The Role of NLRP3 in Health and Disease
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cell Signaling".
Viewed by 50718Editor
Interests: NLRP3 signaling in acute and chronic inflammatory liver diseases; identification of novel prognostic biomarkers in gastrohepatic diseases
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
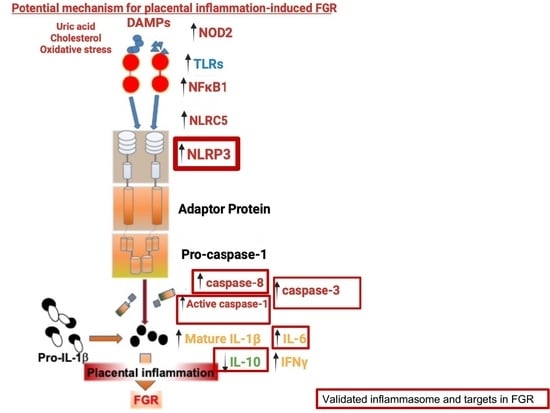
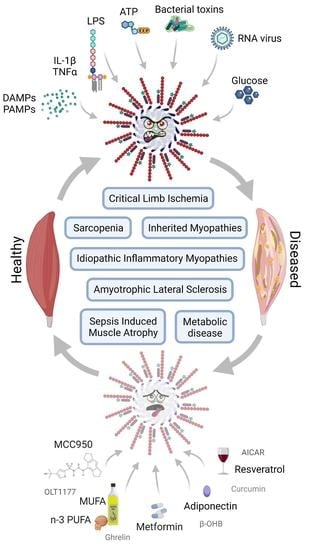
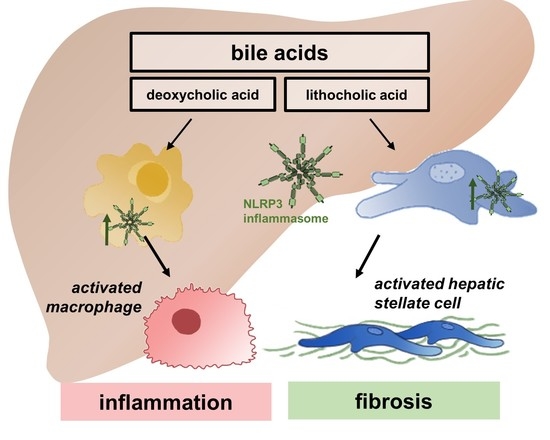
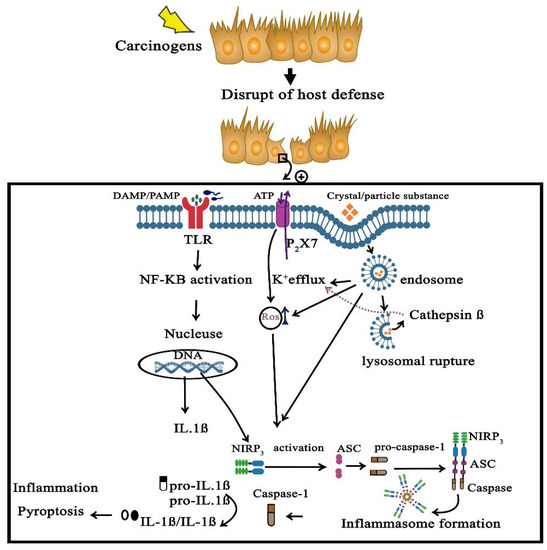
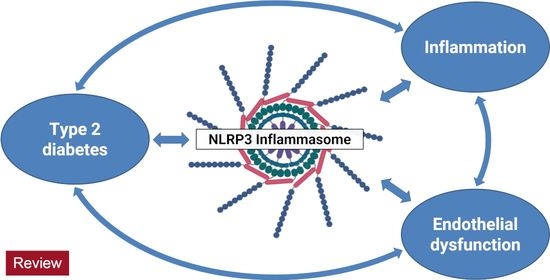
NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its downstream signaling has been shown to be involved in the development and progression of various inflammatory diseases, including NASH, fibrosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic, cardiovascular, as well as pulmonary diseases.
