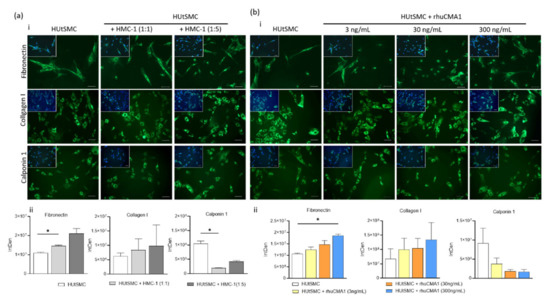
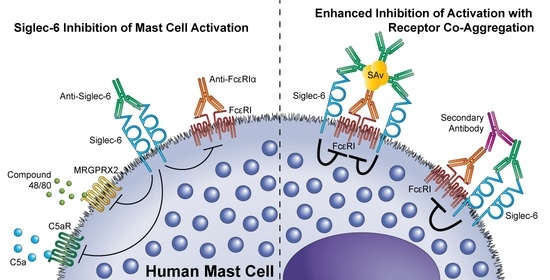
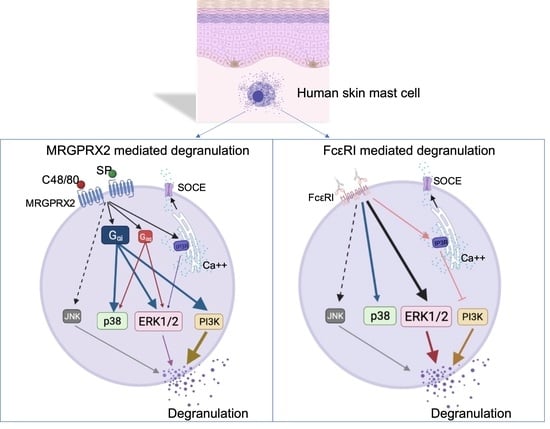
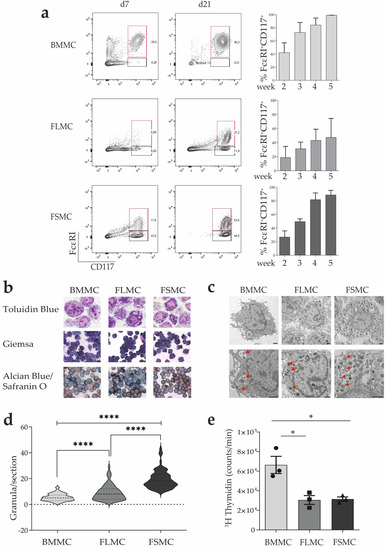
Mast Cells in Health and Diseases
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cellular Immunology".
Viewed by 114456Editor
Interests: human mast cell heterogeneity; the roles of mast cell-derived exosomes in health and diseases; the roles of Mas-related G-protein recepror X2 (MRGPRX2) in diseases; the activation mechanism of mast cells in chronic spontaneous urticaria and rheumatoid arthritis
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
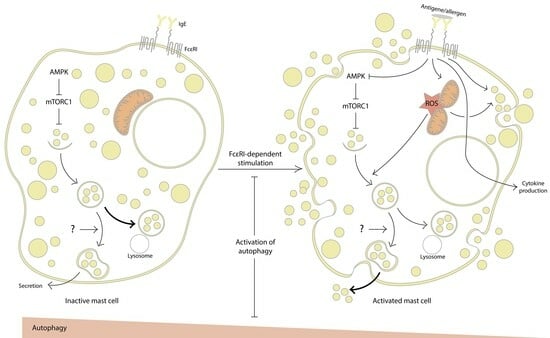
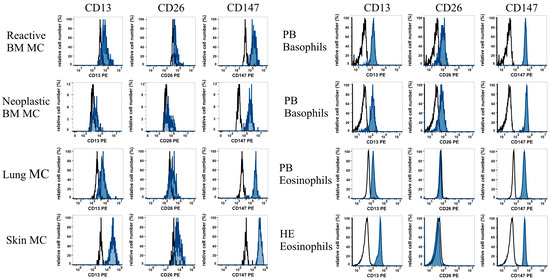
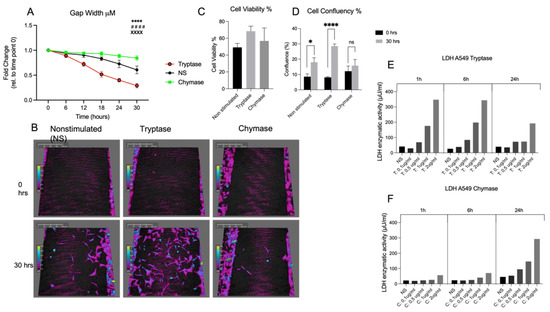
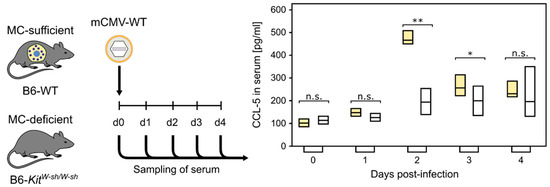
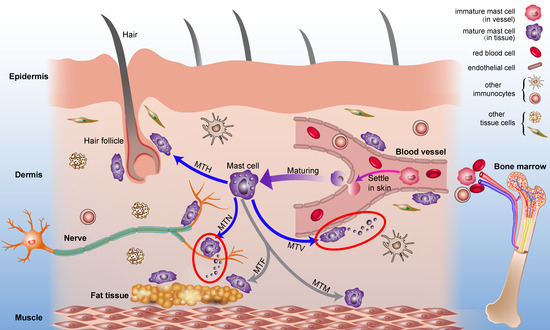
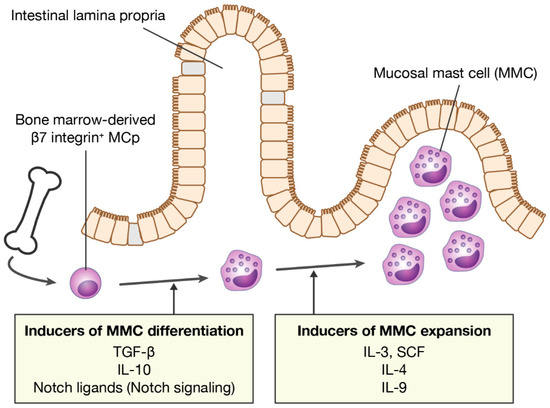
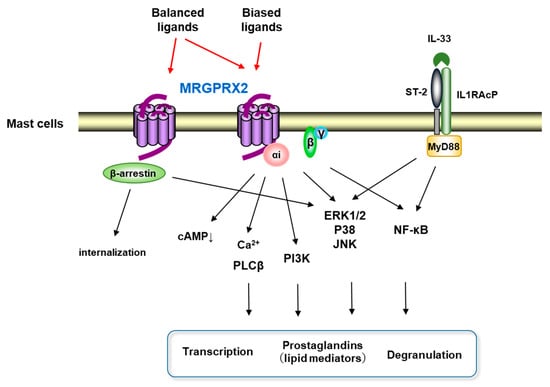
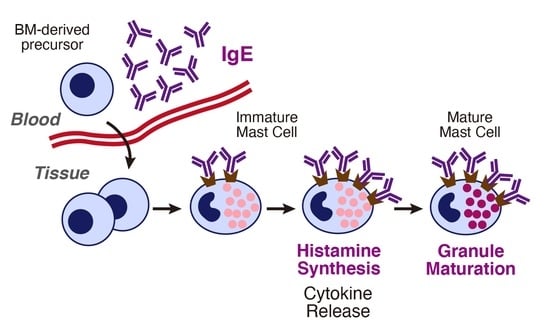
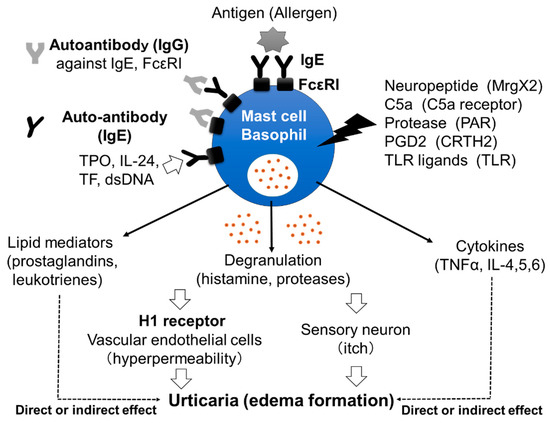
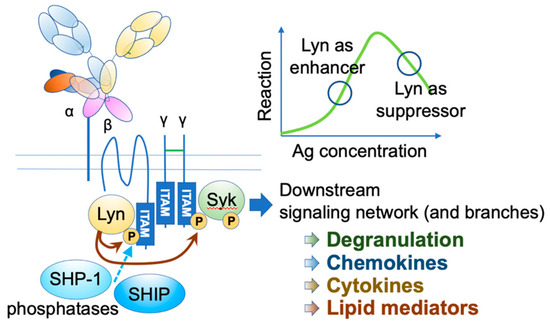
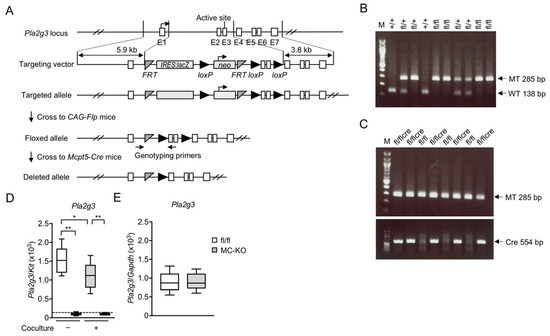
