle (
Myrtus communis L.) extracts. In particular, we previously described that myrtle extracts, rich in bioactive molecules and nutraceuticals, were able to counteract senescence in adipose derived stem cells. In this study, we analyzed the effect of NanoPCL-M on skin stem cells (SSCs) and dermal fibroblasts in a dynamic cell culture model in order to prevent the effects of UV-induced senescence on proliferation and collagen depot. The BrdU assay results highlight the significantly positive effect of NanoPCL-M on the proliferation of both fibroblasts and SSCs. Our results demonstrate that-M is able to preserve SSCs features and collagen depot after UV-induced senescence, suggesting their capability to retain a young phenotype.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
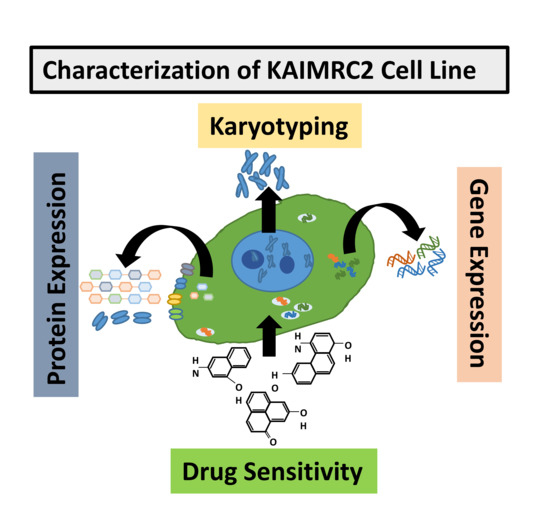
Isolation and Establishment of a Highly Proliferative, Cancer Stem Cell-Like, and Naturally Immortalized Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line, KAIMRC2
by
Rizwan Ali, Hajar Al Zahrani, Tlili Barhoumi, Alshaimaa Alhallaj, Abdullah Mashhour, Musaad A. Alshammari, Yasser A. Alshawakir, Omar Baz, Abdullah H. Alanazi, Abdul Latif Khan, Hassan Al Nikhli, Mohammed A. Al Balwi, Lolwah Al Riyees and Mohamed Boudjelal
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3113
Abstract
In vitro studies of a disease are key to any in vivo investigation in understanding the disease and developing new therapy regimens. Immortalized cancer cell lines are the best and easiest model for studying cancer in vitro. Here, we report the establishment of
[...] Read more.
In vitro studies of a disease are key to any in vivo investigation in understanding the disease and developing new therapy regimens. Immortalized cancer cell lines are the best and easiest model for studying cancer in vitro. Here, we report the establishment of a naturally immortalized highly tumorigenic and triple-negative breast cancer cell line, KAIMRC2. This cell line is derived from a Saudi Arabian female breast cancer patient with invasive ductal carcinoma. Immunocytochemistry showed a significant ratio of the KAIMRC2 cells’ expressing key breast epithelial and cancer stem cells (CSCs) markers, including CD47, CD133, CD49f, CD44, and ALDH-1A1. Gene and protein expression analysis showed overexpression of ABC transporter and AKT-PI3Kinase as well as JAK/STAT signaling pathways. In contrast, the absence of the tumor suppressor genes p53 and p73 may explain their high proliferative index. The mice model also confirmed the tumorigenic potential of the KAIMRC2 cell line, and drug tolerance studies revealed few very potent candidates. Our results confirmed an aggressive phenotype with metastatic potential and cancer stem cell-like characteristics of the KAIMR2 cell line. Furthermore, we have also presented potent small molecule inhibitors, especially Ryuvidine, that can be further developed, alone or in synergy with other potent inhibitors, to target multiple cancer-related pathways.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Non-Tumorigenic Pluripotent Reparative Muse Cells Provide a New Therapeutic Approach for Neurologic Diseases
by
Toru Yamashita, Yoshihiro Kushida, Koji Abe and Mari Dezawa
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 4164
Abstract
Muse cells are non-tumorigenic endogenous reparative pluripotent cells with high therapeutic potential. They are identified as cells positive for the pluripotent surface marker SSEA-3 in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and connective tissue. Muse cells also express other pluripotent stem cell markers, are
[...] Read more.
Muse cells are non-tumorigenic endogenous reparative pluripotent cells with high therapeutic potential. They are identified as cells positive for the pluripotent surface marker SSEA-3 in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and connective tissue. Muse cells also express other pluripotent stem cell markers, are able to differentiate into cells representative of all three germ layers, self-renew from a single cell, and are stress tolerant. They express receptors for sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), which is actively produced by damaged cells, allowing circulating cells to selectively home to damaged tissue. Muse cells spontaneously differentiate on-site into multiple tissue-constituent cells with few errors and replace damaged/apoptotic cells with functional cells, thereby contributing to tissue repair. Intravenous injection of exogenous Muse cells to increase the number of circulating Muse cells enhances their reparative activity. Muse cells also have a specific immunomodulatory system, represented by HLA-G expression, allowing them to be directly administered without HLA-matching or immunosuppressant treatment. Owing to these unique characteristics, clinical trials using intravenously administered donor-Muse cells have been conducted for myocardial infarction, stroke, epidermolysis bullosa, spinal cord injury, perinatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muse cells have the potential to break through the limitations of current cell therapies for neurologic diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muse cells provide a new therapeutic strategy that requires no HLA-matching or immunosuppressant treatment for administering donor-derived cells, no gene introduction or differentiation induction for cell preparation, and no surgery for delivering the cells to patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
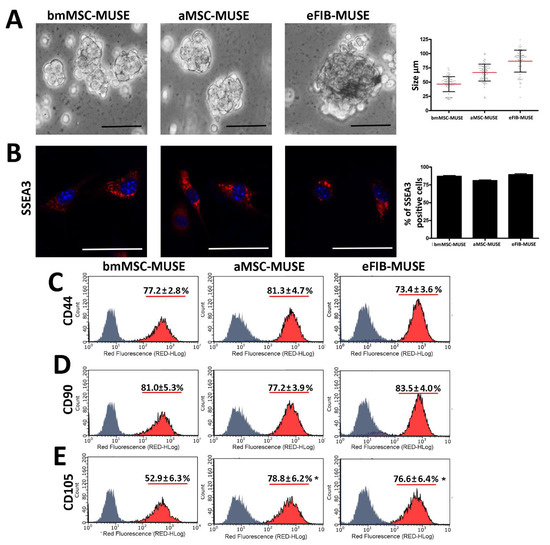
MUSE Stem Cells Can Be Isolated from Stromal Compartment of Mouse Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue, and Ear Connective Tissue: A Comparative Study of Their In Vitro Properties
by
Domenico Aprile, Nicola Alessio, Ibrahim H. Demirsoy, Tiziana Squillaro, Gianfranco Peluso, Giovanni Di Bernardo and Umberto Galderisi
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3118
Abstract
The cells present in the stromal compartment of many tissues are a heterogeneous population containing stem cells, progenitor cells, fibroblasts, and other stromal cells. A SSEA3(+) cell subpopulation isolated from human stromal compartments showed stem cell properties. These cells, known as multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring
[...] Read more.