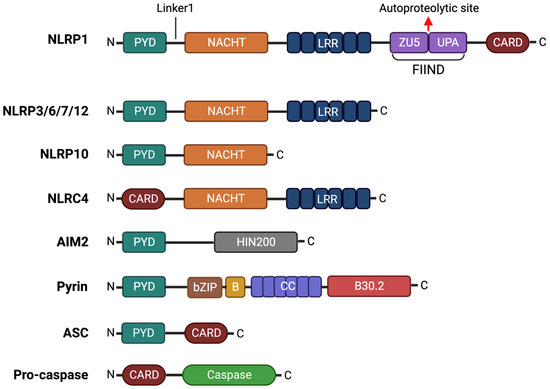
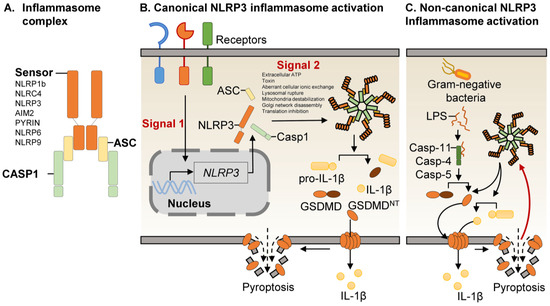
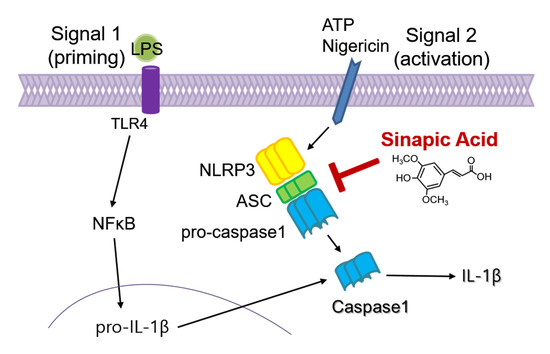
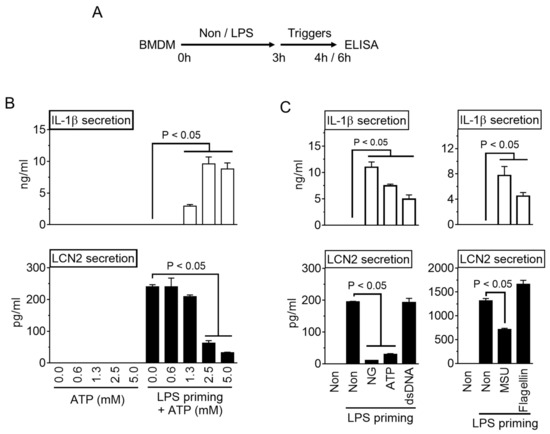
As crucial regulators of inflammation and cell fate, the NLRP3 inflammasomes sense a wide range of danger signals by NOD‐like receptors provoking caspase-1 activation, IL-1β and IL-18 processing and release, as well as the initiation of pyroptosis, a novel form of programmed cell death. NLRP3 dysregulation or hyperactivation result in a spectrum of rare autosomal dominant diseases summarized as cryopyrin-associated periodic fever syndromes. Although recent studies have improved our understanding of inflammasome activation and signaling, several aspects of the NLRP3 inflammasome are not characterized yet or remain unclear.
In this Topical Collection of the journal Cells, I would like to invite you to contribute original research articles, reviews or shorter perspective articles on all aspects related to the theme of “The Role of NLRP3 in Health and Disease”. Expert articles describing mechanistic, functional, cellular, biochemical or general aspects of NLRP3 activation and signaling are highly welcome.
Prof. Dr. Alexander Wree
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Inflammation
- Innate immunity
- Inflammasomes
- NLRP3-mediated signaling pathways and diseases
- Liver diseases
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Gut-liver axis
- Cancer
- Therapeutic targets