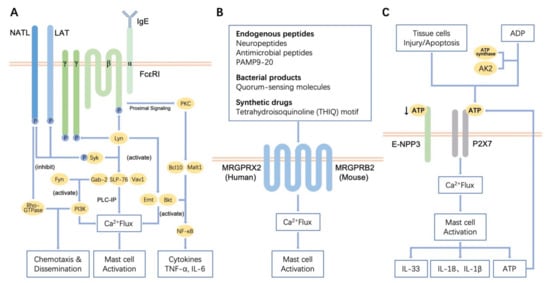
Mast cells leave the bone marrow as progenitors and reach their final maturation within peripheral tissues. Mast cells play a central role in IgE-dependent allergic diseases such as asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis through the release of a variety of vasoactive and bronchospastic autacoid mediators and functionally diverse proteases, chemokines and cytokines. Mast cells play an important role in innate immunity, angiogenesis and tissue repairing through non-IgE-dependent stimulation. In this Topical Collection of Cells, I invite you to contribute, either in the form of original research articles, reviews or shorter perspective articles on all aspects related to the theme of “Mast Cells in Health and Diseases”. Expert articles describing new roles of mast cells in health and diseases, new evidence of mast cell differentiation and maturation, and mast cell heterogeneity are welcome.
Dr. Yoshimichi Okayama
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Mast cell;
- IgE;
- Cytokine;
- Lipid mediator.