The cells present in the stromal compartment of many tissues are a heterogeneous population containing stem cells, progenitor cells, fibroblasts, and other stromal cells. A SSEA3(+) cell subpopulation isolated from human stromal compartments showed stem cell properties. These cells, known as multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring (MUSE) cells, are capable of resisting stress and possess an excellent ability to repair DNA damage. We isolated MUSE cells from different mouse stromal compartments, such as those present in bone marrow, subcutaneous white adipose tissue, and ear connective tissue. These cells showed overlapping in vitro biological properties. The mouse MUSE cells were positive for stemness markers such as SOX2, OCT3/4, and NANOG. They also expressed TERT, the catalytic telomerase subunit. The mouse MUSE cells showed spontaneous commitment to differentiation in meso/ecto/endodermal derivatives. The demonstration that multilineage stem cells can be isolated from an animal model, such as the mouse, could offer a valid alternative to the use of other stem cells for disease studies and envisage of cellular therapies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
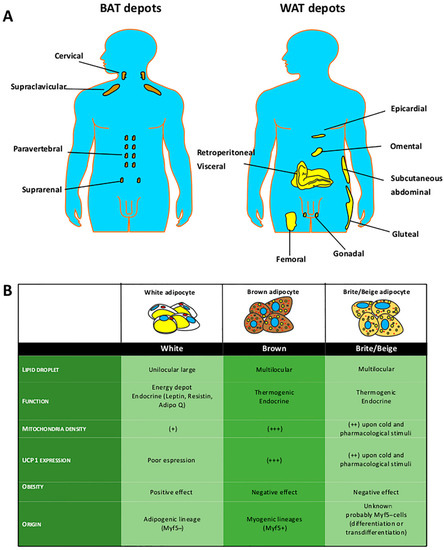
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Browning Agents on the White Adipogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: A Contribution to Fighting Obesity
by
Girolamo Di Maio, Nicola Alessio, Ibrahim Halil Demirsoy, Gianfranco Peluso, Silverio Perrotta, Marcellino Monda and Giovanni Di Bernardo
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3003
Abstract
Brown-like adipocytes can be induced in white fat depots by a different environmental or drug stimuli, known as “browning” or “beiging”. These brite adipocytes express thermogenin UCP1 protein and show different metabolic advantages, such as the ability to acquire a thermogenic phenotype corresponding
[...] Read more.
Brown-like adipocytes can be induced in white fat depots by a different environmental or drug stimuli, known as “browning” or “beiging”. These brite adipocytes express thermogenin UCP1 protein and show different metabolic advantages, such as the ability to acquire a thermogenic phenotype corresponding to standard brown adipocytes that counteracts obesity. In this research, we evaluated the effects of several browning agents during white adipocyte differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). Our in vitro findings identified two compounds that may warrant further in vivo investigation as possible anti-obesity drugs. We found that rosiglitazone and sildenafil are the most promising drug candidates for a browning treatment of obesity. These drugs are already available on the market for treating diabetes and erectile dysfunction, respectively. Thus, their off-label use may be contemplated, but it must be emphasized that some severe side effects are associated with use of these drugs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Starting Point or A Consequence? - the Importance of Stem Cells in Cancer Biology
Authors: Anna Erol; Marlena Tynecka; Alicja Walewska; Magda Niemira,; Adam Kretowski; Marcin Moniuszko; Andrzej Eljaszewicz
Affiliation: Department of Regenerative Medicine and Immune Regulation, Medical University of Bialystok, 15-269 Białystok, Poland
Abstract: Despite significant progress in understanding cancer development and progression mechanisms, to date, the role of different stem cell subsets remains not fully elucidated. Recent evidence showed significant heterogeneity of malignant tissue with the critical contribution of not only cancer cells but also stromal cells including, fibroblasts, immune cells, and different subsets of stem and progenitor cells. Notably, complex mutual interactions of cancerous and noncancerous repertoires have crucial implications for cancer progression and spread. Here we summarized the current understanding of the role of different tumor-associated stem and progenitor cells, including cancer stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and different subsets of progenitor cells, in the development, progression, and metastasis of cancer. We described their mutual interactions with cancer cells and other stroma components, discussed their importance in cancer microenvironment modulation, and their role in drug resistance.